executive Summary
Web3 is a value network represented by blockchain, emphasizing data credibility, data sovereignty and value interconnection. In Web3, all values can be tokenized and efficiently and intelligently combined, transformed, transferred and distributed in the Web3 value network. These values have multi-level meanings of property rights. In addition to ownership, the most important thing is the right to use. For example, only the Token that owns a certain blockchain network, system or application has the right to use the network, system or application. At the heart of the market for access rights is stakeholder capitalism. The organizational form will change a lot, becoming an open source organization, a non-profit organization, or a decentralized autonomous organization (DAO). The tokenization of usage rights is key to understanding the development of blockchain infrastructure over the past 15 years.
In the next 15 years, Web3 applications built on blockchain infrastructure will become a new focus of development and have a revolutionary impact on human economic and financial activities, social interaction, and privacy protection in the digital world. The new Web3 economy will generate new currency markets, capital markets, and commodity markets, which require the use of different types of Tokens as value markers for economic activities, including functional tokens, equity tokens, and non-homogeneous tokens (NFT). Respectively represent the right to use, equity and digital certificates. We call it the "Three Token Model". In the new Web3 economy, the "three tokens" will give full play to the principle of stakeholders through the incentive mechanism on the basis of performing their respective functions.
The foundation of the healthy development of the new Web3 economy is the in-depth research and continuous practice of token economics. In token economics, monetary policy, mechanism design and financial engineering are the "trinity" relationship. The goal of monetary policy is to adjust the supply and demand of Token, so that the effective supply and circulation speed of Token can adapt to the development needs of the new Web3 economy. The goal of mechanism design is incentive compatibility, through the design of dynamic game mechanisms and algorithms for decentralized decision-making, to coordinate the consistent actions of multiple participants under asymmetric information and non-consistent goals. The goal of financial engineering is the conversion of risk and return, and the design of financial products and markets suitable for the new Web3 economy. The overall goal of token economics is to encourage stakeholders to actively participate in Web3 new economic activities by rationally designing token supply mechanisms, application scenarios, and related financial products and markets, so as to promote token value growth.
The new Web3 economy will surpass the Internet economy in terms of economic system, economic organization, financial system, value creation law, value distribution law, stakeholders, business model, distributed decision-making mechanism, and value capture. Different from the "thin protocol, fat application" value capture feature of the Internet economy, the new Web3 economy is "fat protocol, fat application" . The underlying protocol stack of the Web3 new economy has a built-in currency system and value system, and value creation can be performed at the protocol layer. The Web3 new economy will combine many digital technologies at the application layer, and the value creation space will be no less than that of the Internet.
1. Looking forward to the new economy of Web3
(1) Web3: underlying logic and evolutionary trends
Since the mid-nineteenth century, driven by communication technology (CT), information technology (IT) and digital technology (DT), the digital migration of human beings has continued to deepen, and the ability of human beings to collect and process data has continued to improve. Data has become an unprecedented new driving force for the development of human society and economy. The limitations of physical time and space have been broken, economic laws have been reconstructed, and commercial organizations have moved towards open source, openness, sharing and co-governance.
Human beings are social animals, and the history of human development is also the history of network evolution: from the relationship networks of ancient tribes, to public infrastructure networks in various physical forms, and then to digital networks. Human beings are deeply affected by the Internet in work, life, social, economic and political aspects.
The digital network is an efficient information exchange network developed on the basis of the Internet since the end of the last century. The development course of the digital network can be divided into three stages. Web 1.0 is an "information network" represented by portal websites . Users can easily obtain all kinds of online information, but in most cases, information dissemination is one-way. Web 2.0 is a "data network" represented by social media . Users create a large amount of content and leave massive data on online identity and behavior, and information dissemination becomes a two-way interaction. The Web 2.0 platform has generated huge commercial value through the collection and analysis of user data, but it has also caused complex governance issues such as poor user privacy protection, platform monopoly, and free use of news information. Web 3.0 is a "value network" represented by blockchain , emphasizing data credibility, data sovereignty and value interconnection. In Web 3.0, all values can be tokenized (Tokenized), and efficiently and intelligently combined, transformed, transferred and distributed in the Web 3.0 value network. These values have multi-level meanings of property rights. In addition to ownership, the most important thing is the right to use.
(2) The market for the right to use
The importance of access rights is nowhere more evident than in digital products and services. As shown in Figure 1, products in physical form can only be used by the same subject at the same time, and are accompanied by consumption, wear and tear and depreciation during use. Digital assets and services generally have the characteristics of high fixed costs, low marginal costs, and non-competitive use. Digital products and services can be shared by multiple people at a point in time. This has two effects.
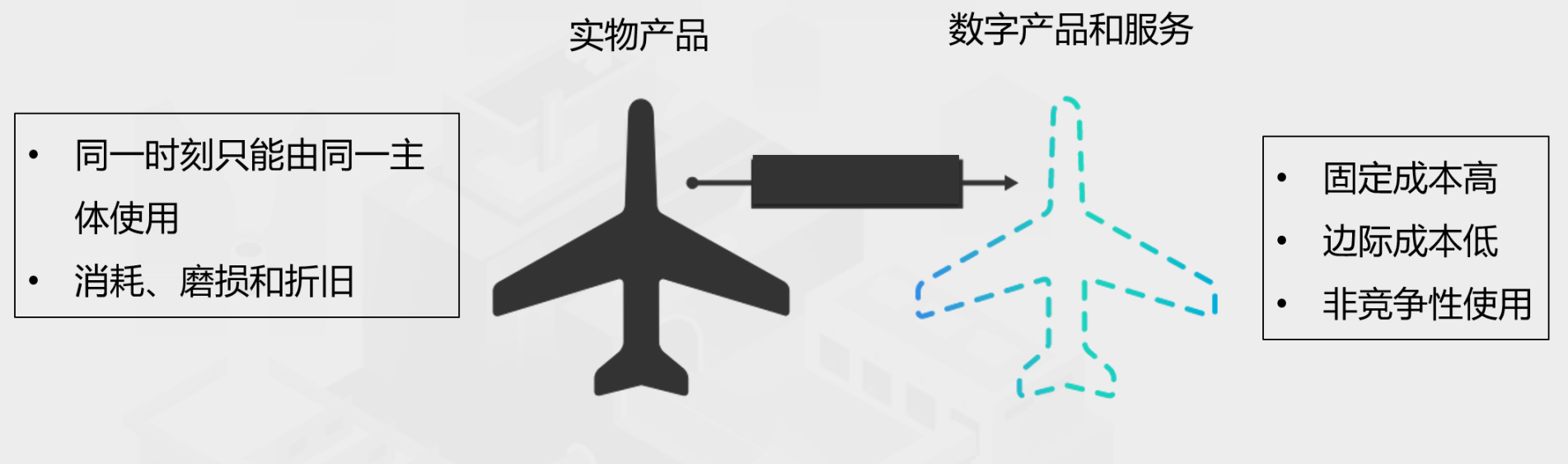
Figure 1: Economic characteristics of physical versus digital products or services
On the supply side, digital products and services have obvious economies of scale—the more produced, the lower the average cost after amortization. For example, developing a piece of software requires a lot of investment, but after the software is developed, whether it is used by one person or 100 million people, the total cost will not be significantly different.
