- As stablecoins increasingly function like money—serving as settlement assets, payment instruments, and stores of value—regulators now treat them as systemically relevant, requiring safeguards similar to those applied to banks and payment systems.
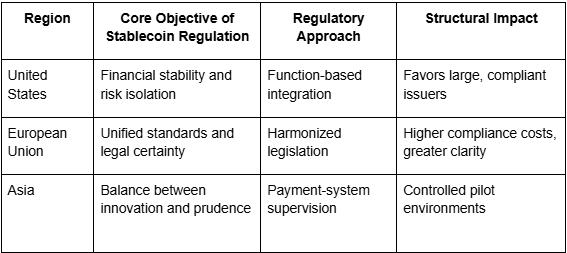
- Regulatory approaches diverge by region, with the United States emphasizing function-based risk isolation and the European Union prioritizing unified legislative clarity, both aiming to integrate stablecoins into institutional finance.
- Rising compliance standards are restructuring the industry, favoring well-governed, transparent issuers and redirecting innovation toward efficiency and scalability within clearly defined regulatory boundaries.
Stablecoin regulation has become a core pillar of global financial governance, reshaping digital finance by embedding stablecoins into financial stability, monetary sovereignty, and institutional risk frameworks rather than treating them as peripheral crypto tools.

Introduction: Why Stablecoin Regulation Has Become a Central Global Financial Issue
Stablecoin Regulation has rapidly evolved from a niche topic within the cryptocurrency industry into a central issue in global financial governance. In the early stages of crypto market development, stablecoins were primarily perceived as functional tools designed to facilitate trading, reduce volatility, and provide on-chain liquidity. Their role was largely confined to crypto-native ecosystems, serving as settlement assets within exchanges and decentralized finance protocols.
However, as issuance volumes expanded and adoption accelerated, Stablecoin Regulation became unavoidable for policymakers. Stablecoins are now deeply embedded in cross-border payments, international settlement flows, and global capital movement channels. In many regions, they are increasingly used as transactional instruments rather than speculative assets. This functional evolution has fundamentally altered their risk profile and regulatory relevance.
Regulators across jurisdictions now recognize that stablecoins exhibit clear quasi-monetary characteristics. Without enforceable Stablecoin Regulation frameworks, weaknesses in reserve management, liquidity mismatches, or governance failures could rapidly propagate across both on-chain and off-chain financial systems. These risks resemble traditional financial instability mechanisms, including bank runs and payment system disruptions.
As a result, Stablecoin Regulation is no longer limited to project-level compliance. It has become a systemic issue tied to financial stability, monetary sovereignty, and payment system resilience. Understanding the institutional logic and regulatory structure behind Stablecoin Regulation is now essential for assessing the long-term viability of digital finance within the global financial system.
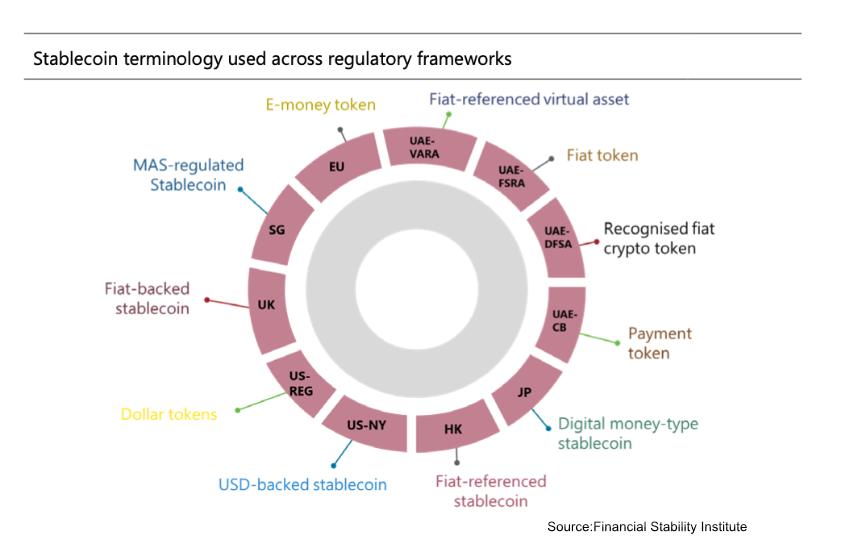
Figure 1: Differences in Regulatory Terminology and Legal Classification of Stablecoins Across Jurisdictions
Why Stablecoin Regulation Has Been Integrated into Financial Stability Frameworks
Quasi-Monetary Characteristics and the Accumulation of Systemic Risk
From a functional perspective, stablecoins increasingly perform the core functions traditionally associated with money. They operate as a medium of exchange, a store of value, and a settlement unit within digital financial ecosystems. A significant share of on-chain trading, lending, derivatives settlement, and treasury management activity is denominated in stablecoins. As a result, their role now closely resembles that of bank deposits and settlement balances in traditional finance.
