Author: Hotcoin Research

introduction
With the booming development of DeFi, Bitcoin, as the cornerstone of the cryptocurrency field, has become the focus of industry attention in terms of its ecological expansion and innovation in application scenarios. However, the Bitcoin network does not naturally support native staking due to its Proof of Work (PoW) consensus, which has caused the huge BTC assets to remain "dormant" in the DeFi field for a long time. The emergence of the Babylon protocol has created a new model for Bitcoin staking: without changing the Bitcoin mainnet, bridging or hosting, you can use the BTC in your hands to provide security for other blockchains and obtain income, introduce Bitcoin into the PoS economy, and make BTC have the dual attributes of value storage and income assets, thereby promoting the rise of the BTCFi ecosystem.
This article will deeply analyze the technical mechanisms and innovations of the Babylon protocol, summarize its pledge data and performance, review the representative projects of the Babylon ecosystem, and explore the challenges and opportunities currently facing Babylon, as well as the outlook for future development.
1. Analysis of the innovative mechanism of Babylon protocol
1. BTC non-custodial staking model
The Babylon protocol is cleverly designed to enable native BTC to participate in staking while maintaining user self-custody. Unlike traditional cross-chain bridges that lock BTC and then issue alternatives such as WBTC, Babylon does not introduce third-party custody or token bridging, and all operations are completed directly on the Bitcoin mainnet. Its core lies in Bitcoin script locking and signature verification: BTC holders generate special staking transactions on the chain to lock BTC in script addresses with time locks and multi-signature conditions. The beacon chain/PoS chain deployed by Babylon can identify these locking transactions and verify the associated Bitcoin signatures, thereby recording which public key addresses have pledged how much BTC. During the staking period, BTC is still under the control of the user's own Bitcoin address, and can only be unlocked when the preset conditions are met (such as the expiration of the pledge or authorized withdrawal). This design realizes a staking mode without trusting a third party and BTC does not leave the mainnet, greatly reducing risks.
2. Overcoming the BTC native staking problem
Currently, about 27% of ETH participates in staking, but almost 0% of BTC can obtain staking income. Babylon activates this untapped potential and realizes BTC cross-chain shared security through the "time-space separation" design: BTC continues to be kept on the Bitcoin network, while the Babylon chain and the PoS network it serves cite the existence of these BTC as economic guarantees. All this does not require the Bitcoin network to upgrade its smart contract capabilities, nor does it require hard forks to adjust rules - Babylon staking transactions are just ordinary Bitcoin transactions, using existing script functions to build staking lock and exit conditions.
3. Finality providers and BTC security grafting
Babylon did not make any changes to the Bitcoin protocol itself, but introduced a "control plane" on top of Bitcoin - Babylon's PoS beacon chain. This chain is built with Cosmos SDK and is the "management" of the Babylon system, responsible for aggregating the security of BTC pledges and providing finality services to other blockchains. When Bitcoin pledgers generate pledge transactions, they entrust their BTC to a "finality provider". Finality providers can be regarded as validator nodes on the Babylon chain and are run by professional organizations. They cannot touch the user's BTC, but have the right to use this part of the Bitcoin economic weight on behalf of the user to vote for the PoS network, provide checkpoints and finality proofs.
4. Security and Exit Mechanism
BTC pledged in Babylon can be withdrawn early at any time. When staking, BTC is locked for up to about 64,000 Bitcoin blocks (about 15 months). If users want to unlock in advance, they need to initiate a destaking transaction, and the constraint committee will verify the validity of the transaction and sign it together, so that BTC will enter a 7-day on-chain unlocking period and then be returned to the user. Throughout the process, the committee can only approve the correct unlocking, and it can neither transfer the user's BTC without authorization nor prevent the automatic unlocking of the pledge upon expiration. In addition, there is no penalty mechanism (slashing) for Bitcoin staking in Phase-1 - users do not need to sign any message agreeing to be fined, and even if the PoS validator they delegate fails to perform his duties, the user's BTC will not be affected. This avoids the concerns of early users about security.
5. Multi-chain sharing and scalability
Babylon's long-term vision is to achieve "one BTC, multiple pledges" in Phase-3. At that time, a certain amount of BTC pledged by a user can be used for the security of multiple PoS networks at the same time (Babylon calls these networks "Bitcoin Secured Networks", BSN, Bitcoin Secure Network). Babylon's PoS chain will act as a control center, coordinating how the same BTC is distributed among different networks, allowing BTC holders to earn multi-chain rewards at the same time. This Liquid Restaking concept is similar to Ethereum's EigenLayer, but the underlying pledged asset is BTC. The introduction of BTC as a shared pledged asset is expected to enhance the volatility resistance and security of the entire PoS ecosystem. And Babylon does not involve cross-chain bridges, which greatly reduces the risk of bridges being hacked.
