Source: The Block
Original title: 2026 DeFi Outlook
Compiled and edited by: BitpushNews

2025 propelled DeFi into a more mature phase, characterized by clear credit cycles, increasing institutional inflows, and increasingly robust trading venues. On-chain credit expansion resumed in the second half of the year as risk appetite returned; while the rise of RWA (Real-World Asset) tokenization indicates that institutions now view blockchain infrastructure as a viable distribution channel.
Trading dynamics have also shifted. Perpetual contractDEXs saw record-high average daily trading volumes (ATH), while spot DEX activity was relatively subdued and primarily driven by inter-chain rotation rather than net growth. Prediction markets remained active post-election and attracted significant investment.
In conclusion, 2025 showed that DeFi is moving towards a more sustainable state of equilibrium, with mature primitives and expanding institutional alliances laying the foundation for broad growth in the future.
On-chain lending continues to expand
The DeFi lending engine continued to expand in 2025, albeit on an uneven trajectory. Total outstanding loans across major lending protocols grew by 37.2% throughout the year, lagging behind the 48.1% growth rate of stablecoin market capitalization.
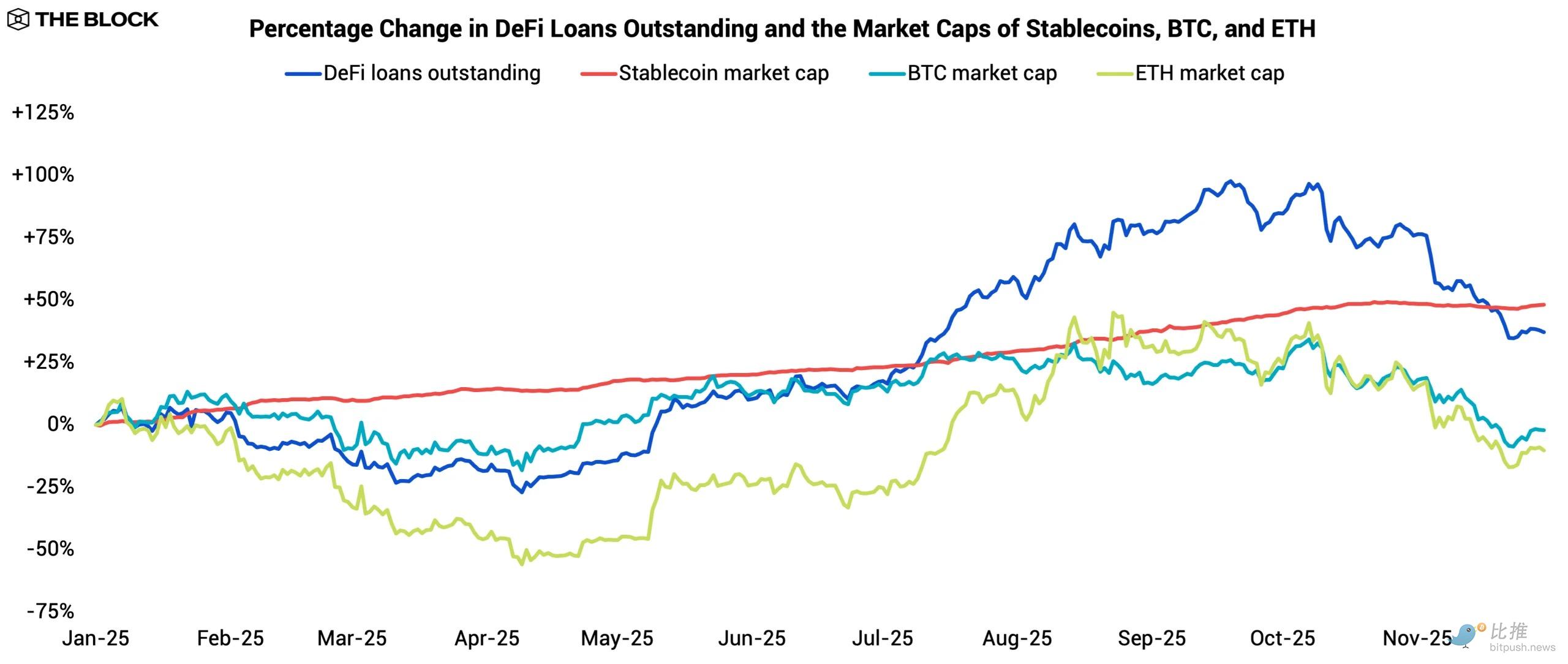
Credit contracted in the first half of the year as borrowers remained cautious; however, this trend reversed in the second half, with borrowing activity accelerating and credit growth catching up with liquidity inflows. The full-year overview reflects a market shift from risk aversion to re-engagement: leverage was rebuilt as digital asset valuations rose, followed by a significant deleveraging process as valuations softened in the fourth quarter.
Aave solidified its position as the dominant lending venue, with its share of total debt rising from 52.0% to 56.5%. This trend reflects Aave's ability to retain and attract lending activity as liquidity returns to the system. Its core strength on Ethereum remains anchored in deep liquidity, while its multi-chain strategy continues to play a role. The integrations with Plasma and Linea in Q3 contributed significantly to activity, bringing in $1.8 billion and $190 million in borrowed liquidity, respectively.
