Introduction
With the continuous development of blockchain technology, Bitcoin not only exists as a cryptocurrency, but its ecosystem is also constantly expanding and deepening. The Bitcoin ecosystem encompasses various Layer 2 solutions and applications, which not only improve the transaction speed and efficiency of Bitcoin, but also provide support for emerging fields such as smart contracts, decentralized finance (DeFi), and non-fungible tokens (NFTs). These innovations have made the application scenarios of Bitcoin more extensive, no longer limited to value storage and peer-to-peer payments, but able to meet more complex and diverse demands, driving the progress of the entire blockchain industry.
However, with the expansion of the ecosystem, security issues have gradually emerged. The new technologies and applications bring more potential risks and challenges, and how to ensure the security of the system while enhancing its functionality has become a key issue. Security vulnerabilities, attack incidents, and technical defects not only threaten the asset security of users, but may also affect the overall stability and credibility of the Bitcoin network. BitsLab's ScaleBit has written this article to delve into the construction process of the Bitcoin ecosystem, the security incidents faced, and the future outlook on security. By analyzing the current technical solutions and security challenges, the aim is to provide valuable insights and suggestions for the development of the Bitcoin ecosystem, ensuring that it can maintain a high degree of security and reliability as it continues to expand.
The Bitcoin Ecosystem Expansion
What is the Bitcoin Ecosystem Expansion?
The Bitcoin ecosystem expansion mainly refers to the various extension solutions and application ecosystem developed around the Bitcoin base network. Bitcoin was initially designed primarily for peer-to-peer payments and value storage, but with the development of blockchain technology, the Bitcoin community and developers have also been exploring how to add more functionality on its basis, especially in the areas of smart contracts, decentralized finance (DeFi), NFTs, and more efficient transaction expansion.
How does the Bitcoin Ecosystem Expansion work?
The operation of the Bitcoin ecosystem expansion mainly depends on the extension technologies and protocols built on or outside the Bitcoin mainnet, which enable Bitcoin to support more diverse application scenarios. The following are the operating principles of several key technologies in the Bitcoin ecosystem expansion:
(1) Lightning Network
The Lightning Network is one of the most mature and widely used Layer 2 solutions for Bitcoin. It establishes payment channels to move a large number of small transactions off the main chain, significantly increasing the transaction speed of Bitcoin and reducing transaction fees.
Trend: The Lightning Network infrastructure is constantly improving, and the user experience is also improving, with more and more merchants starting to support Lightning payments.
Challenge: Liquidity issues and routing efficiency still need further optimization, especially in large transaction scenarios.
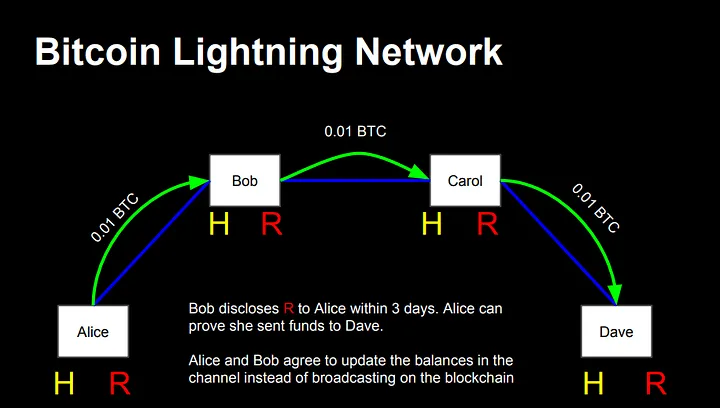
Source of Image 1:
https ://lightning.network/lightning-network-presentation-time-2015-07-06.pdf
(2) Liquid Network (LQ)
Liquid Network is a sidechain that runs on the open-source Elements blockchain platform, designed to enable faster transactions between exchanges and institutions. It is governed by a distributed alliance of Bitcoin companies, exchanges, and other stakeholders. Liquid uses a two-way peg mechanism to convert BTC to L-BTC and vice versa.