Source: https://babylon.foundation/blogs
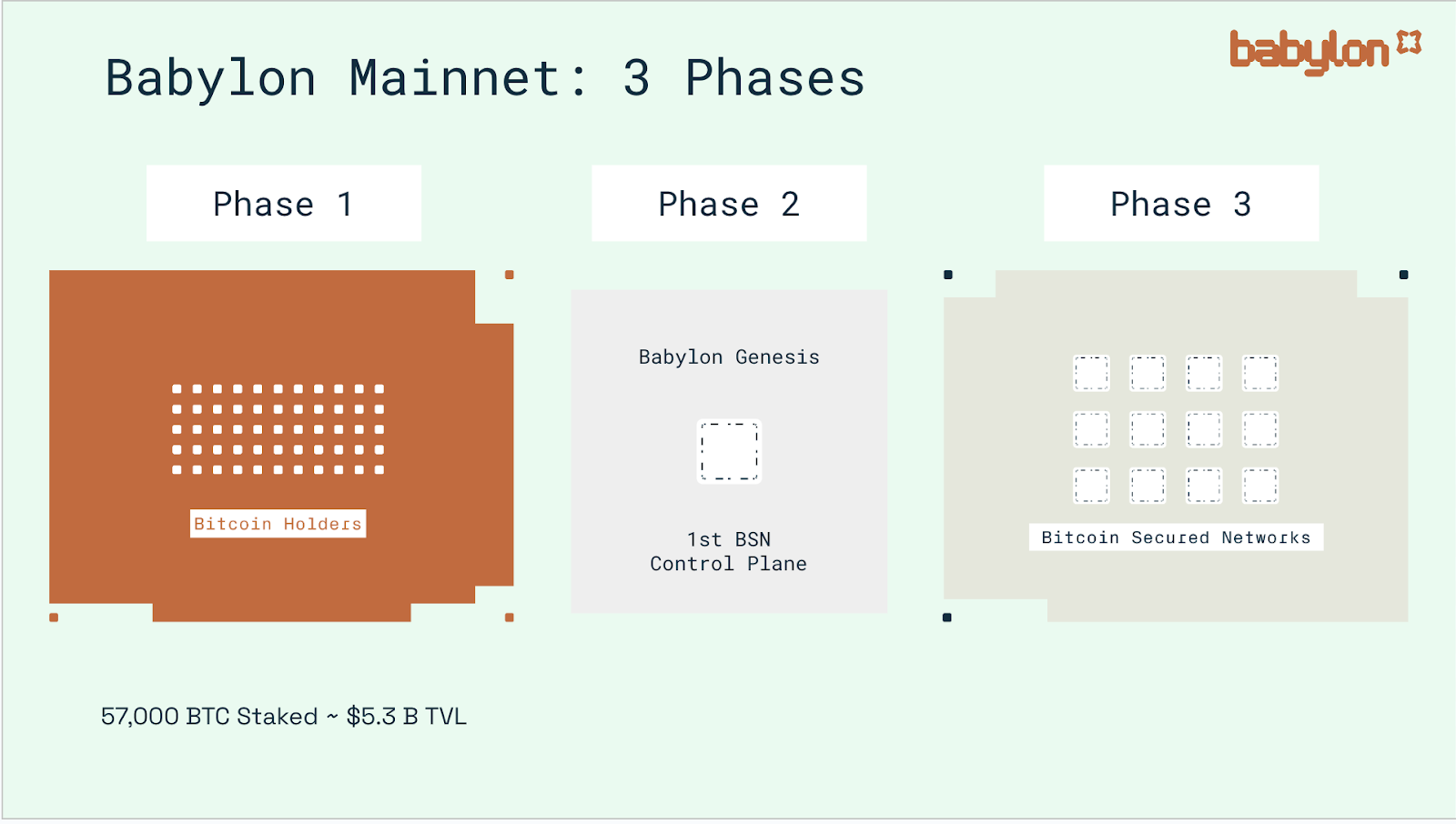
2. Babylon Bitcoin Staking Progress and Performance
The Bitcoin staking protocol Phase-1 launched by Babylon in 2024 adopts a phased approach to open staking. The official Phase-1 is divided into three phases (Cap-1, Cap-2, Cap-3), each of which differs in staking amount, participation rules, etc., in order to gradually test and expand the scale of BTC staking.