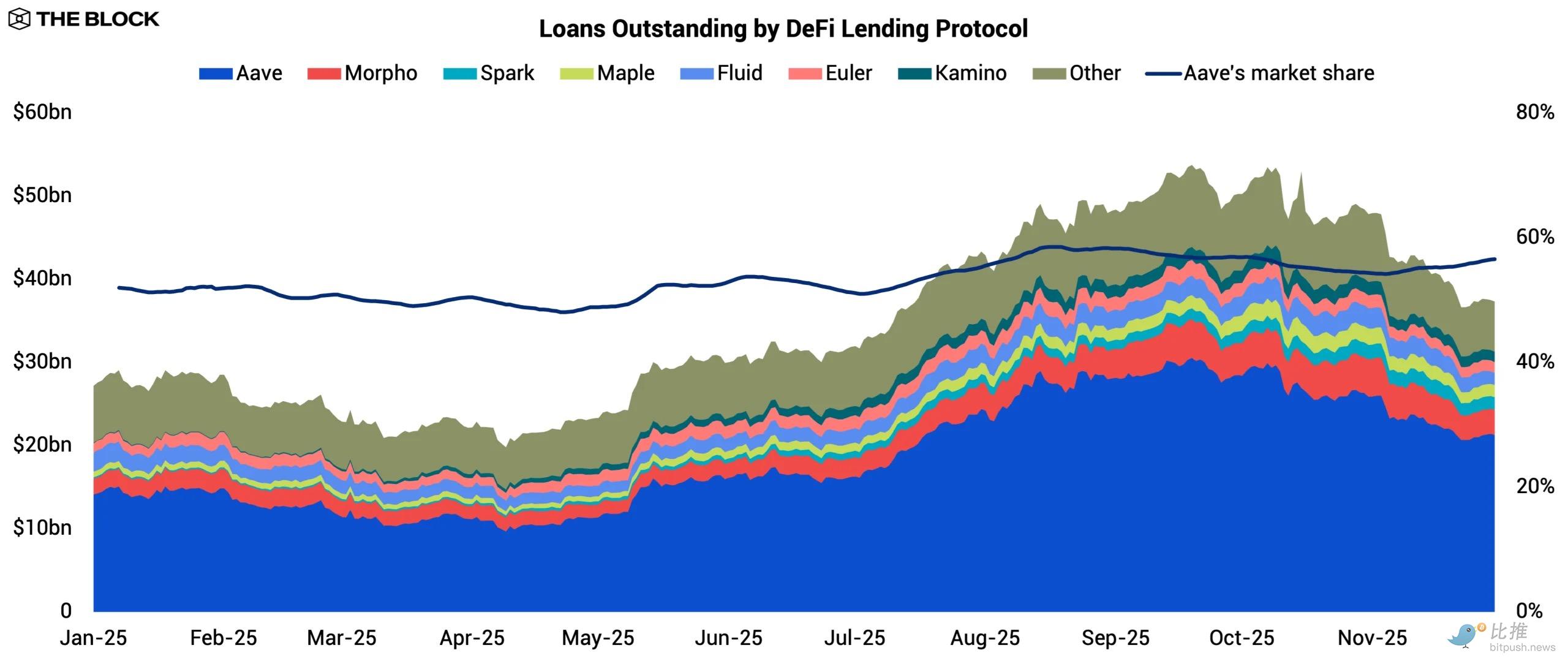
Aave is also expanding its distribution in several areas. Its RWA-focused money market, Horizon , boasts over $176 million in outstanding loans, marking its formal entry into the tokenized private lending space. Meanwhile, the upcoming mobile app for retail users signals its efforts to solidify its presence in the retail market.
Meanwhile, challengers have also made progress. Morpho surpassed Spark , growing its outstanding loans from $1.9 billion to $3 billion, establishing itself as the second-largest lending protocol. Its strategy is to expand into markets where Aave's services are slower. Morpho currently supports 29 chains, compared to Aave's 19. On the Base chain, it has become the largest lending market, with $1 billion borrowed, ahead of Aave's $539 million.
A major catalyst was Coinbase's integration of Morpho into the underlying infrastructure of its crypto-secured lending products. This distribution channel significantly accelerated Morpho's growth. Subsequently, Morpho V2 expanded to include fixed-rate lending with fixed terms, giving the protocol a differentiated product line rather than relying solely on broad coverage.
Maple has been this year's dark horse. Its outstanding loans grew eightfold, from $181 million to $1.5 billion. Maple has a strong presence in the private lending market, with its syrupUSD pool experiencing robust demand. Users can deposit stablecoins permissionlessly and earn yield tokens backed by a portfolio of short-term, overcollateralized loans to businesses and lenders.
SyrupUSD integrated with major DeFi protocols including Spark, Morpho, Fluid, and Pendle during 2025. Spark also allocated $610 million to syrupUSD pools, a major driver of its expansion. By packaging institutional private lending into an accessible and liquid token, Maple expanded the addressable market (TAM) for on-chain lending and captured a segment that other major lending protocols failed to serve effectively.
Across the industry, established lending protocols have solidified their positions, while new competitors have carved out new territories. Aave is expanding on multiple fronts, Morpho has gained a strong distribution channel, and Maple is bringing private lending on-chain by improving accessibility.
The result is a more competitive and diversified lending landscape. Looking ahead, continued growth will require entry into new borrower segments and stronger distribution channels, but ultimately depends on rising valuations of digital assets to provide a collateral base for further credit expansion.
Open Market RWA Crosses the Adoption Barrier
2025 marked a breakout year for RWA tokenization. After stagnating during the liquidity crunch following 2022, the RWA market regained momentum. The value of tokenized RWA in the public market grew from $5.6 billion to $16.7 billion, marking the strongest expansion in the industry's history. This growth was not limited to a single asset class; significant inflows were seen in U.S. Treasuries, commodities, and institutional funds, driven by various demand catalysts.
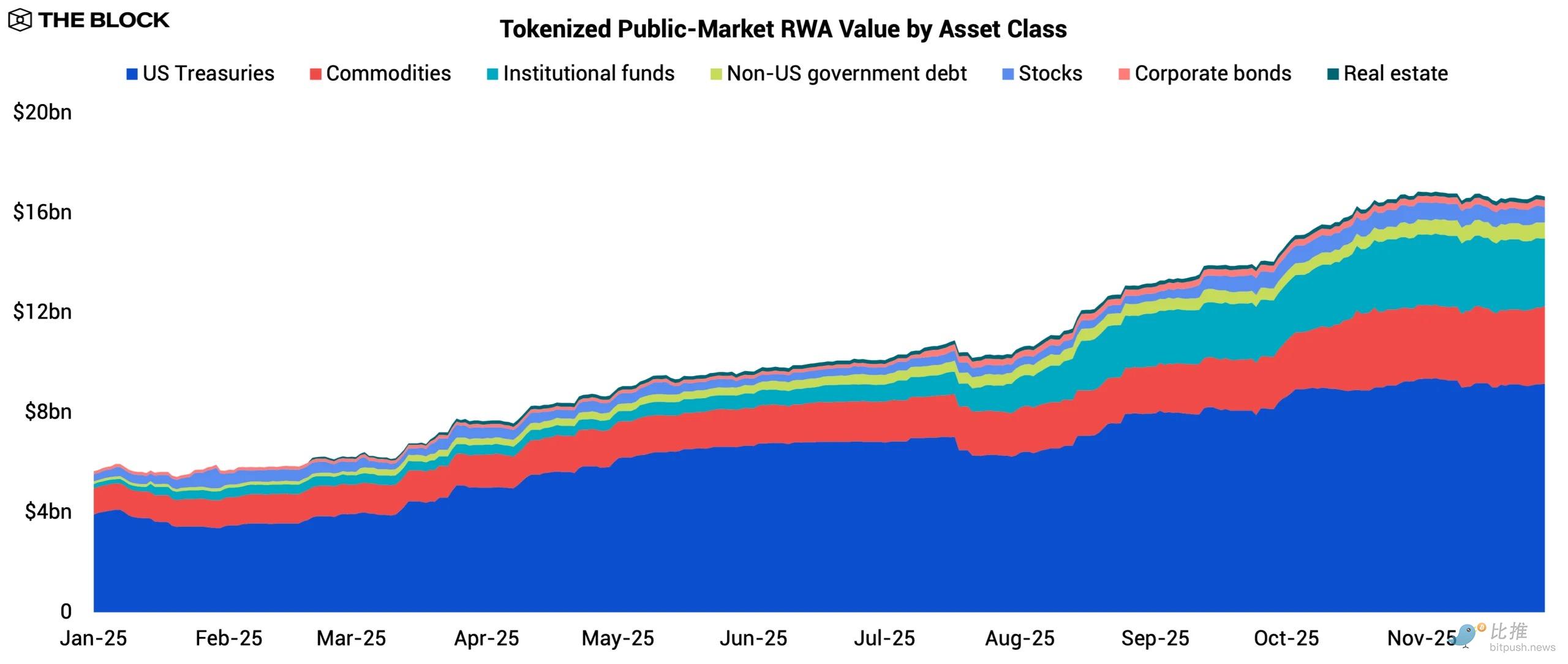
Tokenized U.S. Treasuries remain the largest category of RWA, with tokenized value rising from $3.9 billion to $9.2 billion. A standout product is BUIDL , issued by BlackRock through Securitize , with assets under management (AUM) reaching $2.3 billion. BlackRock's presence provides a credibility anchor for institutions previously hesitant to adopt tokenized fixed-income products.
