Preface
Bitcoin is the first successful practical project of blockchain technology, which makes the concept of decentralization deeply rooted in the hearts of the people. In the more than 10 years since the birth of Bitcoin, various other types of blockchain projects have emerged in an endless stream. They have more advanced technology, higher TPS, and more complex and diverse ecology. In contrast, in terms of functionality, the main function of Bitcoin's blockchain network is the realization of value transfer, which is to transfer a certain amount of BTC from one address to another.
Recently, the release of the Ordinals protocol has made it possible for people to create NFTs on the Bitcoin chain. So what is the principle of Ordinals, and why can it create NFT on the "ancient" chain of Bitcoin? Does the NFT on the Bitcoin chain have any participation value and how to participate? Let's take a deeper look today.
(Figure: As of March 15, 463K BTC Inscriptions have been generated)
Section1 History
1.1 BTC network development history
Bitcoin (Bitcoin) is the world's first widely accepted and used cryptocurrency. After more than ten years of development and evolution, it has now become a leading global open decentralized digital currency. Bitcoin's success is largely due to its unique blockchain technology, a major innovation based on a decentralized network, making it a digital currency with no central administrator or institutional control.
1. Origin
The origin of Bitcoin (Bitcoin) can be traced back to 2008, and it was proposed and realized by one or a group of mysterious figures named "Satoshi Nakamoto". Satoshi Nakamoto introduced the basic ideas and technical solutions of Bitcoin in a white paper titled "Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System". After that, Satoshi Nakamoto started to implement the Bitcoin project and launched the first Bitcoin blockchain on January 3, 2009.
2. Start-up stage
In the early days of Bitcoin (Bitcoin) development, it received only a small number of people's attention, but it soon began to attract more and more users and investors. In May 2010, bitcoin was used to buy pizza in a transaction, which marked the beginning of bitcoin becoming the world's first commercial digital currency. In 2011, bitcoin prices began to rise, peaking at $30 per unit from a few cents at the time, and a short-lived boom ensued. However, since then, the price of Bitcoin has dropped rapidly to below $2 per unit, and the liquidity, inventory and acceptance of Bitcoin have all been staggeringly hit.
3. Maturity stage
In 2012, due to the uniqueness of Bitcoin and its possible significance to the economy, some prominent financial experts began to pay attention to Bitcoin. In June of this year, the first Bitcoin mining reward halving event took place, which halved Bitcoin’s mining reward from 50 BTC to 25 BTC and paved the way for similar events to be implemented every four years in the future . This has attracted more and more people to participate in Bitcoin mining and trading. In 2013, Bitcoin broke through the $100 price mark, the activity of the Bitcoin community increased rapidly, and more Bitcoin trading platforms and blockchain innovation companies began to appear at home and abroad.
4. Global Expansion
The global acceptance and popularity of Bitcoin has also gradually increased over time. In 2014, the price of Bitcoin fell from $1,200 to $200 in a short period of time, and it has fluctuated in price in the following years. At the same time, Bitcoin's technical ecosystem has grown and many new applications and services have emerged. In 2017, the price of Bitcoin began to rise rapidly, rising from a few thousand dollars to more than 20,000 dollars, creating a new historical record and attracting widespread attention around the world. In 2018, the price of Bitcoin once again became the focus, falling by more than 80%, but the Bitcoin market still maintains a strong vitality. It has become a mature and widely recognized asset class rather than a revolutionary digital currency, and the block Chain technology is more and more widely used in finance, logistics, healthcare and other fields. In the following ten years, BTC led the encrypted digital currency to set off a turbulent wave in the field of global financial wealth.
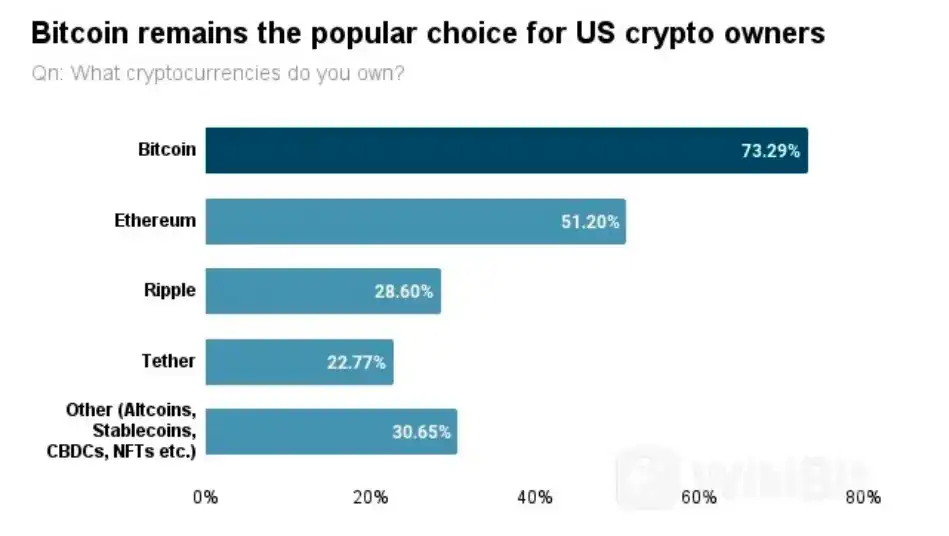
As of 2022, the average global cryptocurrency ownership rate is 4.2%, with more than 320 million encrypted users worldwide. Retail investors and institutions continue to pour in, and research from Triple A shows that 81% of American adults have heard of cryptocurrencies in 2022. Bitcoin is a popular choice among U.S. cryptocurrency owners, with more than 73% of cryptocurrency owner respondents owning Bitcoin.
