TL;DR
- The FIT21 bill is the first to establish a complete and clear crypto bill for the crypto industry. It was passed by the House of Representatives on May 22. If the bill is officially signed into law, it will have a far-reaching impact on the entire crypto industry.
- The United States has adopted a joint regulatory model for a long time. Each federal regulatory agency has its own regulatory model for the crypto industry, resulting in a "separate regulatory framework". Due to the lack of a sound legal path, the various federal agencies cannot coordinate their claims of jurisdiction, so the U.S. crypto industry regulation has been in a chaotic and difficult-to-regulate environment.
- The FIT21 Act regulates various core regulatory issues. The bill first clarifies that the SEC and CFTC will serve as the main regulatory agencies for the crypto industry, and for the first time clarifies the classification of cryptocurrencies as securities and commodities, which solves the long-standing core regulatory conflicts in the crypto industry.
- The bill specifies in detail the registration standards for cryptographic entities with the SEC and CFTC, providing practitioners with clearer regulatory guidance. At the same time, the bill also provides sound consumer protection measures, such as a 12-month token lockup for token issuers to prevent short-term speculators from endangering the health of the industry.
- In the bill, Congress is very optimistic about the crypto industry and actively encourages American companies to combine blockchain technology in innovative ways, while urging the SEC and CFTC to conduct research on DeFi to assist in subsequent supervision.
- If FIT21 can officially become law, industry practitioners will have clearer legal guidance to prevent erroneous practices, and consumers will also be better protected under this regulatory framework. In the future, the entire market is very likely to usher in rapid growth on both the consumer and innovation sides, helping the entire industry to accelerate its escape from the regulatory Wild West that has lasted for more than a decade and allowing cryptocurrency to truly enter the mainstream vision.
- The passage of the FIT21 bill was mainly the result of the active promotion of the Republican Party and the continued support of both parties. The bill was originally initiated by a Republican-led committee, and almost all Republican members of the House of Representatives voted in favor of it, and some moderate Democratic members also agreed to the bill. In this process, leading companies in the crypto industry also called on lawmakers to pass FIT21, which shows the importance of the bill.
- With the general election approaching, the crypto industry's continued expansion of influence has made crypto as a whole an important voting base in inter-party games. Candidates who are optimistic about the crypto industry will gain more favor from voters, which will also have a very positive impact on the passage of FIT21.
- FIT21 has not yet been signed into law. The next step will be to move to the Senate for a vote, and the final integrated text will be signed by the president. Patrick McHenry said at the CoinDesk Consensus conference a few weeks ago that the bill is expected to be officially signed into law within the next year.
On May 22, local time in the United States, the Republican-led FIT21 bill was passed by the U.S. House of Representatives with 279 votes in favor and 136 votes against. The passage of this bill is an extremely important moment for the crypto industry, symbolizing that the crypto industry has made important legislative achievements in the U.S. Congress. Its influence has already reached the highest power center in the United States. As the first bill in the crypto industry to establish a complete regulatory system, FIT21 is also the first step in helping the crypto industry move out of the Western world.
1. Current regulatory status of the US crypto industry
The crypto industry has spawned many businesses, such as centralized exchanges, mining, staking services, and other crypto businesses supported by smart contracts. The United States currently adopts a joint regulatory model for cryptocurrencies . Different federal agencies can regulate businesses within their jurisdiction. Important federal agencies such as the SEC (U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission), CFTC (U.S. Commodity Futures Trading Commission), FinCEN (U.S. Financial Crimes Enforcement Network) and OFAC (Office of Foreign Assets Control) are all involved in the supervision and crackdown on illegal activities in the crypto industry. These different federal agencies have had varying degrees of impact on the industry.
1.1 Regulatory agencies are “further apart”

Figure 1: Current regulatory landscape for the crypto industry
Since the crypto industry lacks a systematic regulatory framework and adopts a joint regulatory model, it is very easy for each law enforcement agency to assert its own views and a "hundred schools of thought" regulatory landscape.
The SEC plays an extremely important role in the regulation of the crypto industry. Its main responsibility is to define whether different crypto asset entities are securities. It mainly uses the Howey Test to determine whether they fall under its regulatory framework . In order to better help practitioners determine whether the digital assets they issue are "investment contracts" and should be included in "securities", the SEC issued a guidance document in 2019 entitled "Analysis Framework for Whether Virtual Assets Are Investment Contracts". Although the document has no formal legal effect, it provides guidance for practitioners.