Liquid supports confidential transactions and tokenization, making it suitable for enterprise applications. If Bitcoin is the value layer of the internet, and Lightning is the peer-to-peer payment network driven by Bitcoin, then Liquid is the financial layer, adding multi-asset support and financial instruments such as securities and commodities.
Compared to Lightning, Liquid is a Layer 2 solution for Bitcoin, focusing on facilitating larger and more complex transactions, such as issuing and trading assets (like securities and stablecoins). Liquid has built-in confidential transaction features that hide transaction amounts and asset types, while Lightning primarily provides privacy through its off-chain transactions. While Lightning excels at small payments and everyday transactions, Liquid is more suitable for institutional finance, asset issuance, and cross-border transactions.
Currently, more than 50 exchanges have adopted the Liquid Network, and it has facilitated billions of dollars in transactions, demonstrating its effectiveness in enhancing the utility of Bitcoin for institutional trading. The Liquid Network can provide exchanges with faster settlement times, improving the liquidity of the Bitcoin market and enabling institutions to operate more efficiently and securely.
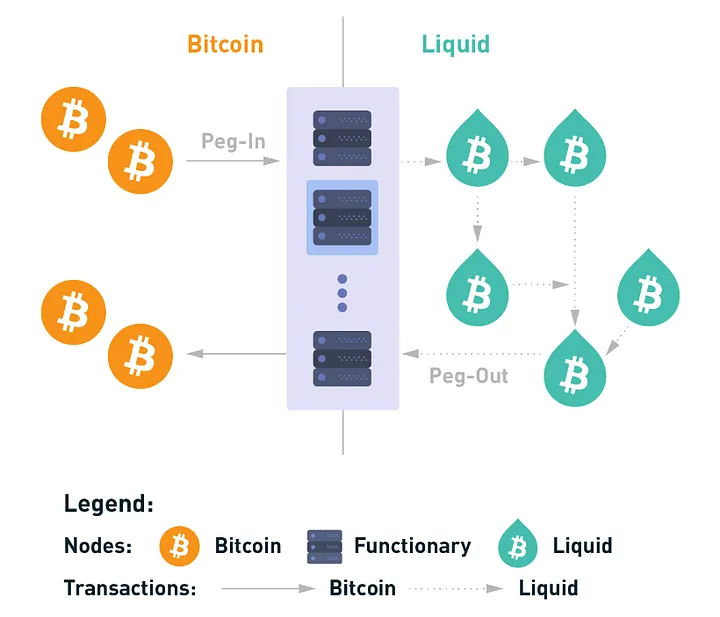
Source of Image 2:
https ://docs.liquid.net/docs/technical-overview
(3) Rootstock (RBTC)
Rootstock, which was born in 2015, is the longest-running Bitcoin sidechain and launched its mainnet in 2018. Its unique feature is the combination of Bitcoin's Proof-of-Work (PoW) security with Ethereum's smart contracts. As an open-source, EVM-compatible Bitcoin Layer 2 solution, Rootstock provides an entry point for the growing dApp ecosystem and is committed to achieving complete decentralization.
Similar to Liquid, Rootstock also uses a two-way peg mechanism, allowing users to easily exchange between BTC and RBTC. RBTC is the native currency of the RSK blockchain, used to pay miners for processing transactions and contracts. While Liquid focuses on fast, confidential transactions and asset issuance, Rootstock expands the DeFi and dApp ecosystem of Bitcoin through smart contracts.
As of the time of writing, Rootstock's Total Value Locked (TVL) has exceeded $170 million, with a market capitalization of $380 million.
(4) B² Network
The B² Network's technical architecture includes a two-layer structure: a Rollup layer and a Data Availability (DA) layer. B² Network aims to redefine users' perception of Bitcoin's second-layer solutions.
B² uses ZK-Rollup as the Rollup layer. The ZK-Rollup layer adopts a zkEVM solution, responsible for executing user transactions and outputting the relevant proofs within the second-layer network. User transactions are submitted and processed in the ZK-Rollup layer, and user states are also stored in the ZK-Rollup layer. The batched proposals and generated zero-knowledge proofs are then forwarded to the Data Availability layer for storage and verification.
