Author: Tan Zixin,Top Technology

Image source: Generated by Boundless AI
Large language models (LLMs) are changing the way software development is done, and whether AI can massively replace human programmers has become a topic of great concern in the industry.
In just two years, AI large models have evolved from solving basic computer science problems to competing with human experts in international programming competitions, such as OpenAI o1 winning a gold medal in the 2024 International Olympiad in Informatics (IOI) under the same conditions as human participants, demonstrating strong programming potential.
At the same time, the iteration rate of AI is also accelerating. On the SWE-Bench Verified code generation evaluation benchmark, GPT-4o's score was 33% in August 2024, but the new generation o3 model's score has doubled to 72%.

To better measure the software engineering capabilities of AI models in the real world, today, OpenAI has open-sourced a brand-new benchmark SWE-Lancer, which for the first time links model performance to monetary value.
SWE-Lancer is a benchmark that includes more than 1,400 freelance software engineering tasks from the Upwork platform, with a total real-world reward value of about $1 million, to see how much money AI can earn by programming.
The "Features" of the New Benchmark
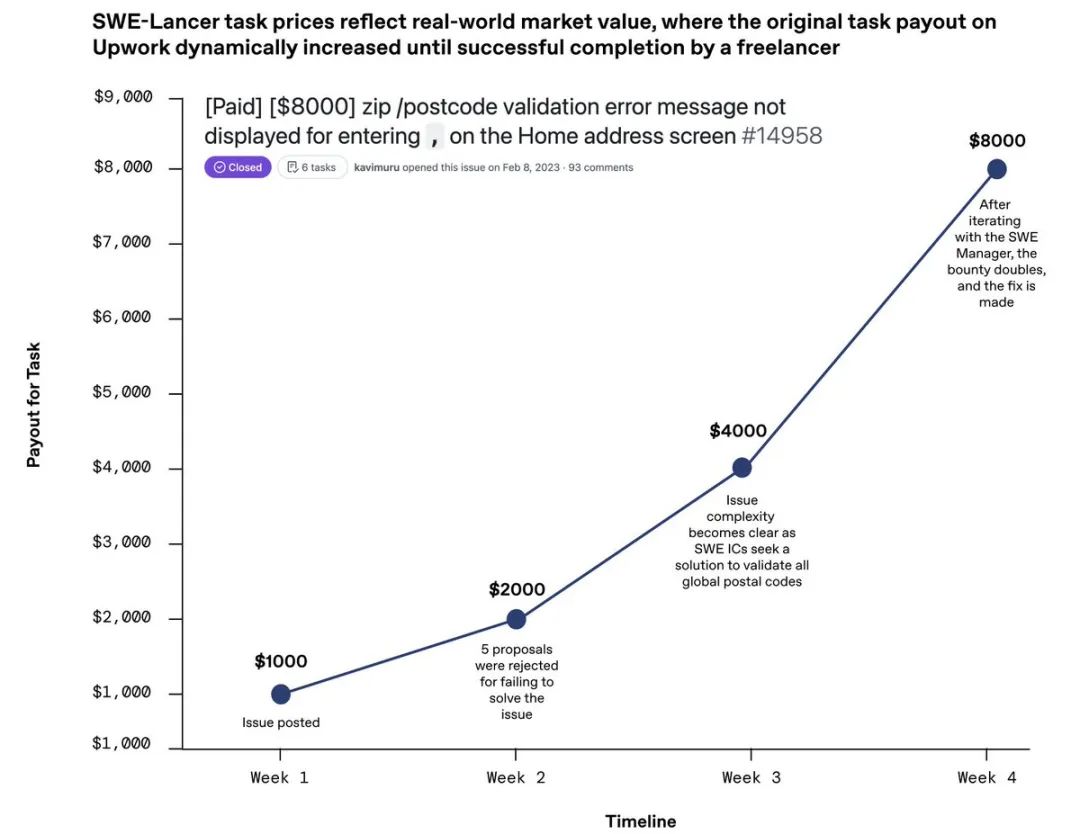
The SWE-Lancer benchmark task prices reflect real market value, with more difficult tasks having higher rewards.