On the demand side, when digital products and services are used by multiple people, enormous economic and social value is generated through network effects. Kevin Kelly summed up this more than 20 years ago as the "fax machine effect." Suppose someone buys a fax machine for $200, his cost is $200. But after his fax machine is connected to a fax machine network consisting of 10 million fax machines, he can exchange faxes with other people, and the network value he enjoys is much higher than the cost of buying a fax machine. Therefore, the fax machine also represents the right to use the fax machine network.
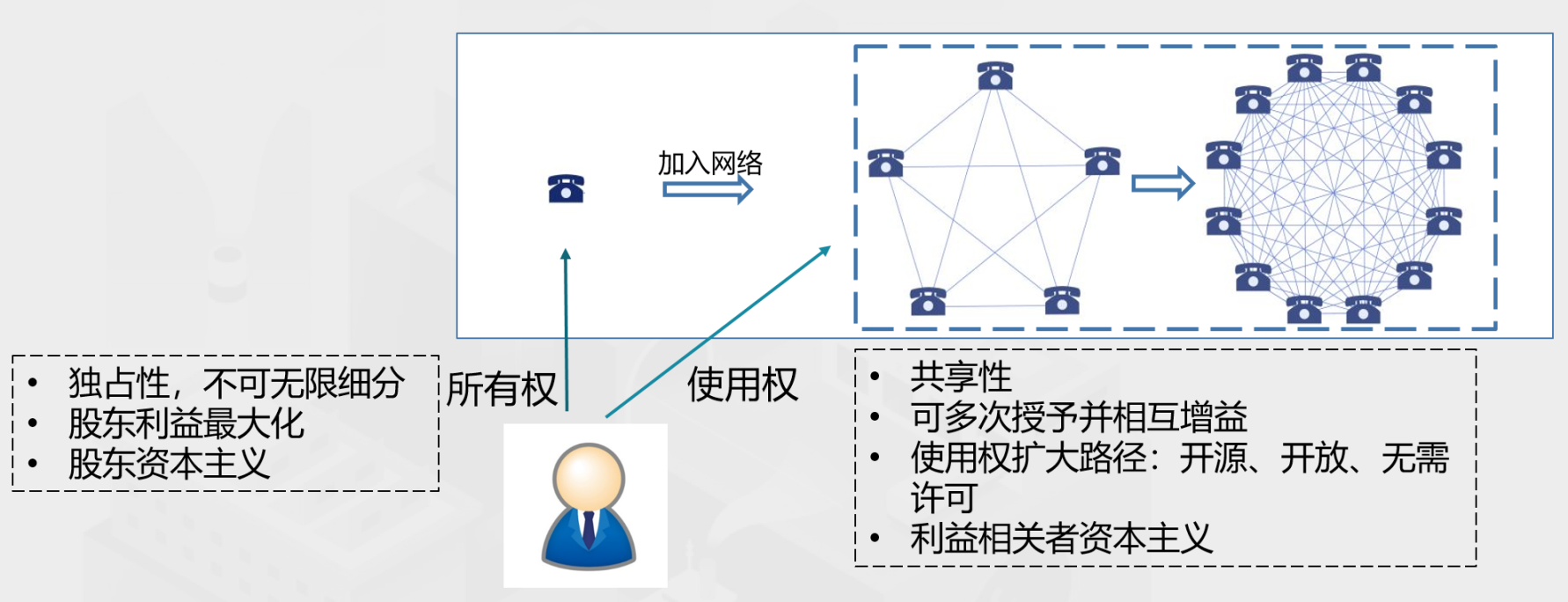
Figure 2: Comparison of ownership and usage rights
Use rights and ownership rights, although belonging to different dimensions of property rights, are very different. As shown in Figure 2, ownership is exclusive and cannot be infinitely subdivided. Under the ownership system, the goal of the company's operation is to maximize the interests of shareholders. This is known as shareholder capitalism, and it is most evident in the stock market. The right to use is shared, and can be granted multiple times and benefit each other. For many digital products and services, the right to use can theoretically be granted indefinitely, and the path to expanding the right to use is open source, open, and license-free.
At the heart of the market for access rights is stakeholder capitalism. The organizational form will change a lot, becoming an open source organization, a non-profit organization, or a decentralized autonomous organization (DAO). These organizations pursue the maximization of organizational value (or common interest). All participants in the organization collaborate on a large scale as stakeholders, make their own contributions, and share organizational value. In these organizational forms, ownership becomes irrelevant, and what is really valuable is access. Although the right to use cannot be denominated, it can be tokenized.
(3) The core position of blockchain in Web3
In the past 15 years, with the rapid development of the public chain ecology represented by Bitcoin and Ethereum, the underlying technology of the blockchain has matured. The blockchain research and development mechanism is rooted in the open source community, which embodies the characteristics of openness, sharing and unbounded innovation. Blockchain infrastructure is an important public product that is not owned by any individual or institution. The distributed ledger of the blockchain can extract the right to use from digital products and services, standardize and share the right to use in the form of Token, and form a digital asset market on this basis. The digital asset market can provide services such as the issuance and trading of usage rights on a global scale. In terms of value capture, the blockchain embodies the characteristics of "fat protocols, thin applications".