The Data Availability layer includes distributed storage, B² nodes, and the Bitcoin network. This layer is responsible for permanently storing copies of the Rollup data, verifying the Rollup's zero-knowledge proofs, and ultimately executing the final confirmation on Bitcoin.
Distributed storage is a key aspect of the B² Network, serving as the repository for Rollup user transactions and their associated proofs. By decentralizing storage, the network fundamentally improves security, reduces single points of failure, and ensures the immutability of the data.
To guarantee data availability, B² also writes a Tapscript script to the Bitcoin network in each block, as shown in the image below. This script anchors the data path and zero-knowledge proofs of the Rollup that are effectively stored in the decentralized storage for that time period, a cost-effective process generating 6 transactions per hour. Therefore, when verifying, users will cross-reference the transactions and the Taproot script data on the Bitcoin Layer 1 to ensure the ultimate trustworthiness of the Rollup data.
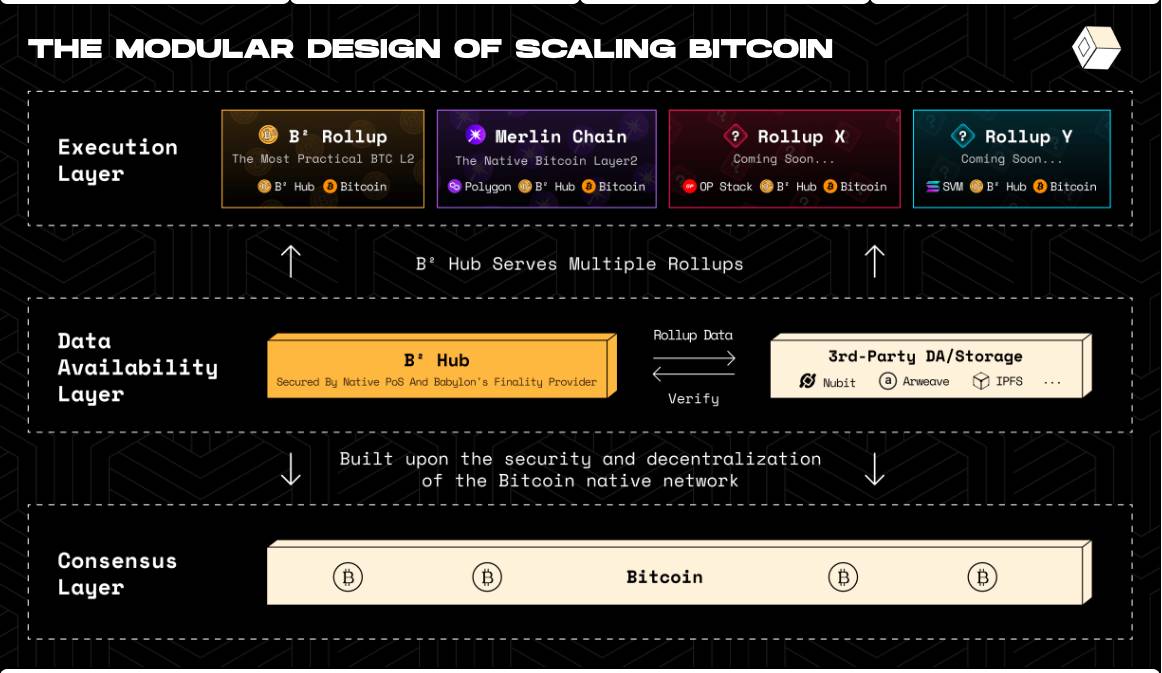
Image 3
(5) Stacks Protocol (STX)
Since its mainnet launch in 2018 under the name Blockstack, Stacks has become a leading Bitcoin Layer 2 solution.
