 Key Points:
Key Points:
- Pectra is the next major upgrade for ETH, involving changes to the execution layer (Prague) and consensus layer (Electra), planned to launch on the testnet in February and March, with mainnet expected to be activated in April.
- This upgrade brings critical improvements to staking, Layer-2 scalability, and user experience (UX), laying the foundation for future changes.
- Major changes include raising the validator staking cap, flexible staking withdrawals, enhanced account abstraction, and increased blob throughput, helping to improve network efficiency and security.
Introduction
Nearly 29 months after the "Merge", 22 months after "Shapella", and 11 months after "Dencun", Ethereum is welcoming its next major upgrade - the Pectra hard fork. As the largest proof-of-stake (PoS) blockchain, Ethereum has locked approximately $90 billion in ETH staking, over $135 billion in stablecoins, and about $4 billion in tokenized assets, continuously developing through gradual upgrades.
Pectra will become the hard fork with the most Ethereum Improvement Proposals (EIPs) in Ethereum's history. Building on last year's Dencun upgrade, Pectra introduces features to improve user experience (UX), validator operations, and further Layer-2 expansion, demonstrating its broad impact on Ethereum stakeholders. In this week's Coin Metrics 'State of the Network' report, we will analyze the key changes of Pectra and their significance for users, stakeholders, and investors, with the mainnet expected to be activated in early April.
What is Pectra and Why is it Important?
Similar to previous Ethereum upgrades, Pectra makes changes to both the execution layer (EL) and consensus layer (CL). Its name reflects this dual focus: "Prague" is named after the city hosting Devcon 4, representing the execution layer upgrade; "Electra" is a star in the Lyra constellation, symbolizing the consensus layer upgrade.
Pectra was initially envisioned as an ambitious upgrade, planned to include up to 20 Ethereum Improvement Proposals (EIPs). However, as development progressed, to better optimize and manage its complexity, the upgrade was divided into two phases. Currently, Pectra has entered its final stage, planned to launch on the Ethereum testnet in February and March, followed by mainnet activation in early April.
Before delving into individual EIPs, it's crucial to understand Pectra's overall goals, which we can summarize as staking and validator dynamics, user experience (UX), and Layer-2 expansion.
Validator and Staking Improvements
Three main EIPs aim to improve the experience of validator operations in Ethereum's proof-of-stake (PoS) system:
EIP-7251: Increasing Maximum Effective Balance
Ethereum's current staking design limits validators' effective balance to 32 ETH, meaning independent stakers must stake in 32 ETH increments, which is the maximum amount a single validator can stake. Rewards exceeding this limit are not counted in active staking. EIP-7251 raises the Maximum Effective Balance (MaxEB) to 2048 ETH, meaning a single validator can now stake between 32 ETH and 2048 ETH. This is expected to:
- Increase Staking Flexibility: Stakers can now compound rewards on their entire balance, no longer limited to 32 ETH multiples. For example, a validator with 33 ETH can now count the full 33 ETH towards rewards, improving capital efficiency and staking operations flexibility.
- Reduce Validator Numbers: Ethereum currently has 1.05 million active validators on the consensus layer. This EIP will allow large operators to consolidate their validators, expected to reduce the number of validators and alleviate network overhead from the large validator count.
- Reduce Network Load: While a high number of validators enhances decentralization, it also increases bandwidth and computational demands. Increasing MaxEB can make the validator set more efficient, reducing peer-to-peer communication overhead.
