author | MT Capital
The content of this article is only for information sharing and does not promote or endorse any business or investment activities. Readers are requested to strictly abide by the laws and regulations of their region and not participate in any illegal financial activities. The article does not represent Wu Blockchain views.
Original link:
Summary
With the launch of ORDI on Binance , the inscription track of the Bitcoin ecosystem is developing rapidly, with a variety of innovative technologies and concepts emerging. SegWit and Taproot upgrades provide strong support for Bitcoin’s programmability and scalability, driving the rise of projects such as Ordinals , BRC-20 , and Atomics . These technological advancements not only increase the transaction capacity and flexibility of the Bitcoin network, but also create more revenue sources for miners.
introduction
With ORDI listed on Binance, we have witnessed the beginning of a new era: a technological innovation and market prosperity led by the Bitcoin ecosystem. From the inscription craze at the beginning of the year to the renewed craze today, the rapid development of the Bitcoin ecosystem and the huge increase in its value have attracted widespread attention. But behind all this, what drives the enthusiasm of the BTC ecosystem and the rapid expansion of its value?
technology
Before exploring this issue, we first need to understand several key technological advances in the Bitcoin ecosystem.
Segregated Witness (SegWit) is a key upgrade to the Bitcoin core protocol launched in 2017 to address Bitcoin scaling challenges and specific vulnerabilities. It primarily facilitates the inclusion of more transactions by correcting transaction malleability issues and expanding Bitcoin block size limits. SegWit introduces the concept of block weight, replacing the traditional block size limit, so that a fully loaded block can accommodate approximately 2,700 transactions, a significant increase compared to the previous 1,650 transactions.
In addition, SegWit also brings a new encoding method Bech32 and two innovative script types.

With the Taproot upgrade at the end of 2021, the Bitcoin ecosystem began to support more complex scripts and data types, which brought huge progress to the programmability and scalability of BTC. This provides a key opportunity for the explosion of the Bitcoin ecosystem in 2023.
The Taproot upgrade mainly includes changing the transaction confirmation method and introducing the Schnorr signature algorithm. The introduction of Schnorr signatures offers many benefits, including better privacy protection especially in multi-signature wallets. It allows all private keys to be compiled together, making multi-signature transactions look like other transactions, thus improving privacy. Additionally, Schnorr signatures support batch confirmations, making transactions across the network cheaper and faster.
Taproot also brings the potential to create smart contracts to the Bitcoin network. While it may be more expensive and have limited functionality compared to platforms like Ethereum, its ability to enable smart contract interactions on Bitcoin, which is worth up to $700 billion, is huge and could push smart contract technology into the mainstream.
Miners' interests
In terms of miner interests, recent data shows that with the rise of projects like Ordinals and Atomics, the Bitcoin inscription market is experiencing an unprecedented boom. According to data from oklink chain master, the income of Bitcoin miners has increased significantly in the past three months, especially in November. The proportion of on-chain handling fee contribution increased from 2.4% on August 19 to 2.4% in November. 23.46% on the 16th. This growth was mainly due to the introduction of Ordinals trading pairs. This shows that the development of the Bitcoin inscription market has significantly increased the proportion of miners’ fee income. It is expected that this proportion may reach 50% by the time of the Bitcoin production cut in April 2024.

Currently, as U.S. Bitcoin mines are operating at a loss most of the time and the semiconductor industry faces process bottlenecks, the competition for mining machine computing power is easing. As a result, miners may turn to Bitcoin Inscription as a new source of income. For example, less than a year after the launch of Ordinals, more than 50,000 tokens have been issued in the market, and the number of mint and transactions has grown rapidly, which has greatly contributed to the increase in miner fee income.
The expansion of the Inscription Track not only drives the growth of miners’ income, but may also become the main driving force for the Bitcoin Inscription Track. However, miners are more concerned about the increase in the number of transactions than the fluctuations in the price of inscriptions.
The above factors work together to promote the rapid development of the Bitcoin Inscription track. But we must also realize that this development is not just a simple market craze, but represents deep-seated changes and technological progress in the Bitcoin ecosystem. As Bitcoin continues to demonstrate its strong potential in all aspects, we have reason to believe that the Bitcoin Inscription Track will become a key factor in promoting the development of the entire cryptocurrency industry.