In the next 15 years, Web3 applications built on blockchain infrastructure will become a new focus of development and have a revolutionary impact on human economic and financial activities, social interaction, and privacy protection in the digital world. First of all, the blockchain basic protocol will be the basic guarantee for the development of Web3 applications, and the effective operation of business activities on the blockchain will be guaranteed through smart contracts. Second, Web3 applications ensure trust-free, open and transparent systems, and permission-free participation through decentralized governance mechanisms, and distributed autonomous organizations (DAO) will become the main form of organization. Finally, non-homogeneous tokens (NFT) become Web3 application users' identity proof, ability proof, behavior proof, workload proof, contribution proof, activity proof, product and service proof, etc. Based on these proofs, Token will be used as an incentive tool to establish an effective incentive mechanism.
With the clarification of regulatory policies, equity tokens will achieve considerable development. In the distributed economy built around Web3 applications, equity tokens, utility tokens, and non-homogeneous tokens (NFT) will give full play to the stakeholder principle through incentive mechanisms on the basis of performing their respective functions. The new economy of Web3 will embed a new economic system and financial system, and the economic and social value created will be greater than the two organizational forms of profit-making companies and open source communities composed of volunteers, and these values will be composed of equity tokens, functional Shared by token and non-fungible token (NFT) holders. In terms of value capture, Web3 gradually presents the characteristics of "fat protocols, fat applications".
2. All values can be tokenized
(1) Re-acquaintance with Token
Blockchain-based digital assets are essentially tokenized values (Tokenized Value), technically all are Tokens, and Tokens include two types: homogeneous and non-homogeneous. How to understand the important position of Token in the new Web3 economy? As early as in the 1960s when the computer system first came out, as shown in Figure 3, Token (token) represented the permission to access and use the computer system. When the use license of the computer system - Token (token) gradually evolved from the Internet stage to the blockchain stage, the use license was further standardized, shared and financialized, and became the Token in the Web3 new economy. Token is a system for extracting usage rights from digital products and services and capturing value.
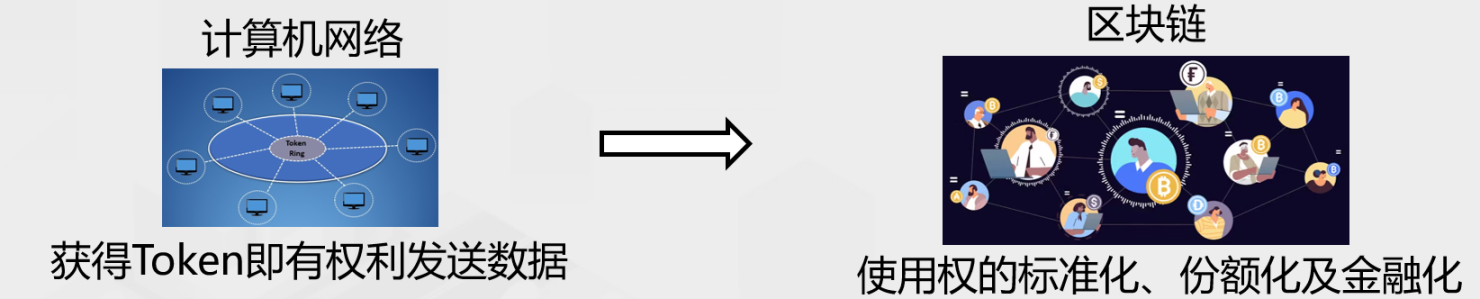
Figure 3: Evolution of Token
In the new Web3 economy, all values can be tokenized. The basis of tokenization is the identity management, currency and payment, asset registration, transaction, and clearing and settlement functions that come with the blockchain. There are 4 main ways of tokenization. First, Token represents the right to use. Second, NFT stands for proof of identity, proof of ability, proof of behavior, proof of workload, proof of contribution, proof of activity, and proof of products and services. Third, Token represents off-chain value, such as central bank digital currency, stable currency, and tokenization of green bonds. Fourth, Token represents income rights, governance rights, or a combination of digital assets.
(2) The real value of Token
First, Token is issued. Token issuance relies on a set of pre-defined algorithm models, the key is to control the number and speed of issuance. The quantity limit and issuance discipline stipulated by the algorithm are the basis of the Token consensus and trust mechanism, which embodies the "Code is Law" principle.
Second, Token represents the right to use. Only those who own a Token of a blockchain network, system or application have the right to use the network, system or application.
Third, the circulation of Token. When users use a blockchain network, system or application, they will consume some Tokens every time they use it. Therefore, Token circulation is a deflationary model as a whole. For example, in Ethereum, the daily gas consumption is greater than the newly issued ETH in the network every day, which plays an important role in supporting the value of Ethereum.
Fourth, the equity attribute of Token. In some application layer protocols on the blockchain, the creation team often not only uses Token for functional purposes, but also uses Token for equity purposes. For example, the founding team usually promises to use part of the cash flow income of the project to repurchase the Tokens circulating in the market, which is essentially to transfer part of the rights to the Token holders.
Fifth, the governance attributes of Token. In the blockchain network or system, some distributed communities or decentralized autonomous organizations (DAO) often transfer some governance rights through Token. Token is a certificate of voting rights, and Token holders can participate in community voting, voting and governance.
(3) The "Three Token Model" of the Web3 New Economy
Because of the global unification of the blockchain basic protocol, the built-in value capture system only requires a "single token model", typical representatives are BTC and ETH. The new Web3 economy will generate new currency markets, capital markets, and commodity markets, which require the use of different types of Tokens as value markers for economic activities, including functional tokens, equity tokens, and non-homogeneous tokens (NFT). Respectively represent the right to use, equity and digital certificates. This is the "Three Token Model".
Utility tokens represent the right to use digital products and services. Only when holding a utility token issued by a certain network, system or application, is the right to use related products and services. The greater the number of ecological applications and users, the greater the market demand for utility tokens. Functional tokens are also a certificate for receiving other rights and interests. For example, the project party locks the address holding a certain token as the target group, and AirDrop the governance token of the project to the address. In practice, functional tokens can be given away as ecological credits for free to motivate users and start the market; functional tokens can be free of financing activities such as "issuance, sale, and subscription", and the price of tokens is discovered by secondary market transactions form. The value sources of utility tokens include: 1. "permission" to use the network; 2. Used to pay Gas fees and commissions; 3. The company uses part of the profits to repurchase; 4. The rights certificate of community governance; 5. Priority to receive AirDrop and add to the whitelist. Utility tokens are the unit of value for network effects.