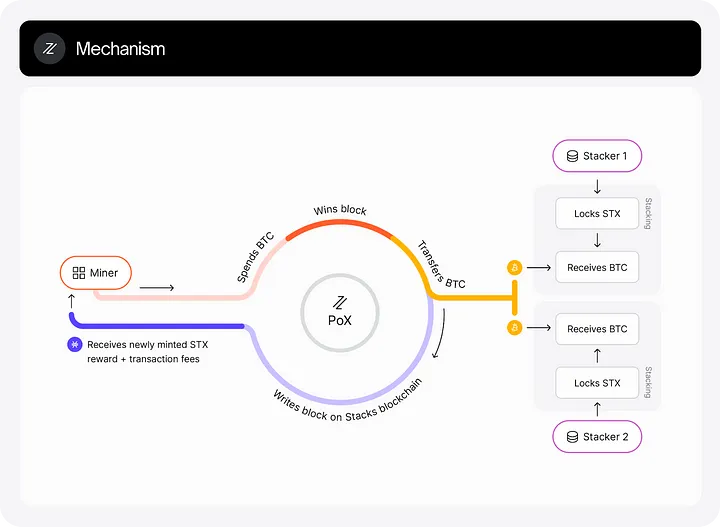
Source of Image 4: https ://docs.stacks.co/stacks-101/proof-of-transfer
Stacks directly connects to Bitcoin, allowing the construction of smart contracts, dApps, and NFTs on Bitcoin, significantly expanding Bitcoin's functionality beyond just a value storage tool. It uses a unique Proof-of-Transfer (PoX) consensus mechanism, directly linking its security to Bitcoin without modifying Bitcoin itself.
Stacks has a Total Value Locked (TVL) of over $99 million, and its established infrastructure and growing developer community make it a significant project in this field.
(6) Babylon
The vision of Babylon is to extend the security of Bitcoin to protect the decentralized world. By leveraging three aspects of Bitcoin - its timestamp service, block space, and asset value - Babylon can transmit Bitcoin's security to numerous Proof-of-Stake (PoS) chains, creating a more robust and unified ecosystem. Babylon's Bitcoin staking protocol uses a remote staking method, overcoming the lack of smart contracts through cryptography, consensus protocol innovations, and optimized use of the Bitcoin script language. Babylon's staking protocol allows Bitcoin holders to stake Bitcoin in a trustworthy manner without the need to bridge to PoS chains, providing full and reducible security guarantees for the chain. This innovative protocol of Babylon eliminates the need to bridge, wrap, or custody the staked Bitcoin. A key aspect of Babylon is its BTC timestamp protocol. It timestamps events from other blockchains onto Bitcoin, allowing these events to enjoy Bitcoin's timestamp like Bitcoin transactions. This effectively borrows Bitcoin's security as a timestamp server. The BTC timestamp protocol enables fast stake unbonding, composable trust, and reduced security costs, maximizing the liquidity of Bitcoin holders. The protocol is designed as a modular plugin, usable on top of various PoS consensus algorithms, and provides a foundation for building reset protocols. After discussing various technical solutions for expanding the Bitcoin ecosystem, we can clearly see that these innovations not only significantly improve the performance and functionality of the Bitcoin network, but also provide a solid foundation for diversifying its application scenarios. However, as the expanding ecosystem continues to grow and the technology becomes increasingly complex, security issues have also emerged as an important aspect that cannot be ignored. The new expansion technologies have introduced more potential risks and attack vectors, posing greater challenges to the overall security of the system. In this context, ensuring the security of the Bitcoin expansion ecosystem is not only about protecting user assets, but also about the stability and credibility of the entire network. Therefore, this section will provide detailed information on the vulnerabilities of the Lightning Network in 2023, providing valuable reference for future security protection. Bitcoin Expansion Ecosystem Security Incidents In October 2023, a potential security vulnerability was discovered in the Bitcoin scaling technology - the Lightning Network. Developer Antoine Riard publicly disclosed the details of this vulnerability after the discovery. This vulnerability, known as the "replacement cycling attacks", could jeopardize the security of funds flowing through the Lightning Network, leading to delayed or unexpected processing of transactions, and potentially causing the risk of fund loss within the Bitcoin Lightning Network channels. This event highlights that in the rapidly evolving expansion ecosystem, security must always be the top priority. Developers and the community need to continuously monitor and improve the existing expansion solutions to prevent potential security threats and ensure the safety of user funds. Outlook for Bitcoin Expansion Ecosystem Security Although the Bitcoin expansion ecosystem has made significant progress in improving transaction efficiency and functional diversity, its security still needs to be continuously strengthened. This section will explore the future development directions and challenges of the