Written by: Chia Jeng Yang & Caroline Cahilly, Pantera Capital
Compiled by: TechFlow TechFlow
Pantera Capital recently published a long article, describing in depth and detail their trends, investment strategies, focus areas and trend predictions for the 2024 crypto market.
Since the article is long, we have divided it into different parts according to the content theme.
This article is the fourth of the full text and was written by Chia Jeng Yang, executive director of Pantera, and intern Caroline.
It can be seen that he is interested in the combination of AI and Web3, and has made a detailed division of the combination of AI and encryption. He believes that Web3 can play a role in the reasoning, data privacy and incentives of AI systems. Related tracks It also contains opportunities.
TechFlow has compiled this part, and the following is the main text.
The speed at which innovation occurs in the blockchain technology ecosystem creates new markets and verticals with each cycle. The research we conduct expands our thesis and helps us stay ahead of the curve, while also helping us maximize our coverage when finding and investing in deals. In the following articles, we will share the areas we are actively focusing on.
AI x WEB3
AI: merging human and computer intelligence
The output generated by artificial intelligence models, such as large language models, should be the result of optimal interaction between human and computer brains, data and motivation systems.
Being able to communicate in natural language is what’s exciting about LLM, because humans and AI can use the same language to detail complex processes. This is an important step towards a future of coordinated systems that include humans. To make this collaboration even better, we still need to develop powerful human-machine frameworks, mechanisms, and tools that will encourage AI systems to think more efficiently, produce more useful answers, and achieve optimal results.
How Web3 drives this interaction
Computer-native incentive frameworks will determine how humans interact with AI by incentivizing crowdsourcing, accountability, and more. We want to consider products that maximize/optimize the interaction that occurs between the computer/AI brain and the human brain on the other hand (e.g. token holders, developers), with a special focus on medium to long-term use cases.
Looking forward, we will delve into the following three aspects of human-computer interaction in the era of artificial intelligence:
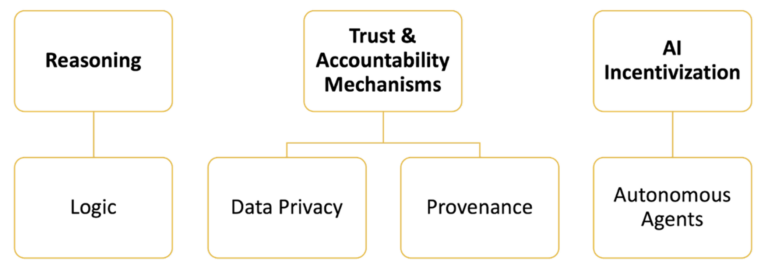
Here are some highlights of what cryptocurrencies can offer AI, which will be covered throughout the paper:
Payments: Traditional financial payments are clearly defined. Cryptocurrency only requires a few lines of code. Programmability provides simplified integration of software products, developers only need to embed wallet addresses into the code base. Programmability also provides flexible calculation-based payments, which require too much audit cost in existing infrastructure. . By avoiding outdated global financial infrastructure, it lowers barriers to market entry for products with an international user base. Additionally, crypto transactions can offer lower fees than traditional payments. Simple and low-cost integration is particularly beneficial for open source projects, which often have limited resources and simplicity is key to collaboration and adoption.
Crowdsourcing: As human feedback on LLM models becomes increasingly important, Web3 incentives enable data crowdsourcing to occur at greater speed and scale. A structured system of rewards (and penalties) should also promote high-quality information that attracts a large number of contributors from a variety of backgrounds.
Data Control: Controlling your own data (requiring data provenance and privacy) becomes increasingly important in this context because:
a. If users can easily get paid or get a better experience, then they may actively control their data (this seems possible now). With the rise of autonomous agents, users will be able to be paid for their data without the need for active intervention. And users who take control of their own data deserve a better experience than the shoddy one currently provided by personalization algorithms. Unlike previous data wallet attempts, LLM can now not only automate manual data collection across platforms at scale, but also better contextualize unstructured natural language data.
b. The company may take the lead in controlling data to protect confidential information. The new standards will then apply to individuals.