The CFTC's attitude towards digital assets is clearly stated on its official website, stating that virtual assets, including all virtual currencies, are commodities, so the CFTC has the power to regulate manipulation and fraud in the digital asset futures market . Subsequently, the revised "Digital Commodity Consumer Protection Act" was passed in 2022 to give the CFTC exclusive jurisdiction over "digital commodity" transactions and platforms, authorizing it to register and regulate spot exchanges, which means that spot exchanges follow the same rules as other commodity exchanges.
FinCEN is mainly engaged in anti-money laundering, combating terrorist finance, and KYC . FinCEN's main rights are granted by the Bank Secrecy Act (BSA), which clearly stipulates that if the crypto business involves the production, transfer and trading of virtual currency, it must be regulated by BSA. In 2013, FinCEN issued a management framework for virtual currency and identified crypto asset trading service providers as money service businesses (MSBs). This indirectly recognized virtual assets as currencies , and cryptocurrency trading platforms must obtain FinCEN's license and implement anti-money laundering mechanisms .
OFAC is responsible for monitoring all financial transactions in the United States and sanctioning any individuals, organizations or countries that pose a threat. With the rise of digital assets, due to their technical characteristics, some transaction participants have been provided with new means of evading detection , making OFAC's enforcement more difficult. Unlike the SEC and CFTC, OFAC's main enforcement scope is mainly focused on processing transactions for users in sanctioned regions and providing money laundering assistance for illegal activities outside the United States.
It can be seen from this that each law enforcement agency has its own regulatory model and attitude towards the crypto industry . The supervision of the crypto industry is too fragmented and unsystematic, which will inevitably cause some regulatory conflicts that make it impossible for crypto practitioners to follow legal practices, and they are easily faced with unreasonable lawsuits that affect the development of the industry.
The historical enforcement actions of each regulatory agency can be found in the Appendix.
1.2 SEC’s “Intimidation” Enforcement
In addition to the jurisdiction granted by the U.S. Congress, the SEC can use the "Regulation by Enforcement" method to define whether cryptocurrencies are "securities." Since U.S. court precedents can serve as an important basis for jurisdiction, the SEC will use administrative enforcement to bring civil lawsuits or administrative penalties against founders, executives, etc. for violations of U.S. securities laws, and determine its jurisdiction over the crypto assets based on the court's decision . For example, in December 2020, the SEC filed a civil lawsuit against Ripple, claiming that Ripple failed to register the issuance and sale of XRP with the SEC, thereby violating the relevant provisions of the Securities Law regarding the sale of securities. At the same time, the SEC's lawsuits are not only aimed at the characterization of cryptocurrencies, but also deal with business issues of some crypto companies . For example, in June 2023, the SEC filed a lawsuit against Coinbase, accusing it of illegally operating a crypto asset securities business without registration, and the court ultimately basically supported the SEC's allegations. This shows that the SEC is constantly expanding its regulatory scope through administrative means, and due to the ambiguity of the regulatory framework of the crypto industry, such lawsuits by the SEC are very likely to lead to "intimidation"-style law enforcement , and practitioners find it difficult to protect themselves based on reliable laws, which has a relatively serious impact on the development and innovation of crypto companies.
1.3 Regulatory Conflict
The current fragmented regulatory situation makes it difficult to avoid enforcement conflicts between regulatory agencies due to unclear jurisdiction. The most intense conflicts are between the SEC and the CTFC, because these two regulatory agencies are targeting the most core asset classification issues in the crypto industry . The SEC tends to believe that most digital assets can be identified as securities because these assets can easily pass the Howey Test, while the CFTC regards most cryptocurrencies as commodities, which will cause the SEC and CFTC to have overlapping jurisdiction when regulating some tokens, and it is difficult to clarify the division of regulatory powers without a unified regulatory framework. In addition, the two have also had overlapping supervision of crypto companies. For example, in the 2023 Binance prosecution, both the SEC and the CFTC filed a lawsuit against Binance, and the accusations against Binance by both parties had a lot of similarities. Overlapping enforcement may lead to unnecessary fines. In the case of unclear supervision, regulatory overlap will also have a great impact on the industry.