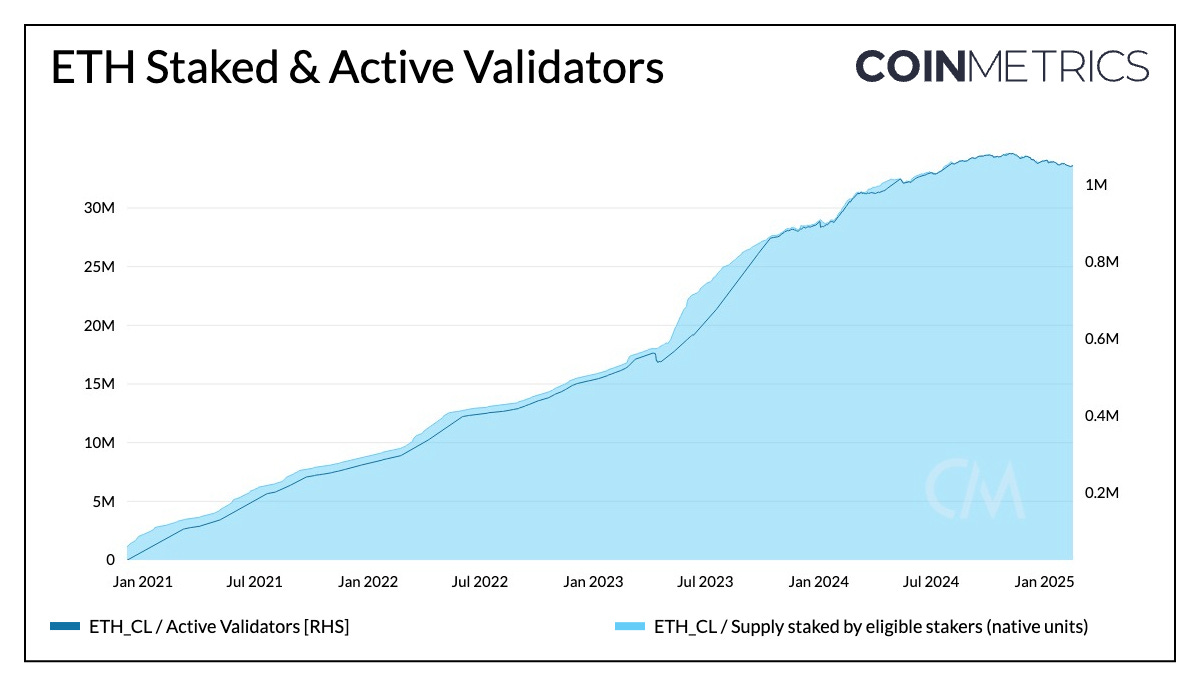
Source: Coin Metrics Network Data Pro
EIP-7002: Execution Layer Withdrawal Triggering
This EIP expands validator functionality, complementing the previous EIP. EIP-7002 enables validators to directly initiate exits and partial withdrawals through their execution layer (0x01) withdrawal credentials. Validators have two keys: an active key for performing validator duties and a withdrawal key for accessing and managing staking funds. Previously, only the active key could trigger exits. Now, the withdrawal credentials address can also initiate exits, allowing larger withdrawals and reducing dependence on node operators. This change enhances validators' control over funds and supports fully trustless staking pools, improving security and decentralization.
EIP-6110: On-chain Validator Deposits
EIP-6110 simplifies the validator joining process by improving the deposit processing between Ethereum's execution layer (EL) and consensus layer (CL). Currently, when a new validator deposits on the execution layer (EL), they must wait for the consensus layer (CL) to identify and process it, causing delays. EIP-6110 allows the execution layer to directly transmit validator deposit information to the consensus layer, eliminating additional verification processes and reducing activation delay from about 9 hours to approximately 13 minutes.
Blob Expansion and Layer-2
EIP-7691: Increasing Blob Throughput
Beyond validator improvements, Pectra brings key changes to Ethereum's data availability and scalability. Last year's Dencun upgrade introduced blobs as a new efficient method for storing Layer-2 rollup data. Blobs are now widely adopted by Ethereum Layer-2, with an average of 21,000 blobs published daily. However, blob usage continues to reach capacity limits, leading to rising fees and throughput constraints.
