Layer 1 blockchain underlying protocol
Since the blockchain is an open network system, anyone has the right to act as a node to participate in bookkeeping. How to formulate a set of game rules for all nodes to abide by, so that the blockchain can operate smoothly is a very important issue.
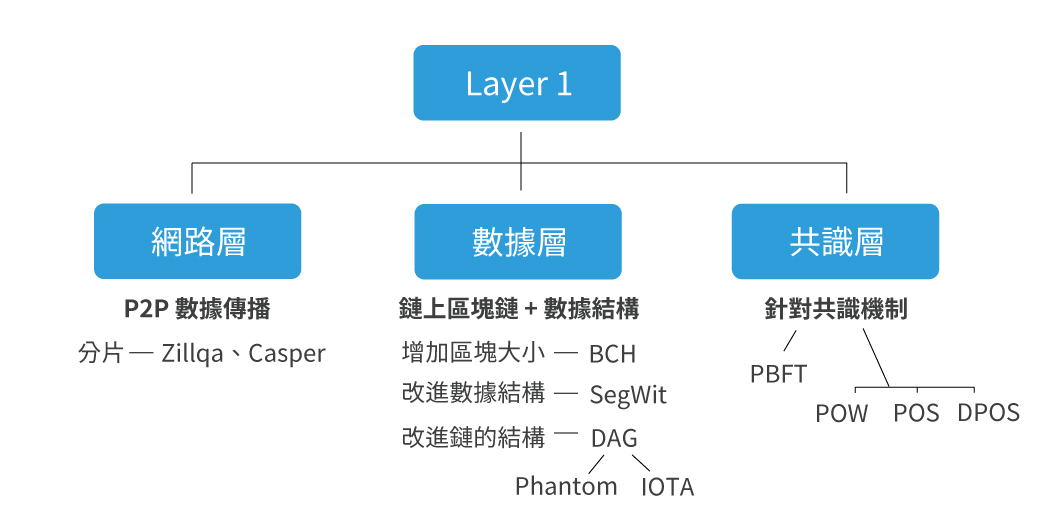
Layer 1 is also called the bottom layer, which is the rules that all miners must abide by. It is designed to allow the blockchain to maintain the " book consistency " and " transaction finality " of the state, so that nodes can be anchored in an unchangeable way. Determining data transactions and cryptographically reaching consensus without central review. To put it simply, Layer 1 is the protocol of the blockchain. The consensus mechanism, block, private key or address that you often hear, etc., are all Layer 1 categories.
Layer 1 expansion solution
The Layer 1 expansion solution focuses on how to improve the transaction processing speed of the blockchain under the premise of ensuring the consistency and finality of the "state" of the blockchain in the entire network. In the past, most of the Layer 1 expansion solutions were aimed at the optimization of the data layer and the consensus layer. In recent years, the " sharding technology " of the network layer has become the research focus of major public chain projects. For example, the goal of Ethereum 2.0 is to use " Fragmentation technology" improves the current bottleneck of Ethereum in transaction processing speed.
(Supplement: "Computation" on the blockchain is also called "state generation". The reason why the word "state" is used is that in general computing models, there are no trust and security issues, and only the calculation results need to be generated. That's good, no verification is required; but in the blockchain network, in addition to calculating the transaction result, it also needs to be verified.)
Further reading - Layer 2 - Buildings within buildings in blockchain protocols