5. Today and the future
At present, millions of people around the world use Bitcoin for transactions, and the use of Bitcoin is constantly expanding. Blockchain assets such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Litecoin have been widely recognized, and a large number of traditional investment companies and funds have begun to invest in this field. At present, many financial services for Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies have emerged around the world, such as Bitcoin trading platforms, wallet providers, payment processors, etc. In the future, Bitcoin and blockchain technology have huge development prospects and application space, and have more and more intersections with technologies and business models in other fields. However, there are also many challenges faced by Bitcoin and blockchain technology, such as scalability, sustainability, security, supervision and other issues, which require continuous technological innovation and improvement.
1.2 Taproot update
What is Taproot? Wikipedia gives the following definition:
Taproot: "The taproot is a large, central, dominant root from which other roots sprout from its sides. Typically, the taproot is somewhat straight, then tapers in shape, and grows straight down. In e.g. In plants like carrots, the tap root is a very well developed storage organ that has been cultivated as a vegetable."
Gregory Maxwell, the creator of the Taproot solution, said:
"The term originated from the visualization of a tree with a thick center like a dandelion taproot (a technique that is useful because assuming there is one high-probability path, the rest are blurred). I think this is a good approach as it validates the cost of the script path by utilizing a hidden commitment in the root.
... Alas, calling a hash tree with sorted internal nodes a "Myrtle tree" didn't catch on. (Myrtle tree is a family of trees that includes the Melaleuca tree, the tea-tree, which sounds like 'merkle'. :p)"

(Picture: Taproot upgrade has greatly improved the privacy, scalability, security and other features of the BTC network)
Specifically, BTC in 2021 underwent a Taproot update, adding the following:
1. Transaction verification optimization: Taproot combines multiple Bitcoin transaction verification conditions into a single condition, which greatly simplifies the verification process, reduces the transmission of uplink information during the transaction process, and improves transaction efficiency and transaction confirmation speed. It also increases the scalability of the Bitcoin network. At the same time, it is also beneficial to improve privacy.
2. Schnorr signature: Taproot uses Schnorr signature to reduce transaction signature information and improve transaction privacy. Most importantly, Schnorr signatures are much more amenable to batch verification, and are even able to combine multiple signatures. In Taproot, this is used to hide redundant, slightly public information in the Bitcoin network to preserve the privacy of transactions.
3. ASCII-style scripting support: In the Taproot upgrade, new computer languages can now be written using Bitcoin's scripting language. This enables Bitcoin users to create more complex applications, and more flexibly enhances the flexibility and variety of Bitcoin Script. This would facilitate, for example, node voting, lightning transaction spending, or complex Bitcoin-based transactions.
4. Redundant conditions: Taproot provides comprehensive support for the redundant conditions of the Bitcoin network. This technology can transform multiple conditions of Bitcoin transactions into a very efficient transaction method, which can easily deal with many different transactions and application scenarios.
5. MAST support: MAST is a highly flexible contract form that supports custom combinations of tree-based standard contracts. Taproot supports MAST in P2SH (Pay-to-Script-Hash), which improves the flexibility and diversity of Bitcoin.
6. Enhanced cryptographic protection: Although Bitcoin has proven to be a digital currency with strong security, the Taproot upgrade will bring additional protection measures, including the participation of BIP-Schnorr, environmental protection through the program The constructed Tapscript technology and the integration of Schnorr signatures into the Bitcoin scripting language ensure that the facilities and processes of Bitcoin transactions cannot be tampered with or hijacked by hackers.
Taproot, a more complex and advanced type of Bitcoin transaction, allows for more privacy and flexibility in transaction structure. Using Taproot, multiple parties can agree on a complex transaction without revealing all the details to the world. The upgrade of Taproot will urge Bitcoin to upgrade various scenarios such as smart contract deployment and expansion of use cases. That said, Taproot transactions can be more complex and subtle than sequential transactions, and it is this flexibility that makes NFTs on Bitcoin possible.
1.3 Definition of Ordinals
The very nature of Bitcoin is inextricably linked to the philosophies that guided its design and development. First, it is a philosophy that aims to maximize the ability of individuals to own and control their assets and identities through cryptography. It also enshrines money as a public good - free from state control - subject to purely mechanical and predetermined issuance. The concept of immutability in protocol design, transaction finalization, and issuance schedules is firmly rooted in the design and community of participating and using the network. Therefore, it is surprising to witness a new use case for Bitcoin emerge so suddenly, as was the case with Ordinals.
Ordinals are a mathematical concept that extends the set of natural numbers (1, 2, 3, ...) to include a notion of order. If we think of satoshis (sats) as the fundamental particles of Bitcoin, the smallest, indivisible constituent elements, we can define the mapping between sats and ordinal numbers by naturally counting the minting order of these sats. Mathematically, we can say that the set of satoshis is ordered because there is a definite sum between the order in which these sats were minted (ordered and recorded in the bitcoin chain) and the set of natural numbers we use to calculate them Well-defined mappings.
This mapping is possible because while the exchange value of BTC applies equally to all satoshis, the identity of each satoshi is uniquely determined by blockchain records, making each satoshi non-fungible because each satoshi Completely different from every other satoshi and can be distinguished. Thus, while the concept of fungibility usually centers around the exchange value of an asset, the perfect (i.e. complete, unique) history of each satoshi, from the moment it was minted, through every transaction, allows us to A satoshi assumes an identity - an identity that may in turn affect exchange value. However, this is not the only way to classify satoshis, as other equally valid numbering systems can be implemented, such as first-in-first-out vs. last-in-first-out.
Ordering satoshis out of the 1.9 trillion satoshis that have been mined to date naturally leads to multiple interpretations of a satoshi's relative rarity and value. Therefore, we can consider the first satoshi coin minted in a block to be much rarer than the average satoshi coin, since there are ~776,400 blocks in total. We can further identify the first satoshi in a difficulty adjustment, which occurs every two weeks (there are ~242 difficulty adjustments in total), or even the first satoshi after the halving, which occurs every four years (so far There are 3 halvings) to determine the incredibly rare satoshi. However, this attribution system is completely arbitrary, and as such, other methods of conferring rarity on sats may end up being more dominant than the previously described system based on the issuance of sats. Other schemes for defining names, numbers, coordinates, percentages, etc. in terms of satoshi order are equally conceivable.