It includes both independent engineering tasks and management tasks, with the ability to choose between technical implementation solutions. This benchmark is not only for programmers, but for the entire development team, including architects and managers.
Compared to previous software engineering test benchmarks, SWE-Lancer has several advantages:
1. All 1,488 tasks represent the real rewards paid by employers to freelance engineers, providing a natural, market-determined difficulty gradient, with rewards ranging from $250 to $32,000, which is quite substantial.
35% of the tasks are worth more than $1,000, and 34% are between $500 and $1,000. The Individual Contributor (IC) Software Engineering (SWE) tasks group contains 764 tasks with a total value of $414,775; the SWE Management tasks group contains 724 tasks with a total value of $585,225.
2. Large-scale software engineering in the real world not only requires the ability to write code, but also the ability to manage technical coordination. This benchmark uses real-world data to evaluate models in the role of "technical manager" for SWE.
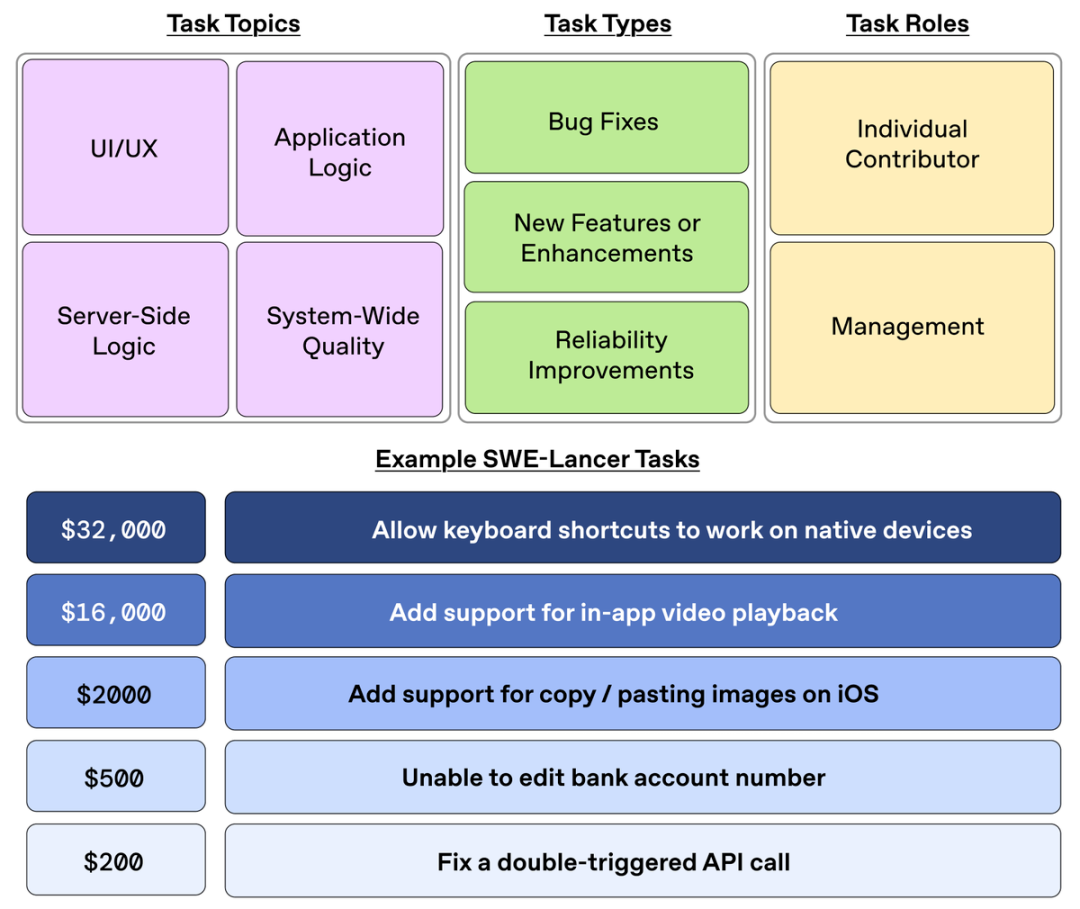
3. It has the capability to evaluate advanced full-stack engineering. SWE-Lancer represents real-world software engineering, as its tasks come from a platform with hundreds of millions of real users.