Ordinals & BRC20
The Ordinals project was launched by developer Casey Rodarmor in December 2022. Thanks to Bitcoin's SegWit and Taproot upgrades, the flexibility and functionality of Bitcoin scripts have been improved. Ordinals give each Satoshi a unique serial number and track them in transactions, allowing additional data to be attached. Ordinals allows users to inscribe data, such as images, text, audio, etc., on specific unspent transaction outputs (UTXO), realizing the concept of asset transfer. At the beginning of this year, Ordinals was officially launched, quickly igniting the BTC ecosystem.
The emergence of the Ordinals protocol and the adoption of Taproot complement each other and promote the encoding and writing ofNFT data into Bitcoin blocks. The NFT image is permanently engraved into the BTC block. This method is more decentralized than ETH NFT, and the NFT can be viewed and transferred without relying on a third party.
Ordinal number theory mainly focuses on the tracing of the smallest unit of Bitcoin, sat, by designing rules so that each sat has a unique number. Based on ordinal theory, on-chain data can be associated with sats to form inscriptions. The inscription is stored in the taproot script and is identified and displayed by the off-chain index node. Due to being limited by indexes and unable to operate on the chain, the expansion of inscription functions relies on the development of ord, such as father and son inscriptions and curse inscription indexes. Inscriptions are similar to Colored Coin in that they store data in transactions for off-chain program indexing, but inscriptions are stored in the input Taproot script, while Colored Coin is stored in the output.
The implementation of Ordinals completely relies on the basic functions of BTC, and NFT transfers are completely processed by the BTC network. Due to its artistic attributes, Ordinals has limited development potential, but its emergence was still quickly adopted by the BTC fundamental community.

Initially, Ordinals was mainly used to create NFTs, but on March 8, 2023, anonymous developer Domo launched BRC-20 based on the Ordinals protocol, an ERC-20-like Bitcoin Altcoin issuance protocol that defines a A json data packet in a specific format and engraved on the BTC chain through Ordinals. Deployers of BRC20 can decide the total amount and name of the tokens themselves, and follow the first-come, first-served principle. $ORDI is the first BRC20 token deployed by Domo.
BRC-20 further develops on the basis of inscriptions to achieve homogeneous tokens and writes the minting and transfer process of tokens into the BRC-20 indexer. However, BRC20 requires the use of a third-party sequencer to record the ledger off the BTC chain, which adds additional complexity and becomes a weak point of the system.
BRC20 transfers are not executed on the BTC main chain and need to be divided into two-step BTC transactions (collection first and then transfer), resulting in a large number of junk transactions. Therefore, although BRC20 is sought after for its broad applicability and liquidity, it has been plagued by controversy due to a lack of support from the BTC core community. Recently, some developers have begun to develop decentralized sorters, such as #Trac, but this is still limited by the overall framework and it is difficult to achieve breakthroughs. The Inscription-Based Virtual Machines and Rollup concepts proposed by Domo, the founder of BRC-20, at the Ordinals Summit indicate that BRC-20 may move towards the development of Layer 2 networks.
With the launch of BRC-20, the scope of use of the Ordinals protocol has expanded, but it has also caused Casey's dissatisfaction. Casey’s team even asked Binance to remove the association with Ordinals from the ORDI token introduction to draw a clear line. This shows that although both Ordinals and BRC-20 are promoting the development of the BTC ecosystem, they have obvious differences in community acceptance and development direction.
Atomics & ARC20
Atomics is an optimization project for Ordinals and BRC20, focusing on homogeneous tokens and solving the problem of BRC20's over-reliance on centralized off-chain indexing. It utilizes and extends Bitcoin's UTXO model, treating the UTXO of each Satoshi (the smallest unit of Bitcoin) as a specific Atomic token or digital object, thereby creating and managing complex digital objects and tokens on Bitcoin. system (ARC20).