Three ideas we're particularly excited about are:
Human feedback reasoning: logical reasoning through crowdsourced (zk) knowledge graphs
Machine Learning (ML) Tracking Artificial Intelligence Generated Content (AIGC) Royalties: Use ML Tracking to Calculate Royalties on the Raw Data Content Behind AIGC
Advertising Digital Twins: As LLMs replace search engines as the form factor for information retrieval, user preferences will be driven by interacting with LLMs rather than searching through websites. Advertising in an AI world will require infrastructure that enables advertising technology to automatically extract personal preferences from digital twins.
reasoning
Despite the market hype, LLM has shown difficulty in planning, reasoning, understanding the physical world and similar tasks at which humans excel. These errors may occur because a large number of LLMs imitate reasoning based on data patterns without truly understanding the underlying logical/physical principles, so LLM performance is not good enough by human standards.
The value of principled reasoning lies in the ability to deal with unknown problems, especially given the strong evidence that transformers cannot outperform training data. We are looking for solutions to the inference problem that can help both the base model and any LLM ensemble system today, with a focus on human feedback mechanisms for better inference.
logic
Knowledge graphs (a method of capturing relationships between entities, events, and concepts using a structured database) provide an interesting way to incorporate logical reasoning into LLM.
Here are examples of how they can be incorporated:
Dynamic knowledge retrieval: During the reasoning process, relevant information is dynamically retrieved from the graph according to a certain attention mechanism.
Feedback loop: If the output deviates significantly from the understanding of the chart, use this feedback to make further fine-tuning.
Crowdsourced Knowledge Graph : Crowdsourcing will redefine information collection and certification, helping to develop a “warehouse containing all human knowledge and culture.”
Crowdsourced knowledge graphs will incentivize users to contribute data and their logical connections through automatic payments when models access their contributions. To maintain accuracy, incorrect contributions are penalized, which is determined by a group of validators who enforce an agreed-upon set of standards. Defining these criteria (for each chart) will be one of the most important considerations for success.
Web3 provides a way to incentivize the creation of knowledge graphs at the necessary scale. Additionally, gaps in LLM inference will be a moving target, and Web3 provides a way to incentivize provision of specific data when gaps occur.
Additionally, a structured system of rewards (and penalties) will promote high-quality information and attract a large number of contributors from diverse backgrounds. Notably, users create value by sharing data in a productive, non-zero-sum way, unlike zero-sum prediction markets and decentralized oracles.
Finally, crowdsourcing these graphs at the limits of current artificial intelligence will help maintain relevant accuracy (i.e. not replicate the inference capabilities of existing LLMs).
trust and accountability mechanisms
1. Data Privacy
The AI being developed to control user data could soon rival Apple's hardware ecosystem. We must consider data privacy because:
As AI seamlessly penetrates every aspect of our lives, from smart home devices to healthcare applications, the amount of AI data collection is growing exponentially.
We are approaching an inflection point in AI’s ability to create personalized content (e.g. using LLM) and users’ belief in this ability. As users increasingly turn to AI to deliver truly personalized experiences and products more frequently and at scale, the rate at which data is shared with AI will increase dramatically.
Data privacy is therefore critical to building user trust in AI systems and enabling developers to avoid data misuse such as unauthorized access, identity theft and manipulation.
Web3 technologies such as zero-knowledge proofs (zk-SNARK) and fully homomorphic encryption (FHE) will enable individuals to truly own/control their own data by enabling encrypted interactions and ensuring that sensitive information remains in the hands of the user.
The recent US executive order on artificial intelligence emphasizes the importance of "enhancing privacy-protecting research and technology, such as encryption tools to protect personal privacy" and introduces reporting requirements for large models. This means increased regulatory openness to Web3 privacy/origin methods, and even the potential for these methods to become compliance standards.
Crowdsourced ZK Knowledge Graphs : Through crowdsourced zero -knowledge graphs, AI can benefit from private data. Specifically, they will have "public" nodes, which contain public data, as well as "private" nodes, which contain encrypted data. Models can use logical connections between nodes to arrive at answers without revealing the knowledge itself, i.e. the nodes referenced in the final answer will be public, but the nodes used to arrive at the answer need not be public.
These graphs can also make it easier to delete user data, since accessing them in real time (e.g. through dynamic knowledge retrieval) avoids implicitly storing the data in the trained model.
2. Source
Without provenance, AI may create an environment of deepfakes and unfettered use of personal/private/proprietary data. With Web3, we can determine the origin of data used by NFTs, other media assets, and models, providing many promising solutions.
Machine learning traces AI-generated content royalties: In addition to deepfakes, the rise of AIGC in the arts poses unique challenges for intellectual property and royalties. For example, if the AIGC system creates a mashup of songs by two famous artists, how should credits and financial rewards be distributed to the artists? Traditional models used to determine such allocations are increasingly inappropriate for AIGC given their complexity and variability.