This shift fundamentally changes the nature of risk associated with stablecoins. When stablecoins are widely used for transactional and settlement purposes, confidence in their redeemability becomes critical. If issuers fail to maintain transparent, liquid, and adequately managed reserves, even a small shock can trigger large-scale redemptions. Such dynamics mirror traditional financial runs and can escalate rapidly due to the speed and global reach of blockchain-based systems.
Stablecoin Regulation is therefore designed to address these systemic risk channels. By imposing requirements related to reserve composition, disclosure, redemption mechanisms, and governance standards, regulators aim to prevent localized failures from cascading into broader financial instability. The integration of Stablecoin Regulation into financial stability frameworks reflects the recognition that stablecoins are no longer peripheral innovations but systemically relevant financial instruments.
Macroeconomic Stability and Monetary Sovereignty Considerations
Another core driver of Stablecoin Regulation lies in macroeconomic and monetary policy considerations. Stablecoins denominated in major fiat currencies circulate globally and, in some jurisdictions, function as de facto payment instruments. This phenomenon can weaken domestic monetary policy transmission and complicate capital flow management, particularly in economies with less developed financial infrastructure.
From a regulatory perspective, unchecked stablecoin adoption may undermine monetary sovereignty by shifting transactional demand away from domestic currencies. Stablecoin Regulation is therefore not intended to suppress innovation but to establish institutional boundaries that preserve macroeconomic control. By embedding stablecoins within regulated frameworks, authorities seek to balance technological efficiency with monetary and financial governance objectives.
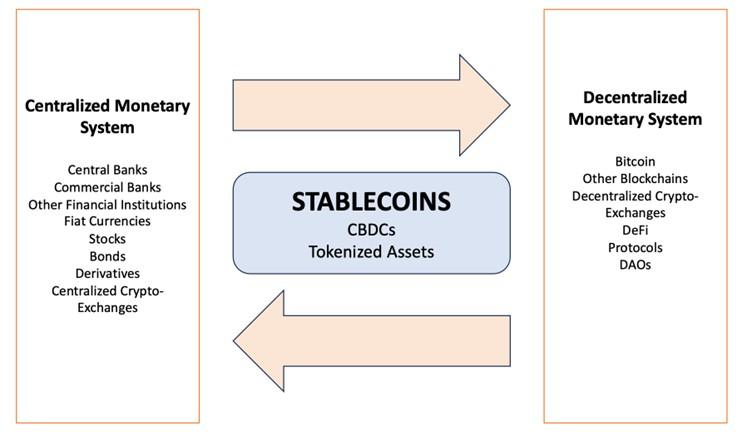
Figure 2: The Bridging Role of Stablecoins Between Centralized and Decentralized Financial Systems
Divergent Stablecoin Regulation Approaches Across Major Jurisdictions
The Risk-Oriented Logic of Stablecoin Regulation in the United States
In the United States, Stablecoin Regulation follows a risk-oriented and function-based approach. Rather than creating an entirely new regulatory category, U.S. authorities tend to classify stablecoins according to their economic function. As a result, stablecoin issuers and service providers may fall under banking supervision, securities regulation, payment system oversight, and anti-money-laundering requirements simultaneously.
The core objective of this approach is risk isolation. By strengthening reserve transparency, redemption guarantees, and compliance obligations, regulators aim to ensure that stablecoins do not become sources of systemic risk during periods of market stress. While this framework raises compliance costs in the short term, it also creates a pathway for stablecoins to be integrated into institutional-grade financial applications over time.
The European Union’s Unified Legislative Framework for Stablecoin Regulation
In contrast, the European Union has adopted a more centralized and legislative approach to Stablecoin Regulation. Through harmonized regulatory frameworks, the EU seeks to establish consistent standards across member states and reduce opportunities for regulatory arbitrage. This model emphasizes ex-ante authorization, continuous disclosure, and ongoing operational supervision.
From an industry perspective, EU-style Stablecoin Regulation significantly increases compliance requirements. However, it also provides legal certainty and predictable regulatory boundaries. Over the long term, this clarity supports market consolidation and encourages the development of stablecoins as standardized financial infrastructure rather than fragmented experimental products.