Key features of Atomics include:
1. Use Satoshi as the basic unit to represent tokens.
2. Allows the creation, transfer and update of digital objects on Bitcoin.
3. Provide a tokenization method that is decentralized and consistent with Bitcoin culture.
4. Use Proof of Work (POW) to increase fairness and decentralization of the minting process.
5. Aims to expand the functionality of Bitcoin and support a wider range of applications.
Atomics fundamentally rethinks how tokens are issued on Bitcoin in a centralized, immutable, and fair manner. It uses Satoshi as the basic "atom", and each Satoshi's UTXO represents a Token. When verifying an Atomics transaction, simply query the Bitcoin chain for the corresponding UTXO. The atomicity of ARC20 tokens is consistent with the atomicity of Bitcoin itself, and its transfer calculations are handled entirely by the Bitcoin network.
Compared with BRC20, ARC20 transactions require significantly less third-party sequencers, improving the decentralization of the system. The composability of UTXO makes the ARC20 token more programmable. For example, in theory, the exchange of BTC and ARC20 only requires the exchange of the input and output of UTXO.

After the Atomics protocol was launched in September, the first token ATOM was mined quickly. Compared with BRC-20, ATOM’s mining process is more technically demanding and fair.
Atomics is minted and spread based on Bitcoin's UTXO. 1 token is equal to 1 sat, which is technically more in line with Bitcoin fundamentalism. The Atomics protocol has defined the ARC-20 token standard and other use cases.
The Atomics protocol is highly respected by the community and is considered a complete protocol. The ARC-20 token standard is minted and transmitted based on Bitcoin's UTXO. Each unit of ARC-20 token is always supported by 1 sat, that is, 1 Token = 1 sat. All operations on ARC-20 tokens can be done relying on the Bitcoin network, with no additional steps required.
Atomics introduced POW in the ARC20 minting process. Minters must calculate the hash value of a specific prefix character to mint, which is a more decentralized and fair distribution method. The Atomics protocol provides Bitwork Mining prefix parameter settings for ARC-20, allowing participants to directly mine inscriptions/NFTs. The ARC-20 token standard remains true to Bitcoin fundamentalist principles, and the emergence of related tools in the future will enhance its liquidity.
In summary, Atomics, as a competitor of Ordinals, focuses on the decentralized creation and management of homogeneous tokens and digital objects. By extending the UTXO model of Bitcoin, it achieves a more decentralized and more consistent Bitcoin culture. Token system. With its technical advantages and design consistent with Bitcoin fundamentalism, the ARC-20 token standard is expected to gain support from the Bitcoin core community and bring wider application possibilities to the Bitcoin ecosystem.
Rune & PIPE
The RUNE protocol originated from Ordinals founder Casey Rodarmor's recognition of the shortcomings of existing fungible token schemes on the Bitcoin network, such as BRC20 and Taproot Assets. Casey proposed the idea of a UTXO-based fungible token protocol that aims to address the limitations of these solutions.
The main features and design concepts of the RUNE protocol include:
1. Based on UTXO : Runes balance is stored in UTXO, and each UTXO can contain any number of Runes.
2. Transaction and protocol information : The output of a specific script is considered part of the protocol information, which defines how Runes are transferred and distributed.
3. Flexibility : The transfer of Runes is implemented by interpreting data push in transactions, providing flexible allocation methods.
4. Release mechanism : The second data push is regarded as a release transaction, allowing the creation of new Runes.
5. Simplicity and decentralization : The Runes protocol is as simple as possible, does not rely on off-chain data or native tokens, and is adapted to Bitcoin’s UTXO model.
6. Symbol allocation : Runes can be associated with symbols, but the protocol does not involve symbol squatting issues to maintain simplicity.
Although RUNE only exists in the conceptual design stage, BennyTheDev implemented the PIPE Protocol based on the technical architecture proposed by Casey. PIPE is an important part of the TRAC ecosystem, which also includes the BRC20 token $TRAC, Bitmap, and the OrdFi ecological protocol TAP Protocol developed by BennyTheDev for BRC20, which allows BRC20 to implement DeFi functions such as token exchange (Swap).

BennyTheDev is an active Bitcoin community developer. He launched the BRC-20 auxiliary tool LooksOrdinal in March, deployed the TRAC token in May, released the Tap Protocol positioned on OrdFi in August, and launched the OrdFi-based Tap Protocol in October. An improved Pipe protocol based on Runes ideas.