The founding team and early investors play a vital role in the project from initiation to landing. At this stage, if there are only utility tokens, the incentives for the founding team are not enough, and the rate of return cannot attract early investors. Therefore, it is necessary to introduce equity tokens, which represent equity granted to project parties and early investors. In terms of economic nature, there is no essential difference between equity tokens and stocks. Equity tokens will not be listed and traded on stock exchanges, but will enter virtual asset exchanges in the form of STO (Equity Token Issuance). STO is sold on a global network such as a public chain, and is on the same trading platform as functional tokens, combining users and investors, and usually achieves a higher valuation level.
Non-homogeneous tokens (NFT) play an important role in the confirmation, licensing and certification of fully digital things, and are truly "digital certificates". NFT can capitalize things with confirmed rights and circulate them in secondary transactions to enhance the liquidity of assets. NFT can be a record of the contribution, activity, and behavioral capabilities of stakeholders in the Web3 economic system, and these records can be used as the basis for rewarding stakeholders. In short, NFT can connect everything, including connecting Web2 and Web3, connecting the real world and the virtual world, connecting offline, off-chain and online, on-chain, connecting digital twins and digital natives, connecting users and communities, and connecting consumption and experience. The value sources of NFT include "Play NFT to Earn" and "Play NFT to Owns".
In general, the new Web3 economy is essentially a distributed network. In the distributed network, value is continuously generated, combined, transformed, circulated and distributed. Utility tokens act as usage rights for distributed networks to capture network value. Some value is deposited in the enterprise node, and the equity token represents the equity of the enterprise. NFT functions as a digital token in a distributed network.
3. Token Economics
(1) "Trinity" methodology
In token economics, monetary policy, mechanism design and financial engineering are the "trinity" relationship. The goal of monetary policy is to adjust the supply and demand of Token, the goal of mechanism design is incentive compatibility, and the goal of financial engineering is the conversion of risk and return.
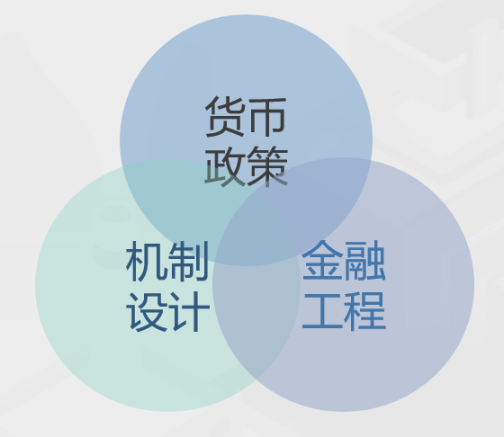
Figure 4: The “Trinity” methodology of token economics
All token economic systems are affected by the supply and demand of Token at the macro level, and are affected by the incentive mechanism of stakeholders at the micro level, and are inseparable from financial engineering methods in financial product and market design. The research goal of token economics can be summarized as: through rational design of Token supply mechanism, application scenarios and related financial products and markets, to motivate stakeholders to actively participate in Web3 new economic activities, thereby promoting the growth of Token value.
(2) Monetary policy
1. Impossible triangle of token economics
Innovation in the Web3 field will mainly revolve around two "impossible triangles", as shown in Figure 5. The first is the "Blockchain Impossible Trinity", which means that no blockchain network or system can achieve the three goals of decentralization, scalability, and security at the same time. The second is the "Impossible Trinity of Token Economics", which means that no token economic model can simultaneously achieve the three goals of free trading, price anchoring and independent issuance. The "Impossible Trinity of Token Economics" is the key to understanding the sustainability and inherent stability of token economic models. In a certain sense, the breakthrough of the "impossible triangle of blockchain" is the fundamental driving force for the innovation of the underlying technology of the blockchain, and the breakthrough of the "impossible triangle of token economics" is the fundamental driving force of the innovation of token economics.