Source: https://babylonlabs.io/blog
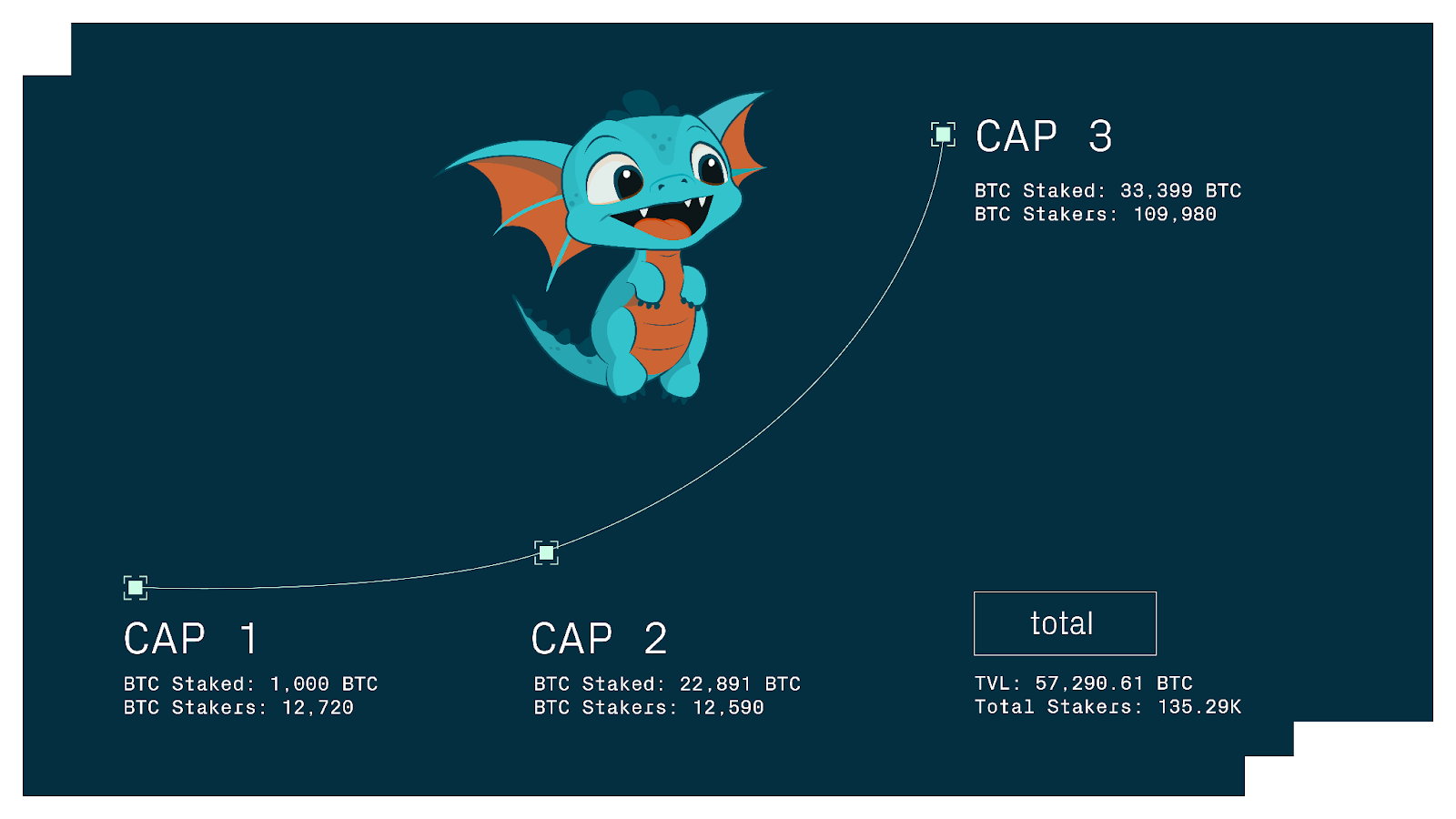
1. Cap-1: Initial 1,000 BTC limit to ignite participation enthusiasm
Time and rules: Cap-1, as the starting stage of Phase-1, will be opened on August 22, 2024. For security reasons, Babylon has set an initial staking cap of 1,000 BTC. Participation is based on a first-come, first-served principle: staking transactions are recorded in chronological order on the Bitcoin blockchain, and no more staking will be accepted once the total amount reaches 1,000 BTC. To encourage widespread participation, Cap-1 sets a minimum of 0.005 BTC and a maximum of 0.05 BTC for each staking transaction. The 0.05 BTC cap ensures that at least thousands of transactions are required to fill the 1,000 BTC cap, preventing a few whale from taking up all the quotas. Therefore, Cap-1 is more like a community event that attracts a large number of ordinary BTC holders.
Participation: After Cap-1 was opened, the market response was extremely enthusiastic - the 1,000 BTC quota was sold out in just 3 hours. According to statistics, a total of 12,720 BTC pledgers participated and submitted about 20,610 pledge transactions. Such a high level of participation even caused the Bitcoin network fee to soar 120 times: during the period when the pledge was opened, the total hourly transaction fee of Bitcoin soared from 0.5 BTC to 60 BTC. Users were willing to pay high mining fees to grab the pledge quota.