Detailed explanation of Section2 protocol
2.1 Ordinals agreement
The full name of NFT is Non-Fungible Token (Non-Fungible Token). Unlike Bitcoin (Bitcoin), which is a typical homogeneous currency Token (FT), each NFT is unique and different from any other NFT. Since the design of the Bitcoin network does not allow NFTs, Ordinals proposed a new way of handling these BTC Tokens.
There are a total of 2,100,000,000,000,000 minimum units of Bitcoin, namely Satoshi (Satoshi), and 1 BTC = 100,000,000 Satoshi. So the total number of Bitcoins is 2,100,000,000,000,000 Satoshi. Ordinals distinguishes these Satoshis by sequentially numbering these Satoshis, which is also the origin of the project name "Ordinals: Ordinal Numbers".
There are many ways of numbering, such as directly according to the sequence number of pure numbers such as [2099994106992659](https://ordinals.com/sat/2099994106992659), or according to the block number + offset of each Satoshi occurrence position such as [ 3891094.16797](https://ordinals.com/sat/3891094.16797) etc. Once a Satoshi is numbered, any asset, such as an NFT, security token, account, or stablecoin, can be attached to a Satoshi using the serial number as a stable identifier. Ordinals refers to this "attach" action as inscribe, which is similar to the minting (mint) behavior of Ethereum NFT.
The next question is how does Satoshi differ from other Satoshi? For example, in many magic shows, magicians use items such as coins and playing cards as magic props. In order to prove that the magician has not changed the coin secretly, and has not modified it, the magician will ask the audience to make a mark on the coin, implying that this coin is unique in the world and different from other coins, so the magician cannot Use other coins to trick viewers. The method of Ordinals ordinal number theory achieves the effect that each Satoshi is different from other Satoshi by marking on Satoshi.
Many people may think this approach is a bit far-fetched, but the emergence of a new thing is often accompanied by controversy. In addition, marking Bitcoin is not the first time, such as Namecoin (BIP15) trying to create a DNS on Bitcoin, Colorcoin trying to add a mark to Bitcoin, etc. Ordinals is the latest and most successful of these attempts. Unlike the NFT system built by smart contracts such as Ethereum, all the data of Ordinals inscriptions are stored on the chain and do not depend on external storage such as IPFS or AWS S3. It is truly decentralized and is like all Bitcoin transactions. Saved in the blockchain. For example, Taprootwizards, the Bitcoin NFT image that first came into view, was stored on-chain at block number 774628.
However, storing the image on-chain takes up space from other normal Bitcoin transactions. This is another aspect of Ordinals' controversy. It "polluted" the financial transaction system of Bitcoin and occupied the precious storage space of normal transfer transactions. But from another point of view, this also opens up the application scenarios of Bitcoin, allowing Bitcoin to produce more functions besides transfer.
Technically speaking, the Bitcoin protocol has no type restrictions on this part of the data. Ordinals follows the MIME protocol. The data type can be pictures, videos, texts, identities or others, so Bitcoin is the strongest With a large decentralized consensus, there is still a lot of room for ecological imagination related to Bitcoin NFT in the future.

(Picture: Taproot Wizard became the largest BTC block in history, occupying close to the 4M upper limit of the BTC block)
The official Ordinals gave more information about the advantages of sat inscriptions compared to Ethereum NFT in the document. The two NFT forms have their own characteristics. Bitcoin NFT gives people a feeling of steampunk, using primitive mechanical infrastructure to build some retro but advanced worldviews. The following introduces some relevant technical background and issuance methods.
2.2 Technical Explanation of Inscriptions
Bitcoin Script (Bitcoin Script) is a set of programming environments built into the Bitcoin network. It uses a set of stack-based script codes composed of some simple operation codes (Opcodes) to enable Bitcoin to realize the programmable payment function. For example, the most basic P2PK (Pay to Public Key) payment method defines the checking process of how to pay to the public key through scripts.
Bitcoin Script (Bitcoin Script) is not a Turing-complete programming language. Its definitions and functions are mainly set up to complete various payment scenarios, and cannot be used for more complex business logic. And the Bitcoin community is quite restrained in adding new OP_CODE. It is also because the programmability of Bitcoin scripts cannot be given to make more complex functions. At that time, Vitalik, an important member of the Bitcoin community, wanted to build a blockchain with more complete programmability to support more complex decentralization. Application development, which is one of the reasons why Ethereum was born. .
Ordinals inscription content is entirely on-chain, stored in the spend script of the taproot script-path spend scripts script path. Taproot scripts have very few restrictions on their content, and also receive witness discounts, making storage of inscription content relatively economical. Taproot is the latest stage of bitcoin expansion after segwit. The expansion of bitcoin is to increase the transaction volume of bitcoin, but it also objectively creates conditions for the emergence of ordinals.
The expansion of Bitcoin has created the conditions for the realization of the Ordinals inscription. From a technical point of view, the more decentralized the blockchain, the less efficient it is. Today, the single block size of Bitcoin is still 1M, which is the same size as the first block dug out by Satoshi Nakamoto. The Bitcoin community did not go directly to the simple and crude solution of increasing the block size, but took the way of Segregated Witness that does not require Hard fork.
The following are the underlying BTC technologies/features that Ordinals rely on:
Segregated Witness
Each transaction information in Bitcoin is divided into two parts: basic transaction data + witness data, the former records the account balance, and the latter is to verify the identity of the user. For users, what they care about most is the core information related to assets such as the account balance, and the verification of user identity does not need to occupy too much cost in the transaction. In simple terms, the recipient of the transfer only needs to confirm that the asset is available, and does not need to know the details of the sender. However, in the Bitcoin transaction structure, witness data, that is, signature information takes up a lot of storage space, which in turn delays transfer efficiency and increases packaging costs. The isolated witness technology is to separate the witness data from the transaction information and store it separately.
