Written by Glendon, Techub News
As Bitcoin continues to soar, breaking through the $123,000 mark and repeatedly setting new historical highs, the industry's highly anticipated "Cryptocurrency Week" is about to begin.
The U.S. House of Representatives will launch the "Cryptocurrency Week" agenda at 4:00 p.m. local time on July 14 (4:00 a.m. Hong Kong time on July 15), focusing on reviewing three key bills that are likely to rewrite the history of cryptocurrency, including the "Guidance and Establishment of a United States Stablecoin National Innovation Act" (Stablecoin "GENIUS Act", also known as the "Genius Act"), the "Digital Asset Market Clarity Act" ("CLARITY Act"), and the "Anti-CBDC Surveillance State Act" (HR 1919).

For the cryptocurrency industry, this meeting led by House Republicans is of great significance. It is related to whether the industry can obtain a "pass" to the mainstream financial world under the clear regulatory rules of the United States. Next, this article will explore the core content of these three bills, what positive effects will be produced if passed, and the possibility of their passage.
Detailed explanation of the core contents of the three bills
The GENIUS Act: Establishing a Regulatory Framework for Stablecoins
On February 4, 2025, Bill Hagerty, a Republican senator from Tennessee, first proposed the GENIUS Act, which aims to build a regulatory framework for stablecoins. On May 15, the bill was revised to respond to Democratic lawmakers' concerns about the Trump family's potential conflicts of interest and to gain more support from lawmakers. After the revision, the bill added asset reserve requirements for stablecoin issuers, requiring them to hold 100% of USD equivalent assets, while explicitly prohibiting members of Congress and their families from profiting from stablecoins.
But it is worth noting that the bill does not restrict the president and his family from profiting from the issuance of stablecoins, which has intensified Democrats' criticism of Trump and his family's "cryptocurrency corruption."
On June 17, the U.S. Senate held a final vote on the GENIUS Act, which was formally passed with 68 votes in favor and 30 votes against. It established the first federal regulatory framework for cryptocurrency stablecoins pegged to the U.S. dollar, marking the first time that the crypto asset industry has been included in U.S. federal-level legal supervision. At the same time, the GENIUS Act has officially entered the House of Representatives process.
Unlike the fragmented regulatory approach of the U.S. government over the years, the GENIUS Act establishes clear and unambiguous standards in the field of digital assets:
- Strictly define the attributes of payment stablecoins: It is clear that payment stablecoins are digital assets used for payment or settlement, which must be exchanged with legal currencies (such as the US dollar) at a 1:1 ratio and do not fall into the category of securities or commodities. At the same time, issuers are prohibited from providing interest income to users through stablecoins to prevent them from evolving into speculative financial products.
- Clarify the access restrictions for issuers: Only three types of entities can legally issue payment stablecoins, including subsidiaries of insured banks (such as JPMorgan Chase), federal non-bank issuers approved by the Federal Office of the Comptroller of the Currency (OCC), and state-level qualified issuers that meet federal standards, and implement hierarchical management. Issuers with a scale of more than US$10 billion are subject to direct federal supervision (such as the Federal Reserve, OCC, etc.), and smaller issuers are governed by state-level regulators to reduce compliance costs. Existing non-compliant issuers (such as Tether) must complete rectification or exit the market within 3 years.
- It covers asset reserves and transparency requirements, consumer protection and anti-money laundering mechanisms: reserve asset types are limited to high-liquidity assets such as US dollar cash, short-term US Treasury bonds maturing within 93 days and government money market funds; issuers are required to disclose reserve composition reports on a monthly basis, and they must be reviewed by a third-party accounting firm; issuers with a scale of more than US$50 billion are required to submit annual audited financial statements, etc.
The CLARITY Act: Drawing a Line for Digital Asset Market Structure
The Digital Asset Market Clarity Act (CLARITY Act) is the full name of the “Digital Asset Market Clarity Act of 2025”. It was proposed by French Hill, Chairman of the U.S. House Financial Services Committee and Republican Congressman from Arkansas, and co-sponsored by five Republicans and three Democrats, eventually forming a bipartisan proposal.
The bill aims to establish a clear and unified regulatory framework for the U.S. digital asset market, clarify the regulatory methods of the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) and the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC), create a clear regulatory framework for cryptocurrencies, and require digital asset companies to make customer disclosures and isolate customer funds. While protecting investors and combating fraud, the bill leaves room for exemptions and research for innovation (DeFi, stablecoins, NFTs, etc.).
On June 11, the U.S. House of Representatives Agriculture Committee and Financial Services Committee voted to pass the CLARITY Act with 47 votes in favor and 6 votes against and 32 votes in favor and 19 votes against respectively. The bill was then submitted to the House of Representatives for a vote in the plenary session. Interestingly, according to Bitcoin Laws, the amendment in the bill to "prohibit President Trump and his family from profiting from trading or promoting crypto assets" was also rejected.