Therefore, for a long time, the crypto industry in the United States has been in a chaotic and difficult-to-control regulatory environment. Due to the lack of a perfect legal path, various federal agencies cannot coordinate their claims of jurisdiction . The resulting regulatory conflicts have had an extremely unstable impact on the development of the industry. At the same time, in the absence of a regulatory framework, crypto companies find it difficult to protect their rights and interests in the face of unreasonable accusations from some law enforcement agencies, which to a certain extent hinders the flexible innovation and development of the crypto industry in the United States. The FIT21 Act is the beginning of changing the current chaotic regulatory landscape.
2 Detailed explanation of FIT21 Act
FIT21 stands for the Financial Innovation and Technology for 21st Century Act , or HR 4763. The bill redefines the different jurisdictions of the SEC and CFTC over crypto assets, establishes a clearer and more comprehensive legal regulatory framework for the crypto industry , and also includes crypto market consumer protection measures and a series of regulations to address the unique structural problems of virtual assets. The clarity and comprehensiveness of the bill make it the most important bill in the crypto industry to date.
FIT21 was first initiated on July 20, 2023 by Glenn Thompson, Chairman of the House Agriculture Committee, Patrick McHenry, Chairman of the House Financial Services Committee, Tom Emmer, Party Discipline Committee Member, and three other House members . During the committee review stage, the bill passed the House Agriculture Committee with unanimous bipartisan approval . At the same time, the House Financial Services Committee also passed the FIT21 bill, which was supported by all Republicans and six Democratic members on the committee. It can be seen that the introduction of the FIT21 bill is not only the result of the joint efforts of the two House committees, but also the joint support of the Republican and Democratic parties. It is worth mentioning that the CFTC and SEC are regulated by the Agriculture Committee and the Financial Services Committee respectively. Based on the influence of the CFTC and SEC on the crypto industry, these two committees should naturally become important participants in promoting the FIT21 bill.

Figure 2: FIT21 initiators
2.1 Contents of the Act
The FIT21 Act is 253 pages long. It sets out preliminary regulatory provisions in six areas, including the definition and registration of digital assets, the division of powers between the SEC and the CFTC, and guidance on innovation in the crypto industry. The core content of each part will be summarized and analyzed below.
PART 1: Definition of assets and division of responsibilities of regulatory agencies
In the first part of the bill, FIT21 refers to three different securities and commodities exchange acts to define crypto-asset related terms such as "blockchain protocol", "decentralized governance system" and "decentralized trading system". The most important content is the definition of "digital assets". The bill defines "digital assets" as "digital homogeneous value carriers that can be held or transferred without relying on any intermediaries, and all transactions will be recorded in a distributed ledger protected by an encryption system". In addition, another definition worth mentioning is " digital commodities". The original definition is slightly complicated but can be simply understood as "any digital asset obtained through legal issuance channels and purchased and held on an exchange". This definition does not essentially add or change the definition of "digital assets", so digital assets are regarded as commodities by default, but FIT21 also clarifies that the CFTC and SEC, as the main regulatory bodies for crypto assets , need to jointly explore and further clarify all terms related to crypto assets, so the definition will be further improved later .
More importantly, the classification of digital currencies is clarified in this section. The bill stipulates that if a blockchain running digital assets is a functional system and decentralized, then the digital asset will be deemed a commodity and regulated by the CFTC. If the digital asset does not meet the definition of decentralization, it will be deemed a security and regulated by the SEC. The bill defines a decentralized system as no individual has unilateral power to control the blockchain, and no issuer has 20% or more control over digital assets or voting rights in digital assets . The clarification of this classification standard is of great significance to crypto assets. This standard clarifies the regulatory scope of the SEC and CFTC, which can greatly avoid regulatory confusion and conflicts.
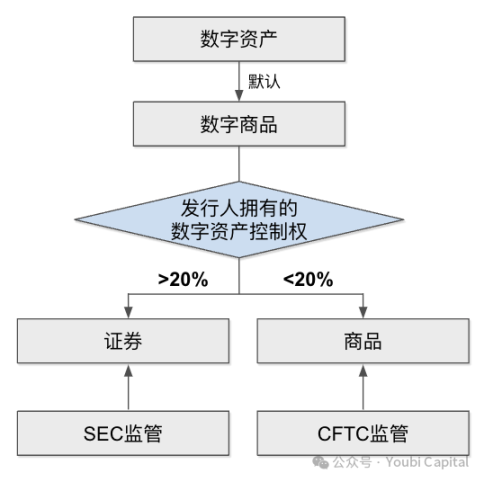
Figure 3: Asset Definition and Regulation
PART 2: Clarity of investment contract assets
Due to the different structures and natures of crypto assets, FIT21 has revised the federal securities-related laws, mainly targeting the definition and regulations of "investment contract assets", aiming to provide sufficient clarity and clarity for some assets in the market.