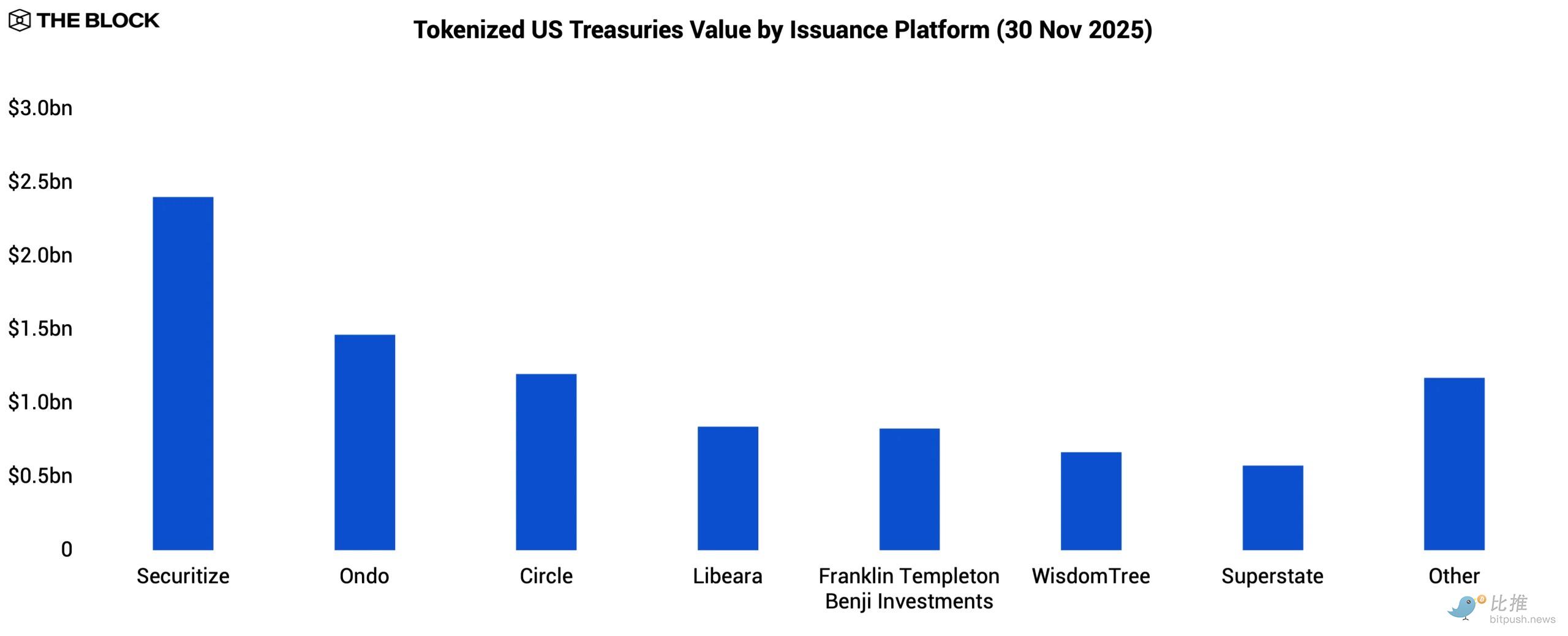
More and more on-chain products are now built directly on top of BUIDL. Ethena's USDtb and Ondo's OUSG both utilize BUIDL as their core reserve asset, effectively making it the back-end collateral layer for the ever-expanding range of tokenized cash and government bond products.
Tokenized goods remain the second largest category, with their tokenized value nearly tripling from $1.1 billion to $3.1 billion. This expansion was primarily driven by tokenized gold products such as Tether's XAUT and Paxos' PAXG. Gold's year-to-date performance of +60.7% and its record highs attracted retail speculators seeking alternative risk exposure, allowing them to navigate the changing macroeconomic environment without leaving the DeFi ecosystem.
Tokenized institutional funds are a clear rising star this year. Their tokenized value has surged from $170 million to $2.7 billion as crypto-native investors begin diversifying their investments beyond digital assets. Anemoy's JAAA leads the segment with $1 billion in AUM, its seed funding provided by Grove, an institutional-grade credit infrastructure protocol within the Sky ecosystem. JAAA offers on-chain participation in AAA-rated CLOs, designed for capital preservation and stable returns.
Other notable tokenization funds include Superstate 's USCC (offering crypto futures-cash arbitrage strategies with a total AUM of $440 million) and Blockchain Capital 's digital venture fund BCAP (with AUM reaching $359 million). These products demonstrate that RWA tokenization can support actively managed strategies, not just passive fixed-income exposures.
Some smaller categories have also gained attention, but remain niche, including non-U.S. sovereign debt, publicly traded equities, corporate bonds, and real estate. Limited liquidity and operational constraints may keep these areas small, although early experiments suggest that issuers are testing a wider range of asset classes as infrastructure matures.
The defining theme for 2025 is that tokenization has finally become a distribution technology that institutions are willing to use at scale. Public blockchains have proven to be increasingly efficient venues for issuance, settlement, and investor access, while interoperability with major DeFi protocols has enhanced the utility of tokenized RWA beyond simple holding.