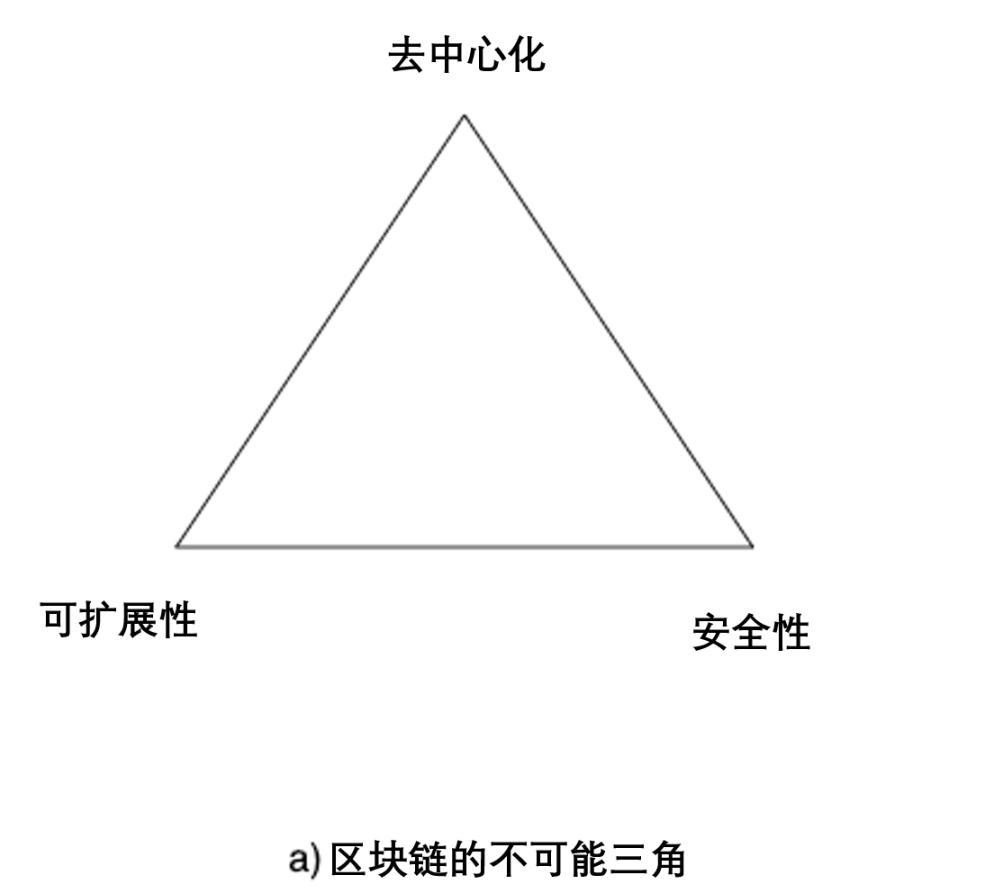
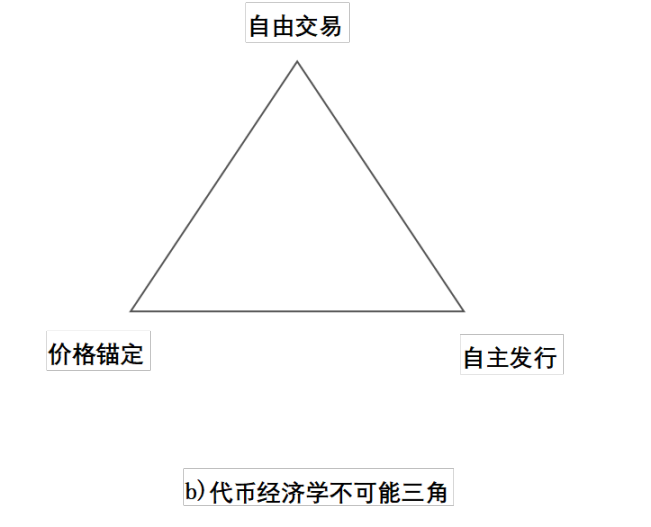
Figure 5: Two "impossible triangles" in the Web3 field
2. Separation of asset function and currency function
In the Web3 new economy, Token prices will fluctuate due to factors such as ecological development, secondary market liquidity, and investor sentiment. If Token is used as a payment tool for economic activities, price fluctuations may inhibit the development of economic activities. Token price fluctuations may also lead to inherent instability in token economic models.
In order to ensure the stability of the Web3 economic system, it is necessary to separate the asset function from the currency function when designing the token economic model. The Token that assumes the asset function represents the participants' shares in the Web3 new economy, and the goal is to capture the value brought by economic development. The Token that assumes the currency function can isolate the impact of the previous Token price fluctuation on economic activities, enabling participants to focus on economic activities themselves. In some stages of the development of the new Web3 economy, it is inevitable that token prices will fall, and it is necessary to avoid irreversible damage to economic activities and community cohesion caused by token price drops. In this way, when the market fundamentals improve, Token prices can be repaired upwards.
The token economic model requires a built-in stabilization mechanism: during the period of token price decline, the participation cost of economic activities decreases, and economic activity increases, accompanied by the decrease of token issuance speed and circulation velocity. This will form a strong support for Token value and prevent the occurrence of "death spiral".
3. Token issuance and return mechanism
Token issuance and return mechanisms have a crucial impact on the stability of the token economic model. In the real world, the growth rate of money supply is generally equal to the sum of GDP growth rate and inflation rate. In the new Web3 economy, the effective supply and circulation speed of Token must adapt to the development needs of the new Web3 economy. The core issues include: first, the initial issuance quantity and speed; second, the issuance speed after the secondary market price appears; third, the relationship between Token price and mainstream tokens or related tokens (Token exchange rate model), and The impact on the economic model; Fourth, Token's return, repurchase, destruction, and precipitation in usage scenarios.
Some mechanisms can regulate the effective supply and circulation speed of Token. First, expand the application scenarios of Token, so that a part of Token "precipitates" in the application scenarios instead of entering the secondary market circulation. Second, introduce the destruction mechanism of Token. For example, in some application scenarios, the Token paid by the user is automatically destroyed. The repurchase mechanism of Token is also very important. The repurchase speed can be non-linear or accelerated, and the goal is to achieve the deflation effect. Third, the staking mechanism is essentially to regulate Token liquidity in different time intervals. In the near future, the pledge will "freeze" some Tokens; but in the long run, these Tokens will be released, and the pledge rate of return changes with the new issuance of Tokens. If the fundamentals of the new Web3 economy can be improved during the staking period, it will be able to absorb the Token liquidity released in the future.
(3) Mechanism design
Every rational economic person will participate in market activities in accordance with the rules of self-interest, but individual pursuit of self-interest may violate collective interests or affect the overall goals of society. If there is a mechanism design that enables each participant to pursue the behavior of maximizing their own interests, which coincides with the goal of maximizing collective interests, the mechanism design is incentive compatible.