The Pipe protocol follows Casey's RUNE protocol idea and uses UTXO-based technology to achieve homogeneous tokens. The release of the Pipe protocol attracted enthusiasm from BRC20 and quickly completed the first round of hype. Although RUNE's acceptance in the Bitcoin community may face challenges, its legitimacy is still stronger than BRC20.
In general, the emergence of RUNE and PIPE protocols reflects the Bitcoin community's continuous exploration and innovation in the implementation of homogeneous tokens. Although these protocols are still in their early stages, they are already showing potential and could bring more transaction fee revenue, developers, and users to the Bitcoin ecosystem.
Bitmap & BRC420
Bitmap.land is the first Metaverse project in the Bitcoin ecosystem. It is based on Ordinals theory and Bitmap theory.
Ordinals theory numbers the smallest unit of Bitcoin, Satoshi, and defines the scarcity of Satoshi. This can be visualized as each "Satoshi" is a numbered box, whose scarcity is determined by the time of production, and can be used to load data.
Bitmap theory was proposed by Twitter user @blockamoto on June 13, 2023. This theory maps each transaction input in the Bitcoin block into a parcel (Parcel), forming a block or district (District). The difference in size of different transaction inputs results in different sizes of mapped plots.
Buyers of Bitmap.land were influenced by Decentraland and The Sandbox and adopted a method of dividing land and drawing patterns on the map, which is similar to the logic of buying land on these two platforms. Users write data into Satoshi through inscriptions and obtain ownership of specific Bitcoin blocks, similar to free minting.
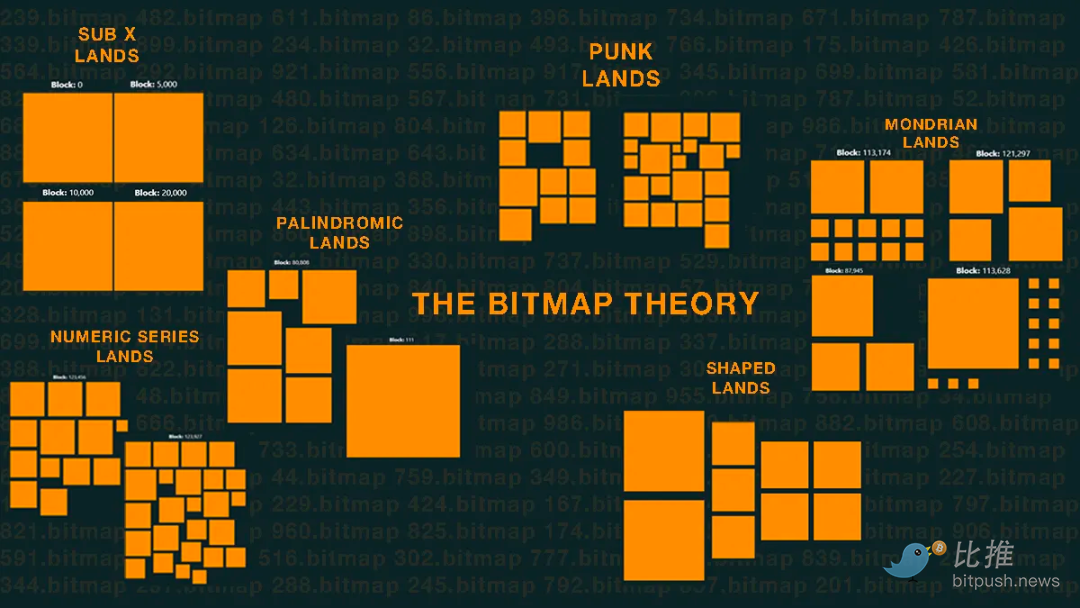
On the Bitcoin blockchain, each block is divided into four parts to represent different halving cycles. Users can check the number and color of each block on the Bitmap.land website. Different colors represent different selling statuses.
The sale of Bitmap.land is closely related to ordinal theory, similar to the virtual land sale of Decentraland and The Sandbox, which relies on the ERC-721 standard. Ordinal theory is similar to the principle of early colored coins, but in the context of Bitcoin’s current narrative, consensus, ecology, and infrastructure, the two are different. While ordinal theory is not as innovative as ERC-721, BRC-20's approach is more original.
