This report was written by Tiger Research . As Bitcoin prices have fallen, attention has turned to DAT companies holding the largest amounts of Bitcoin. Strategy is one of the most notable players in this group. The key questions are how the company has accumulated its assets and how it manages risk during periods of heightened market volatility.
Key points summary
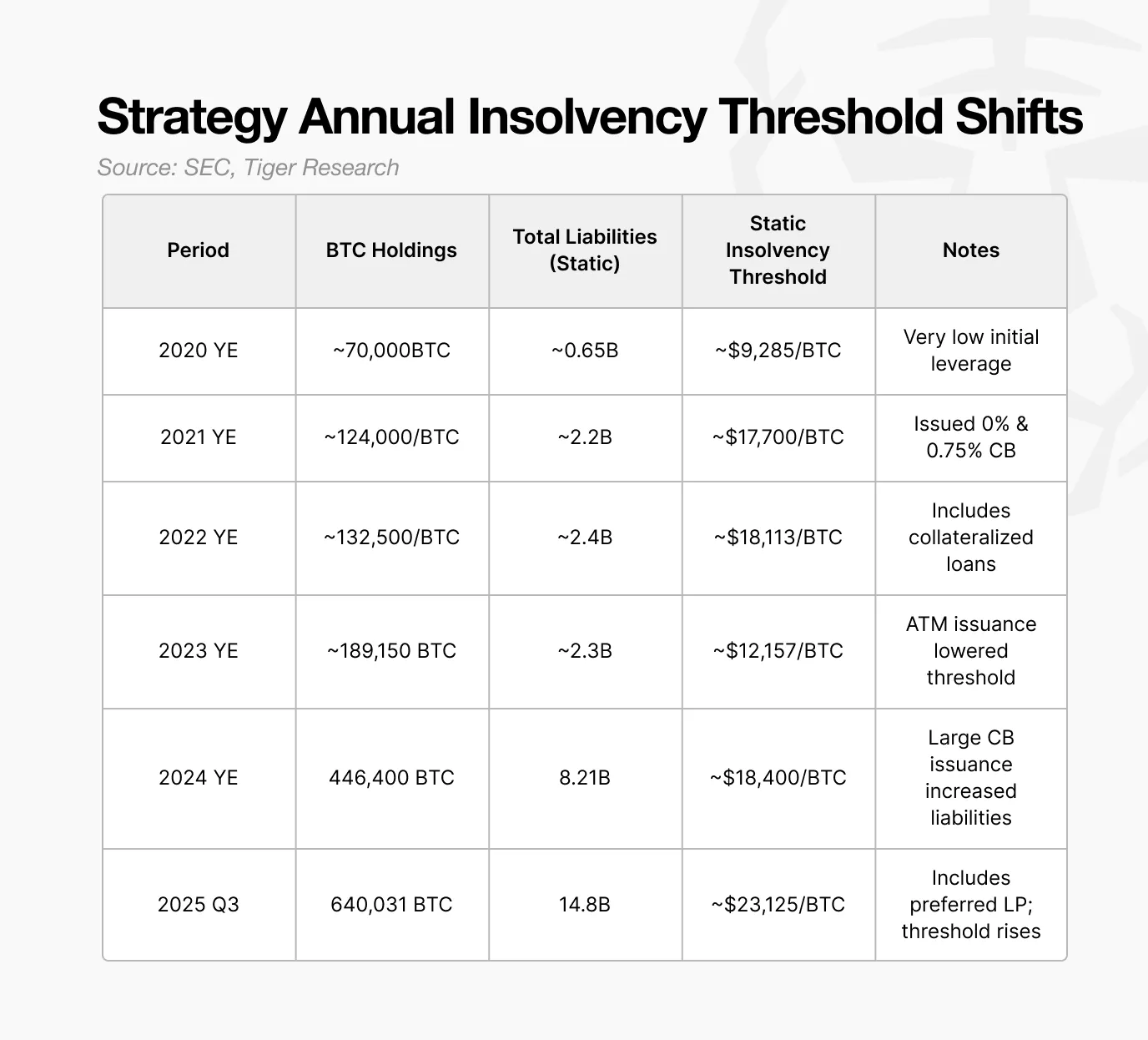
Strategy's static bankruptcy threshold is projected to be around $23,000 in 2025, almost double the $12,000 level in 2023.