Looking ahead, institutional participation is likely to deepen as the product spectrum expands. Further integration with lending markets and on-chain finance systems will increase RWA's usability and appeal, making tokenization a core pillar of the digital capital markets.
Perpetual Contract DEX Breaks Record
2025 was a landmark year for on-chain derivatives. The ratio of perpetual contract trading volume between DEXs and CEXs (centralized exchanges) more than tripled from 6.3% to 18.7%, marking a significant shift in a market long dominated by centralized venues. This trend reflects a narrowing efficiency gap, as the execution speed, liquidity depth, and overall user experience of perpetual contract DEXs have improved to accommodate more sophisticated traders. October recorded the highest on-chain derivatives trading volume to date, driven by the market crash on October 10th.
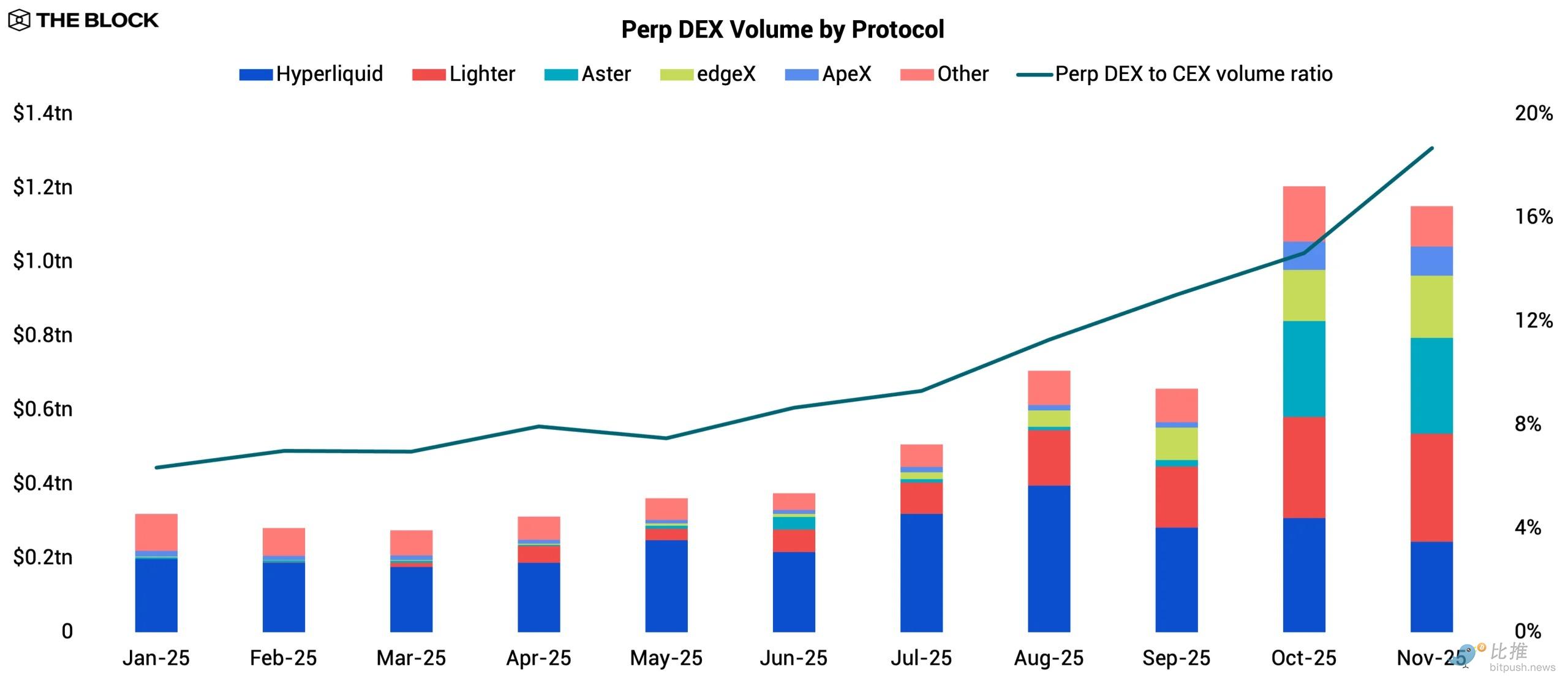
Hyperliquid was the undisputed leader among perpetual contract DEXs at the beginning of the year. Its annualized trading volume grew from $564.7 billion in 2024 to $3 trillion in 2025. In terms of revenue captured by the protocol (excluding supply-side revenue paid to liquidity providers), it has consistently been one of the most profitable protocols in DeFi. Its moat is built on speed, deep organic liquidity, and a sticky user base. However, by mid-year, Hyperliquid's dominance began to face real pressure from a new wave of well-funded challengers.
Lighter emerged as the most aggressive new entrant in the second half of the year. Its "zero-fee" model attracted crypto-native traders, while its multi-stage points system, directly linked to future airdrop prices, drew a large number of incentive hunters. Lighter completed a funding round at the end of its explosive year, which included a rare strategic participation from Robinhood, signaling a potential future integration or alliance between centralized trading applications and on-chain derivatives infrastructure.
Aster also garnered attention in the fourth quarter, primarily driven by its association with Binance. Backed by YZi Labs (formerly Binance Labs) and closely integrated with the BNB Chain ecosystem, Aster benefits from distribution channels accessible to very few protocols. It also narrowly cuts Hyperliquid's transaction fees, positioning itself as a low-cost alternative. Its multi-stage points system, modeled after Lighter, helps accelerate user acquisition. This combination of distribution, cost advantages, and incentives makes Aster one of the protocols capable of challenging Hyperliquid's leading position.
Across the board, the competitive landscape is intensifying. Hyperliquid remains the established player, but the influx of capital and incentives suggests its leading position is not a permanent fixture. This dynamic is similar to previous cycles, most notably the rise and fall of dYdX—early dominance does not always translate into permanent market share.
Looking ahead, the arms race is likely to continue. Well-funded challengers will continue to erode Hyperliquid's position using low-fee structures, points systems, and strategic partnerships. However, this competition is also improving the overall user experience and continuing to narrow the gap with centralized competitors.
Prediction Market
Following the US presidential election in November 2024, prediction markets experienced a slowdown, with trading volumes declining in the following months. Even so, the election cycle demonstrated the potential of prediction markets to a wider audience, and despite lower overall trading volumes, monthly active traders on Polymarket actually increased after the election as users remained to participate in newly listed event markets.
Trading activity rebounded in September 2025 with the emergence of new catalysts. This shift was driven by Kalshi 's partnership with Robinhood, which opened up a massive retail distribution channel; in addition, the start of major sporting seasons also drove traffic to Kalshi's sports marketplace.