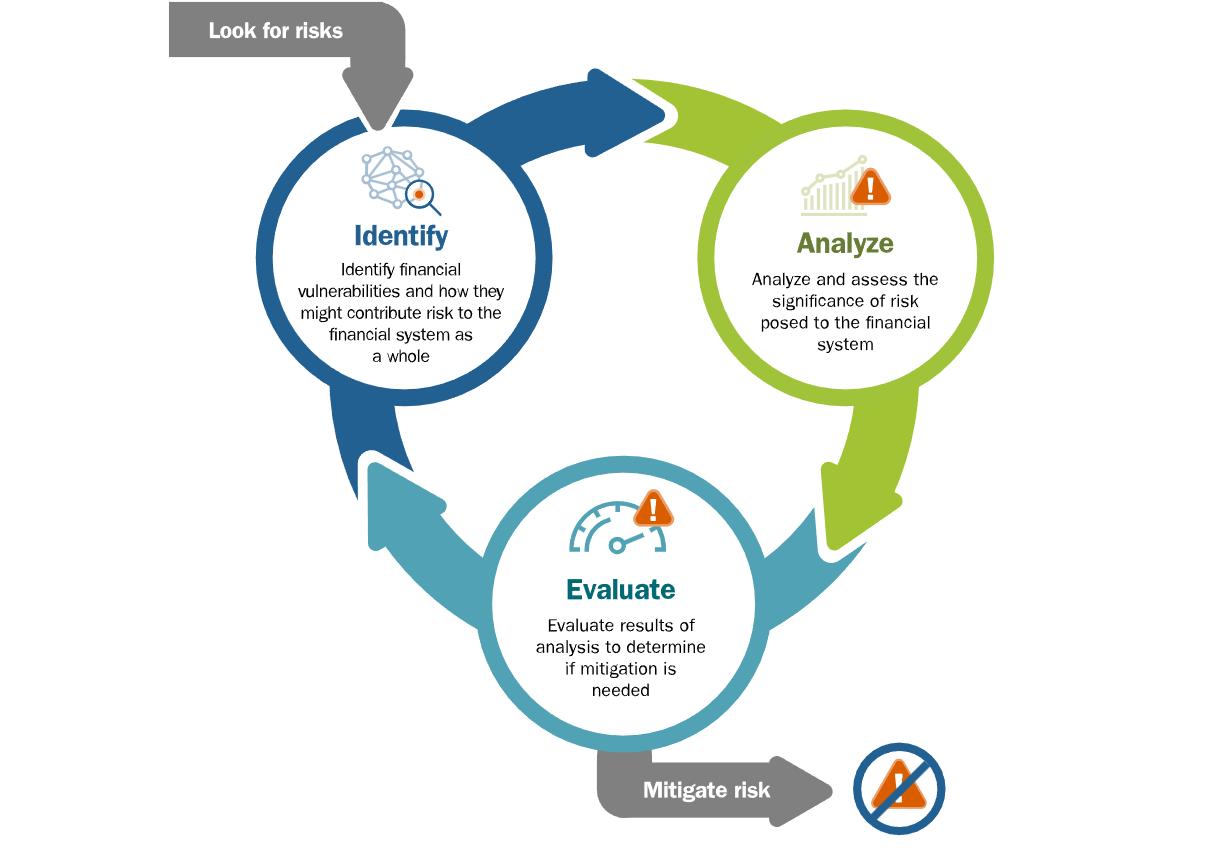
Figure 3: A Cyclical Framework for Risk Identification, Analysis, and Evaluation in the Financial System
Structural Impacts of Stablecoin Regulation on Industry and Business Models
Rising Compliance Thresholds and Market Restructuring
As Stablecoin Regulation becomes more comprehensive, the competitive landscape of the industry is undergoing fundamental restructuring. Projects that previously relied on rapid expansion, aggressive incentives, or high-risk yield strategies face increasing pressure under stricter regulatory scrutiny. Compliance capabilities, governance quality, and long-term sustainability are replacing short-term growth metrics as the primary determinants of competitive advantage.
Over time, Stablecoin Regulation is likely to increase market concentration. Highly compliant issuers with strong risk management frameworks are better positioned to survive and scale, while weaker projects may exit the market. This process does not suppress innovation but accelerates the transformation of stablecoins into core financial infrastructure.
Innovation Shifts Toward Efficiency Within Regulatory Boundaries
Stablecoin Regulation does not eliminate innovation; instead, it redirects it. Future innovation is expected to focus on efficiency improvements within regulated environments, including faster cross-border settlement, institutional-grade payment systems, on-chain treasury management, and deeper integration with traditional financial institutions.
By clearly defining permissible activities and risk boundaries, Stablecoin Regulation enables sustainable innovation. Projects that operate within these institutional frameworks are more likely to achieve long-term adoption and systemic relevance.
Featured Table: Comparison of Stablecoin Regulation Characteristics by Region
Stablecoin Regulation Is Defining the Long-Term Boundaries of Digital Finance
Stablecoin Regulation is not a rejection of digital finance innovation but an inevitable stage in its institutional maturation. As the global financial system undergoes structural realignment, Stablecoin Regulation is defining the boundaries within which digital assets can operate sustainably. It determines which models can integrate into mainstream finance and which remain confined to experimental margins.
With clearer regulatory frameworks, Stablecoin Regulation will increasingly function as a benchmark for credibility, resilience, and long-term value creation. Over the next decade, the evolution of Stablecoin Regulation will play a decisive role in shaping the structure of global digital finance and determining whether crypto-based financial systems can achieve durable, system-level integration.
Read More:
STABLECOIN OVERSIGHT GOES GLOBAL
USDe Market Cap Halved: A Test of Trust and Mechanism for Crypto-Native Stablecoins
〈Stablecoin Regulation: Institutional Logic, Regulatory Paths, and Structural Impact on Global Finance〉這篇文章最早發佈於《CoinRank》。