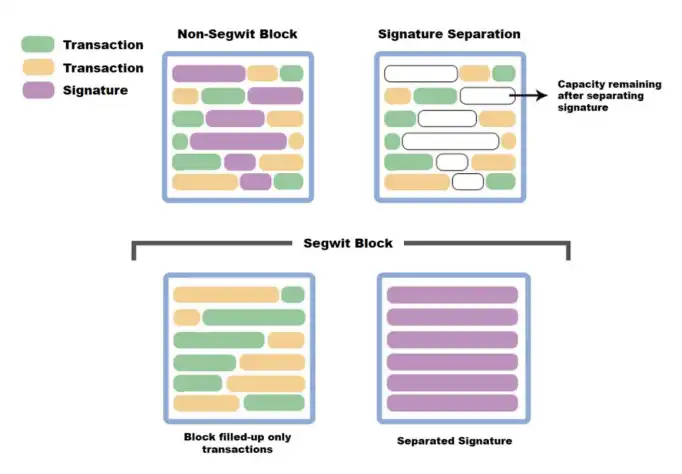
(Figure: Segwit technology updated by BTC in 2016)
Taproot
Taproot is a soft fork that optimizes Bitcoin Script, improving privacy, efficiency, and the network's ability to handle smart contracts. This is a recognized major upgrade of Bitcoin since the SegWit upgrade in 2017.
The Taproot upgrade consists of 3 different Bitcoin Improvement Proposals (BIPs): Taproot, Tapscript and, at its core, a new digital signature scheme called "Schnorr Signatures". Taproot aims to bring many benefits to Bitcoin users, such as improving transaction privacy and reducing transaction fees. It will also allow Bitcoin to perform more complex transactions, thus broadening the application scenarios. The ordinals protocol is the additional data implemented by the taproot script-path spend scripts script, so if you want to use the ordinals first inscription, you need to use the address of the P2TR script type.
lightning network
The technical requirements of the lightning network and the ordinals protocol are not directly related, but because the ordinals address is a bitcoin address that supports the lightning network, and the lightning network can reduce transaction fees and speed up transaction confirmation, it can be used in the casting process of inscriptions.
2.3 Encoding method of BTC NFT
How Inscriptions are Encoded in Transactions
Since taproot script spending can only be made from existing taproot output, inscriptions are made via a two-phase commit/reveal procedure. First, in a commit transaction, create a taproot output that is committed to the script containing the inscription content. Second, in a reveal transaction, the output created by the commit transaction is spent, revealing the inscription on the chain.
Inscription content is serialized using data pushes in unexecuted conditions, called "encapsulation". An envelope consists of an OP_FALSE OP_IF ... OP_ENDIF wrapped around any number of data pushes. Because envelopes are effectively no-ops, they do not change the semantics of the script that encloses them, and can be combined with any other locking script.
A text inscription containing the string "Hello, world!" is serialized as follows:
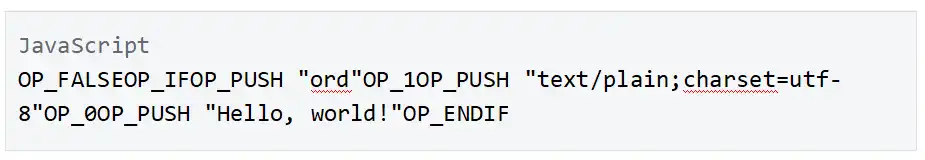
The Ordinals protocol essentially serializes this piece of code into the witness script.
We use an example to illustrate the encoding, which is the inscription numbered 139342, which engraves a time string "Fri Feb 17 05:02:18 PM CET 2023" on the sat numbered 1324061169091174, and it is shown below Links to the ordinals browser.
We can view the details of this transaction inmempool.space :
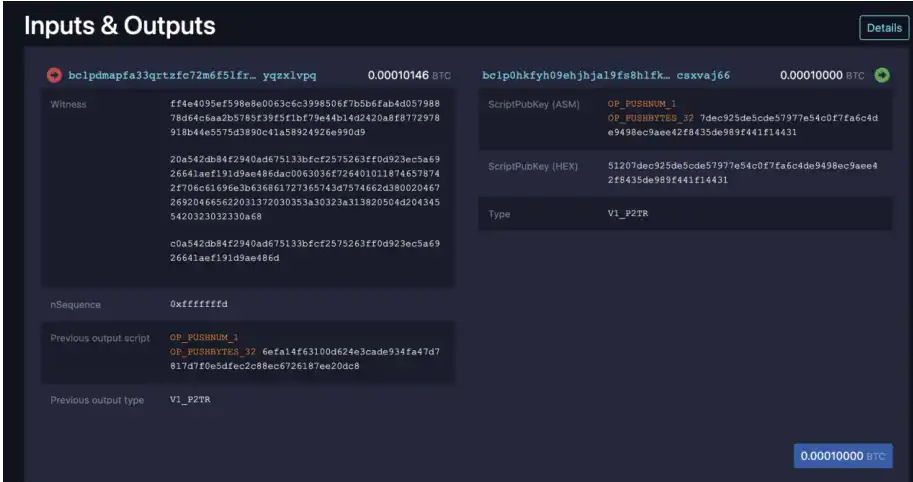
We conduct encoding analysis on the second part of the witness field to understand the serialized encoding content:
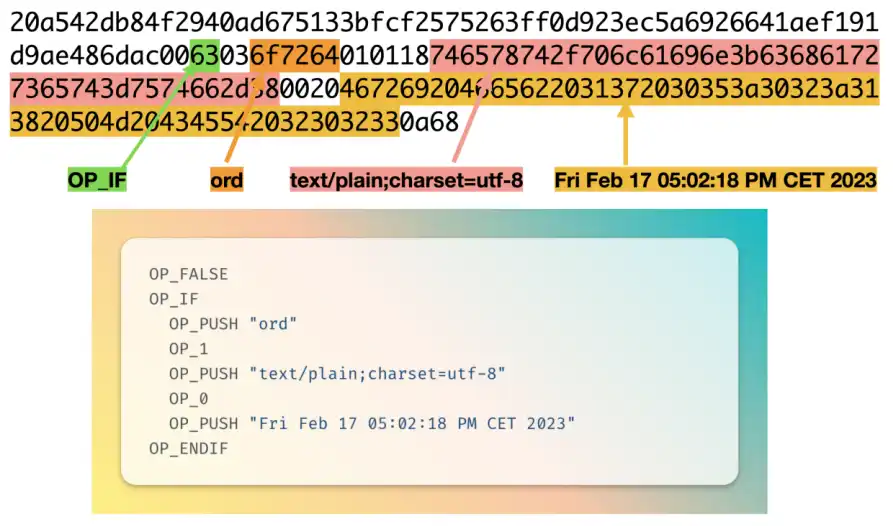
So as long as we can decode this part of the code in the witness script, we can know the content of the inscription. The encoding here is plain text information, and other data such as html, pictures, videos, etc. are similar. In theory, users can define their own encoded content, even encrypted content that only they know, but these content cannot be displayed in the ordinals browser.
