This article will try to avoid obscure professional terms and formulas as much as possible, and strive to outline the overall picture of Bitcoin Layer 2 ecology in an easy-to-understand way. At the same time, the author will analyze from the perspective of ecological implementation, what type of BTC Layer 2 is easier to obtain success.
What is BTC Layer2? And what are the success factors that a BTC Layer2 that can be implemented should have?
BTC Layer2 is essentially the same as ETH Layer2. It is essentially decentralized cross-chain + a high-performance smart contract network . The core significance is that high-performance scenarios and complex applications that cannot be realized by Layer1 can be switched to Layer2 for implementation. . Therefore, a BTC Layer2 that can be implemented is essentially two parts: it can cross-chain the BTC of Bitcoin Layer1 to Layer2 in a decentralized manner, and then allow BTC to implement a series of complex smart contract application scenarios on Layer2 (mainstream Ethereum Layer 2 also follows this principle)
Based on the above consensus, we can further conclude that a successful BTC Layer2 must at least follow the following design principles:
1. Whether BTC cross-chains to Layer 2 in a decentralized manner
The first step for users to use Layer2 is to transfer assets from Layer1 to Layer2. Whether this process is decentralized and secure enough determines the size of Layer2's assets and directly determines the life and death of Layer2. Before Bitcoin’s Taproot upgrade, Bitcoin was unable to achieve true decentralization across chains. Most BTC running on other chains used centralized encapsulation or multi-signature solutions. For example, RenBTC uses multi-signature to implement it (later stopped running due to team problems), while WBTC relies on the endorsement of BitGo. None of the so-called BTC Layer2 born before 2021 has achieved true decentralization across chains. Therefore, the BTC Layer2 ecosystem has not grown up. However, Bitcoin’s Taproot upgrade in 2021 brings the Schnorr signature algorithm and Musig2 aggregate signature technology, which lays the technical foundation for decentralized BTC cross-chain.
2. Whether BTC Layer2 can gain the consensus and support of Layer1 mainnet users
Since Layer2 is an expansion of Layer1, Layer2 relies on Layer1 for its existence. At the same time, Layer2 can also feed back and gain Layer1. Whether the operation of the Layer2 network uses the Layer1 mainnet token as Gas is almost the only criterion for judgment. If the Layer 2 network only uses Layer 1 as a data backup layer, Layer 2’s economic system and GAS taxation will not benefit Layer 1 at all, and it will definitely not be able to obtain the support of Layer 1. This is no different from rebuilding a new Layer 1, and the difficulty of success can be imagined. Know. Currently, the mainstream Layer 2 of the Ethereum ecosystem uses ETH as GAS, while some projects in the Bitcoin ecosystem that claim to be BTC Layer 2 do not use BTC as GAS. Therefore, they have not achieved good development. Therefore, whether BTC Layer2 uses BTC as GAS determines whether it can gain consensus and support from the Bitcoin community.
3. Is BTC Layer2 friendly enough for developers and users
The core significance of the existence of Layer 2 is to help Layer 1 expand applications and scenarios, so that functions that cannot be implemented in Layer 1 can be easily and conveniently implemented in Layer 2. Therefore, the development language and entry threshold of Layer 2 should be as friendly to developers and users as possible. . If the design of layer 2 is too complicated or the entry barrier for developers and users is too high, it will be difficult for Layer 2 to exert its true expansion value. As we all know, the current smart contract developers in the entire Crypto field have grown and expanded in the EVM ecosystem. According to public data, there will be approximately 400,000 smart contract developers in the world in 2022, of which more than 80% are EVM ecosystem developers. Therefore, we see that most successful Layer1 and Layer2 are started in an EVM-compatible manner, while most Layer1s that are not EVM-compatible face the problem of high migration costs for developers and users, making it difficult for the ecosystem to grow.
Therefore, whether it is Bitcoin Layer 2 or Ethereum Layer 2, whether it is compatible with EVM is not only a matter of choice of development language, but also involves a strategic issue of whether Layer 2 can really help Layer 1 achieve ecological prosperity. What Layer 2 should consider is how to quickly In order to obtain developers and users, we should consider more about reality and implementation, rather than blindly pursuing the so-called native and showy skills. Most of the successful Ethereum Layer 2 have chosen to be compatible with EVM, while many Bitcoin Layer 2 have vigorously promoted the so-called Bitcoin fundamentalism or so-called orthodoxy and refused to be EVM compatible, and instead adopted or created some relatively niche programming languages. and development environment, which is also one of the important reasons why many Bitcoin Layer 2 have not developed.