Bitcoin expansion ecosystem in terms of security. The Bitcoin expansion ecosystem aims to solve the transaction throughput problem of the mainnet, while ensuring security and decentralization. Trust model of off-chain transactions: The Bitcoin expansion ecosystem uses off-chain technologies to improve transaction speed, and developers need to ensure the trust mechanism of off-chain transactions is reliable enough. For example, the bidirectional payment channels in the Lightning Network require the use of multi-signature technology, and the channel closure process must be secure to prevent fund freezing or loss. Privacy and transparency: While the channel transactions in the Lightning Network can be completed without being publicly disclosed, which enhances privacy, it also increases the difficulty of regulation and potentially leads to malicious behavior. Layer 2 networks need to strike a balance between privacy and transparency, by selectively disclosing part of the transaction records to enhance compliance. User experience and security: The complexity of the expansion ecosystem brings difficulties in user operation, such as the channel management in the Lightning Network may not be user-friendly for ordinary users, increasing the risk of operational mistakes. The Bitcoin expansion ecosystem can improve user experience and reduce security risks by designing more user-friendly interfaces and simplifying operation tools. Looking to the future, the Bitcoin expansion ecosystem needs to continuously optimize technical solutions, improve user experience, and strengthen regulatory compliance, while maintaining decentralization and security, to achieve more robust and widespread applications. Summary The Bitcoin expansion ecosystem has significantly improved the functionality and transaction efficiency of the Bitcoin network through various Layer 2 solutions and innovative protocols, driving the development of emerging fields such as smart contracts, DeFi, and Non-Fungible Tokens. However, as the ecosystem continues to expand, security issues have gradually emerged, requiring the attention of developers and the community. In the future, the Bitcoin expansion ecosystem must continuously strengthen its security mechanisms, optimize user experience, balance privacy and transparency, and ensure its more widespread and robust development on the basis of decentralization and security, while pursuing higher transaction throughput and diversified applications. To read the full report, please click: https://bitslab.xyz/reports-page About ScaleBit ScaleBit, the security sub-brand of BitsLab, is a blockchain security team that provides security solutions for Web3 Mass Adoption. Leveraging our expertise in blockchain cross-chain and zero-knowledge proof technologies, we primarily provide meticulous and cutting-edge security audits for ZKP, Bitcoin Layer 2, and cross-chain applications. The ScaleBit team is composed of security experts with rich experience in both academia and industry, dedicated to providing security assurance for the scalable blockchain ecosystem's mass adoption. About BitsLab BitsLab is a security organization committed to safeguarding and building the emerging Web3 ecosystem, with the vision of becoming a respected Web3 security institution. It has three sub-brands: MoveBit, ScaleBit, and TonBit. BitsLab focuses on infrastructure development and security audits for emerging ecosystems, covering but not limited to Sui, Aptos, TON, Linea, BNB Chain, Soneium, Starknet, Movement, Monad, Internet Computer, and Solana. BitsLab also demonstrates deep professional capabilities in auditing various programming languages, including Circom, Halo2, Move, Cairo, Tact, FunC, Vyper, and Solidity. The BitsLab team is composed of top-tier vulnerability research experts who have won international CTF awards and discovered critical vulnerabilities in projects such as TON, Aptos, Sui, Nervos, OKX, and Cosmos. Visit the BitsLab website: https://bitslab.xyz/ Visit the ScaleBit website: https://www.scalebit.xyz/ BitsLab official Twitter: https://x.com/0xbitslab Join the official Telegram community: https://t.me/BitsLabHQ