In 2024, the company shifted its financing model from simple cash and small convertible bonds to a diversified mix including convertible bonds, preferred stock, and ATM issuances.
Investors holding call options are allowed to redeem them before expiration. If the price of Bitcoin falls, investors are likely to exercise these options, making 2028 a critical window of risk.
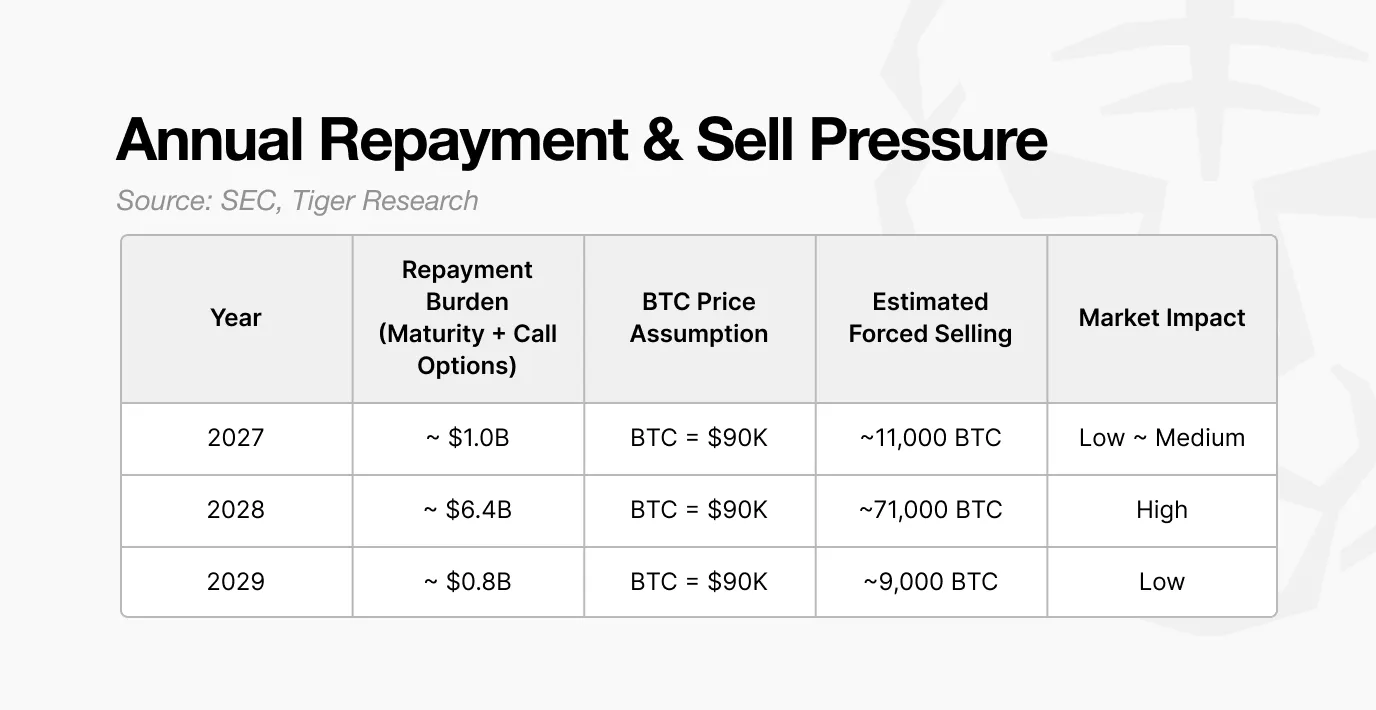
If the 2028 refinancing fails, assuming a Bitcoin price of $90,000, Strategy might need to sell approximately 71,000 Bitcoins. This equates to 20% to 30% of its daily trading volume, which would put significant pressure on the market.
1. Regarding the stability of the Strategy
The recent decline in Bitcoin has caused DAT's stock price to fall by approximately 50%. This raises a core question in the market: with both the stock price and the company's core assets declining, does Strategy still possess stability? This concern has been further exacerbated by JPMorgan Chase's indication that Strategy may be removed from the MSCI index.