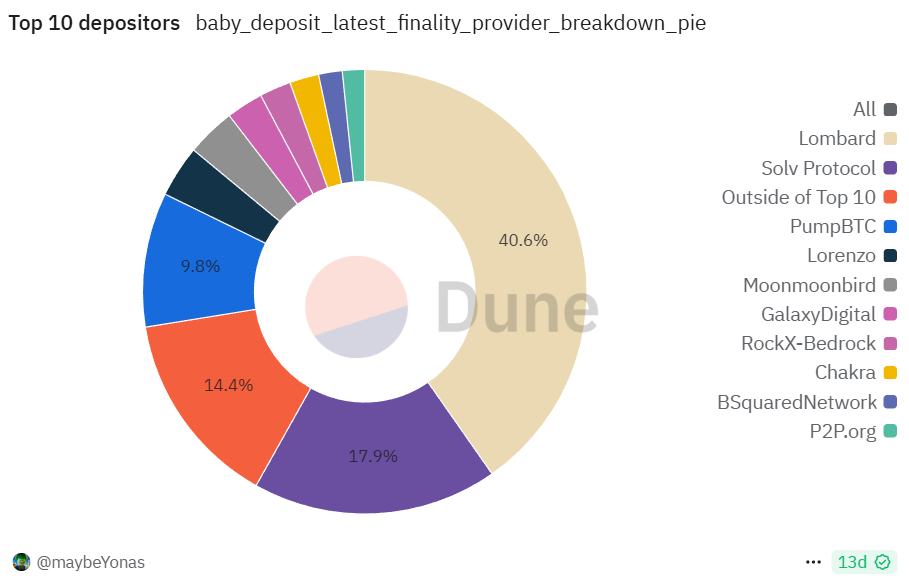
Performance of ecosystem-related protocols: In Cap-1, Bitcoin LSD protocols accounted for a considerable share, providing users with a one-stop BTC staking portal and additional rewards. For example, Solv Protocol pledged 250 BTC, accounting for 25% of the total amount. Solv not only aggregated user BTC through its product SolvBTC.BBN, but also announced that it would fully reimburse all participants in Cap-1 for staking-related BTC mining fees to reduce user costs. In addition, Bedrock under RockX contributed about 297.8 BTC (about 30%); Lorenzo Protocol about 129.4 BTC (12.9%); PumpBTC about 118.4 BTC (11.8%); Persistence's pSTAKE about 10 BTC (1%); ordinary retail users directly participated through exchange wallets, etc., which constituted the rest. Babylon introduced the "Babylon Points" points system to measure contributions. During Cap-1, each Bitcoin block was allocated 3,125 points, which were allocated according to the proportion of each actively staked BTC in the block. These points are recorded under the user's public key and may be used for reward distribution in the future.
2. Cap-2: Capacity increased significantly, institutional entry and billion-level TVL
Time and rules: After verification of Cap-1, Babylon launched the second phase of Phase-1, Cap-2, on October 9, 2024. Cap-2 adopts a different strategy: canceling the total upper limit and limiting the pledge opening window to only 10 Bitcoin blocks. 10 blocks are about 90 minutes, during which all valid pledge transactions are accepted. Cap-2 also significantly increases the upper limit of a single pledge to 500 BTC, allowing institutions to pledge large amounts of BTC at one time. In addition, the point reward per block is increased to 10,000 points, which is about 3.2 times that of Cap-1. The higher reward attractiveness and looser limits mean that Cap-2 is designed to introduce institutional players.
Participation: Cap-2 has proven to have attracted the participation of many institutions and custodian platforms. In just 10 blocks, the scale of staking has exploded: a total of about 22,891 BTC was successfully staked in the Cap-2 phase, which is more than 22 times that of Cap-1, pushing Babylon's total stake to billions of US dollars, establishing Babylon's position as the "world's largest BTC staking platform". Despite the surge in total staked BTC, the number of participating addresses in Cap-2 is 12,590, which is comparable to Cap-1. This shows that Cap-2 is mainly composed of a small number of large stakes: in fact, according to statistics, there are more than 1,000 BTC addresses that have staked more than 23,000 BTC in total. Among them, Lombard Finance received a total of about 22,503 BTC in the Cap-2 window, accounting for about 98%, almost covering most of the staked shares in Cap-2.
Performance of relevant protocols in the ecosystem and expansion of cooperation: Cap-2 marks the official debut of institutions and large custodians on the Babylon stage. Top compliant custodians such as Anchorage Digital and Hex Trust announced support for clients to participate in Babylon staking, making it easier for large holders to obtain additional BTC income. In terms of exchanges, Binance provides a one-click staking entry through its decentralized wallet (Binance Web3 Wallet) and launches related activities during Cap-2; OKX's OKX Earn also cooperates with Solv and others to provide users with Babylon staking services. In addition to Lombard, Solv continues to play a role in Cap-2 of the LSD protocol; in addition, Bedrock, Lorenzo, PumpBTC and others have launched "Cap-2 pre-staking" activities in advance to attract users to deposit BTC into their platforms.