The tasks involve engineering development for mobile and web, interaction with APIs, browsers, and external applications, as well as verification and reproduction of complex problems.
For example, some tasks cost $250 to improve reliability (fix a double-trigger API call issue), $1,000 to fix a vulnerability (solve a permission difference issue), and $16,000 to implement a new feature (add in-app video playback support on web, iOS, Android, and desktop).
4. Diverse domains. 74% of IC SWE tasks and 76% of SWE management tasks involve application logic, while 17% of IC SWE tasks and 18% of SWE management tasks involve UI/UX development.
In terms of task difficulty, the tasks selected for SWE-Lancer are very challenging, with the average task in the open-source dataset taking 26 days to solve on Github.
Furthermore, OpenAI states that the data collection was unbiased, as they selected a representative sample of tasks from Upwork and hired 100 professional software engineers to write and verify end-to-end tests for all tasks.
AI Coding Earning Ability Comparison
Although many tech leaders have been constantly claiming that AI models can replace "low-level" engineers, whether enterprises can completely replace human software engineers with LLMs is still a big question mark.
The initial test results show that on the complete SWE-Lancer dataset, the AI champion models currently being tested are earning far less than the potential total reward of $1 million.
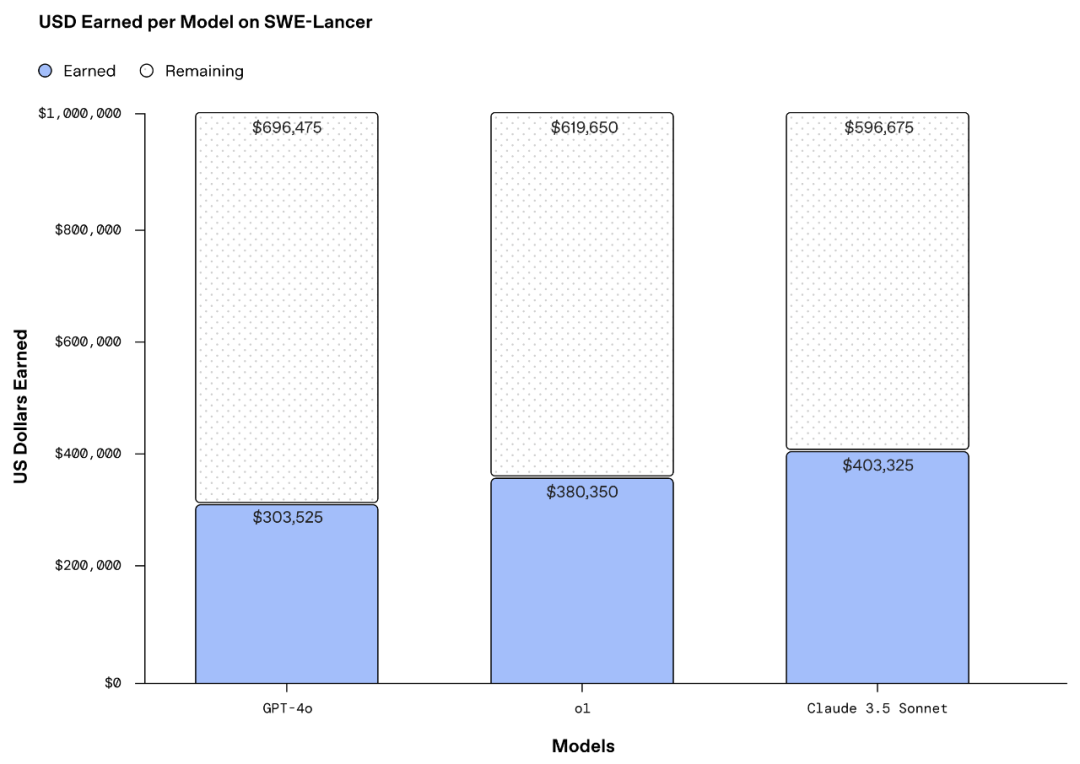
Overall, all models perform better on SWE management tasks than on IC SWE tasks, and IC SWE tasks are still largely unresolved by AI models, with the best-performing model so far being the Claude 3.5 Sonnet developed by OpenAI's competitor Anthropic.