People aren't just focused on this stock. Strategy holds a massive amount of Bitcoin, enough to influence the wider market, far exceeding the size of a typical whale. This raises two key questions.
At what price level will Strategy's balance sheet collapse?
When and under what conditions can this company have an impact on the market?
This report reviewed documents from the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) to determine Strategy's effective bankruptcy threshold, the period of increased risk, and the potential market impact should a stress scenario occur.
2. Strategy faces risks: $23,000 threshold
Before proceeding with the analysis, let's clarify the concept of static bankruptcy. Static bankruptcy refers to a situation where a company is unable to repay its debts even if all its assets are liquidated.
In simple terms, static bankruptcy refers to a situation where assets are less than liabilities. For example, if Echo owns a property worth 1 billion Korean won and 100 million Korean won in cash, but has liabilities of 1.2 billion Korean won, then from a balance sheet perspective, the company is insolvent. DAT faces the same situation. If the price of Bitcoin falls below a certain level, the book equity will become negative, and the company will be unable to repay its debts. This level is called the static bankruptcy threshold.
To determine Strategy's static bankruptcy threshold, we first examined how the company accumulated its Bitcoin holdings.
Strategy has held Bitcoin as a strategic asset since 2020, but its accumulation model changed after 2023. Prior to that, the company primarily relied on cash reserves and small amounts of convertible bonds to purchase Bitcoin. Its holdings remained below 100,000 Bitcoins, and its refinancing needs were relatively limited.
Since 2024, Strategy has changed its financing strategy. The company has increased its leverage by combining the issuance of preferred stock, ATM stock programs, and large-scale convertible bonds to raise funds to purchase more Bitcoin.
This led to a rapid increase in the rate at which Bitcoin was accumulated. This structure created a cycle: the higher the price of Bitcoin, the larger the company's market capitalization, and the higher the leverage ratio, thus supporting even more purchases.
The objectives remain the same, but the funding structure and risk profile have changed. This structural shift has now become a core factor exacerbating Strategy's risk of bankruptcy.