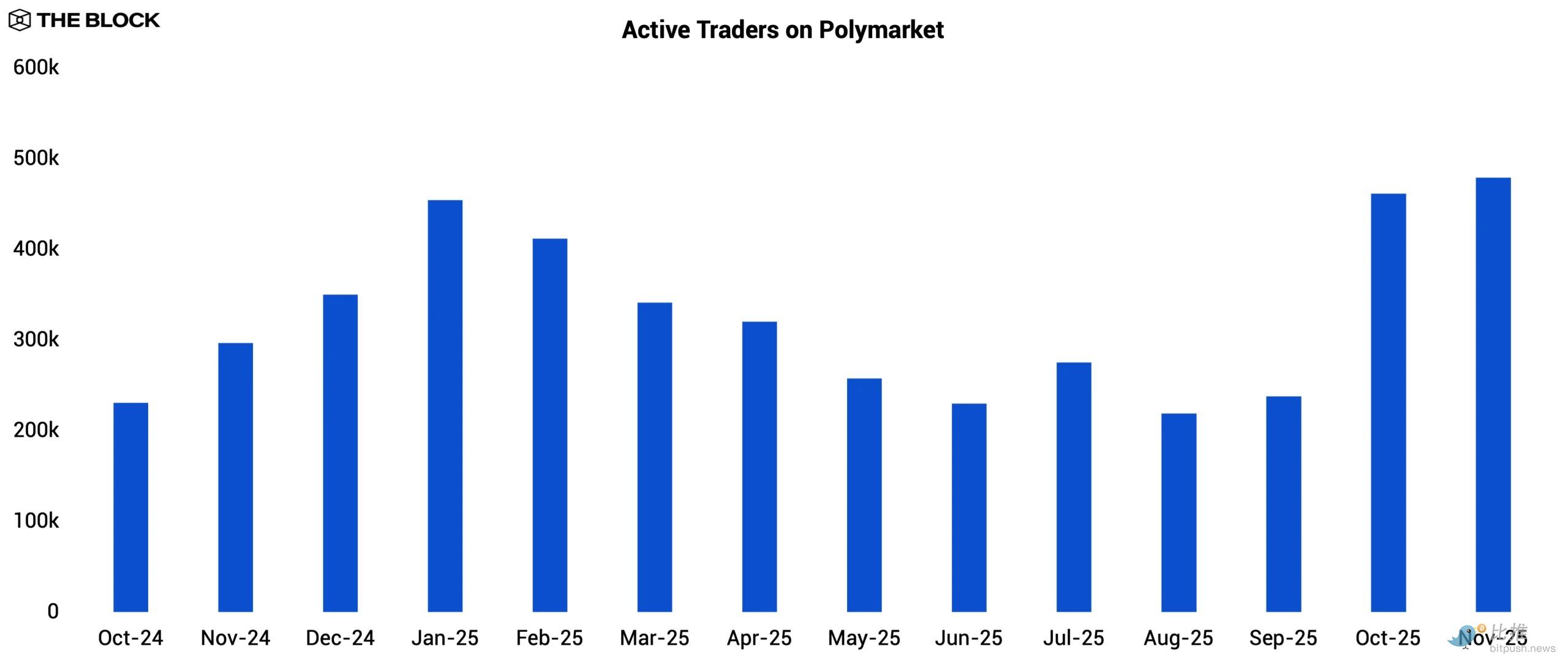
This competitive pressure appears to have prompted Polymarket to accelerate the creation of new marketplaces starting in September in order to retain user engagement. Both platforms subsequently set records in November: Kalshi processed $5.8 billion, while Polymarket reached $1.9 billion.
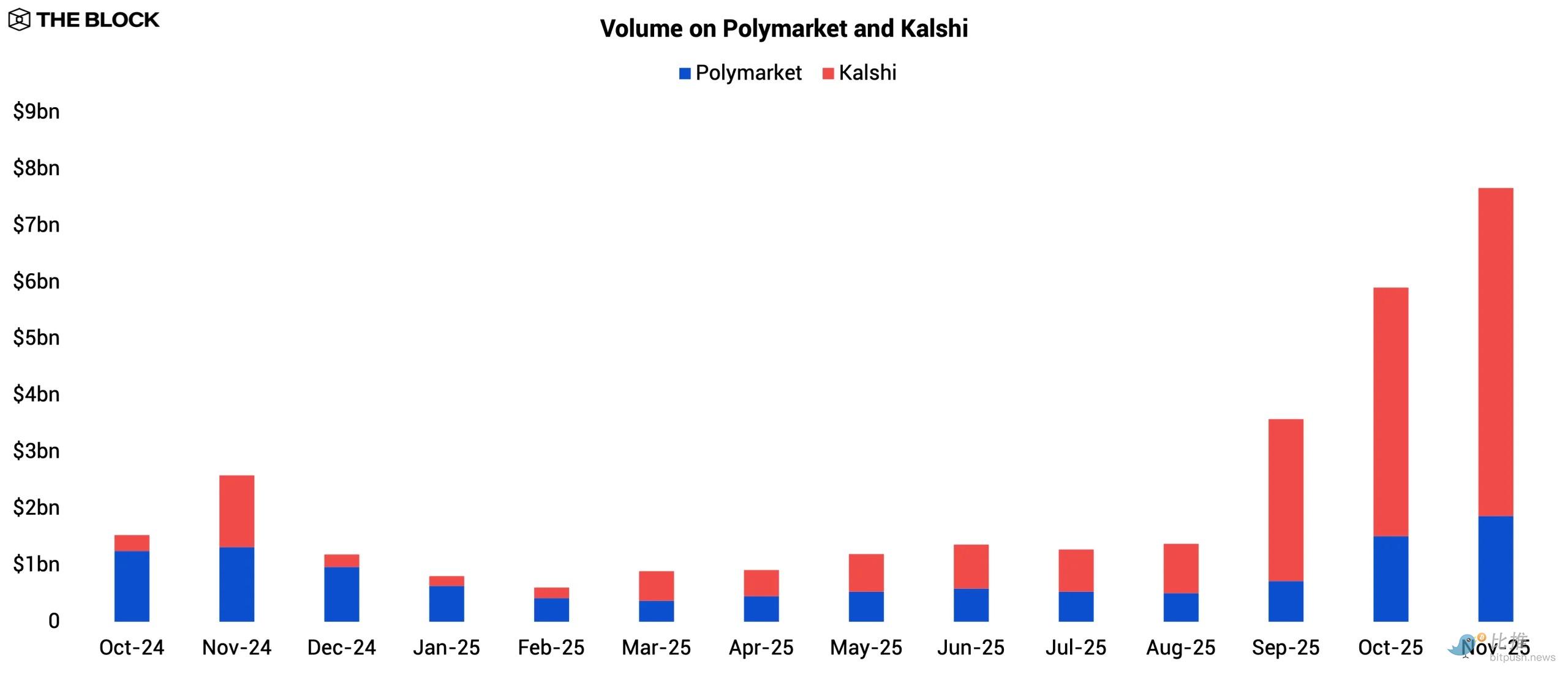
Kalshi operates as a centralized platform regulated by the CFTC, while Polymarket is entirely on-chain. In 2025, Polymarket acquired a CFTC-licensed derivatives exchange and clearinghouse for $112 million, enabling it to re-enter the US market after receiving CFTC approval in November.