Inscriptions stand alone - one can now put more arbitrary content on-chain than previous solutions like OP_RETURN or encoding data into multiple transaction outputs. But if users adopt Ordinals, these inscriptions can also be tied to individual satoshis, enabling them to be traded and transferred as NFTs. Importantly, the association of inscriptions with individual satoshis is based on an off-chain method for classifying individual satoshis that participating nodes must adhere to and agree to in order for any such connection between inscriptions and satoshis to be possible." exist" in any meaningful sense. While the inscription itself is published to the actual blockchain data, and all full archive nodes can see, instantiate, support and believe in the existence of the ordinal itself requires social consensus.
2.4 Use ord to issue NFT
The official document provides the ord tool to engrave Inscrptions on BTC . You can refer to the release document, which introduces Inscriptions and how to use ord to create and transfer Inscriptions. Inscriptions can be used to record arbitrary content and can exist in Bitcoin wallets. Like Bitcoin, Inscriptions are durable, immutable, secure, and decentralized. Issuing Inscriptions maintenance requires a Bitcoin full node to view the current state of the Bitcoin blockchain, and a wallet that can create Inscriptions and execute sat controls to construct transactions sent to another wallet. ord is a command-line tool written in Rust that can be built on top of the Bitcoin Core wallet. It provides commands to create, use and transfer Inscriptions. This document provides detailed instructions on how to install Bitcoin Core, sync the Bitcoin blockchain, create a Bitcoin Core wallet, receive and send Inscriptions.
The inscription of the inscription significantly expands the design space of Bitcoin and opens up more scene applications. This will form a whole new narrative, developing layers of culture. It is a challenge and exploration of the original Bitcoin function and use. Inscriptions have become a form of value collection. The types of Bitcoin OrdinalsNFT mainly include four categories: image, text, video, and audio. In the future, the Bitcoin NFT market ecology will be more diversified, and the construction of infrastructure and the use of tools are crucial to this emerging field.
At the same time, Bitcoin's Ordinals NFT is significantly different from traditional NFT issuance:
Bitcoin's Ordinals NFTs are always immutable, while Ethereum-based NFTs can technically be changed or deleted by the contract owner.
Bitcoin Ordinals NFTs always have on-chain content and cannot be lost. Inscription creators must pay a fee proportional to the size of the content. In contrast, Ethereum NFT content can be stored off-chain on platforms such as IPFS and can be lost.
Bitcoin Inscription is more secure. Inscriptions can be sold together with PSBT without the need for a third party (such as a trading platform or marketplace) to make the transfer on behalf of the user. Ethereum NFTs, on the other hand, tend to grant intermediary platforms unlimited permission to user NFTs, which can be difficult for ordinary non-technical people who want to trade digital art to interact with using complex smart contracts.
Section3 Oridnals project and platform status
1. Twelve Fold

TwelveFold, a Bitcoin NFT project by Yuga Labs, is a collection of 300 unique pieces of generative art. Created by the team using 3D modeling and algorithmic construction and high-end rendering tools, these artworks contain 3D and hand-drawn elements, all stored in a 12 base art system positioned on a 12 x 12 grid. TwelveFold uses the Ordinals protocol to engrave each work into a certain number of satoshis on the Bitcoin blockchain, making it non-tamperable and permanent.
TwelveFold started the auction on March 4, 2023 and closed within 24 hours, raising a total of $16.5 million. The auction adopts a blind auction method, that is, participants cannot see how much other people bid, but can only see their current ranking. The highest bid was 10 BTC and the lowest bid was 0.01 BTC. After the auction closes, the first 288 successful bidders will receive their purchases, which can be displayed or traded on the Xverse platform.
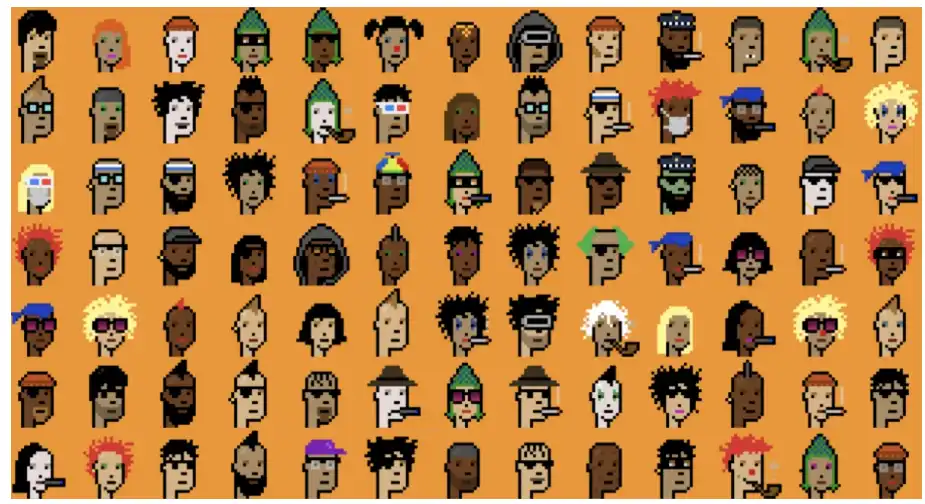
2. Bitcoin Punks
Bitcoin Punks is an NFT project imitating CryptoPunks on Ethereum, with a total of 10,000 different 8-bit pixel-style character avatars, each with unique attributes and scarcity. Bitcoin Punks will be minted on the Ordinals protocol on February 9, 2023, and traded on platforms such as Opensea.