Based on the above BTC Layer2 design principles, let’s take stock of some of the current mainstream BTC Layer2s and compare the pros and cons of each.
Stacks
Stacks is positioned as the smart contract layer of Bitcoin, and the mainnet will be launched in 2018. It uses the "hook" method to realize BTC cross-chain, which is achieved by issuing sBTC on the Stacks network, which is essentially a centralized mapping method; its network Gas uses its mainnet token STX instead of BTC, and miners participate Stacks' network mining will consume pledged BTC to mine its network tokens. Such a network design will not only not gain support from Bitcoin users, but will even generate great resentment; its ecosystem uses the relatively niche Clarity as a programming language. It also greatly limits the influx of developers. Its ecology has been developed for 5 years, but most projects have received mediocre response or are in a stagnant state. The TVL of the entire ecology is currently less than 25 million US dollars.
summary:
Based on the three principles of BTC Layer2 design, Stacks’ Bitcoin cross-chain solution is still a centralized approach; the Stacks network does not use BTC to operate and has little benefit to Bitcoin Layer1, making it difficult to gain support from the Bitcoin community; its network development language Clarity is relatively It is a niche and it is difficult to introduce developers. The ecosystem has not achieved large-scale development in the past five years. Facts have proved that the design direction of Stacks is not an ideal BTC Layer 2 solution.
Lightning Network
Lightning Network is the most "orthodox" Bitcoin Layer 2. Its goal is to realize Bitcoin's "global payment". The core is to allow Bitcoin to realize fast and convenient small payments on the Lightning Network, a second-layer network. However, Lightning Network Smart contracts are not supported, therefore, ecological application development related to Bitcoin cannot be carried out on Lightning Network. Currently, the number of BTC pledged on the Lightning Network network is approximately 4,000. Perhaps in view of the success of the Ordinals protocol, the Lightning team recently proposed Taproot Assets’ Bitcoin asset issuance protocol. However, even if assets can be issued based on Taproot Assets and then quickly circulated on the Lightning Network, such a combination only provides a solution for the issuance and circulation of Bitcoin assets and still cannot support the development of complex decentralized applications based on BTC. .
summary:
Lightning Network is undoubtedly the most "orthodox" BTC Layer 2, but its network does not support smart contracts. The goal of its birth is to expand the payment scenarios of Bitcoin. Therefore, it is not a typical Bitcoin Layer 2. Lightning Network currently has 4,000 Bitcoins pledged, about 140 million US dollars. Although it has been running for 3 years, its ecological development is still in its early stages.
RSK:
RSK is positioned as Bitcoin Layer 2 that supports smart contracts. It uses a Hash lock to cross the mainnet BTC to the RSK network. However, the Hash lock is still a centralized method and it is difficult to gain the trust of Bitcoin users. Therefore, using The number of BTC cross-chained by RSK is only a handful; at the same time, the current consensus algorithm of the RSK network is still POW. As a second-layer network, it still uses the POW consensus mechanism with poor performance. Its ecology is naturally difficult to develop. Therefore, the RSK main Although the Mainnet was launched in 2018, its ecology has hardly developed at all. As one of the "top ten king-level projects" of that year, it has gradually been forgotten by people.
summary:
According to the three principles of BTC Layer2 design, RSK's cross-chain solution for Bitcoin assets is centralized; the performance of RSK's mainnet is poor, and ecological development is better than nothing. It turns out that RSK is not an ideal BTC Layer 2 solution either.