Strategy projects a static bankruptcy threshold of approximately $23,000 by 2025. Below this level, the value of its Bitcoin holdings would fall below its liabilities, resulting in insolvency on its balance sheet.
The key point is that this threshold has been rising. In 2023, the company could withstand a Bitcoin price of around $12,000. In 2024, this threshold rose to $18,000, and by 2025 it reached $23,000. As Strategy increases its Bitcoin holdings, this key level also rises.
Therefore, the $23,000 threshold represents the minimum price required for Bitcoin to operate stably. This means that Bitcoin would need to fall by approximately 73% from its current level to trigger bankruptcy risk.
3. Convertible bonds: The problem lies in the holder's put option, not the maturity date.
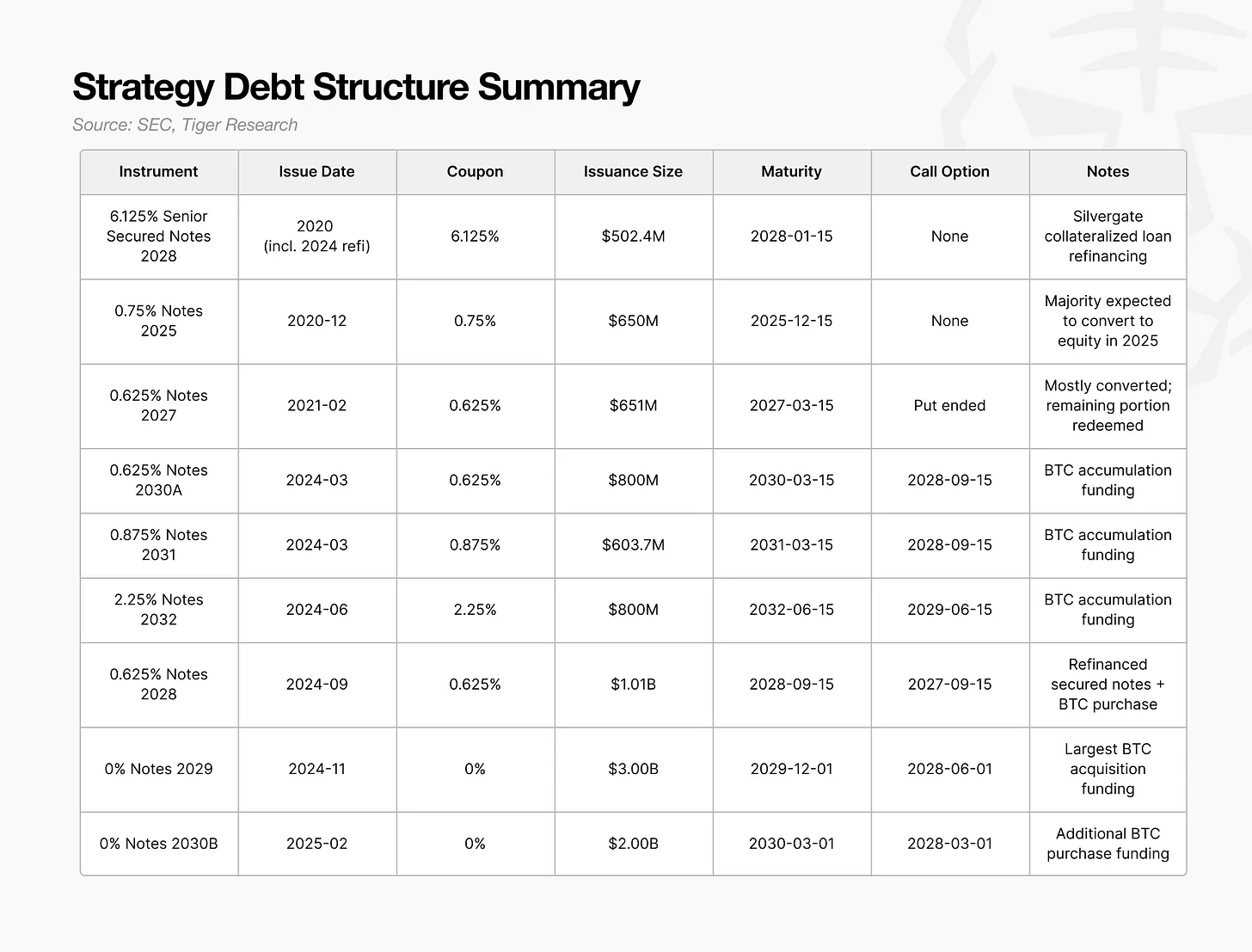
As mentioned earlier, Strategy's static bankruptcy threshold has risen to $23,000 because its debt is growing faster than its Bitcoin holdings. The next question is, how was this debt structured?
Between 2024 and 2025, Strategy adopted a new financing model that combined convertible bonds, preferred stock, and ATM stock programs. Among these instruments, convertible bonds accounted for the largest share and had the most significant impact on the market.
The key is not the size or maturity date of the convertible bonds, but the timing of when the holders exercise their put option.
This clause allows investors to demand early repayment, which the company cannot refuse. Most of the large convertible bonds issued in 2024-2025 have redemption dates concentrated around 2028, making 2028 a crucial year for Strategy to demonstrate its refinancing capabilities.
If Bitcoin prices approach bankruptcy thresholds or market conditions deteriorate in 2028, investors are likely to exercise put options rather than wait for expiration. A wave of put option exercises would require Strategy to raise billions of dollars in cash immediately.
The problem is that almost all the funds raised through these convertible bonds were used to buy Bitcoin. If these funds were invested in productive assets that generate cash flow, the company would naturally have a source of repayment. However, the focus on accumulating Bitcoin has left very little cash available for redemption.
Therefore, repaying the debt will require selling assets. If the price of Bitcoin is low when the options window opens, Strategy could immediately face a liquidity shortage. Forced selling would further depress the price, raise the bankruptcy threshold, and potentially trigger a vicious cycle.