3. Cap-3: Open window and integral stimulation
Time and rules: The final phase of Phase-1, Cap-3, will start at 11:00 UTC on December 10, 2024, and will last until December 17, covering about 1,000 Bitcoin blocks (about a week). Cap-3 removes the total limit and adopts a time window system (lasting 1,000 blocks) to accept all pledge transactions. During this period, the upper limit of each pledge is further increased to 5,000 BTC (500 BTC in Cap-2), and the minimum lower limit remains at 0.005 BTC. At the same time, in order to further incentivize staking in the short term, Babylon introduced a tiered point reward in Cap-3: the first 300 BTC blocks are allocated up to 100,000 points per block, and the next 700 blocks are allocated 21,000 points per block. The reward of 100,000 points/block is about 10 times that of Cap-2. .
Participation: Cap-3 has attracted a wider user base due to its relaxed restrictions and generous rewards. In the 7-day window, a total of 109,980 addresses participated in staking, accumulating 33,399 BTC, setting a new single-stage high. The number of participants in Cap-3 has increased dramatically, far exceeding the sum of the first two stages, indicating that a large number of small and medium-sized BTC holders have also joined the Babylon staking ranks. Babylon has made more people understand how to stake "sleeping" BTC for profit. Since Cap-3 has no total upper limit and lasts for a long time, the Bitcoin on-chain fee has not skyrocketed again, and staking transactions can be completed in a relatively stable environment.
Ecosystem synergy and activities: Many partners took advantage of Cap-3 to launch joint incentive plans. For example, Corn Network, as one of the Bitcoin Secured Networks, announced that it would issue additional "Kernels" points to BTC staking users during Cap-3. In addition, Babylon also held community activities such as the "BTC Staking Marathon" with wallets, node service providers, etc., providing badges and lucky draw opportunities for users who continuously stake for a certain period of time or amount. These initiatives further fermented on social media, increasing Babylon's popularity. Babylon Phase-1 attracted a total of 57,290.61 BTC to be successfully staked, accounting for about 0.27% of the circulating supply of Bitcoin, and 135,290 addresses participated in the staking. Babylon officials call Phase-1 the launch of the supply side: a large number of BTC have been "warehoused for use", and the next Phase-2 will focus on the demand side, that is, launching Babylon's own PoS chain and connecting more BSN networks, so that these BTC can be truly put into safe production and generate actual benefits.
3. Babylon Ecosystem Map
During its rapid development, Babylon has built a multi-level ecological partner network covering infrastructure, protocol cooperation, wallet exchange support, etc. The strong cooperation landscape provides driving force and synergy for Babylon's growth.

1.LST Protocol
The LST protocol solves the liquidity problem after users pledge BTC by issuing BTC's liquid staking tokens (LST, Liquid Staking Token). Currently, 12 mainstream LST protocols use Babylon as the underlying staking channel, including Lombard, Bedrock, PumpBTC, Lorenzo, Solv, pSTAKE, Chakra, etc., as well as emerging projects such as Allo and Stakestone. Babylon provides them with security and a source of income, while these protocols guide users to Babylon and improve the stickiness of staking. For example, users can get double rewards by staking BTC through the LSD protocol: Babylon points on the one hand, and the protocol party's own tokens or points on the other hand. In addition, LST tokens (such as LBTC, uniBTC, etc.) can also be used in other DeFi scenarios such as lending and providing liquidity, further improving the utilization rate of BTC assets.
2. Bitcoin Security Network (BSN)
BSN refers to blockchain networks that integrate Babylon Bitcoin staking security. Currently, 25 projects/networks have been announced as BSN candidates, and plan to integrate BTC security after Babylon Phase-2 goes online. Typical representatives include:
BOB (Build on Bitcoin): A hybrid Layer2 that combines the features of Bitcoin and Ethereum to create a Bitcoin DeFi platform. BOB is integrated with Babylon, and provides Bitcoin ultimate security for its L2 through Babylon's BTC pledge, improving security credibility. BOB claims that this makes it a "hybrid chain that ensures security with Bitcoin" and plans to use Babylon to achieve cross-chain asset bridging such as BTC and ETH.
Corn: An innovative network deployed on Arbitrum, Corn has partnered with Babylon to become the world's first BSN, with Bitcoin and Ethereum double-layer security superimposed on Ethereum L2. To incentivize BTC stakers, Corn has also launched the "Kernels" points program, which issues Corn ecological points based on the number of BTC staked by users within a certain period of time.
B² Network: A Bitcoin Layer2 project with a modular design, B² embeds Babylon's BTC pledge into its Hub consensus, introduces Bitcoin Data Availability Sampling (DAS) and ZKRollup technology, and creates a "BTC-secured execution layer". Babylon pledge provides economic guarantees for the verification of B² Rollup, and B² also supports various DeFi operations of BTC pledge derivatives on its Rollup.
Through the BSN plan, Babylon extends its tentacles to blockchain projects in different tracks, including Layer1 main chain, Layer2 Rollup, oracle network, data availability layer, etc., to promote BTC-as-a-Service: Babylon contributes nearly 60,000 BTC "security pool" to various networks, and each network in turn introduces more applications and transactions, improving the activity and value capture on the BTC chain. This positive cycle has huge potential and also makes Babylon occupy a unique position in the cross-chain ecosystem.