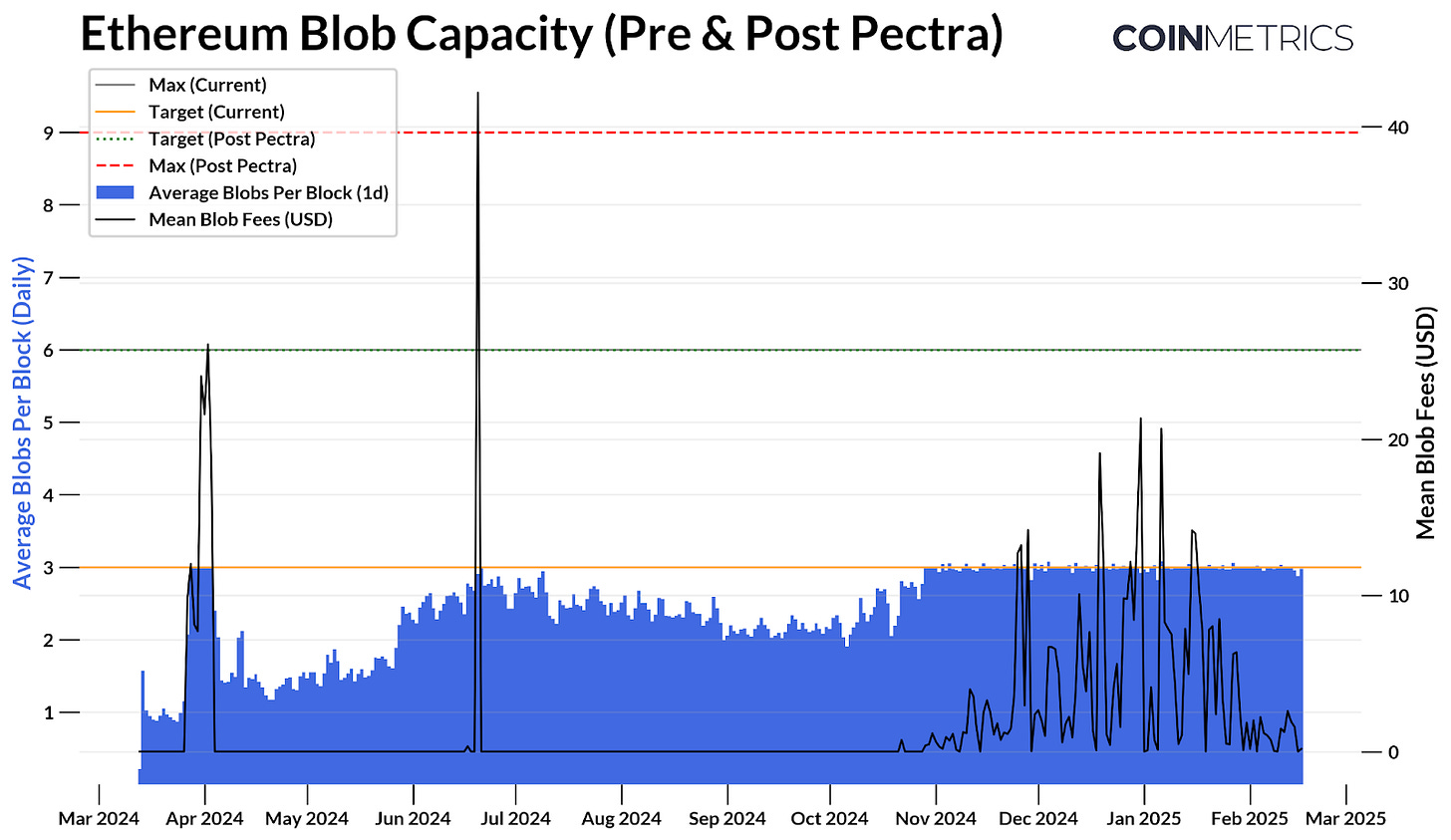
Source: Coin Metrics Network Data Pro, Blob Metrics
The network currently targets an average of 3 blobs per block, with a maximum of 6. EIP-7691 raises the target to 6 and the maximum to 9, increasing data storage capacity and thus improving throughput and scalability. Data storage costs will decrease, and Layer-2 blob fees will become cheaper, ultimately reducing end-user transaction fees.
EIP-7623: Increasing Calldata Costs is another EIP that complements blob adoption. Before blob introduction, Layer-2 used calldata to store data on Ethereum, sometimes still using calldata for cost-effectiveness. By increasing calldata costs, this change can incentivize Layer-2 to specifically use blobspace, making rollup transactions more efficient.
User Experience (UX) Enhancements
EIP-7702: Setting EOA Account Code
EIP-7702 is a highly anticipated change as it brings Ethereum closer to account abstraction. It is expected to greatly improve user experience (UX) and wallet functionality by allowing externally owned accounts (EOA, i.e., user wallets) to temporarily operate as smart contract wallets. This enables them to execute smart contract-like logic, providing users with greater flexibility and programmability for wallets and applications.