Bitmap theory adds a new interpretation to Bitcoin blocks, providing a topicality despite lacking practicality. It changes the connection between Bitcoin and the Metaverse, giving each block of the Bitcoin blockchain a new dimension and making it part of the Metaverse by allowing users to own and record individual blocks.
Bitmap theory attracted the attention of the Ordinals community and inspired the inscription craze. Any block on the Bitcoin blockchain can become part of the Metaverse through Bitmap, bringing new creation and ownership opportunities to the community.
Bitmap.land blurs the lines between Bitcoin and the Metaverse through bitmap theory, paving the way for ownership, creativity, and community development. As the inscription craze continues, it means huge potential for those looking to carve out a niche in the digital realm.
The BRC-420 protocol has become one of the active token protocols in the Bitcoin ecosystem since November 13, 2023, with the total number of Ordinals inscriptions exceeding 40 million. Unlike traditional token protocols, BRC-420 focuses on on-chain inscription modularity, creating a new asset type on Bitcoin. Its first token, commonly known as “Blue Box,” has achieved significant market growth, growing from an initial $0.15 to $1,000, with developers earning significant on-chain royalty income in a short period of time.
The BRC-420 protocol is an asset protocol based on Bitmap. By combining multiple inscriptions into a complex asset, various assets ranging from small characters and pets to complete game scripts and virtual machines are created. Due to the open source nature of these assets on the chain, any client can run or verify them, fully embodying the "Client Agnostic" spirit of the full-chain game. Although RCSV's Bitmap browser dominates the market, other teams have had the opportunity to develop clients to run BRC-420's assets.
From a market perspective, Bitmap's number of holder addresses has exceeded 25,000, surpassing Sandbox and becoming the Metaverse asset with the largest number of holders in the entire chain. This achievement is due to its fair launch mechanism and the collective efforts of more than 200 development teams surrounding Bitmap. The market value of BRC-420 has grown with the launch of the Bitmap browser and the protocol itself, and currently reaches approximately US$30 million.
RCSV, the project party of BRC-420, is actively promoting the full-chain game plan of the Bitcoin ecosystem. The plan emphasizes the assets, gameplay, logic and data on the entire chain, aiming to create a truly decentralized gaming ecosystem on the Bitcoin chain. For example, developers can use the "fighting module" on the BRC-420 to quickly develop and release new games while only paying royalties through the agreement.
RCSV also proposed an expansion plan for the Bitcoin network to solve the capacity limitations of the Bitcoin network when processing a large number of transactions. This solution aims to migrate assets from the first layer to the second layer and implement a complete virtual machine environment on the next layer of the module. This arrangement aims to provide a low-fee, high-efficiency interactive environment for Bitcoin's first-tier assets while ensuring security to the greatest extent.
Overall, the BRC-420 protocol and related Bitmap projects are stimulating innovation and vitality in the Bitcoin ecosystem. By creating complex, modular digital assets, BRC-420 is enabling new economic opportunities and interactive experiences for creators, developers and users. With the continuous efforts of the RCSV team, the full-chain game and metaverse concepts of the Bitcoin ecosystem are gradually becoming a reality, showing the broad prospects of Bitcoin technology and applications.
BRC100
BRC-100 is an extension protocol based on the Ordinals theory, specifically designed to implement various decentralized applications on Bitcoin Layer 1. This protocol not only takes over the basic functions of brc-20 on Bitcoin, such as creation, minting and transactions, but also introduces the concept of decentralized computing. This means that based on the BRC-100 protocol stack, various decentralized applications such as DeFi, SocialFi and GameFi can be developed, bringing true decentralization, trustlessness, censorship resistance and permissionless to the first layer of Bitcoin. Application scenarios.
A major feature of the BRC-100 protocol is its interoperability, which not only allows all protocols and applications within its protocol stack to be compatible with each other, but also supports interoperability with BTC, BRC-20 or other layer 1 chains such as Ethereum and Stacks to interact with. In addition, the protocol also introduces the UTXO model and state machine model to enhance its security and computing capabilities.