Bitcoin Punks is the first project to successfully upload original Ethereum CryptoPunks to the Bitcoin blockchain using Ordinals, all assets have been minted by collectors for free. According to its development team, they are checking the hash value of each image uploaded to Ordinals and comparing it to the original 10,000 Crypto Punk images. The link to Bitcoin Punks must be the first occurrence of the inscription, which must also Contains the corresponding hash on the Ordinals protocol.

3.Ordinal Punks
Ordinal Punks is an exclusive collection that pays homage to CryptoPunks, one of the original collection of Ethereum NFTs. In homage to CryptoPunks, Ordinal Punks are a collection of BTC based NFTs, which are one-of-a-kind personal figure (PFP) collectibles that come in 100 different styles. Ordinal Punks, minted in Bitcoin's first 650 inscriptions, are 192 by 192 pixel images created using an open-source algorithm from anonymous Web3 creator FlowStay. Since Bitcoin's infrastructure requires users to operate a full Bitcoin node to craft inscriptions, bids and asks for Ordinal Punks are conducted on Google Sheets run by FlowStay, the community essentially using the project creator as a host on Discord people. dingaling purchased 7 Ordinal Punks for 211 ETH .

4. Sats.id
Project Introduction
Sats Names is a standard for defining domain names for Bitcoin using the Orinals protocol. The goal is to build a domain name ecosystem for Bitcoin, established by Bitcoin enthusiasts, and developed entirely based on the Bitcoin network. The project has three main goals:
• All domain names will be built entirely on the Bitcoin network
Transactions on the Bitcoin network are all that is required to register and renew SAT domain names. A single Bitcoin node can contain all the information needed for the state of a domain name. Without any other database or decentralized storage service, any client can independently calculate the true state of all domain names.
• The domain name agreement will remain absolutely neutral and trustworthy
Stay absolutely decentralized, no one can shut down the protocol or prevent others from registering domains, no smart contracts or frontends with privileged access, no tokenomics, no advance reservations, no gas tokens, no governance, no incentives whatsoever.
• All domain names will be held and controlled by the first minter, and domain names will not be duplicated
For example, the first user to mint an inscription containing "satoshi.sats" owns that domain name and the right to update it. The agreement guarantees the rights and interests of the first minter through uniqueness. Because of sequence numbers, anyone can write any data they want, including duplicate names, which will lead to collisions and competition in naming standards. Therefore, the Sats.id protocol proposes the "First is First" protocol principle.
Application Scenario
• In the Nostr social protocol, you can use this domain name as your identity
• As an address on the Lightning Network
• As an address on the Bitcoin network
• Log in to various apps as a username
• Quick lookups available in Bitcoin web browsers
Status of Domain Names
As of the Bitcoin network block height 16826243:
Sats.id domain name
Total Transactions: 66,210
Number of unique domain names: 54,134
Number of Independent Casters: 29,106
Generated gas fee: 131,773,878 sats
Section4 related infrastructure
1. Casting tools
Ordinals Bot
Ordinals Bot is a tool for minting Bitcoin NFTs on the Ordinals protocol, created by Ordinals founder Satoshibles team. The tool saves users from running a Bitcoin node when minting Bitcoin NFTs. After the user enters the official website and uploads the file, the casting fee is paid through the Lightning Network or the regular network, and the casting is carried out after the transfer is completed. If the user provides an NFT receiving address, the NFT will be automatically sent to the user; if the user does not provide an NFT receiving address, Ordinals Bot will keep the inscription for it until the user sets it. Once users have set up their wallets, they simply need to visit the order check tool to add addresses and receive NFTs.
Gamma.io
Gamma, the NFT market on Stacks, was originally named STXNFT, and it was announced on April 27, 2022 that it will be renamed Gamma. The platform aims to bring collectors, creators and investors together to explore, trade and showcase NFTs in the Bitcoin ecosystem. Gamma platform consists of three core products: NFT market, Launchpad and social platform. Gamma.io supports both primary and secondary markets for Bitcoin NFTs. Gamma.io offers a casting method called Gamma bot. Users can use Gamma bot to mint their own unique digital creations, collect them or sell them. Users can mint NFTs through simple commands without coding or technical knowledge: just add Gamma bot on Discord and enter commands such as create to create an NFT. Gamma.io also launched a . BTC domain name marketplace, allowing users to have their own decentralized identities and websites. Register, buy, sell, and transfer . BTC domain names on Gamma.io, and bind them to your own NFT.
ORDSWAP
https://ordswap.io/ ORDSWAP is an Ordinals market and wallet built on the Bitcoin network, on which ordinals inscriptions can be minted and traded. The website provides a temporary wallet, but it saves the private key directly in the webpage, I'm not sure if it's safe to do so. But it can be seen that they want to make an easier-to-use Ordinals infrastructure for more people.
Scarce City
https://scarce.city/ Scarce City is not a market specifically for Ordinals, but a relatively general trading market using Bitcoin technology, selling Bitcoin commodities in Bitcoin. Support hosting for auctions.
Ordinals directory
https://ordinalsdirectory.com/ only provides the basic inscription display function, the transaction function needs to be adjusted to the project discord community in a P2P manner, and the inscription casting directly jumps to ordinalsbot.com.