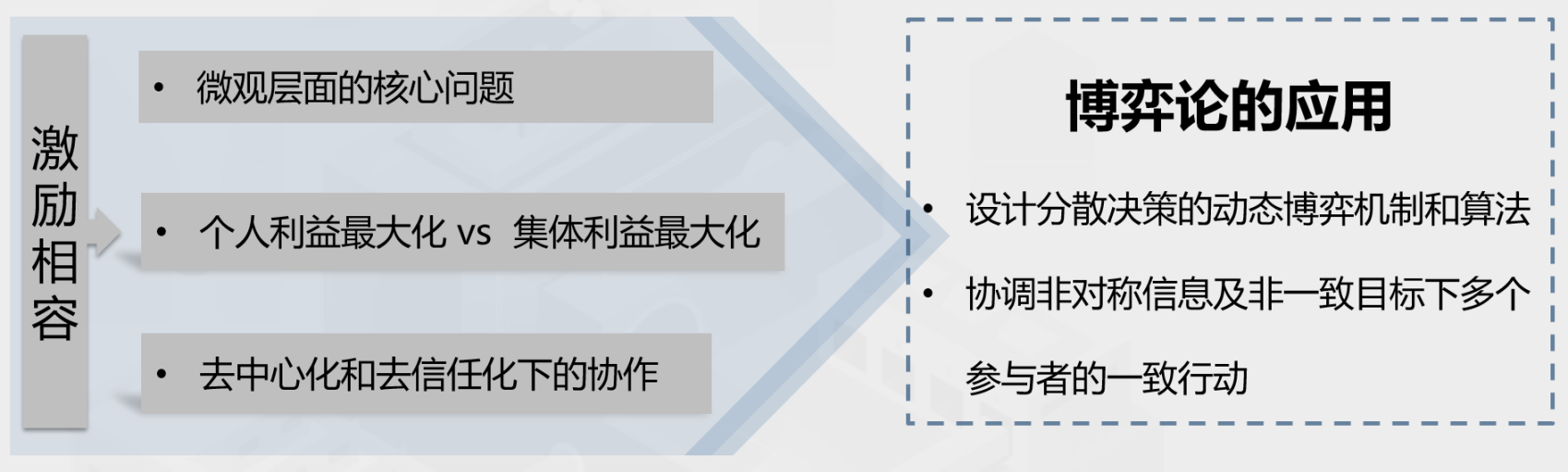
Figure 6: Core principles of token mechanism design
As shown in Figure 6, incentive compatibility is the core principle to be followed in the design of the token economic model. Only when the conditions of incentive compatibility are met, can collaboration be promoted in a decentralized and trustless environment, so that the individual interests of participants are consistent with the collective interests, and the internal division of the community due to unfair incentives can be avoided.
In the new Web3 economy, there are great differences among participants in psychological factors, cognitive biases, and behavioral tendencies. Therefore, perfect incentive compatibility is difficult to achieve in mechanism design. How to design a dynamic game mechanism and algorithm for decentralized decision-making to coordinate the concerted actions of multiple players under asymmetric information and non-consistent goals is an important issue.
In the "Three Currency Model" of the Web3 new economy, mechanism design has important application value. Equity tokens are the subject of securities regulation, and they need to meet the requirements of securities regulation or meet the standards of exemption conditions during issuance and trading. For example, the US Securities Regulatory Commission (SEC) uses the Howey test to determine whether a digital asset has securities attributes. The Howey test includes four criteria: monetary investment, commitment to a common project, no need to run it yourself, and expectation of profit. In the design and use of functional tokens, in addition to not touching the four criteria of the Howey test, it is best to distribute them free of charge through ecological rewards. In this case, before the functional token enters the secondary market circulation, the starting price cannot be determined based on past financing, but the starting price can be guided by a bilateral Dutch auction. Dutch auctions are carried out on the blockchain in an open, transparent, secure and unmanipulated manner by centralized institutions. Whether functional tokens can be listed on the exchange can also be decided through community quadratic voting.
(4) Financial engineering
Token economics uses financial engineering methods for risk-return conversion. There are five main goals: first, support resource allocation across time and space; second, design corresponding financial products according to different scenarios and different user needs; third, flow property management, especially reducing liquidity costs; fourth, asset pricing; fifth, risk management.
4. The new economy of Web3 surpasses the Internet economy
In terms of economic system, economic organization, financial system, value creation law, value distribution law, stakeholders, business model, distributed decision-making mechanism, and value capture, the new Web 3 economy will surpass the Internet economy.
(1) Economic system
From the perspective of the property rights system and capital income distribution system, the economic model can be divided into the "main street model" under the industrial economic model, the "Silicon Valley model" under the Internet economic model, and the "shared capital model" under the Web3 new economic model.
The "Main Street Model" is centralized in terms of property rights, and capital gains are exclusive, so there are a large number of big capitalists at this stage.
Property rights in the "Silicon Valley model" are decentralized. The scope of capital has been expanded, capital is no longer limited to the amount of money, and knowledge has also become an important capital. Entrepreneurs attract venture capital and realize the realization of knowledge through business plans. The "Silicon Valley model" is no longer a model of monopoly capital and exclusive income, but a share of rights and interests through shareholder capitalism, which has become a share that can be shared.
The "shared capital model" is a model that goes further than the "Silicon Valley model". All stakeholders can share all the value of economic organization or business organization. Entrepreneurs under the "Silicon Valley Model" become the initiators of the "Shared Capital Model".
(2) Economic organization
Economic organizations under the "Main Street Model" and "Silicon Valley Model" are usually centralized corporate organizations. When the company organization was rising, it mainly adopted a top-down decision-making mechanism, which was a U-shaped structure. With the diversification and globalization of the company's economic activities, business divisions and regional divisions have gradually emerged, and the power of the group headquarters has been gradually dispersed, presenting an M-shaped structure in terms of structure.
The "shared capital model" essentially inherits the M-shaped structure of the company organization, and gradually forms the form of a distributed autonomous organization (DAO), and distributes the rights or interests of the organization to stakeholders through tokenization.
(3) Financial system
There may be two sets of capital market systems in the new Web3 economy. The first is shareholder capitalism based on the equity system and capital income distribution mechanism of the industrial economy and the Internet economy. The form of financial activities of shareholder capitalism is shown in Figure 7. Companies raise funds from the market through equity. Equity is the standardization and financialization of company ownership. Holding equity can obtain the company's profit dividends and governance power.