The protocol also includes a series of innovative features, such as inheritance concepts, application nesting, address and application state, permission settings, and decentralized governance. For example, the inheritance concept introduced by BRC-100 allows protocols to directly or indirectly inherit the characteristics of BRC-100. At the application level, applications deployed based on BRC-100 and its extended protocols can be nested to form sub-applications. At the same time, the protocol also introduces two roles: owner and administrator, providing a foundation for decentralized governance of applications.
The utility of BRC-100 is reflected in its diverse application cases, from governance protocol BRC-101 to automated liquidity protocol BRC-102, as well as functions such as staking, airdrops, lending and stablecoin pools. These extended protocols enable BRC-100 to not only be limited to token transactions, but also support more complex financial operations and calculations.
Overall, the BRC-100 protocol opens up a new field of decentralized applications on the Bitcoin chain through its innovative features and powerful computing power. It not only inherits the advantages of BRC-20, but also provides a framework for an open protocol, providing new possibilities for the future development of the Bitcoin ecosystem.
Taproot Assets & Nostr Assets
Taproot Assets is a protocol launched by the famous Lightning Labs to create and trade various digital assets on the Bitcoin network and integrate with the Lightning Network. The Lightning Network has gained widespread recognition from the Bitcoin community as a mature Bitcoin derivative protocol. The update of Taproot Assets expands the functionality of the Lightning Network from a simple peer-to-peer transaction payment channel to a peer-to-many model that enables asset distribution and circulation. The feature of Taproot Assets is that Token information is recorded in the UTXO output script of the Bitcoin mainnet as a registration, and functions such as transfer transactions are implemented in the lightning channel. The biggest difference from BRC20 and ARC20 is that Taproot Assets are released in a way that is pre-minted and then distributed by an owner, rather than free casting.
Taproot Assets is backed by Lightning Labs and Twitter founder Jack Dorsey, who have extensive financing backgrounds, giving it an edge over other grassroots projects in terms of formality and community support.
NostrAssets is an open source protocol that introduces Taproot assets and Satoshis (Bitcoin units) to the Nostr ecosystem. Users can send and receive assets at the Nostr protocol layer using Nostr's public and private keys. The settlement and security of assets rely on the Lightning Network, and the Nostr Asset Protocol itself does not issue assets, but only introduces assets to Nostr through the protocol.
Features of NostrAssets include seamless integration of Taproot assets and Bitcoin into the Nostr ecosystem, providing developers with tools to create innovative products, enriching the value of the Bitcoin and Lightning Network ecosystem, and enabling a seamless experience from chat to transaction. In the future, NostrAssets plans to import Taproot assets from other Daemon Universes, allowing receiving and sending Taproot assets to and from Nostr.
NostrAssets' vision is to drive users to join the Bitcoin ecosystem and deliver Taproot assets to users around the world. By providing modular development tools, NostrAssets aims to facilitate the construction of decentralized applications that provide user-friendliness and commercial practicality.
Nostr Assets also announced the upcoming launch of the Fair Mint feature and is looking for projects on Twitter that are interested in issuing assets for cooperation. This means that once the feature goes live, a large number of new assets are expected to appear on the protocol, potentially attracting widespread attention and participation from the community. This flurry of activity demonstrates that Nostr Assets is actively expanding its ecosystem and preparing for future growth.
Ethereum Inscription
Ethscriptions are an alternative to smart contracts and L2 protocols that allow users to share information and perform calculations at low cost on Ethereum L1. It enables decentralized computing by applying rules to Ethereum call data to bypass smart contract storage and execution. In August 2023, Ethscriptions introduced a virtual machine (ESC VM) to enhance its functionality and make it a general computing engine.
The founders of Ethscriptions are Middlemarch (similar to BRC20 domo) and Michael Hirsch. Its first protocol token is $eths, which as the current leading token has brought significant returns to investors. Although this result is not as good as $ORDI and $SATS of the BRC20 track, it has shown significant growth compared to other inscription tracks.