The bill mainly made two amendments to the Securities Act of 1933. The first amendment explicitly excluded "investment contract assets" from the definition of "securities", making "investment contract assets" an independent definition and giving crypto assets an intermediate definition. If an asset is identified as an investment contract, it will not be defaulted to a security in the traditional sense. The second subsequent amendment supplemented the definition of "investment contract assets":
- Assets must be transferable digital value entities that can be recorded on a public distributed ledger protected by a cryptographic system without an intermediary.
- The asset must be sold or otherwise transferred, or intended to be sold or otherwise transferred, as part of the investment contract.
- Assets are not considered securities under the Securities Act of 1933
In the guidance document previously released by the SEC, if an asset passes the Howey Test and is identified as an "investment contract" and is then classified as a security , it will also be considered a security and regulated by the SEC. However, due to the unique structural nature of crypto assets, digital assets may be considered commodities and can also be sold as part of an investment contract. As investment contracts and securities are not mapped , traditional asset categories are not fully applicable to crypto regulation. Therefore, the FIT21 Act explicitly excludes "investment contract assets" from the definition of "securities", providing greater regulatory flexibility for cryptocurrencies , and no longer using a single "Howey Test" standard to determine whether an asset is a security. This helps to qualitatively standardize crypto assets and improves the classification tolerance to fit the unique structure of cryptocurrencies, so as to prevent crypto assets from being directly identified as securities and causing unreasonable regulation.
Secondly, the separation of "investment contract assets" from securities also solves the current problem of regulatory divisions for the same digital asset. For example, in the Ripple case mentioned above, the court determined that the financing of XRP private placement for institutional professional investors met the three criteria of the Howey Test and constituted a "securities" offering, while the offering of XRP through other channels did not constitute a "securities" offering. As a result, XRP sold through different channels has been subject to multiple supervision and unclear supervision . If the FIT21 Act is passed, the regulatory agencies corresponding to "investment contract assets" under different conditions will be further clarified in the future, the regulatory responsibilities of institutions will be clarified, the regulatory efficiency of each department will be improved, and the problem of confusion in regulatory responsibilities for the same digital asset at different issuance or sale stages will be reduced, bringing greater regulatory flexibility to market participants.
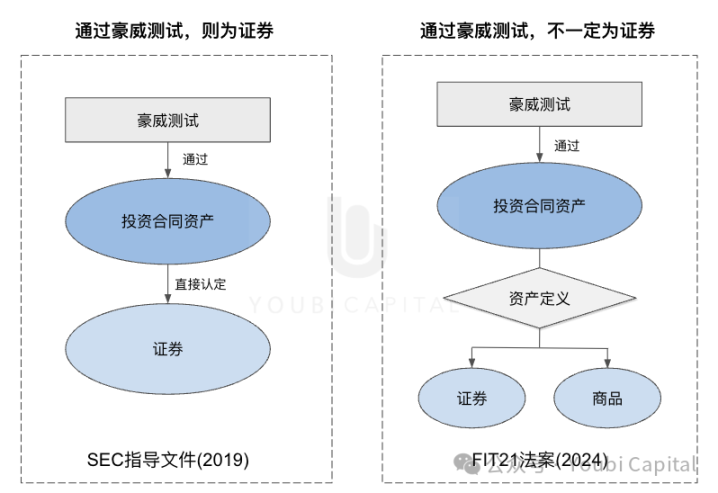
Figure 4: Howey Test decision logic
PART 3: Registration exemption and lock-up requirements for digital asset issuance
Regarding the issuance of digital assets, the FIT21 Act also explains the issuance exemption standards, issuance information disclosure requirements, and asset certification. In the exemption standards, the Act mainly stipulates that if the total value of the digital asset issuance does not exceed $75,000,000, and any purchaser does not own 10% of the asset issuance volume during the issuance stage, then the transaction of the digital asset issuance will be exempted from registration . Subsequent bills also set a series of basic requirements for the issuance of digital assets and strengthened the provisions for information disclosure , such as the issuer needs to provide source code, token transaction history, and token economy, etc. At present, the overall situation of asset issuance in the industry is more in line with the requirements for information disclosure, and the information disclosure requirements will further protect the rights and interests of consumers.