OrdinalHub
https://www.ordinalhub.com/ In addition to providing basic inscription display and project display pages, OrdinalHub also provides an education page for popularizing Ordinals. A calendar is also provided for upcoming project releases. However, it is difficult to distinguish the authenticity of the released projects, and the ordinalhub website itself only provides a twitter, and there is no community entrance.
2. Trading platform
ordinals.market
Ordinals Market is an open and decentralized platform where anyone can publish their own works or collect others' works. Ordinals Market also supports access to third-party applications and services to provide more functions and experiences. Ordinals Market allows users to use ETH to buy or sell BTC NFT, as well as browse and collect various interesting and unique works. The TwelveFold from Yuga Labs is available in the Ordinals Market. Linked to verified Opensea listings via Emblem Vault, a protocol that allows NFTs to be easily traded across chains, Ordinals Market provides users with all legitimate Bitcoin Punk NFTs to avoid being scammed.
Tweet
Twetch is a "Play to Earn" social network built on BSV that allows users to earn money by posting content. The platform also includes an NFT marketplace, a BSV wallet and several other features such as chat functionality and job boards. With the rise of the Ordinals protocol, Twetch has also started supporting BTC NFTs, and now they intend to integrate the Ordinals ecosystem into their infrastructure.
Twetch has also minted a series of NFTs called Planetary Ordinals on the Bitcoin blockchain through the Ordinals protocol, which are planet-themed works of art.
openordex
OpenOrdex is a decentralized trading platform for Ordinals. It is a geek project created by community developer Oren Yomtov. The UI style is very hardcore. Basic functions such as Collection display have been developed successively. It is worth mentioning that the centralized order The book is developed based on the previous smash hit Web3 communication protocol Nostr. The current version of openordex only supports the buying and selling operations of the Bitcoin cli client (the node client command line window) and the Sparrow Wallet client.
3. wallet
Inscriptions (Inscrptions) on BTC is a brand new ecosystem with rapid growth in infrastructure and tools. As the basis for constructing a deep liquid market, the wallet will be the key construction of the market foundation. The emergence of new wallets improves the portability of inscriptions, and from a custody perspective, inscriptions may be better and more secure than Ethereum NFTs. Inscriptions are bound to a single satoshis and custodians are not required to support the new token standard. The Bitcoin custodian only needs to provide UTXO-level escrow to ensure the security of the escrowed inscriptions. However, since Taproot is a more complex type of transaction, it may be more difficult for some users to create and manage NFTs on the Bitcoin blockchain.

Inscrptions&Ordinals Ecosystem Map
Ordinals Wallet
Ordinals Wallet is a browser wallet for sending and receiving BTC NFT on the Ordinals protocol. In addition to basic wallet functions, it also supports Bitcoin NFT inscription browsing, retrieval, Collection upload and other functions. It has a high degree of completion. Currently It is still being updated, including functions such as improving transmission efficiency, UI optimization, and reading wallet balances.
In addition, Ordinals Wallet also carried out an NFT AirDrop named Pixel Pepes on February 28, with a total of 1,563 pieces. Users only need to make one transaction in the wallet to get the AirDrop, but the AirDrop has now ended.
Sparrow Wallet
Sparrow Wallet is an open-source Bitcoin-based wallet that supports multiple transaction types and hardware devices. Sparrow Wallet also supports the Ordinals protocol, and the creator of Ordinals highly recommends the wallet. Users can use Sparrow Wallet to receive, manage and transfer BTC NFT. Users can also use Sparrow Wallet to create NFT, as long as they have a Taproot (P2TR) account and operate on some websites that support ordinals.
Sparrow Wallet engraves some data (such as text, pictures or videos) on a satoshis, and uses the Taproot signature scheme to ensure the integrity and immutability of the data. In this way, each satoshi becomes a unique digital artwork, that is, BTC NFT.
Hiro Wallet
Hiro Wallet is a wallet developed based on the Stacks chain, mainly used to manage STX Token. Support for Bitcoin NFTs has already begun. Browser extension users can use the same key or hardware wallet device to send bitcoin from their Hiro wallet to manage their STX and other assets across accounts, users can view their BTC holdings under "Balance", and also This address can be copied under Receive and will soon reveal the Taproot address for depositing BTC NFTs. As a Bitcoin ecological wallet, Hiro Wallet has many convenient built-in functions. Users can directly use credit cards, debit cards or even bank transfers to purchase STX in Hiro Wallet, and then directly participate in the pledge in the wallet.
Currently, the wallet supports browser extension versions of Chrome, Firefox, and Brave, as well as desktop versions of MacOS, Windows, and Linux systems. With support for Ordinals, users can pay for new BTC NFTs and deposit them directly into their accounts as “collectibles” by connecting Hiro Wallet to apps like Gamma. In addition, you can share your BTC NFT personal gallery.
Xverse
Xverse is a Stack-based Bitcoin non-custodial wallet and one of the largest markets in the Bitcoin NFT ecosystem.
Xverse allows users to create, distribute, buy, and sell various types of NFTs, including artwork, music, games, domain names, and more. Xverse supports the use of STX Token or other cryptocurrencies (such as BTC, ETH , etc.) for transactions, and also supports the use of Hiro Wallet or other wallets for connection.
Support for the Ordinals protocol has been added to support the display of BTC NFT; at the same time, Xverse has now supported the transfer of Ordinals, and related functions are still being improved.
Bitcoin.com Wallet
This is a mobile wallet that supports multiple cryptocurrencies including BTC and NFTs (called BNT) minted on the Satoshi Vision (SV) network. The wallet also plans to support the BTC NFT minted on the Ordinals protocol and provide corresponding display and transaction functions. Currently, the function supporting the Ordinals protocol has not yet been launched.