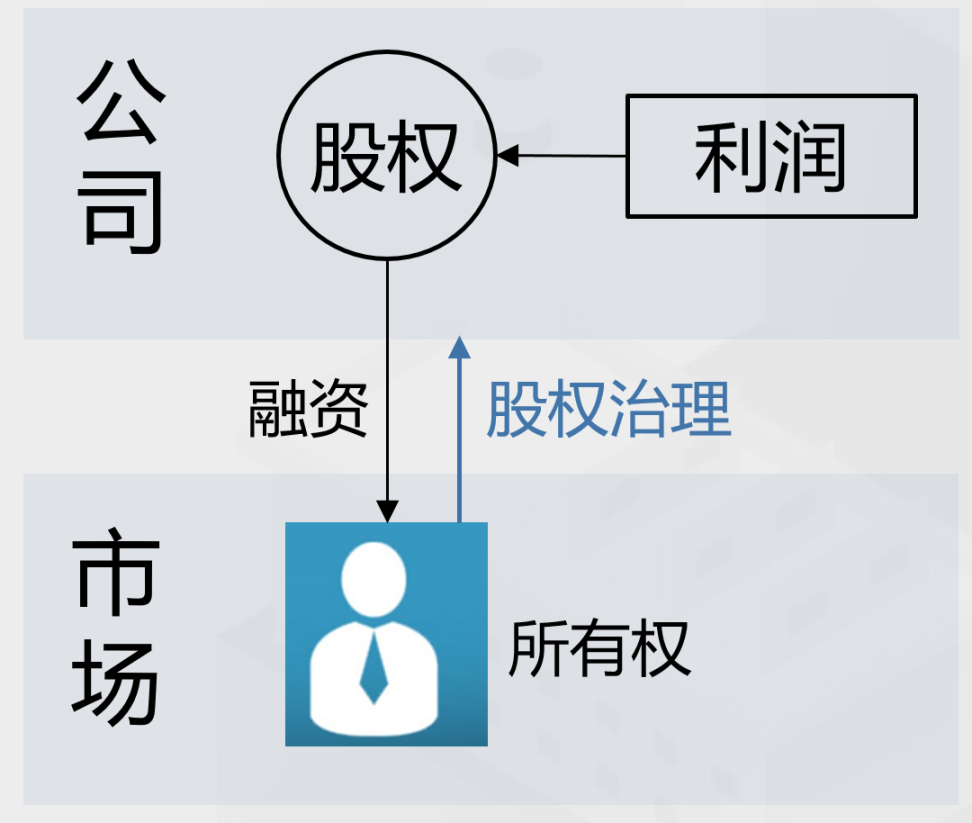
Figure 7: Financial Activity Forms of Shareholder Capitalism
The second is stakeholder capitalism based on the new Web3 economy. Shareholder capitalism emphasizes ownership, using equity as an incentive to encourage the creation of new companies and businesses. Stakeholder capitalism emphasizes the right to use, and through Token, stakeholders can "share" and share capital gains. The form of financial activities of stakeholder capitalism is shown in Figure 8. Token is the standardization, sharing and financialization of the right to use the open ecology. Holding Token means the right to participate in the governance of the open ecology and the right to use the open ecology digital products or services in .
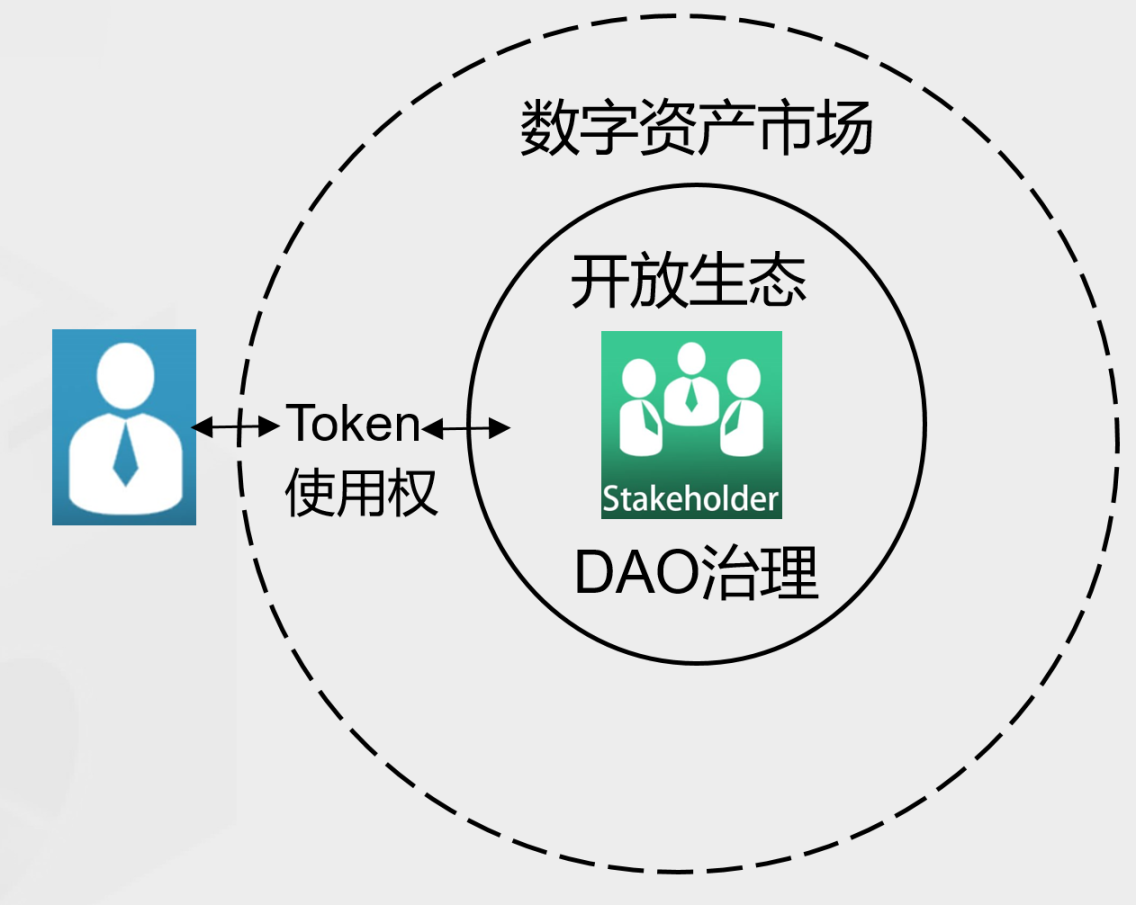
Figure 8: Financial activity forms of stakeholder capitalism
Shareholder capitalism and stakeholder capitalism can be fused with each other. As shown in Figure 9, some enterprise nodes will appear in the new Web3 economy. Enterprise equity is not only a compliant financing channel, but also provides an incentive mechanism for entrepreneurial teams and early investors. Enterprise shareholders can transfer part of their interests to functional tokens in the enterprise ecology, and the functional tokens will play a network effect, thereby promoting the development of the enterprise ecology. As long as the network value shared by shareholders is greater than the benefits transferred, shareholders and holders of utility tokens will form a win-win situation. Functional tokens can start the market through non-financing issuance, represent ecological use rights and governance rights, and capture value from open ecology.