More importantly, the bill also sets requirements for the lock-up period of tokens held by issuers. The bill stipulates that any relevant entity of a token issuer needs to lock up the tokens for 12 months before selling them . This rigid regulation can curb short-term speculative behavior of some practitioners, prevent market overheating, and protect consumers. At the same time, it can promote long-term innovation of blockchain products and help the industry retain innovators and long-termists.
PART 4 and PART 5: SEC and CFTC’s regulatory scope for crypto companies
Parts 4 and 5 of the Act mainly stipulate the regulatory authority of the SEC and CFTC over digital assets and the registration requirements of relevant business entities. The Act clearly stipulates that cryptocurrency trading platforms, brokers and market makers will be regulated by law enforcement agencies . If the business of the business entity involves securities or commodity crypto assets, it is necessary to submit registration applications to the SEC and CFTC respectively. The Act allows the same business entity to register with the SEC and CFTC at the same time. In addition, the focus of supervision by the SEC and CFTC is slightly different. The Act clearly stipulates that crypto asset trading platforms need to provide the SEC with relevant transaction information and records in the system and need to review the security and integrity of the trading system, while the CFTC focuses on the review of customer funds custody . At the same time, the CFTC will also supervise the Commodity Pool Operator and Commodity Trading Advisor.
The current regulations indicate that DeFi activities are not subject to this bill, and the SEC and CFTC will subsequently jointly study and formulate detailed regulatory rules.
PART 6: Congressional attitude and technological innovation supervision
In the last part of the bill, the views and opinions of Congress on encryption technology are summarized. Congress first affirmed that entrepreneurs and innovators in the encryption industry are building and deploying the next generation of the Internet, and believed that the digital asset ecosystem has the potential to enhance the efficiency of social activity management, resource allocation and decision-making. At the same time, it emphasized that the United States should try to explore the potential of the encryption industry and the potential opportunities it brings . American companies should try to combine blockchain technology in innovative ways to explore new user participation structures. While affirming that encryption assets will bring innovation, Congress also pointed out the need to cooperate with encryption industry practitioners to establish a basic framework for blockchain technology risks and investor protection. Overall, Congress is generally optimistic about digital assets and the encryption industry . While supporting the development of the industry, it also hopes that there will be a systematic framework for supervision to maximize the unique innovations that blockchain technology can bring.
In order to further respond to the development of blockchain technology and the impact of digital assets, the bill proposes to expand the research responsibilities of the SEC's Innovation and Financial Technology Strategic Center (FinHub) and the CFTC Laboratory (LabCFTC) for the crypto industry, and help the committee formulate policies and establish a supervision system for financial technology . In addition, the bill also proposes to establish a joint CFTC and SEC Digital Asset Advisory Committee, which will specifically study issues related to digital assets. The committee will mainly strengthen cooperation between the CFTC and the SEC to better regulate digital assets, and the committee will also appoint at least 20 practitioners to assist and strengthen close ties with the industry.
This part of the bill also proposes research on DeFi and NFT . The bill requires the SEC and CFTC to jointly conduct in-depth research on the purpose, scale, advantages and disadvantages of DeFi protocols, and potential risks or improvements to financial market stability. The research on NFT will be conducted by the Comptroller General of the United States, mainly exploring the practical uses of NFT and how to integrate it with traditional markets.
2.2 Industry Significance
The passage of the FIT21 bill in the House of Representatives is an extremely important moment for the crypto industry, marking a major victory and legislative achievement for the crypto industry in the U.S. Congress, and its growing influence has already reached the highest center of power in the United States.
In the above article, we mentioned the fragmentation of the regulatory system of the US crypto industry. Different law enforcement agencies have advocated the establishment of bills or proposed guiding documents for crypto assets. Fragmented regulation not only leads to conflicts in jurisdiction and unhealthy law enforcement, but also a steady stream of law enforcement lawsuits, which are great challenges to the sustainability and innovation of the industry. At the same time, practitioners cannot rely on the applicable legal framework for advance regulation or resistance. It can be said that the crypto industry has suffered from regulation for a long time! The promotion of the FIT21 Act is changing all this!