3. Wallet and exchange support
In order to lower the threshold for user participation, Babylon actively cooperates with many mainstream crypto wallets and trading platforms. Binance not only developed a Web3 wallet to support the native BTC staking interface, but also launched the "BTC staking to earn points" activity in its Earn financial management area, so that users who are not familiar with self-managed wallets can also participate conveniently. OKX also integrated Babylon through OKX Earn, and carried out joint publicity with Solv, PumpBTC, etc. In addition, 12 Web3 wallets announced support for Babylon Phase-1, including multi-chain wallets and Bitcoin-specific wallets. For example, decentralized wallets ZenGo, Blocto, etc. have launched Babylon staking tutorials; Bitcoin native wallet Xverse also participated in the discussion of the Ordinals community docking with Babylon. The endorsement of wallets and exchanges has increased users' trust in Babylon to a certain extent, playing an "endorsement" role.
4. Infrastructure and service providers
In the Babylon ecosystem, node service providers and custodians also play an important role. Professional node operators such as Blockdaemon, InfStones, stakefish, Figment, etc. have become part of the Babylon finality provider network, providing customers with staking as a service. Custodians such as Cobo and Coincover cooperate with LSD Protocol (PumpBTC, etc.) to execute staking transactions on behalf of users while ensuring the security of BTC private keys. Compliance custodian giant Anchorage Digital announced that it will provide Babylon staking channels for US institutions to achieve "institutional-level one-click staking"; Asian custodian Hex Trust is also involved. The addition of these infrastructure partners makes it possible for large amounts of funds to enter Babylon safely, and also makes Babylon's network more decentralized and reliable.
Through the above-mentioned multi-level cooperation expansion, Babylon has built a thriving ecosystem, and all parties in the Babylon ecosystem have formed a synergistic effect - the expansion of the pledge scale has attracted more partners to join, and in turn, the joining of partners has promoted the further increase of the pledge scale.
4. Inventory of representative projects in Babylon ecosystem
A number of protocols and applications centered around BTC staking have emerged in the Babylon ecosystem. Each of them has a unique positioning and together they enrich the Bitcoin DeFi landscape.
Source: https://dune.com/pyor_xyz/babylon-chain
1. Lombard Finance (LBTC)
Lombard is a protocol within the Babylon ecosystem that focuses on Bitcoin liquidity staking. Lombard aims to establish a market between BTC stakers and PoS chain demanders, connecting Bitcoin to every chain and every DeFi protocol. Users can deposit BTC on the Lombard platform, and Lombard will stake these BTC agents on Babylon to earn income. At the same time, users mint LBTC tokens on Ethereum at a 1:1 ratio. LBTC is an ERC-20 token issued by Lombard, representing the BTC principal staked by the user. Users holding LBTC can accumulate points on Babylon and invest LBTC in DeFi protocols to release the liquidity of the staked assets. Lombard has launched the Lux and Luminary reward programs, and early participants can obtain the governance/reward token (Lux) issued by Lombard. The token has not yet been publicly sold and may play a governance role after the launch of the Babylon mainnet.
2. Bedrock (uniBTC)
Bedrock is a multi-asset liquid staking protocol incubated by RockX, a veteran node service provider, that supports multi-chain staking such as ETH, BTC, and IoTeX. Bedrock received investment from OKX Ventures and others in May 2024, focusing on providing institutional-level liquidity staking services. Its BTC staking token is named uniBTC. Bedrock's feature is that it supports wBTC staking: users can stake WBTC directly to Bedrock on the Ethereum chain. Bedrock pledges an equal amount of real BTC to Babylon through a cooperative custodian, allowing WBTC holders to participate in Babylon staking without having to operate the Bitcoin chain themselves. Bedrock provides two modes: one is "proxy staking", where users pledge WBTC to stay in Ethereum, and Bedrock completes BTC staking in the background; the other is "one-click exchange", where Bedrock helps users exchange WBTC for BTC and stake it. Staking rewards are issued in the form of uniBTC, which is a BTC staking certificate issued by Bedrock on Ethereum and can be used in DeFi. Bedrock also supports the pledge of assets such as BTCB on BSC and FBTC on Filecoin, empowering Babylon for BTC derivative assets on different chains.
3. PumpBTC (pumpBTC)
PumpBTC is a Bitcoin restaking protocol launched in 2024. Its slogan is "maximizing returns for BTC holders" and it conducts business centered on pumpBTC tokens. PumpBTC adopts a cross-chain aggregation model: users can pledge BTC-anchored assets such as WBTC, BTCB, and FBTC to obtain 1:1 anchored pumpBTC tokens. Subsequently, PumpBTC entrusts an equal amount of real BTC to Babylon on the Bitcoin mainnet through a cooperative third-party custodian (such as Cobo and Coincover). The income generated by Babylon is then exchanged back to pumpBTC, making pumpBTC a revenue-accumulating LST. At the same time, PumpBTC has designed a point reward and team invitation mechanism. Staking any amount of pumpBTC can obtain pump points, which can be used to obtain PUMP token airdrop rewards.