The framework proposed by the bill mainly includes four core contents:
- Clarify the classification of digital assets and the division of regulatory responsibilities: Security tokens (such as fundraising tokens) are regulated by the SEC and must comply with the registration and disclosure requirements of the Securities Act; digital commodities are under the jurisdiction of the CFTC, such as mainstream cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin and Ethereum.
- Establish a blockchain "maturity" certification mechanism: the value mainly comes from the actual use of the blockchain, requiring no single entity to control it (for example, the largest coin holder's coin holding ratio must not exceed 20%), and a 4-year observation period (starting from the passage of the bill or the first token sale).
- Includes DeFi and infrastructure exemption clauses: six types of non-custodial services are clearly not subject to the Securities Exchange Act, including node operation and maintenance, oracle services; front-end interface development; liquidity pool provision; non-custodial wallet services; DeFi protocol development and maintenance; transaction verification and forwarding services.
- Scope of regulation: The SEC is responsible for the registration of security tokens and anti-fraud enforcement, while the CFTC is responsible for exercising jurisdiction over the digital commodity spot and derivatives markets, and requiring exchanges, brokers and other intermediaries to register and segregate customer funds.
During this period, the Blockchain Regulatory Certainty Act (BRCA) was also incorporated into the newly revised CLARITY Act, which aims to protect developers of non-custodial, peer-to-peer technologies while strictly regulating custodial financial institutions.
Anti-CBDC Surveillance State Act
The CBDC Anti-Surveilance State Act was first proposed by House Majority Whip and Republican Congressman Tom Emmer in September 2023. Its purpose is to curb the development of the digital dollar and prohibit the Federal Reserve Bank from providing products and services directly to individuals. The consideration behind this is that the supporters of the bill believe that the digital dollar is very likely to become a financial surveillance tool that undermines the traditional American lifestyle.
On May 26, the U.S. House of Representatives voted on the revised version of the bill (HR 1919), which was passed with 216 votes in favor and 192 votes against.
The core content of the bill covers several key aspects: prohibiting the issuance of retail CBDC, that is, the Federal Reserve cannot issue central bank digital currency to individuals without the authorization of Congress, to prevent the government from excessively intervening in the payment system and personal financial freedom; prohibiting the government from collecting citizens' transaction data through CBDC, restricting data collection behavior from the source to protect personal privacy; ensuring that CBDC and private stablecoins (such as USDC) are clearly distinguished to prevent the central bank from excessively intervening in the payment field.
After gaining an in-depth understanding of the goals and core content of these bills, a key question emerges: If these bills are eventually passed, what impact will they have on the entire cryptocurrency industry?
Impact of the bill and likelihood of passage
The GENIUS Act marks a major shift in U.S. cryptocurrency regulation, and with bipartisan support in the Senate, it is expected to lay the foundation for a more mature, transparent, and innovation-friendly digital asset market in the U.S. Once passed, the bill will significantly enhance market trust and stability in the cryptocurrency industry, clarify regulatory rules (such as 100% reserve requirements) to reduce fraud, such as decoupling incidents caused by opaque reserves, and attract institutional investors to enter the market, driving the growth of compliant stablecoins such as USDC.
However, the bill will also increase regulatory pressure on some stablecoin issuers. For example, the stablecoin giant Tether, whose current reserve composition does not meet the requirements of the bill. Analysts at JPMorgan Chase have analyzed that Tether may need to sell non-compliant assets to comply with the proposed US stablecoin regulations, including Bitcoin, precious metals, corporate notes and secured loans. However, Tether CEO Paolo Ardoino expressed his willingness to launch products that comply with the GENIUS Act.
On the other hand, the bill will promote innovation and compliance development, provide a "safe harbor" for DeFi and payment stablecoins, reduce legal uncertainty, and thus encourage companies to develop new products (such as cross-border payment solutions) under a transparent framework.
For the United States, the GENIUS Act can strengthen financial security and consumer protection, enforce disclosure of reserve information and redemption policies, and prevent systemic risks similar to Terra-Luna. By making stablecoins pegged to the U.S. dollar more compliant and increasing the use of the U.S. dollar in international payments, it can also maintain and consolidate the dollar's global dominance. In addition, the bill is likely to become a global standard, provide a regulatory template, and promote other countries or regions to establish similar frameworks, reducing regulatory arbitrage and market fragmentation.
The CLARITY Act also has some similar effects, but compared to the digital asset market foundation established by the GENIUS Act, this bill is more inclined to provide a clear regulatory framework, end the ambiguity of the current US government regulation, and clarify the jurisdictional boundaries of the SEC and CFTC, thereby providing exchanges and issuers with a predictable compliance path and reducing legal risks. On this basis, this bill may prompt some projects and investments to return to the United States, as Coinbase has clearly stated its support for the bill.