First of all, FIT21 is the first bill in the history of the crypto industry that provides a complete regulatory framework for the industry . The regulations specified in the bill are all core issues facing the crypto industry. For example, the bill also clearly states for the first time that the SEC and CFTC are the primary regulatory agencies in the crypto industry , and for the first time stipulates the classification of whether cryptocurrencies are securities or commodities . Therefore, the qualitative classification of different tokens will no longer be a matter of different opinions between the SEC and CTFC.
At the same time, the bill also provides sound consumer protection measures , as well as clear registration requirements for crypto companies, token lock-ups by issuers, and enhanced information disclosure to further protect consumers, promote the health of the entire market, and prevent bad actors from continuing to release products and tokens that harm consumer rights through regulatory gaps.
In addition, Congress' attitude towards cryptocurrencies in the bill is also very optimistic. While encouraging innovation, it also prompts the SEC and CFTC to jointly study DeFi for further better regulation, which is of great significance for the industry's continued innovation and more detailed bills.
If FIT21 can officially become law, industry practitioners will have clearer legal guidance to prevent erroneous practices , which will have a positive effect on the development and innovation of crypto companies, and consumers will also be better protected under this regulatory framework. Coupled with the continued expansion of the influence of cryptocurrencies, the entire market is very likely to usher in rapid growth on both the consumer and innovation sides in the future , allowing cryptocurrencies to truly enter the mainstream vision.
A tall tree has deep roots. FIT21 is precisely the first step, which can serve as a cornerstone for subsequent more comprehensive legislation, continue to pave the way for innovation in the crypto industry under the supervision of regulators, help the entire industry accelerate its departure from the regulatory Wild West that has lasted for more than a decade, and truly influence the future of the entire industry.
3 FIT21 key promoters
3.1 Republican-led, bipartisan support
From a political perspective, the Republican Party played a crucial role as the main promoter . The bill was initially passed by the Agriculture Committee and the Financial Services Committee of the House of Representatives. At the same time, the party structure of these two committees is dominated by the Republican Party , with 28 and 29 Republican members respectively. Therefore, in the early stage of the bill, during the committee review stage, the Republican Party can use its numerical advantage to pass the bill and submit it to the House of Representatives for voting. Although the Republican Party is the main promoter, it is worth mentioning that during the voting stage of the Agriculture Committee, all Democratic members also voted in favor, which means that the bill was supported by both parties in the early stage . The FIT21 bill eventually received 208 votes from the Republican Party and 71 votes from the Democratic Party in the House of Representatives vote. The results also show the Republican Party’s support for the bill and the change in attitude of some Democratic members. Combined with Trump’s recent positive attitude towards cryptocurrencies, the entire Republican Party has played a great role in promoting the crypto industry.
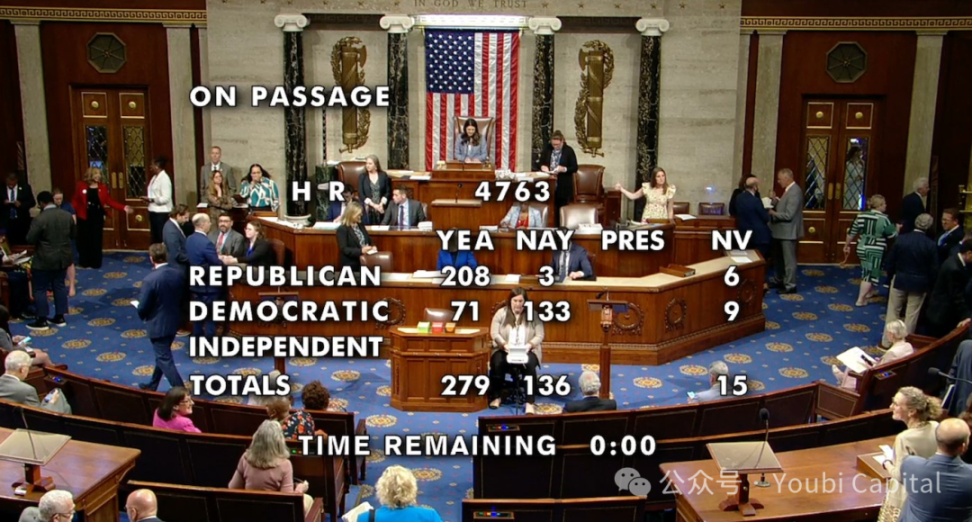
Figure 5: FIT21 bill voting results
3.2 High attention from crypto industry practitioners
Crypto industry practitioners and companies also attach great importance to this important bill that affects the blockchain industry. On May 16, the Crypto Council for Innovation (CCI) and 60 other companies issued a letter of support calling for the passage of the FIT21 bill . The letter united a16z, Coinbase, Circle, Block and other important industry participants. The letter expressed the importance of FIT21 to the crypto industry and the backward regulatory problems faced by the United States, and urged legislators to support HR 4763 to help the crypto industry establish a clear regulatory environment.