Liquid
Liquid is a second-layer Bitcoin network launched by Blockstream. Essentially, Liquid is a Bitcoin side chain. Liquid serves mainly institutions and asset issuers, and provides asset issuance and circulation based on Bitcoin side chains for the B-side. Therefore, Liquid’s Bitcoin cross-chain solution is relatively centralized, using 11 certified multi-signature nodes to host Bitcoin. Liquid’s solution is similar to the alliance permission chain. Since it provides financial asset issuance services to institutions, Liquid considers security and privacy more. Therefore, the Liquid network is a consortium chain solution that requires permission for access. As a Bitcoin side chain network for B-side services, Liquid has its own rationality. However, in order to gain broad support and use from the Bitcoin community and crypto users, decentralized and permissionless BTC Layer 2 is the more promising direction.
summary:
Liquid is a Bitcoin side chain for institutional services. It is essentially a permission-only alliance chain. Its service targets are mainly traditional institutions and asset issuers with high requirements for security and privacy, and Liquid's main functions are concentrated. In asset issuance and trading, it is not friendly to complex smart contract functions. Therefore, Liquid's service scope is relatively limited and is essentially different from the mainstream decentralized BTC Layer2.
RGB
RGB's goal is to build BTC Layer2 based on BTC UTXO and Lightning Network. Since RGB was proposed in 2018, it has been in a slow development stage due to the difficulty in realizing many of its technical points. The core design of RGB is divided into three points: UTXO state compression and encapsulation, client verification, and bridging the Lightning Network to run non-shared smart contracts. The most orthodox thing about RGB is that the data running on RGB will be compressed and encapsulated into Bitcoin. In each UTXO, that is, the core data running on RGB is attached to the Bitcoin blockchain with the help of UTXO, and the Bitcoin network is used to ensure the security of assets. However, this is also a function that RGB has not been able to achieve; even if this function The implementation still faces two problems. Since the client needs to trace the upstream UTXO of each asset when verifying assets, a large amount of data verification is involved. The more times the assets are transferred, the greater the verification difficulty and verification cost; even if the assets can It has been verified that RGB smart contracts do not really run on the chain. Each RGB-based smart contract cannot interact and is independent. If two tokens issued based on RGB need to build a Swap, it cannot Swap interaction is implemented directly like the assets issued on the EVM, but it needs to be transferred to the Lightning Network for interaction, and its complexity is evident.
summary:
According to the three principles of BTC Layer2 design, Layer2 needs to carry the historical mission of high performance, easy development and user-friendliness. BTC Layer2 is directly oriented to applications and users, and cannot just stay on the so-called cool design concept. At this point, RGB’s architecture is undoubtedly not in compliance with the three principles of BTC Layer2. Whether it is unverified UTXO state encapsulation, client verification, or running non-shared smart contracts on the Lightning Network, these are undoubtedly detrimental to BTC Layer2. It brings huge barriers to entry for developers and users. When building Bitcoin applications on such Layer 2, the user experience can be imagined. Since it was proposed in 2018, the development progress of RGB has been slow. To some extent, it also reflects the high complexity of RGB and the difficulty of its implementation. The entry threshold for its future ecological developers and users may also be Just imagine.
BEVM
BEVM is a Bitcoin Layer 2 that uses BTC as GAS and is compatible with EVM. The core design of BEVM is based on the Taproot upgrade of BTC in 2021, using the Musig2 aggregate signature algorithm to achieve decentralized BTC cross-chain. The Musig2 aggregate signature algorithm is brought about by the Taproot upgrade and can allow 1,000 Bitcoin light node addresses to be formed. A centralized asset network, through which the transfer of BTC assets is processed to ensure the security of assets on BTC Layer2; at the same time, the BEVM network uses BTC as GAS, and applications on Layer2 will use BTC as Gas; the most important thing is BEVM Fully compatible with EVM, DeFi, GameFi and other applications that can run in the EVM ecosystem can be seamlessly migrated to Bitcoin Layer 2. Users can directly use BEVM ecological applications in mainstream encryption wallets (such as Metamask, OK Wallet, etc.). In the future, BEVM will also be compatible with more non-EVM Layer 1 networks, thereby expanding BTC and BTC on-chain assets to any chain and maximizing the expansion of the Bitcoin ecosystem. At present, the BEVM Xianxian Network has been launched, and there are nearly 10 applications in the ecosystem. For example, users can use the completely decentralized BTC DEX on BEVM. Users can deposit BTC/Sats and other assets to do LP, and enjoy DEX benefits, etc.