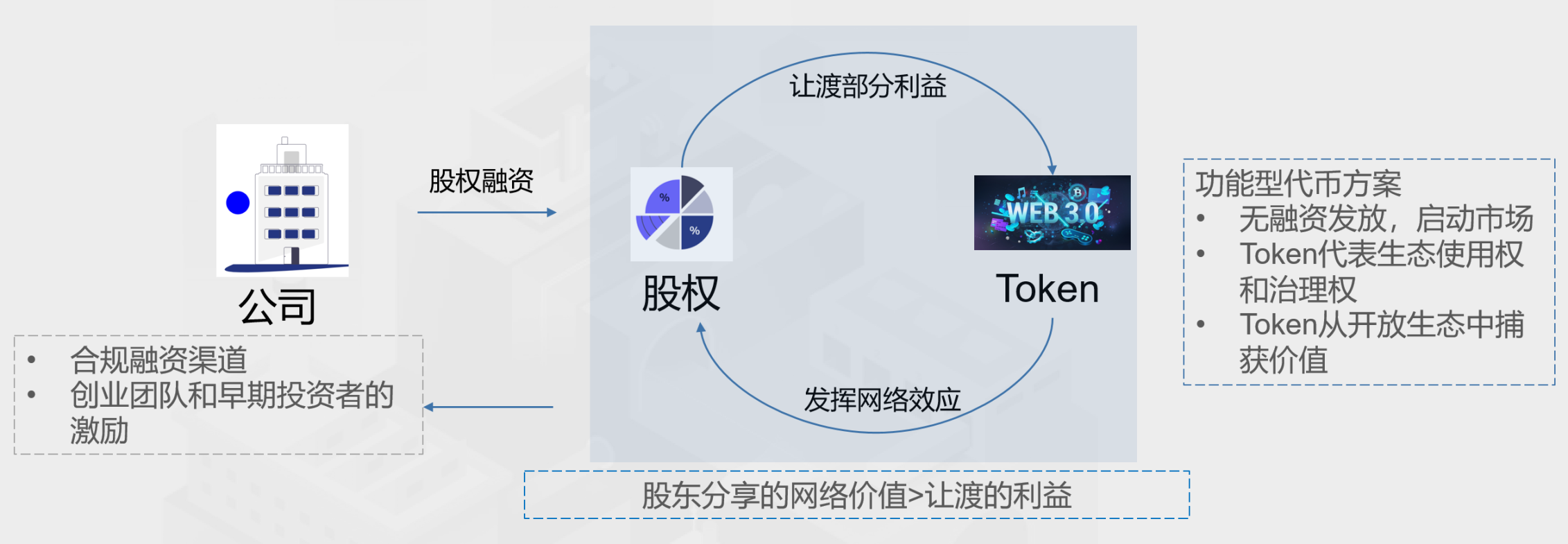
Figure 9: Convergence of shareholder capitalism and stakeholder capitalism
(4) Laws of value creation
The industrial economy pursues the maximization of company value, the Internet economy pursues the maximization of shareholder interests, and the Web3 new economy pursues the maximization of organizational interests.
(5) Law of value distribution
Industrial economy is characterized by high fixed costs and increasing marginal costs. Therefore, the pricing model of the industrial economy is basically a cost plus, and there can be no free model.
In the era of the Internet economy, the free model dominates the mainstream. The image is that "the wool comes from the pig, and the dog pays the bill." The reason why it is free is that the Internet economy is characterized by high fixed costs, but diminishing marginal costs or even approaching zero. Seemingly free Internet products may actually be more expensive than "rare things are more expensive" manufacturing products, which has also created some Internet companies with a market value of more than one trillion US dollars.
The value distribution of the new Web3 economy follows a set of fair, just and open distribution mechanisms, allowing stakeholders to share benefits.
(6) Stakeholders
The business model of the new Web3 economy is described as "Player to Earn", where Player refers to stakeholders, including developers, creators, contributors, consumers, and investors. All participants will be Web3 players, no longer limited to an independent benefit-sharing role of shareholders.
(7) Basic business model
The classic business models of the Web3 new economy should be "Play NFT" and "Earn Token". As mentioned above, NFT is a proof of contribution, and Token is a standardized and shared right to use. The right to use can be traded in the secondary market to realize the realization of contribution value.
(8) Distributed decision-making mechanism
The decision-making mechanism of the new Web3 economy is a decentralized (or distributed) mechanism. Decentralization is not for anti-censorship, rejection of compliance, or rejection of regulation. The decentralization of the Web3 new economy is mainly to introduce a more fair business decision-making mechanism through digital technology. Between efficiency and fairness, the business scenarios of the new Web3 economy need to find a suitable balance point. The more infrastructure-oriented the decision-making, the more emphasis needs to be placed on fairness, and the higher the level of application, the more emphasis must be placed on efficiency.
(9) Value capture
The value capture of the Internet economy is often referred to as "thin protocol, fat application", while the new Web3 economy is "fat protocol, fat application". The difference between fat and thin lies in the ability to capture value.
The core of the Internet is the TCP/IP model, which assigns network addresses through the IP protocol and relies on the TCP protocol for communication. The Internet protocol lacks a value capture system, so the Internet economy is not friendly to protocol layer developers. The Internet application layer relies on "surveillance capitalism" to capture a lot of value through data privacy data and attention (including users passively watching advertisements pushed by Internet platforms).
The underlying protocol stack of the Web3 new economy has a built-in currency system and value system, and value creation can also be performed at the protocol layer. The Web3 new economy will combine many digital technologies at the application layer, and the value creation space will be no less than that of the Internet. Both the Web3 protocol layer and the application layer are Token-based distributed economy, which is essentially a market network for direct transactions between participants, and the economic value is also shared by stakeholders.
The commercial value of the distributed economy is not reflected in the equity of shareholders, but is contained in the market network, and finally reflected in the value of Token, and the value of Token is positively related to the economic scale supported. Token-based distributed economy has a strong network effect. The increase in the value of the distributed economy (n^2 order of magnitude) is higher than that of centralized commerce (linear order of magnitude). Therefore, the same economic activities can achieve higher commercial value through the distributed economy.