Machine learning traceability provides a way to identify the original components of AIGC works, and controlling provenance at the time AIGC is generated is critical to enabling this traceability.
In the absence of AIGC's strong global payment infrastructure, platforms like YouTube that already have royalty payment mechanisms will have an advantage and have the opportunity to further centralize their power/influence.
To democratize AIGC's creation and ensure artists are fairly compensated, a new payment system is needed. A blockchain payment network natively integrated with the AIGC model enables instant global payments from day one. Machine learning traceability and blockchain can then be integrated into various platforms, reducing the advantages existing platforms like YouTube currently have.
Investment in this technology can support the fair distribution of royalties and can also promote AIGC innovation by opening up opportunities for more creators.
AI incentives
As AI models behave increasingly autonomously, we hope to develop systems that can incentivize them to behave in accordance with human desires.
autonomous agent
Autonomous agents are models that can intelligently interact with their environment (e.g., leveraging tools and generating API calls to access real-time data), interact with algorithms for reasoning and decision-making, and take actions without direct human control. They exhibit goal-directed behavior and can learn from experience, but are only reliable in very narrow environments (e.g. autonomous driving). As AI models increasingly move from information retrieval to autonomous agents verifiably authorized by human users to perform actions on behalf of users, the adoption of commerce using digitally native currencies is likely to increase.
Digital twin targeting : Traditional search-based advertising is declining as conversational AI models like ChatGPT are expected to become the primary source of information retrieval. This poses a challenge to the AdTech industry, as traditional advertising via search engines and cookies faces diminishing returns.
As the market begins to realize that these personal models, rather than cookies, are the fundamental unit of understanding user preferences, models that allow advertisers to extract user preferences from other existing models may begin to dominate. Using these models, advertisers can achieve previously unachievable levels of personalization while maintaining user privacy through encryption methods.
A new platform that facilitates this interaction has the potential to bypass existing software and hardware giants like Google and Apple.
Specifically, when a user decides to create a digital twin, they grant it access to their search history, current account (e.g., Google, ChatGPT, Amazon), hard drive, and more. The twin will develop an initial summary of their data, including companies they interact with, interests, etc., and keep it updated on an ongoing basis.
Users can then set permissions on how and to whom the digital twin is allowed to sell its data. For example, imagine a button that says "Let my ad bot talk to GPT-4, Meta AI, and more." The digital twin will autonomously interact with the advertiser’s AI model. The advertiser's model will determine whether it's worth targeting without even knowing the user's identity. When targeted, users will receive ads in various forms (e.g. via text, discussions with LLM, etc.) and get paid as incentives.
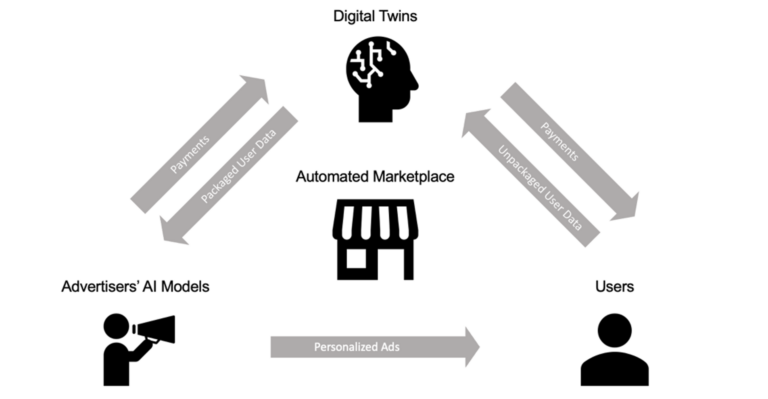
In this market of digital twins, crypto payment networks may be the easiest way to allow models to compensate for their interactions with other models, as transactions only require a few lines of code. Additionally, incentives should be designed to ensure that targeted digital twins are of maximum value to advertisers. Therefore, advertisers should only target digital twins with clean, accurate data that represents user preferences.
Summarize
The combination of AI and Web3 technologies has the potential to revolutionize reasoning, data privacy, and incentives for AI systems. Blockchain-based solutions should facilitate secure and efficient transactions and data processing while incentivizing contributions from different sources to enhance the development and application of artificial intelligence. This symbiosis between artificial intelligence and cryptography has the potential to create more powerful, efficient, user-centered artificial intelligence systems that solve key challenges in the field of artificial intelligence.