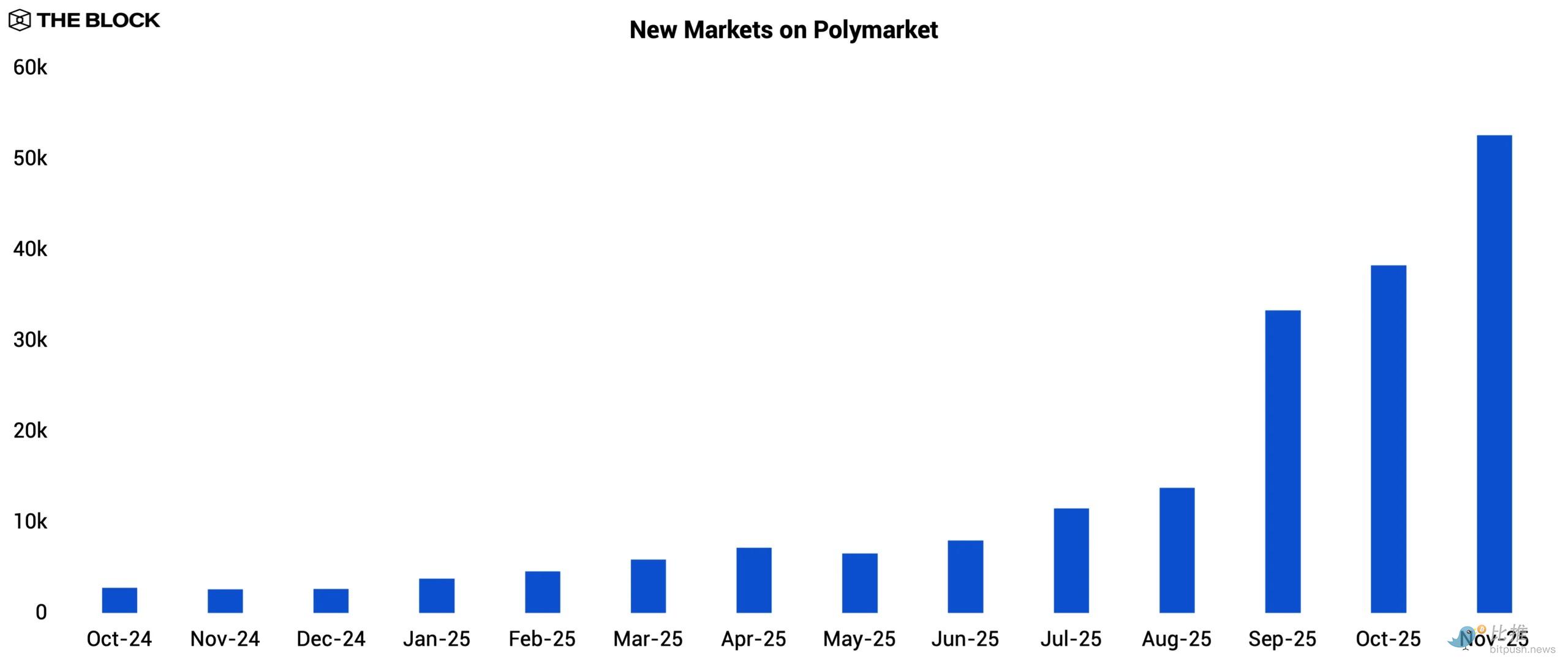
Both platforms secured substantial investments in 2025, highlighting institutional confidence in "event contracts" as an emerging category of derivatives. Polymarket raised $2 billion from Intercontinental Exchange (the parent company of the NYSE) in October, valuing the company at $9 billion. Meanwhile, Kalshi raised over $1 billion in multiple funding rounds this year, with its latest valuation at $11 billion. The size and background of these investors mark a turning point in the industry's legitimacy.
Looking ahead, these two well-funded giants are poised for a head-to-head showdown during the 2026 US midterm election cycle, a period typically marked by surging trading volumes. With strengthened balance sheets, resolved regulatory hurdles, wider distribution, and increasing product depth, the upcoming election cycle is likely to generate the largest prediction market activity to date.
Spot trading activity shifted as the launch pad hype died down.