4 Bitcoin Inscription Future Market
According to the Galaxy Digital report, the Bitcoin NFT market size based on inscriptions and ordinal numbers will reach $4.5 billion in 2025. The rapid emergence of inscriptions coupled with the market/wallet infrastructure that has been launched are key factors in predicting that Bitcoin NFT will reach a market value of $4.5 billion within two years. The NFT encoded by Ordinals turns BTC into a "digital artifact" that is permanently stored in Bitcoin itself.
The introduction of Ordinals means the problem of stored information, which has a direct effect on the development of Bitcoin ecology. The integration of Ordinals NFT puts forward higher requirements on the data storage and cost of network transactions, and the real transaction space will be squeezed by Ordinals NFT. The increase in storage content has increased the block several times. It is true that, as the Bitcoin community disputes, the transaction attributes of Bitcoin itself have been invaded, and the popular Ordinals NFT has opened up a new latitude narrative.
In the future Bitcoin ecology, with the growth of Ordinals NFT, further expansion to mainstream NFT culture, such as PFP, memes and utility projects, will rapidly promote the construction of infrastructure such as markets and wallets. This will give birth to a large number of application tools, and a new narrative ecology will bring about the expansion of market share.
Summarize
The basic settings related to the NFT of the Bitcoin network are currently in a very early stage. The casting cannot be as convenient and simple as the Ethereum network. It is necessary to learn to create different forms of wallets, distinguish different forms of payment methods, and also need to synchronize all nodes of the Bitcoin network to participate. Mint NFTs based on the Ordinals protocol. There is no peer-to-peer trading tool as convenient and safe as Opensea when trading. Instead, a shared spreadsheet is used to update the order book, and sales can only be done through off-exchange transactions or escrow. Inevitably deceit is involved.
Bitcoin Punks can be minted quickly thanks to the full-node Bot developed and built by community members. If it takes a long time for an individual to complete the synchronization of the full node, it cannot be completed overnight. The figure below shows a case where community members are synchronizing all nodes of the Bitcoin network. However, because the casting method is currently in the order number mode, users cannot know whether a certain sequence number has been successfully uploaded to the chain. As a result, when using the full-node Bot, even if the casting is unsuccessful, user fees are charged at the same time, causing some users to use the threshold.
After the launch of the Ordinal protocol, the daily average block size of Bitcoin reached 2,021,079.56, a three-year high. On February 7, Pierre Rochard, vice president of research at Bitcoin mining company Riot Platforms, tweeted that the Inscriptions of the Bitcoin network NFT protocol Ordinal are consuming 50% of the Bitcoin block space, and the block space utilization rate is 100% , the median rate fell.
Therefore, the Bitcoin community is divided on the issuance of NFTs on the Bitcoin network based on the Ordinal protocol. Some believe it will provide more financial use cases for Bitcoin, which will drive demand for block space and hence fees. For example, Bitcoin educator Dan Held believes that as the amount of block rewards becomes smaller and smaller, miners will become more and more dependent on transaction fees. If Ordinals do intensify competition for block space, higher transaction fees may allow miners to continue securing the Bitcoin network.
While others believe it deviates from Satoshi Nakamoto's vision of Bitcoin as a peer-to-peer cash system, and that these NFT-like structures already take up block space on the Bitcoin network, which could drive up transaction fees. For example, in 2010, Satoshi Nakamoto vetoed the idea of expanding the Bitcoin system, saying that "it is impossible to expand every proof-of-work arbitration system in the world in one data set." The following are disputes over the issuance of NFT by Bitcoin point, also worthy of our attention and continue to solve.
Contrary to the original intention of BTC issuance: Some Bitcoin holders believe that Bitcoin exists to become a "peer-to-peer electronic cash system". Collecting BTC inscriptions sacrifices the financial attributes of Bitcoin itself, which deviates from the market for the development of Bitcoin.
Pollution of inscription data: Many operator nodes are not keen on downloading additional additional data. On the only way for nodes to download, the existence of inscriptions is obviously an additional problem for some nodes.
Data redundancy for market activity: After Bitcoin NFT became popular, adding NFT data would take up space in the Bitcoin blockchain database.
Popularity Disrupts Price: If Bitcoin NFTs become popular, the amount of space they take up on the Bitcoin blockchain could drive up the price of Bitcoin transactions. This will do the most harm to users in developing countries, the very users who need decentralized money the most right now. In the future, users who send bitcoins will incur high transaction fees, which is a substantial fee in many low-income countries.
In this regard, PANews believes that many users currently enter the blockchain and enter Web3 not because of Bitcoin, so they know little about the Bitcoin system. A large number of users have never used Bitcoin wallets, never used Bitcoin transfers, and I don't know what Bitcoin full node, lightning network, etc. are. Whether it is the Nostr social protocol or the launch of the Ordinals protocol, it has increased the application scenarios on the Bitcoin network, guiding more users to understand and recognize the Bitcoin ecology, and thus allowing more users to start using Bitcoin. Therefore, it is not a bad thing for the Bitcoin network to open and develop in multiple ways. As for how it develops, whether it is good or bad, it is up to the free game and judgment of the market. I believe that in the future, there will be more voices and trends in the development of the market. The Ordinals NFT on Bitcoin will open a new narrative. The growth and development direction of all parties in the market are full of interest.
For the infrastructure related to the NFT of the Bitcoin network, with the wealth effect and the increase in the number of users, and the continuous competition among ecological products, they will be gradually built and improved. What we can do now is to devote more energy to the ecological development of the Bitcoin network. At the same time, it should be noted that the current NFT projects on the Bitcoin network are in a state of chaos, and most of them are start-up projects, which belong to the sandy gold rush. Users need to make careful adjustments when looking for business opportunities to avoid asset losses.
thank you
https://academy.binance.com/zh/articles/what-is-taproot-and-how-it-will-benefit-bitcoin
https://dune.com/domo/ordinals-sats-names
https://foresightnews.pro/article/detail/27917
https://www.8btc.com/media/6808192
https://www.galaxy.com/research/whitepapers/bitcoin-ordinals-inscriptions-5-billion-nft-market/