4. Lorenzo Protocol (stBTC)
Lorenzo is a Bitcoin yield financial layer based on Babylon, creating more yield opportunities for BTC staking through an innovative principal and interest separation model. The project received investment from Binance Labs in October 2022. Lorenzo introduces a dual token design to represent BTC staking: after users stake BTC or BTCB on the Lorenzo platform, they will receive an equal amount of stBTC (Stake BTC) as the principal token, and continuously accumulated YAT (Yield Accumulation Token) as the yield token. Babylon's staking points and potential returns are reflected in YAT, while stBTC is always anchored 1:1 with the number of staked BTC. Such separation allows users to flexibly dispose of returns and principal: for example, YAT can be traded to lock in future returns, or stBTC can be lent to obtain liquidity. Lorenzo operates through a staking agent mechanism, and all staking operations are currently managed by official agents: agents stake user BTC to Babylon, monitor on-chain proofs, and issue stBTC and YAT accordingly.
5. Solv Protocol (SolvBTC.BBN)
Solv is a well-known decentralized financial asset issuance and management protocol. In July 2024, Solv announced that it would launch solvBTC.BBN in collaboration with Babylon, allowing BTC holders of Ethereum, BSC, Arbitrum and other networks to participate in Babylon staking and receive points rewards. Users lock BTC (or anchored BTC on each chain) on the Solv platform, and Solv will ensure that these BTC are staked to Babylon through custodians (such as Binance's custodian department Ceffu). Users then receive SolvBTC.BBN tokens, which can be used in the Solv ecosystem. Solv plans to expand SolvBTC into a multi-chain BTC reserve, connecting more PoS staking scenarios, not just Babylon.
6. Chakra (Prana)
Chakra is a Bitcoin re-pledge protocol that combines zero-knowledge proof and modular concepts, with the vision of building a BTC settlement network that serves institutions. Chakra completed financing in April 2024, and investors include StarkWare (a well-known Ethereum ZK solution team), ABCDE Capital, etc. Chakra launched a BTC pre-pledge mining pool, allowing users to deposit BTC into the Chakra pool before the Babylon mainnet is launched. These BTC are kept in a multi-signature vault jointly managed by Chakra and custodian partners (such as Cobo). When Babylon opens staking, Chakra will stake the BTC in the vault on behalf of users. During this period, users will receive the incentive token Prana issued by Chakra (currently in the form of points) and are expected to enjoy a portion of the Babylon staking income. Chakra emphasizes that the staking process is transparent and reliable through zero-knowledge proof, while protecting user privacy. In addition, Chakra is committed to modular blockchain architecture and plans to build an independent Chakra settlement network, with Babylon providing consensus security and the Chakra network handling transaction execution.
5. Challenges and prospects of Babylon
Although Babylon has achieved impressive results in 2024, it still needs to overcome many challenges to achieve long-term success. At the same time, the market environment and technological trends also provide Babylon with a series of valuable opportunities. In this section, we comprehensively discuss the core challenges currently facing the Babylon ecosystem and its development prospects.
1. Core Challenges
Technical complexity and security: The Babylon protocol involves a complex combination of technologies such as Bitcoin scripts, Cosmos chains, and cross-chain verification, and has extremely high security requirements. The limitations of the Bitcoin mainnet(1MB blocks, low script programmability) mean that Babylon pledge transactions must be highly optimized, otherwise it is easy to cause network congestion and even cause resentment in some Bitcoin communities. Babylon needs to continue to prove that it will not have a negative impact on the BTC mainnet, and even show a beneficial side to the mainnet(such as increasing mining fee income, increasing UTXO utilization, etc.). In addition, the security of the Babylon chain itself is also crucial: as the final hub, if the Babylon chain is attacked or malicious, it may affect the security of all BSN networks.
Economic model and continuous incentives: During Phase-1, users only receive Points and cannot directly cash in the profits. This arrangement is acceptable in the short term, but in the long term, due to the lack of tangible benefits, user enthusiasm may decline. Therefore, Babylon needs to come up with a clear economic incentive model in Phase-2 and beyond. This includes: Will Babylon issue its own tokens and grant airdrops to Points holders? Can BTC stakers obtain native rewards on the PoS chain (such as BSN chain tokens, or Babylon chain block reward sharing)? Without continuous income incentives, large BTC holders may not be willing to lock up their positions for a long time. In addition, when Babylon allows the same BTC to participate in multi-chain staking, how to distribute income and risks is also a challenge.