Secondly, the bill can also unleash the innovation potential of DeFi. The exemption clauses for non-custodial protocols (such as liquidity pools and oracles) allow developers to build decentralized applications without worrying about securities law liability, thereby promoting the iteration of Web3 technology.
However, we must also pay attention to the negative impact. The biggest impact of the two bills is undoubtedly the increase in compliance costs and the increase in market entry barriers. Small and medium-sized exchanges need to meet both SEC disclosure requirements and CFTC transaction monitoring rules. Due to operating cost constraints, small and medium-sized stablecoin issuers may also be restricted by 100% reserve and strict audit requirements. The final result may lead to the exit of small and medium-sized platforms from the market, thereby exacerbating industry monopoly and allowing large institutions to completely dominate the market.
The Anti-CBDC Surveillance State Act is like a double-edged sword for the United States. While it brings some benefits, it also hides many challenges.
From the perspective of benefiting the cryptocurrency industry, once the bill comes into effect, it will cut off the Federal Reserve's path to providing digital dollars to individuals. In this way, private dollar stablecoins (such as USDT and USDC) will become the only carrier of the digital dollar, which will undoubtedly further promote the expansion of the stablecoin market share.
But for the US government, the bill prohibiting the use of CBDC for economic regulation may greatly limit the government's financial monitoring capabilities. The government needs effective tools and means for economic regulation and financial supervision, and CBDC can provide such support to a certain extent. In addition, most Democratic lawmakers believe that the bill will harm US interests, saying that CBDC can improve payment efficiency and reduce settlement costs, and the ban will delay the upgrade of the US financial system. Maxine Waters, a member of the House Financial Services Committee and a Democratic congressman from California, publicly criticized the bill banning CBDC as "anti-innovation."
For this reason, based on the above analysis of pros and cons, this bill faces many difficulties in making further progress, and the possibility of passing is not very high. This can also be seen from the voting situation in the US House of Representatives. During the voting process, as many as 192 Democratic congressmen voted against it, and only 3 Democratic congressmen expressed support. In addition, the bill will need to be reviewed by the Senate, and the Democratic Party holds a majority in the Senate, which means that the bill will inevitably encounter greater resistance.
In comparison, the GENIUS Act and the CLARITY Act are much more likely to pass the House of Representatives vote. On the one hand, the Republicans have a 220:212 majority in the House of Representatives, the bills are led by the Republicans, and the House of Representatives intends to advance the two bills in parallel in order to complete the two legislations before the August deadline set by Trump.
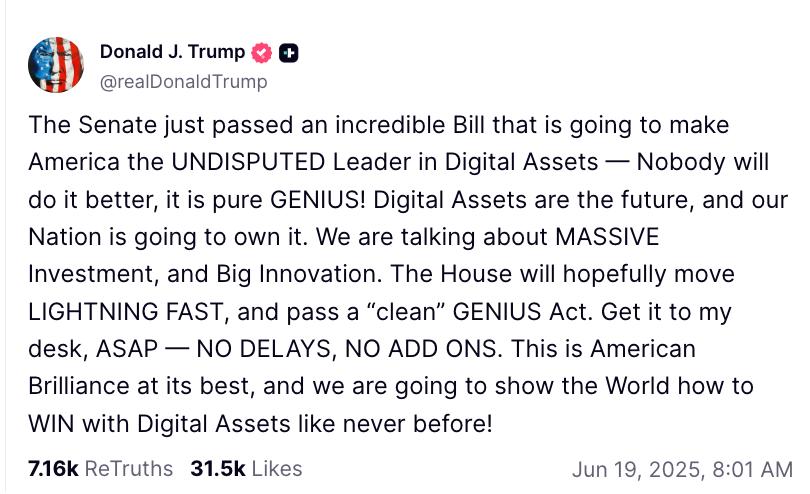
In response, Trump also wrote on Truth Social, urging that the Senate's passage of the GENIUS Act would promote large-scale investment and innovation in the digital asset field in the United States, and called on the House of Representatives to quickly pass the bill and submit it to the President for signature as soon as possible without delay or any conditions. Even U.S. Senator Hagerty said in an interview that Trump is ready to sign the GENIUS Act, and the bill may soon be delivered to his desk.
Although there are still objections to Trump's convenience of "cryptocurrency corruption", according to Caijing, many American legal professionals said that generally speaking, it is more difficult to promote legislation in the US Senate than in the House of Representatives. Compared with the Senate, there are more members in the House of Representatives who support Trump, so the GENIUS Act promoted by Trump is likely to receive majority support in the House of Representatives and eventually pass.
On the other hand, the enthusiasm of the market has been ignited. Some analysts believe that investors' optimism about policy expectations has driven the market up. Whether it is the recent surge in the share price of stablecoin giant Circle or Bitcoin's continuous record highs, it shows that the market is increasingly optimistic about market regulatory policies.
As for whether the final bill can be successfully passed, "Cryptocurrency Week" is coming, let us wait and see!