In addition to $eths, there are other projects worthy of attention on the Ethscriptions track, such as Facetswap. Facet is a decentralized trading platform developed by Middlemarch and Michael Hirsch. It was originally named dumbswap and later renamed Facetswap. Although $Facet's price and market capitalization are temporarily lagging behind $eths, its potential value may be more obvious after the mainnet goes online.
iERC20 is a new Ethereum-based token protocol that provides a low-cost token ecosystem that allows anyone to deploy, mint, and trade tokens on it. $Ethi, as the first token in the iERC20 ecosystem, has received official support. This protocol not only provides Ethereum users with more choices, but also promotes the development of the inscription ecology on the Ethereum chain.
In the latest cryptocurrency development, the iERC20 protocol and Sparkle, a GameFi project incubated by Binance, announced a cooperation with plans to introduce Inscription NFT and other inscription assets on iERC20, aiming to leverage the advantages of inscription to enhance the gameplay of the GameFi ecosystem. This cooperation has attracted widespread attention in the Ethereum community, especially shifting the focus from ETHS to the iERC20 protocol.
The uniqueness of the iERC20 protocol is that it not only develops the Swap function, but also integrates the EVM cross-chain function, building a bridge between Ethereum Inscription and traditional Layer 2. This feature enables the protocol to introduce more mainstream coins and stable coins, thereby expanding the TVL of the Inscription ecosystem and providing more development possibilities for the entire system.
In addition, the iERC20 protocol also plans to introduce a fair mining model of PoW and cooperate with other projects to launch new inscriptions, similar to the mining method of the Atom protocol. This strategy is expected to bring new impetus to the development of the Ethereum ecosystem.
Although $Ethi was launched around the same time as $ETHS, $Ethi initially did not gain fame as quickly as $ETHS due to its relatively low profile in the early stages. However, as the price of $ETHS increased and market attention increased, $Ethi also began to receive more and more attention. $Ethi’s divisible technology makes it more attractive to retail investors. Although the current market capitalization is still lower than $ETHS, its development potential cannot be ignored.
In the iERC20 ecosystem, $Ethi is regarded as an important tool, similar to a shovel, providing special empowerment to its holders. For example, users holding $Ethi may receive inscription airdrops from collaborative projects, such as the recent collaboration with Sparkle. In addition, the FOMO sentiment in the community is spreading, and many investors are optimistic about the future development potential of $Ethi, believing that it is the leading token officially recognized by iERC20 and will grow with the launch of the PoW mechanism and the continued development of the Inscription ecology. value added.
Overall, the ERC20 track is showing its great potential and may create more miracles after BRC20. With the addition of more high-quality projects and the development of the ecosystem, this field is expected to attract more users and innovation.
Other public chain inscriptions
As the wealth effects generated by Bitcoin Inscription spread to other public chains, various "RC 20" tokens began to arouse heated discussions in the community, forming a FOMO phenomenon, including DOGE Inscription, BSC Inscription, Litecoin Inscription, and BASE Inscription. , Polygon inscriptions, Solana inscriptions, etc.

Especially on November 16, the Gas fee of the Polygon network rose sharply, reaching as high as 1800 gwei, because the community discovered the PRC-20 standard token POLS deployed in May this year. According to data from evm.link, the total circulation of POLS is 21 million.
Inspired by missing out on the Bitcoin inscription token SATS, community members began to "play a few defensive measures." Compared with the high cost of BRC and ERC, POLS, which is simple to operate and low-cost, has quickly gained attention in the community. Users can mint POLS by visiting evm.link and paying less than 0.05 Matic.
The community also shared methods for minting POLS in batches through the batch collection function (which requires importing the wallet private key) or scripts. Polygon's low gas fee is considered one of POLS's advantages as an inscription token. If 21 million POLS are fully minted, Polygon may become the chain with the largest number of inscriptions on any EVM chain, including Ethereum. This is naturally reminiscent of the BRC inscription token SATS, which has attracted widespread attention from the community due to its significant increase.
future opportunities
In March 2023, Galaxy Research and Mining predicted that the market value of the Ordinals market would reach US$5 billion by 2025. At that time, the number of inscriptions was only 260,000, but now the number of inscriptions has reached 33 million, in just half a year , an increase of 126 times, and the market value of Longyi ORDI has reached 400 million US dollars, and the market value of Longer SATS has also reached 300 million US dollars. It can be seen that the prediction of the entire inscription market is still far underestimated.