On IC SWE tasks, all models have a single-pass rate and earnings rate below 30%, and on SWE management tasks, the best-performing model Claude 3.5 Sonnet scored 45%.
Claude 3.5 Sonnet showed strong performance on both IC SWE and SWE management tasks, outperforming the second-best model o1 by 9.7% on IC SWE tasks and 3.4% on SWE management tasks.
If converted to earnings, the best-performing Claude 3.5 Sonnet earned over $400,000 on the complete dataset.
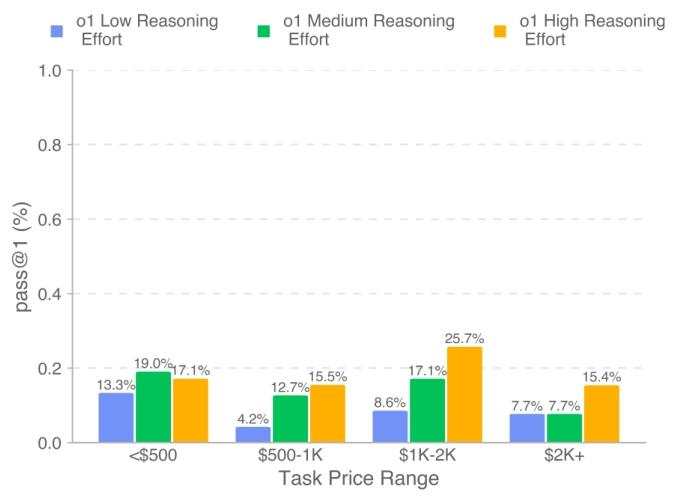
Interestingly, higher reasoning computational power can greatly help "AI earning".
On IC SWE tasks, experiments on the o1 model with enabled deep reasoning tools showed that higher reasoning computational power can increase the single-pass rate from 9.3% to 16.5% and earnings from $16,000 to $29,000, with the earnings rate increasing from 6.8% to 12.1%.
The researchers summarize that while the best model Claude 3.5 Sonnet solved 26.2% of the IC SWE problems, the majority of the remaining solutions still have errors, and much work is needed to achieve reliable deployment. Next is o1, followed by GPT-4o, and the pass rate on management tasks is typically more than twice that of IC SWE tasks.
This also means that even though the idea of AI agents replacing human software engineers has been heavily hyped, companies still need to think carefully, as AI models can solve some "low-level" coding problems, but cannot yet replace "low-level" software engineers, as they cannot understand the reasons for some code errors and continue to make more extended errors.
The current evaluation framework does not yet support multimodal input, and researchers have not yet evaluated "return on investment", such as comparing the cost of paying freelancers to the cost of using APIs, which will be the focus of the next step in refining this benchmark.
Become an "AI-Augmented" Programmer
For now, AI still has a long way to go to truly replace human programmers, as developing a software engineering project is not just about generating code as required.
For example, programmers often encounter extremely complex, abstract, and ambiguous customer requirements, which require in-depth understanding of various technical principles, business logic, and system architecture. When optimizing complex software architectures, human programmers can comprehensively consider factors such as the future scalability, maintainability, and performance of the system, which AI may find difficult to analyze comprehensively.
In addition, programming is not just about implementing existing logic, but also requires a lot of creativity and innovative thinking. Programmers need to come up with new algorithms, design unique software interfaces and interaction methods, and this kind of truly novel ideas and solutions are the weaknesses of AI.

Programmers also often need to communicate and collaborate with team members, customers, and other stakeholders, need to understand the requirements and feasibility of all parties, clearly express their own views, and work with others to complete the project. In addition, human programmers have the ability to continuously learn and adapt to new changes, they can quickly master new knowledge and skills and apply them to actual projects, while a successful AI model still requires various training and testing.
The software development industry is also subject to various legal and regulatory constraints, such as intellectual property, data protection, and software licensing, which AI may find it difficult to fully understand and comply with, thereby creating legal risks or liability disputes.
In the long run, the substitutability of programmer positions due to the progress of AI technology still exists, but in the short term, the "AI-enhanced programmer" is the mainstream, and mastering the use of the latest AI tools is one of the core skills of an excellent programmer.







