Author: Kyle
Prediction markets are surpassing traditional financial tools, becoming the intelligent carrier for information verification, while Info Finance further redefines the value of data through financial incentives and technological innovation. AO's post-scarcity computing architecture and AI agents are driving the intelligence and popularization of prediction markets, creating a new paradigm for the future of the Info Finance field.
Taking prediction markets to the extreme, is it a press conference? In the just-concluded US election, Polymarket, relying on its market-driven data, successfully predicted Trump's winning rate to be higher than traditional polls, quickly attracting the attention of the public and the media. People are gradually realizing that Polymarket is no longer just a financial tool, but a "balancer" in the information field, using market wisdom to verify the authenticity of sensational news.
When Polymarket became a hot topic, Vitalik proposed a brand-new concept - Info Finance. This tool that combines financial incentives and information can disrupt social media, scientific research, and governance models, opening up a new direction for improving decision-making efficiency. With the advancement of AI and blockchain, Info Finance is also moving towards a new turning point.
Facing this ambitious new field of Info Finance, is Web3's technology and ideology ready to embrace it? This article will take prediction markets as the entry point to explore the core ideas, technical support, and future possibilities of Info Finance.
Info Finance: Using financial tools to acquire and utilize information
The core of Info Finance is to use financial tools to acquire and utilize information to improve decision-making efficiency and accuracy. Prediction markets are a typical example, where by linking the problem with financial incentives, these markets incentivize participants' accuracy and responsibility, providing clear forecasts for users seeking the truth.

As a sophisticated market design, Info Finance can guide participants to respond to specific facts or judgments, with application scenarios covering decentralized governance, scientific review, and multiple other fields. At the same time, the emergence of AI will further lower the threshold, allowing micro-decisions to be effectively implemented in the market, promoting the popularization of Info Finance.
Vitalik specifically mentioned that the current decade is the best time to expand Info Finance. Scalable blockchains provide a secure, transparent, and trustworthy platform support for Info Finance, while the introduction of AI has improved the efficiency of information acquisition, enabling Info Finance to handle more refined issues. Info Finance not only breaks through the limitations of traditional prediction markets, but also demonstrates the ability to tap into the potential of multiple fields.
However, as Info Finance expands, its complexity and scale are rapidly increasing. The market needs to handle massive data and make real-time decisions and transactions, posing a severe challenge to efficient and secure computing capabilities. At the same time, the rapid development of AI technology has spawned more innovative models, exacerbating the computing demand. In this context, a secure and viable post-scarcity computing system has become an indispensable foundation for the continuous development of Info Finance.
The current landscape, who will win the post-scarcity computing system
The "post-scarcity computing system" currently lacks a unified definition, but its core goal is to break through the limitations of traditional computing resources and achieve low-cost, widely available computing power. Through decentralization, resource enrichment, and efficient collaboration, these systems support large-scale, flexible task execution, making computing resources tend towards "non-scarcity". In this architecture, computing power is no longer dependent on a single point, and users can freely access and share resources at low cost, promoting the popularization and sustainable development of inclusive computing.
In the context of blockchain, the key features of the post-scarcity computing system include decentralization, abundant resources, low cost, and high scalability.
The high-performance competition of public chains
Currently, major public chains are fiercely competing in performance to meet the increasingly complex application demands. Reviewing the current public chain ecosystem, the development trend is shifting from the traditional single-threaded mode to a multi-threaded parallel computing mode.
Traditional high-performance public chains:
Solana: From the very beginning of its design, Solana has adopted a parallel computing architecture, achieving high throughput and low latency. Its unique Proof of History (PoH) consensus mechanism allows it to process thousands of transactions per second.
Polygon and BSC: These two are actively developing parallel EVM solutions to enhance transaction processing capabilities. For example, Polygon has introduced zkEVM to achieve more efficient transaction verification.
Emerging parallel public chains:
Aptos, Sui, Sei, and Monad: These new public chains are designed for high performance by optimizing data storage efficiency or improving consensus algorithms. For example, Aptos uses Block-STM technology to achieve parallel transaction processing.
Artela: Artela proposes the EVM++ concept, implementing high-performance customized applications through native extensions (Aspect) in the WebAssembly runtime. With parallel execution and elastic block space design, Artela effectively solves the performance bottleneck of EVM, significantly improving throughput and scalability.
The performance competition is in full swing, and it is difficult to determine which one is better. However, in this fierce competition, there is also the AO-represented solution that takes a different path. AO is not an independent public chain, but a computing layer based on Arweave, achieving parallel processing capability and scalability through its unique technical architecture. AO is also a strong contender towards the post-scarcity computing system, and is expected to help the large-scale deployment of Info Finance.
Carrying Info Finance, the construction blueprint of AO
AO is an Actor Oriented (role-based) computer running on the Arweave network, providing a unified computing environment and an open messaging layer. Through its distributed and modular technical architecture, it enables the large-scale application of Info Finance and the integration with traditional computing environments.
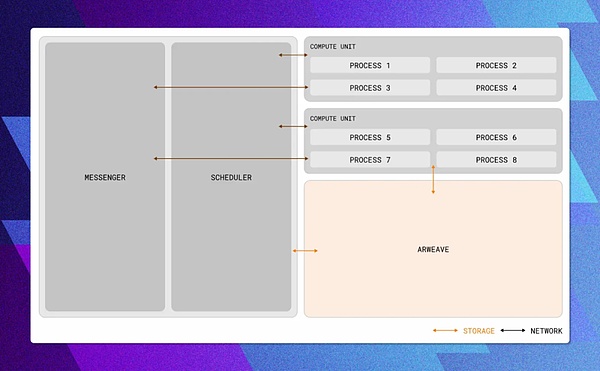
The architecture of AO is simple and efficient, with core components including:
Processes are the basic computing units in the AO network, interacting through Messages;
Scheduling Units (SUs) are responsible for message sorting and storage;
Computation Units (CUs) undertake state computation tasks;
Messenger Units (MUs) are responsible for message delivery and broadcasting.
The decoupled design of the modules endows the AO system with excellent scalability and flexibility, enabling it to adapt to application scenarios of different scales and complexities. Therefore, the AO system has the following core advantages:
High throughput and low latency computing capabilities: The parallel process design and efficient message delivery mechanism of the AO platform allow it to support processing millions of transactions per second. This high throughput capability is crucial for supporting a global-scale Info Finance network. At the same time, AO's low-latency communication characteristics can ensure the immediacy of transactions and data updates, providing users with a smooth operating experience.
Unlimited scalability and modular design: The AO platform adopts a modular architecture, achieving high scalability by decoupling the virtual machine, scheduler, message delivery, and computation units. Whether it is the growth of data throughput or the integration of new application scenarios, AO can adapt quickly. This scalability not only breaks through the performance bottleneck of traditional blockchains, but also provides developers with a flexible environment for building complex Info Finance applications.
Support for large-scale computing and AI integration: The AO platform already supports the 64-bit WebAssembly architecture, capable of running most full-fledged large language models (LLMs) such as Meta's Llama 3, providing a technical foundation for the deep integration of AI and Web3. AI will become an important driving force for Info Finance, involving applications such as smart contract optimization, market analysis, and risk prediction, and AO platform's large-scale computing capabilities enable it to efficiently support these demands. At the same time, through the WeaveDrive technology to access the unlimited storage of Arweave, the AO platform has a unique advantage in training and deploying complex machine learning models.