After Pectra, users and developers can leverage EIP-7702 to achieve:
- Batched Transactions: Bundling multiple transactions or user actions into a single transaction (e.g., approving and swapping tokens in one transaction).
- Gasless Transactions: Allowing Account X to pay transaction fees on behalf of Account Y, or a "paymaster contract" to cover gas fees for users.
- Conditional or Sponsored Transactions: Implementing spending controls, automated actions, or sponsored transactions based on set conditions.
While we've introduced the most impactful changes in Pectra, several other EIPs also contribute to network improvements, including EIP-2513, EIP-2935, EIP-7549, EIP-7865, and EIP-7840, all focusing on optimizing efficiency and reducing network resource consumption.
Conclusion
Ethereum is once again preparing for a major upgrade, which includes a record number of EIPs. Pectra aims to enhance Ethereum's most urgent priorities, including the transition to account abstraction, improving validator operations, increasing network efficiency, and gradually expanding Layer-2 blob usage. At the same time, as Vitalik Buterin emphasized in a recent blog post, despite the rollup-centric roadmap, Ethereum continues to expand Layer-1. The recent increase in gas limit to 36 million is expected to further enhance resistance to censorship, throughput, and scalability.
While Pectra's changes are primarily technical, many may wonder how they will affect ETH's valuation. Historically, ETH has shown significant price fluctuations before and after previous upgrades, but market sentiment—including the crypto market and broader financial markets—tends to have a greater impact than direct changes to Ethereum's economics. Nevertheless, Pectra is expected to drive Ethereum's adoption, and as we move past this upgrade, we will revisit its impact on key network metrics, ecosystem stakeholders, and ETH as an asset.
Network Data Insights
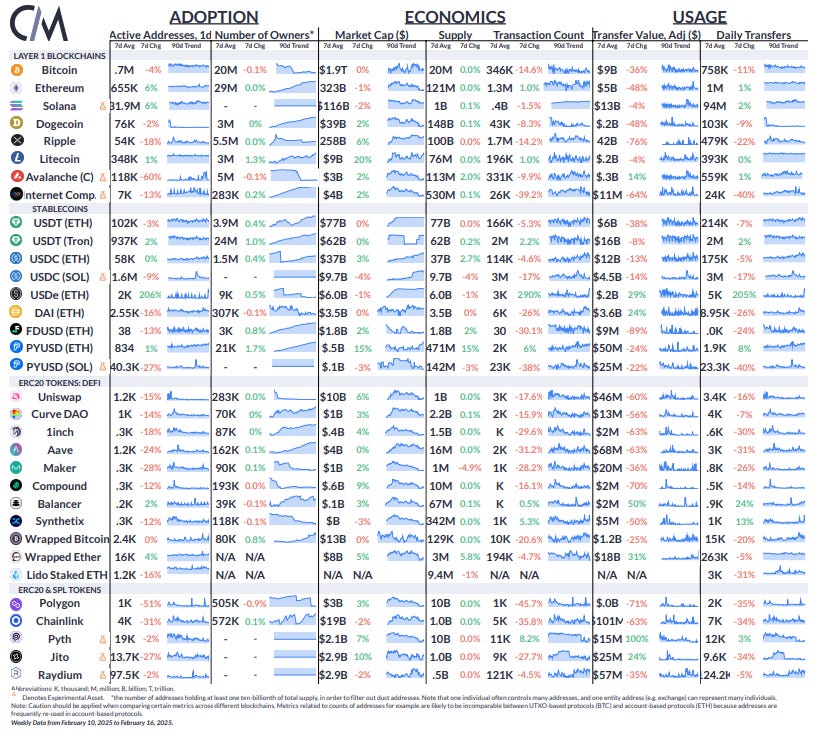
Source: Coin Metrics Network Data Pro
Over the past week, Bitcoin's active addresses decreased by 4%, while Ethereum and Solana's active addresses increased by 6%. USDC's market cap on Ethereum grew by 2.7%, reaching $37 billion, while PayPal USD's market cap on Ethereum increased by 15%, setting a record of $498 million.