Figure 6: Joint appeal letter
3.3 The influence of the crypto industry continues to expand
In addition to the support of parties and practitioners, the influence of the crypto industry and the political situation in the United States have also become important driving factors that cannot be ignored. According to a research report by the non-profit organization Stand With Crypto, there are currently 52 million people in the United States holding virtual currencies, and another survey shows that about 20% of American citizens hold them . Although the data is biased, it can be seen that the holders of digital currencies are no longer a niche group , and their influence is gradually expanding. The crypto industry is expected to create another 4 million jobs by 2030, and its growth potential has a positive impact on the US job market. However, the current US crypto regulatory system is not optimistic , lagging behind 83% of G20 countries, and millions of jobs in the blockchain industry are at risk. At the same time, a large number of practitioners leave the United States every year due to unclear supervision. Driven by various factors, the legislature has to pay attention to the regulatory issues of the crypto industry, so the FIT21 Act is particularly important.

Figure 7: Stand With Crypto poll
3.4 With the election approaching, cryptocurrency becomes an important political bargaining chip
At the same time, the current US election is at a critical stage. The continued expansion of the influence of the crypto industry has made the crypto community gradually become an important voting base for party games . According to multiple opinion polls by Grayscale, DCG and Paradigm, at least 20% of voters hold and pay attention to the cryptocurrency industry . Such a large group cannot be ignored, and in several key swing states, there are also a certain number of voters who believe that cryptocurrency is an important issue in the general election. Then the decision-making attitude of political parties towards cryptocurrency is an extremely important political bargaining chip , which has a very important impact on related crypto bills. Therefore, the political game between parties may be extremely beneficial to the promotion of the FIT21 bill.
- A poll commissioned by cryptocurrency investment firm Paradigm was released on Thursday (March 14), showing that 20% of American voters own cryptocurrencies.
- A Harris poll funded by Bitcoin ETF issuer Grayscale showed that interest in cryptocurrencies is rising among U.S. voters, with 33% saying they would consider a political candidate’s stance on cryptocurrencies before making a voting decision.
- A poll released by blockchain venture capital firm Digital Currency Group (DCG) shows that more than 20% of voters in several key swing states consider cryptocurrency to be a key issue in the upcoming US election.
- Grayscale Poll Report: Nearly Half of American Voters Expect Cryptocurrency to Be Part of Their Investment Portfolio
4 Next Steps
Committee deliberation → Both houses vote → President’s signature
FIT21 has been voted through by the House of Representatives, and will be voted on in the Senate next. The U.S. legislative process can be simply divided into three stages: the committee review stage, the voting stage of the two houses of Congress, and the final unification of the bill and its signature by the president. In detail, the draft legislation is first proposed and reviewed by the members of the committee, and then submitted to the parliament to which it belongs for voting after the committee's review and approval. The bill will then need to be submitted to another parliament for review. The current FIT21 bill has been voted through by the House of Representatives. Next, FIT21 will be transferred to the Senate, but the transfer procedure will be a long and complicated process. At present, FIT21 will face two situations in the Senate . First, the Senate may decide to redraft the relevant bill , which means that it needs to be re-submitted to the Senate through the review stage of the Senate Committee. Even if it goes directly to the Senate for voting , FIT21 is also very likely to face the amendment and addition of the bill, and then return to the House of Representatives to make a decision and unify the text. According to previous reports by CoinDesk, the Senate is likely to redraft the corresponding bill of FIT21 , which means that it may take some time for FIT21 to be officially passed. At the last presidential signing stage, even if the bill is vetoed, both houses can overturn the resolution with at least two-thirds of the votes in favor, so there will be a lot of room for error in the passage of FIT21. At present, the White House has not issued a veto threat to FIT21 , which means that FIT21 has received the attention of the White House and hopes to participate in policy formulation.