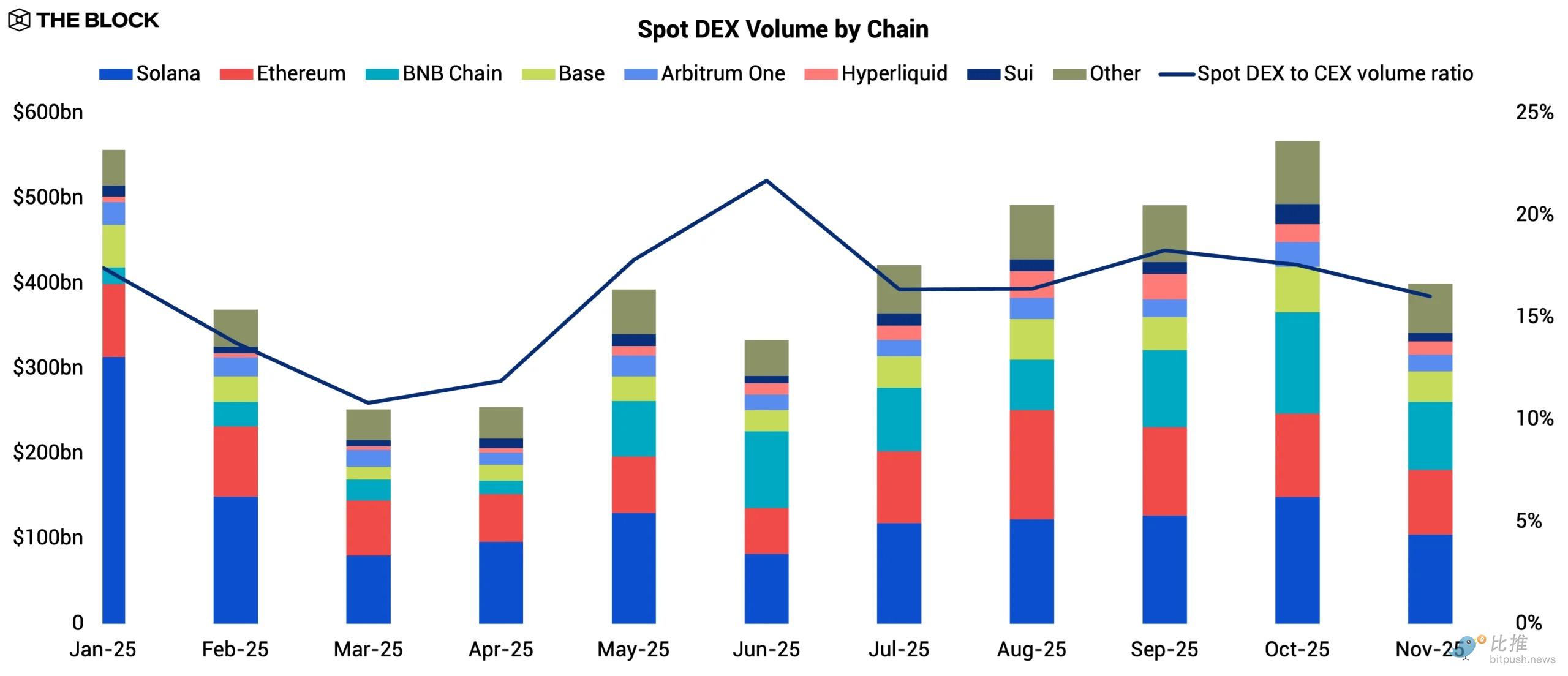
Spot DEX activity in 2025 lacked a clear upward trajectory. Trading volume fluctuated throughout the year but ultimately failed to significantly outperform overall market growth. The most striking change came from chain-level rotation: Solana's monthly spot trading volume plummeted from $313 billion in January to $104 billion in November, a 66.7% drop that marked the end of last year's retail-driven memecoin craze.
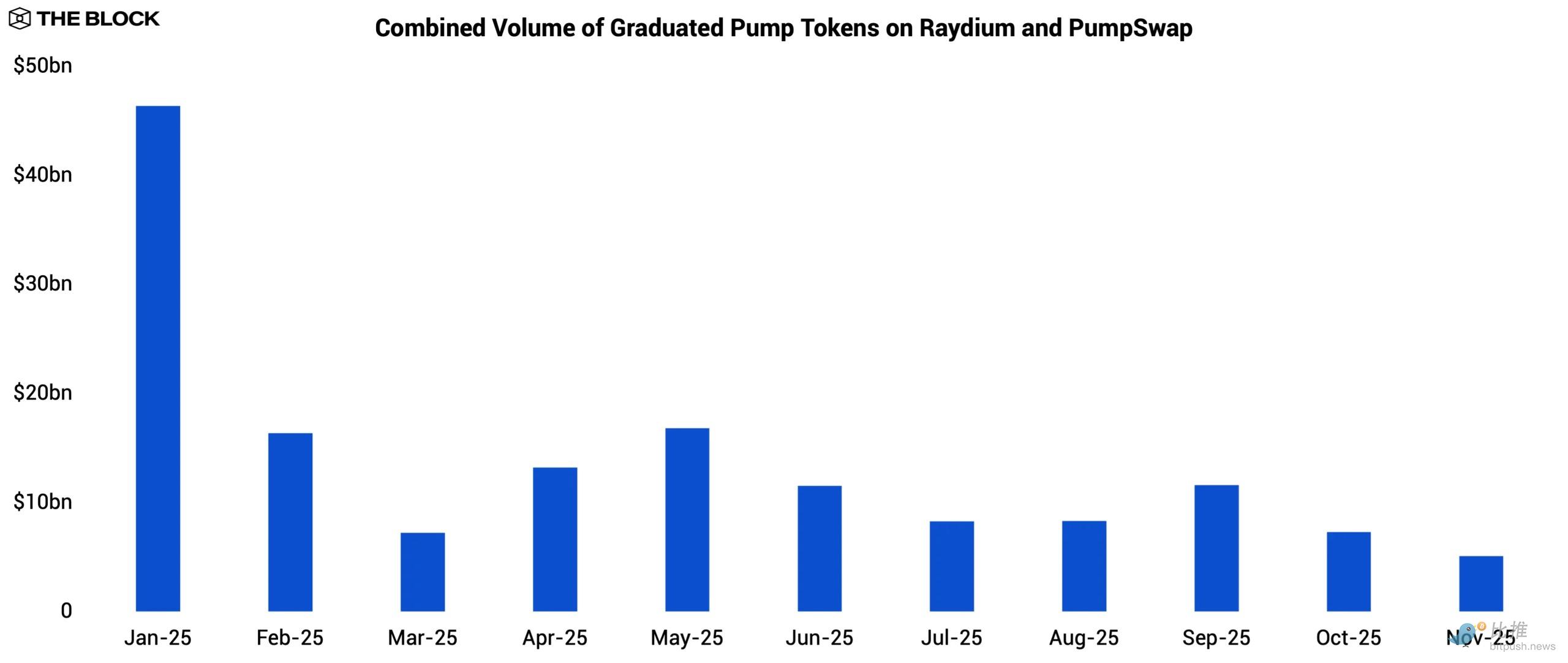
As the token launchpad that dominated Solana in 2024, Pump.fun's "graduating" token trading volume on Raydium and PumpSwap plummeted from $46.4 billion in January to $5.1 billion in November, a drop of 89.0%. The collapse in retail investor enthusiasm for launchpad-incubated tokens meant that the "frequent turnover" cycle that fueled Solana's spot DEX activity in 2024 failed to replicate on a similar scale in 2025.
Meanwhile, BNB Chain moved in the opposite direction, with its monthly spot trading volume more than quadrupling from $19.3 billion in January to $80.3 billion in November. As retail liquidity evaporated on Solana, speculative capital didn't disappear; instead, it migrated to BNB Chain. BNB Chain absorbed a significant portion of retail speculation, and its long-standing microcap trading culture demonstrated resilience during the Solana meme's cooling down.
Across the ecosystem, the ratio of spot trading volume between DEXs and CEXs remained below 20% throughout the year, highlighting that the structural efficiency gap in spot trading has remained largely unchanged, indicating that spot DEXs have matured in terms of infrastructure. The general interest in on-chain spot trading in 2025 has not disappeared, but rather undergone a reshuffling. Unless a new catalyst emerges to drive sustained token turnover, the trajectory of spot DEX activity will depend on changes in retail sentiment shaped by broader macroeconomic conditions.