summary:
BEVM uses Musig2 aggregated signatures to achieve decentralized cross-chain BTC, uses BTC as GAS to gain consensus and support from the Bitcoin community, and is compatible with EVM, which can lower the entry threshold for smart contract developers and users. Therefore, it is more practical and conforms to the three principles of BTC Layer2 design. However, unlike many BTC Layer 2s that promote the legitimacy of Bitcoin, BEVM seems to be less “legitimacy”. BEVM did not improve the design within the limited capacity block space or limited function UTXO of Bitcoin. Instead , it chose to directly introduce BTC into the mature EVM network in a decentralized manner, thus reducing the difficulty of expanding the Bitcoin ecosystem. This is the design highlight of BEVM , and at the same time, it will be labeled as not “orthodox” enough by some Bitcoin fundamentalists. However, in the BTC Layer 2 track, whether "legitimacy" is more important, or whether developers and user experience are more important, I believe the market will give the final answer.
BitVM
BitVM is a BTC Layer2 solution proposed in 2023 and is still in the theoretical stage. The most discussed thing about BitVM is its relatively "hard-core" technical implementation solution. Its core logic is to run a fraud proof similar to optimistic rollups on the BTC script. The so-called fraud proof means that when an asset transaction has objections, users can initiate a report. If there is a problem with the transaction, the assets of the dishonest party will be will be confiscated. Generally, the effective reporting time is within 7 days (which can be simply understood as unconditional return within 7 days). However, if the user initiates a reporting after 7 days, it will be invalid. Even if there is a problem with the asset transaction, it will be automatically saved in Continue to run on the blockchain. BitVM's smart contract layer runs off-chain, and each smart contract does not share state; BTC cross-chain uses traditional Hash locks for asset anchoring, and does not achieve truly decentralized BTC cross-chain.
summary:
The design highlight of BitVM is to abstract the complex smart contracts off the chain into fraud proofs, and let these fraud proofs run on the Bitcoin blockchain in the form of Bitcoin opcodes. As for whether this method can be realized, the Bitcoin community There are still many different voices. However, based on the three principles of BTC Layer2 design, BitVM’s BTC cross-chain solution is still an ancient Hash lock, which has centralization issues ; since its testable network has not yet been released, it is impossible to know what method it adopts. It is developed as a language; given that its biggest design highlight is still in the theoretical stage, we adopt an observational state for BitVM.
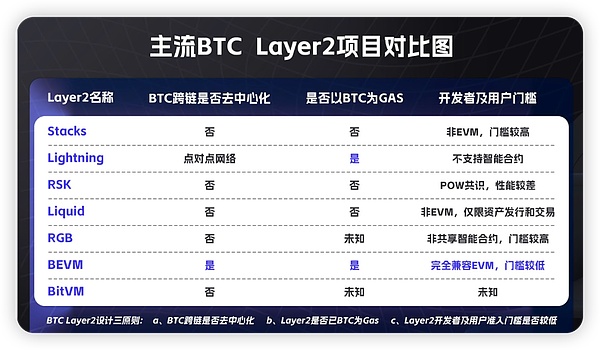
Summarize
Since the Bitcoin blockchain is non-Turing complete and does not support smart contracts, entrepreneurial teams have been exploring Bitcoin Layer 2 for many years. The essence of BTC Layer2 is to use a decentralized approach to free BTC from the constraints of Layer 1, allowing BTC to realize all complex application scenarios on the high-performance and highly scalable Layer 2. Therefore, an excellent Bitcoin Layer 2 that can be implemented should follow some of the most basic design principles, such as whether to cross-chain BTC to Layer 2 in a decentralized manner, which determines the market size and value upper limit of Layer 2; whether to cross-chain BTC with BTC For GAS, this determines whether Layer 2 can gain consensus and support from the Bitcoin community; whether the development language and infrastructure are friendly enough to developers and users, this determines whether the Layer 2 ecosystem can grow rapidly.
By taking stock of the current mainstream BTC Layer2 projects, we can roughly understand the evolution path and development trend of Bitcoin Layer2. The BTC Layer2 track naturally carries the mission of expanding the Bitcoin ecosystem. We have reason to believe that we can gain access to the Bitcoin community. Support, BTC Layer2, which can gain the trust of Bitcoin users and is friendly enough to developers and users, will surely achieve excellent results in this wave of Bitcoin ecology.