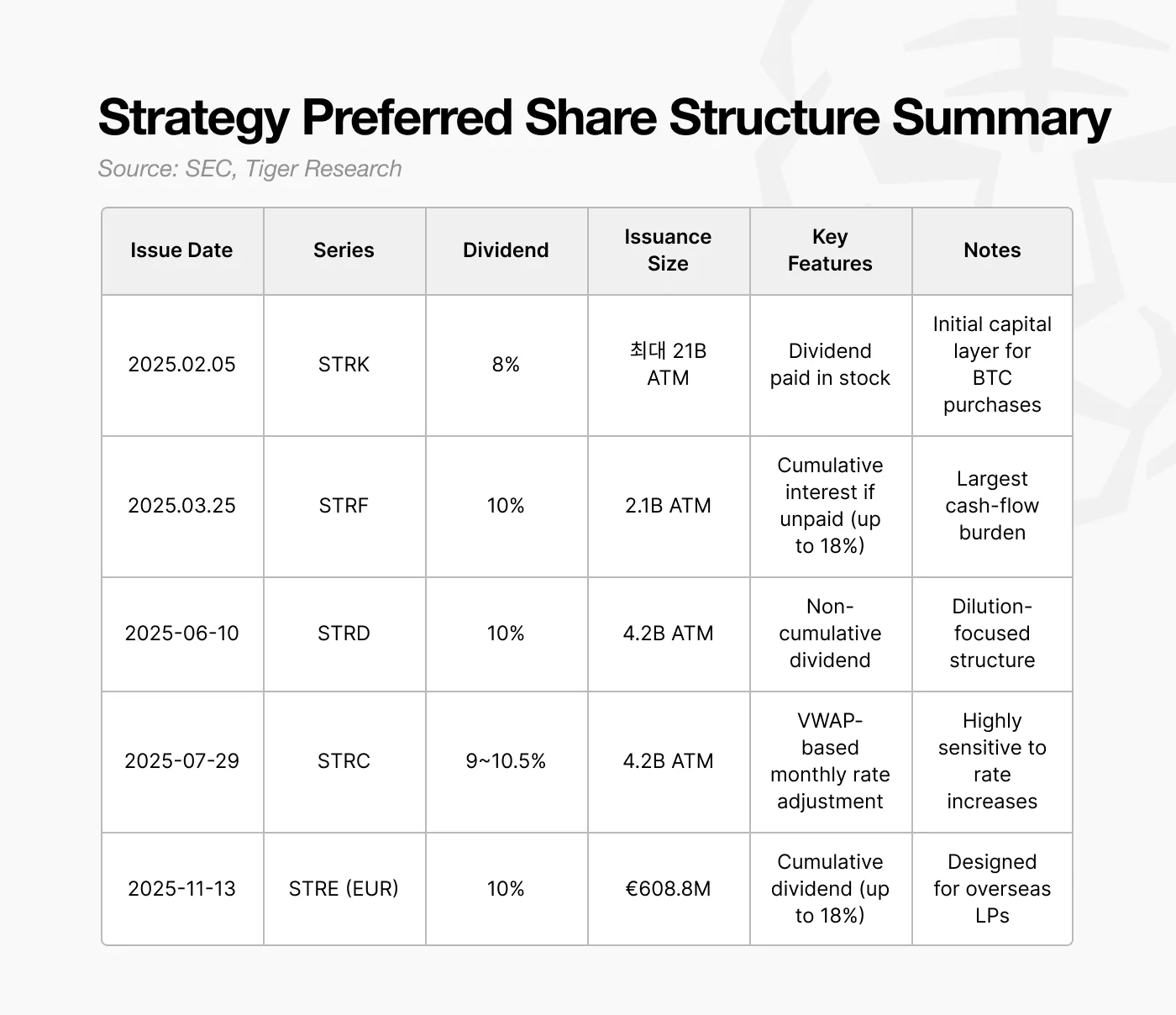
4. Preferred Stock: Why Choose a 10% Dividend Burden?
Starting in 2025, Strategy will shift from issuing near-zero-coupon convertible bonds to issuing preferred stock with a dividend yield of approximately 10%. At first glance, this seems like a more costly option.
However, this decision reflects the increasing refinancing pressures expected in 2027-2028. A large number of bondholders opting to put bonds back in 2028 will significantly increase medium-term repayment risk. Any continued cash outflows during this period will increase the risk of bankruptcy.