Composability amplifies systemic risk
Composability has always been one of the defining advantages of DeFi. Protocols can integrate with each other without permission, assets can be repeatedly staked in different venues, and new financial products can be built by stacking existing primitives like modular components. It improves capital efficiency, enables rapid innovation, and creates powerful network effects.
However, it also creates tight coupling between systems. When an asset or assumption within a single protocol fails, the impact can ripple through the entire ecosystem. The Stream Finance incident in November 2025 serves as the clearest example of how this advantage can evolve into a medium for systemic risk.
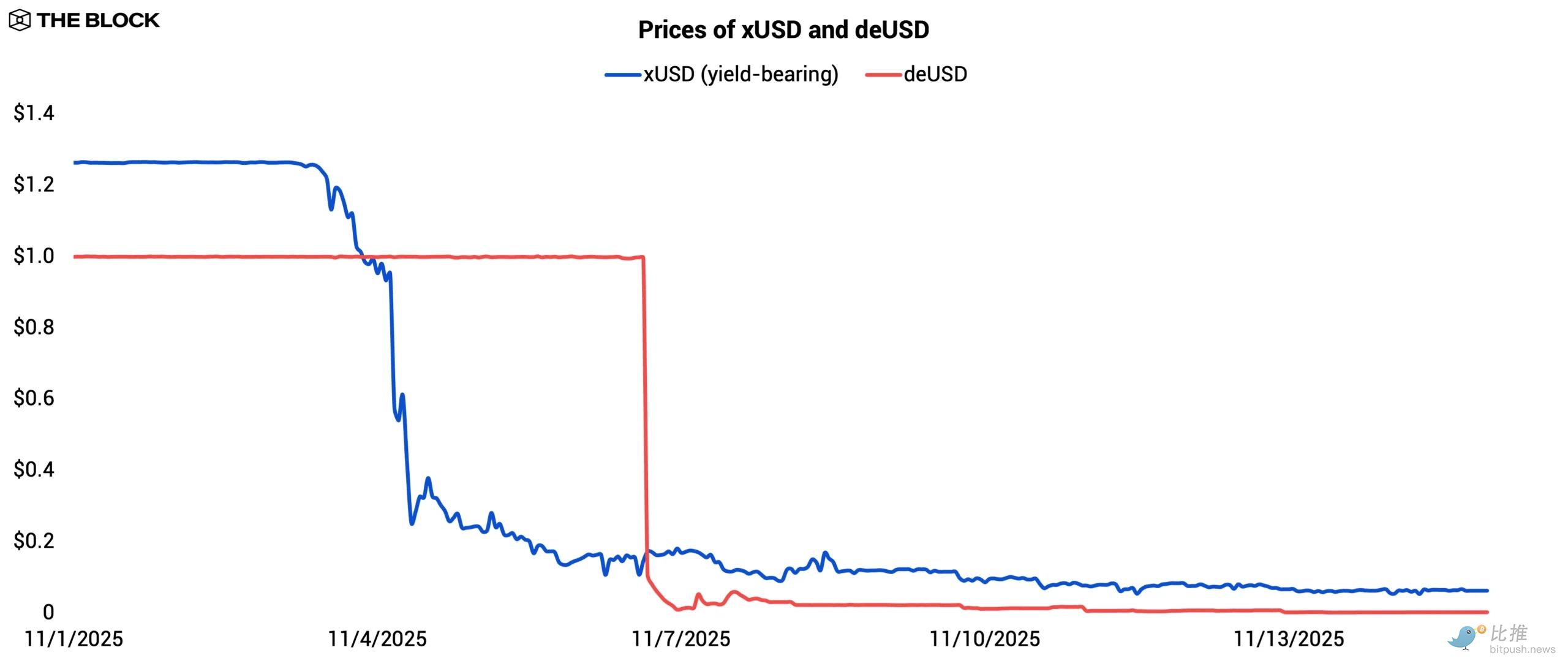
Stream allowed users to deposit assets in exchange for xUSD, a yield-generating stablecoin that claimed to be backed by a market-neutral strategy run by external fund managers. This assumption collapsed when one of the designated fund managers disclosed a $93 million loss while executing a strategy allegedly with minimal directional exposure, leading to severe undercollateralization of xUSD. Stream immediately halted deposits and redemptions, and as confidence evaporated and liquidity fled the secondary market, xUSD began to de-peg.
The de-anchoring quickly exposed the fragility of composability. Elixir's stablecoin deUSD was partially backed by exposure denominated in xUSD, while xUSD itself held deUSD in its collateral portfolio, creating a circular collateral loop. Once xUSD fell below parity, this loop became unsustainable.
Shortly after xUSD de-pegged, Elixir froze the minting and redemption of deUSD, and as the market repriced the interconnected exposure, deUSD also de-pegged. What began as an isolated failure by an external fund manager escalated into a multi-protocol cascade collapse simply because the two stablecoins were tightly linked through a composable collateral framework.
The contagion also spread to lending protocols. Several money markets on Morpho and Euler had hard-coded a $1 collateral value for xUSD. This design was originally intended to prevent accidental liquidations due to temporary market volatility, but once the de-anchoring became persistent, it backfired. Borrowers were able to borrow with xUSD at full face value, trading at prices far below par, creating bad debts and negative points that the protocols were forced to absorb.
Composability itself isn't problematic, but it requires risk controls that assume "any component could fail at any time." Looking ahead, DeFi protocols must account for cross-protocol exposure and design frameworks capable of handling "black swan" events. Composability remains one of DeFi's greatest strengths, but without stronger safeguards, its efficiency in amplifying systemic risk will be just as high as its efficiency in accelerating innovation.
Outlook
The progress made in 2025 has ushered in a stable expansion phase for DeFi. Institutional investment in RWA, derivatives, and prediction markets reflects growing confidence in on-chain infrastructure. These systems are approaching their centralized counterparts in terms of execution and reliability, and the competitive focus is shifting towards distribution and regulatory positioning, rather than just technology.
Even so, macroeconomic conditions remain the primary driver of expansion. Credit creation, market depth, and retail participation will depend on the broader liquidity environment. If global liquidity shifts towards a more supportive stance, the mature infrastructure of DeFi could translate into more sustainable growth. Nevertheless, continued expansion will require stronger risk management to mitigate the systemic vulnerabilities inherent in the composable ecosystem.
Twitter: https://twitter.com/BitpushNewsCN
BitPush Telegram Community Group: https://t.me/BitPushCommunity
Subscribe to Bitpush Telegram: https://t.me/bitpush