Different protocols are emerging on the Inscription Track, and of course the miners are the ones who benefit the most. According to Tokenview on-chain data monitoring, the single-day transaction fee of the Bitcoin network reached US$11.6 million, surpassing Ethereum for the first time since 2020. As Bitcoin is about to be halved, miners urgently need to find supplementary income. The prosperity of Inscription Track not only brings benefits to miners, but also maintains the security of the Bitcoin network in disguise. The reduction in block incentives will also make miners increasingly rely on transaction fee income to pay for operating costs. In the long run, Bitcoin will definitely compete with multiple expansion plans in the future. The outbreak of this round of Inscription Track and the resulting high Transaction fees are the catalyst towards this future. Currently, BRC20 trading activities are mainly concentrated on OKX and Unisat. With the emergence of various other protocols, different trading markets have emerged for different protocols, such as the Atomics Market for ARC20. In the end, the emergence of the leading protocol will surely create a unique trading market, and the competition in the trading market is far from over. The wallet market is similar. Currently, the main wallet of BRC20 is Unisat, but there are still different wallets on the market launched and connected to different inscription protocols.
As funds continue to pour into the inscription market, users are no longer satisfied with the hype of memes and begin to turn their attention to inscription-based applications. The BRC420 mentioned in this article is a typical example. Unisat also brings innovation to BRC20. Through BRC20-Swap, users can exchange BRC20 tokens as easily as AMM DEX. As the first product to improve the liquidity of the Ordinals ecosystem, it is expected to release the potential of the Bitcoin DeFi ecosystem. More features such as lending and derivatives may appear in the future. Recently, Unisat has also opened an API interface, which is very friendly to small developers. It can call many functions, such as automatic batch scanning, monitoring inscriptions and automatic mint, which can generate a lot of tool projects.

ORC20 returned on November 20 with the release of the Nirvana upgrade, improving the inscription format to support BTC DeFi integration, introducing stablecoin support, servicing issuers such as USDT and USDC, and more. Compared with BRC20, ORC20 is obviously more complex. The initial supply and maximum mintage can be changed, and the naming is no longer limited by four-letter words. However, it is also considered by the community to be more centralized, and its upgradability is also considered by the community to violate the immutable spirit of the blockchain. It is worried about problems such as malicious additional issuance and rat warehouses by project parties.
Generally speaking, BRC20 is the most original protocol and the first to be listed on exchanges. It has the strongest community consensus and its fair launch has left an excellent impression on users. With the listing of ORDI on Binance, it also means that all exchanges have begun to recognize and support the innovation of Inscription Track. Because it is technically difficult to support BRC20 deposits and withdrawals and self-built indexes, it is expected that BRC20 tokens will still be prioritized for listing in the future. . The BRC20 token cannot always be a meme. The project team can choose an existing BRC20 token with community consensus as a utility token, which not only avoids regulatory risks, but also obtains a ready-made community.
Summary and Outlook
The development of the Inscription track has shown significant vitality and innovation. The growth of this track is mainly due to the key technological advances of Bitcoin such as SegWit, Bech32 encoding, Taproot upgrades and Schnorr signatures. These technologies not only improve the Bitcoin network transaction efficiency and scalability, and also increases its programmability. With the application of these technologies, the inscription market has experienced rapid prosperity, not only attracting investors and users, but also promoting the development of diverse projects and protocols, such as Ordinals, BRC20, and Atomics.
The growth of this circuit has also had a positive impact on the interests of miners. With the rise of projects like Ordinals and Atomics, miners’ revenue streams have expanded, demonstrating the importance of the Inscription Circuit to the Bitcoin network. In addition, inscription tracks have also begun to appear on other public chains, showing their broad potential and influence.
Looking to the future, Inscription Track is expected to continue to witness technological innovation and promote the realization of more complex functions. The market’s growth is expected to continue, bringing more investment and participation opportunities. At the same time, it is foreseeable that more innovative projects and protocols will emerge to further enrich the inscription ecology of Bitcoin and other public chains. Miner earnings are also likely to continue to grow, as Inscription Circuit provides new revenue opportunities.