A key feature of preferred stock is that dividends do not need to be paid in cash. Strategy's issuance design allows dividends to be paid in stock as needed. This enables the company to raise capital without an immediate cash outflow and fulfill its dividend payment obligations without using cash. In effect, preferred stock helped Strategy avoid selling Bitcoin during the crucial 2027-2028 period.
While a 10% dividend yield may seem high, paying dividends in the form of shares makes it a tool for maintaining liquidity and preventing short-term cash shortages.
However, this structure also presents new challenges. Paying dividends in the form of stock will continuously dilute the equity of common shareholders. Strategy itself already faces potential equity dilution from future conversion of convertible bonds, while preferred stock adds another layer of equity pressure.
Preferred stock also enjoys priority in repayment. If a company faces both debt repayment and operating cost pressures, preferred stockholders must be repaid before common stockholders. Although preferred stock does not have a fixed maturity date, its dividend obligation constitutes a structural fixed cost and affects the company's effective bankruptcy threshold.
By 2024-2025, Strategy had shifted from a model based on low-cost convertible bonds to a hybrid structure combining convertible bonds, preferred stock, and ATM issuance. This shift enabled a rapid expansion of Bitcoin holdings in the short term.
5. What happens if the strategy fails?
If Strategy is unable to refinance in 2028, its impact on the market can be estimated through its repayment obligations.
The large number of convertible bonds issued in 2024-2025 will generate approximately $6.4 billion in potential repayments by 2028. If market conditions deteriorate and preferred stock issuance, ATM issuance, and new convertible bonds cannot proceed, the company will have no choice but to sell Bitcoin.
Assuming a Bitcoin price of $90,000, Strategy would need to sell approximately 71,000 Bitcoins to fulfill these obligations. This is not comparable to the scale of a typical institutional sale.
The current daily trading volume in the spot market is between $20 billion and $30 billion. Selling 71,000 Bitcoins at $90,000 each, equivalent to approximately $6.4 billion, represents about 20% to 30% of the daily trading volume. Such a large-scale sell-off in a short period of time will almost certainly put downward pressure on market prices.
More worryingly, this sell-off is not a one-off event. As the price of Bitcoin falls, the value of Strategy's assets shrinks immediately, weakening its financial ratio. This will further limit its ability to raise funds and may force it to sell more Bitcoin.
This creates a vicious cycle: failed refinancing leads to forced selling, forced selling causes prices to fall, falling prices reduce asset value, and the company is forced to sell even more assets. If this dynamic continues for several quarters, it could deteriorate the balance sheet to an irrecoverable state.
Therefore, Strategy's structural risks are concentrated in 2028. Outside this window, the leverage model appears manageable, but failure to refinance in 2028 could trigger selling pressure sufficient to impact the entire Bitcoin market.
Therefore, 2028 is not only crucial for Strategy's survival, but also for the potential volatility of the entire Bitcoin ecosystem.
6. The strategy is relatively stable, but latecomers face higher risks.
Market narratives often reduce DAT risk to a simple question: can a company survive every Bitcoin dip? However, this analysis suggests that the key to a company's survival is not short-term price fluctuations or stock volatility, but rather its balance sheet and capital structure design.
Therefore, evaluating DAT requires more than just focusing on its stock price or the decline in Bitcoin prices. Key indicators include its static bankruptcy threshold, the duration of cash repayment pressure, and the tools it uses to cover funding gaps. These factors help us understand its structural resilience, rather than short-term volatility.
Not all risks are predictable. ETF fund flows, macroeconomic conditions, and changes in regulatory policies can all reshape the market environment at any time. Even so, the most reliable benchmarks remain the bankruptcy thresholds implied by financial data and the company's fundamental cash flow mechanisms.
Strategy stands out in this regard. The company entered the Bitcoin market in 2020, weathered the downturn of 2022, and accelerated its accumulation through leveraged financing in 2024. Its combination of convertible bonds and preferred stock created a multi-layered buffer.
Therefore, Strategies have a relatively stable foundation. New entrants, on the other hand, have not yet established a mature DAT framework, and their ability to withstand significant price declines is far less stable.