Competition and alternative solutions: Although Babylon currently has almost no direct competitors in the field of "BTC staking", it does not mean that there will be no other solutions in the future. For example, Stacks ecosystem and Drivechain advocates may propose different BTC layer cross-chain income solutions; Ethereum's EigenLayer may also expand support for WBTC staking to divert BTCFi demand. In addition, CeFi institutions are also providing income products such as BTC lending. Once a simpler "lying down to earn BTC income" solution comes out, Babylon may face user loss.
User education and experience: Bitcoin users have long been accustomed to "hoarding coins without moving them". To get them to participate in staking to gain returns, it requires a change in mindset and a sufficiently convenient experience. Although Babylon cooperates with many wallets, staking still involves details such as UTXO selection and fee setting, which are unfamiliar to ordinary users. Especially for small holders, the high BTC on-chain fee will be a barrier. Therefore, improving the user experience (UX) is one of the challenges: including a more friendly staking interface, a more transparent display of expected returns, and lowering the threshold for participation.
2. Development prospects
Babylon Chain Launch: The highlight of Phase-2 is the launch of Babylon’s autonomous Proof-of-Stake blockchain, the so-called Babylon Genesis. According to official statements, the Babylon chain will be the first blockchain to truly use BTC locks to provide economic security. It is also the first Bitcoin Secured Network (BSN) and will be built on the Cosmos SDK. The launch of the Babylon chain means that the nearly 57,000 BTC staked in Phase-1 has finally been put to good use. The Babylon chain will serve as the backbone of the entire Babylon ecosystem: aggregating BTC stake security, exporting finality services to other connected chains, and managing the relationship and reward distribution between stakers and finality providers.
Babylon token issuance and usage scenarios: Babylon is expected to launch native tokens for governance and on-chain payment, and distribute them to Phase-1 points holders, BSN partners, etc. through airdrops and other means to ensure community participation. If issued, Babylon tokens will enable holders to vote on protocol upgrades and parameter adjustments, and may capture part of the revenue (for example, charging BSN a service fee and then distributing it to token stakers). As an independent network, the Babylon chain needs to design a gas fee mechanism. Since BTC cannot be used directly as gas on the chain, Babylon may use its own tokens or stablecoins as a means of gas payment. The Babylon chain economic model will also clarify the distribution of benefits between stakers, validators (finality providers) and BSN users.
Multi-chain staking and full interconnection: After the Babylon chain runs stably, the team's next goal is to achieve multi-chain staking of one coin, allowing Bitcoin holders to use the same BTC to stake on multiple BSNs at the same time, and to achieve this by introducing sub-staking shares. For example, assuming that a user locks 1 BTC in Babylon, the Babylon chain allows users to choose up to N BSNs for staking, and each BSN is assigned a weight ratio or share. The BTC is calculated as a certain amount of staking on each chain, thereby obtaining the rewards of the chain. This shared staking concept is similar to turning BTC into an anchored "staking certificate", and the PoS chain shares the security value of this certificate through Babylon.
Conclusion
The Babylon protocol has successfully solved the historical problem of Bitcoin's inability to natively pledge through mechanism innovation, and opened up a new model for BTC to participate in the security of the PoS chain. Babylon explores how 210,000 Bitcoins can be integrated into the broader blockchain economy. As HashKey Research Institute said, Babylon has opened a new chapter in improving Bitcoin's capital efficiency. If its vision is fully realized, Bitcoin will not only be "digital gold", but also "digital energy" for various blockchains, providing a continuous source of security while also earning returns. This positive cycle will consolidate Bitcoin's core position in the crypto world and make BTCFi an important part of the DeFi landscape that cannot be ignored.
In 2025, we are expected to witness the paradigm shift of BTC from static holding to dynamic staking, and witness the flourishing of various emerging BTC-based protocols on the Babylon chain. Just as the "BTC Renaissance" advocated by the Babylon team, a prosperous era for Bitcoin DeFi is coming.
about Us
As the core investment and research center of the Hotcoin ecosystem, Hotcoin Research focuses on providing professional in-depth analysis and forward-looking insights for global crypto asset investors. We have built a three-in-one service system of "trend analysis + value mining + real-time tracking". Through in-depth analysis of cryptocurrency industry trends, multi-dimensional evaluation of potential projects, and 24-hour market volatility monitoring, combined with the weekly "Hotcoin Selection" strategy live broadcast and "Blockchain Today's Headlines" daily news delivery, we provide investors at different levels with accurate market interpretation and practical strategies. Relying on cutting-edge data analysis models and industry resource networks, we continue to empower novice investors to establish a cognitive framework, help professional institutions capture alpha returns, and jointly seize value growth opportunities in the Web3 era.
Risk Warning
The cryptocurrency market is highly volatile and investment carries risks. We strongly recommend that investors fully understand these risks and invest within a strict risk management framework to ensure the safety of their funds.
Website: https://lite.hotcoingex.cc/r/Hotcoinresearch
Mail: labs@hotcoin.com