Patrick McHenry, co-founder of FIT21, said at the CoinDesk Consensus conference a few weeks ago that the bill is expected to be officially signed into law within the next year . Although the influence of the crypto industry continues to expand and it is the main battlefield of the recent US election, the possibility of FIT21 passing is very high, but the current attitude of the US government towards cryptocurrencies is still relatively vague . For example, Biden recently vetoed the resolution to overturn the SEC's crypto asset accounting standard SAB 121, but took a relatively neutral attitude towards FIT21. At the same time, due to the US election, the FIT21 bill will be handed over to the next Congress . If Trump wins the election, whether he will continue to support the implementation of the crypto bill is also an unknown . But in general, as cryptocurrencies are important political bargaining chips, the prospects for FIT21 are still relatively optimistic.
appendix
SEC (Securities and Exchange Commission)
- In December 2020, the SEC filed a civil lawsuit against Ripple, claiming that Ripple had violated the relevant provisions of the Securities Act regarding the sale of securities by failing to register the issuance and sale of XRP with the SEC. The court subsequently determined that the XRP private placement round for institutional professional investors met the three criteria of the Howey Test and constituted a "securities" offering, while the sale of XRP through other channels did not constitute a "securities" offering. Currently, the SEC has appealed the case.
- In June 2023, the SEC filed a lawsuit against Coinbase, accusing it of illegally operating a crypto asset securities business without registration, and the court's final ruling supported most of the SEC's allegations.
- In November 2023, the SEC filed a lawsuit against Kraken, accusing it of illegally facilitating the purchase and sale of crypto-asset securities, failing to register its various businesses with the commission, and selling 11 unregistered securities. In response to the lawsuit, state officials accused the SEC of overstepping its authority, believing that the SEC was expanding the definition of "investment contracts" and automatically classifying crypto assets as securities. Kraken was subsequently fined $30 million.
- The SEC’s jurisdiction is not even limited to the United States. For the Gram tokens issued by Telegram, since it issued tokens to U.S. citizens, the SEC took enforcement measures against Telegram on the grounds of protecting the interests of U.S. investors. Although Telegram was registered in the UK, Telegram eventually returned the raised funds and was fined $18.5 million.
CFTC (Commodity Futures Trading Commission)
- On September 14, 2021, the CFTC filed a lawsuit against Tether and Bitfinex Exchange, accusing the two companies of fabricating trading volume, misappropriating customer funds and suspected violations of anti-money laundering laws. The two parties finally reached a settlement in October 2022, with Tether fined US$41 million and Bitfinex fined US$1.5 million.
- In October 2020, the CFTC, the FBI and the U.S. Department of Justice (DOJ) jointly sued BitMEX and its founders and executives. The CFTC claimed that BitMEX had not registered with the CFTC as a commodity futures trader. In the end, the two parties reached a settlement agreement and BitMEX paid a fine of US$100 million.
FinCEN(Financial Crimes Enforcement Network)
- In 2015, FinCEN imposed an administrative penalty of $700,000 on Ripple Lbas Inc. for failing to apply for an MSB license and failing to establish a corresponding anti-money laundering mechanism.
- In 2020, FinCEN imposed a $60 million civil penalty on the developers and managers of the Helix and Coin Cinja mixers, and FinCEN accused Coin Ninja of violating BSA-related anti-money laundering regulations.
- In 2023, FinCEN and OFAC sued Binance, accusing it of violating BAS and failing to comply with AML obligations.
OFAC (Office of Foreign Assets Control)
- In December 2020, OFAC and Bitcoin trading platform BitGo reached a settlement on charges of violating sanctions against the Crimea region, Iran, Syria, and Cuba between 2015 and 2019. BitGo agreed to pay a fine of $98,830.
- Subsequently, OFAC also sued platforms such as Kraken, CoinList and Binance with similar accusations of "processing transactions for users in sanctioned regions", and all the cases were ultimately resolved through fines and settlements.
FTC (Federal Trade Commission)
The FTC is mainly responsible for consumer privacy protection and information security. In July 2023, the FTC filed a lawsuit against Celsius Network and other affiliated companies and executives, claiming that Celsius deceived consumers into transferring assets to the platform and lied that deposits were safe, but in fact user assets had been misappropriated and Celsius could not provide sufficient liquidity. In the end, the FTC reached a settlement with Celsius, permanently prohibiting the platform from handling consumer assets.








