Compiled by: Block unicorn
Credit is the time machine of the economy. It enables businesses to incorporate future cash flows into today's decisions .
I believe this is one of the most underestimated aspects of the financial world.
People rarely notice the role credit plays, but it truly impacts how businesses operate. An effective credit system allows businesses to replenish stock before shelves are empty, factories to upgrade equipment before it becomes obsolete, and founders to hire new employees before a human resource redundancy crisis erupts.
The gap between good ideas and actual implementation often stems from limited access to credit. Banks, however, are committed to bridging this gap.
Banks accept deposits from customers through bank accounts and provide credit to those who need loans . They pay lower interest rates to depositors and higher interest rates to borrowers; the difference is their profit . However, bank lending also faces many challenges. One of the most significant challenges is the mismatch between credit supply and demand.
Private lending has filled gaps in areas where bank lending falls short, but a gap still exists. This gap reflects investors' reluctance to lend in the current credit market.
In March 2025, the International Finance Corporation and the World Bank jointly released the report "Financing Gap for SMEs," which estimated that the financing gap in 119 emerging market and developing economies (EMDEs) would be approximately US$5.7 trillion, or about 19% of their total GDP.
Against this backdrop, I think the progress in the on-chain lending space last week was exciting . On-chain lending is not a new thing. We experienced a crazy cycle in 2022, and people are still talking about it for various reasons. But the current cycle feels different.
In this article, I will delve into all the changes happening in the on-chain credit market and tell you why I think it could revolutionize the credit industry.
Let's begin.
Money markets have existed on Ethereum for years. Overcollateralized lending, liquidation bots, yield curves, and the occasional chain liquidation are nothing new. So when the credit-related announcements came out last week, what really interested me was the players involved and how they repackaged credit, rather than the money market itself.
What excites me is that these sporadic collaboration announcements collectively foreshadow a broader trend of convergence. The fragmented DeFi landscape of the summer of 2022 is coalescing into a powerful force. Features such as vault infrastructure, non-custodial encapsulation, professional risk management, and automated yield optimization are being integrated and promoted.
Kraken has launched DeFi Earn, a platform for retail users that allows borrowers to deposit funds into a vault (Veda in this case). The vault then directs the funds to lending protocols such as Aave. Chaos Labs will act as the risk manager, overseeing the entire engine. Kraken promises borrowers an annualized yield (APY) of up to 8%.
What changes do vaults bring? They provide lenders with self-custody and transparency of funds. Unlike traditional credit markets where funds are handed over to fund managers and monthly disclosures are awaited, vaults integrate smart contracts that can mold claims on funds and display fund deployments in real time on the blockchain.
At almost the same time, Bitwise, the world's largest crypto fund manager, launched a non-custodial vault strategy on its on-chain lending platform Morpho.
This is not the first time on-chain lending has gained institutional recognition. In 2025, Coinbase launched its USDC lending service, enabling smart contract wallets to connect and route deposits to the Morpho platform via an on-chain vault. Steakhouse Financial uses this platform for cross-market fund allocation to optimize returns.
This comes at a time when the on-chain lending market is about to experience explosive growth, and the data confirms this.
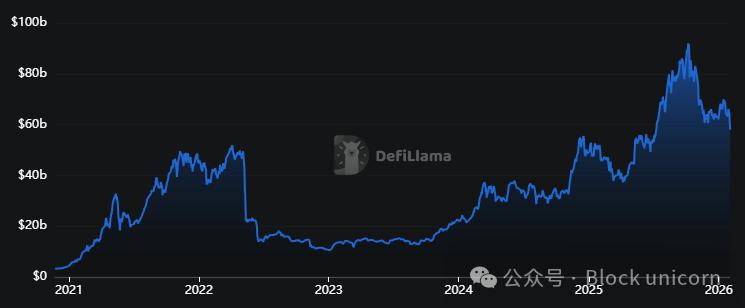
The total value locked (TVL) in lending agreements reached $58 billion, a 150% increase in two years. However, this figure is only 10% higher than the peak in 2022.
Here, the outstanding loan balance dashboard can more accurately reflect the actual situation.
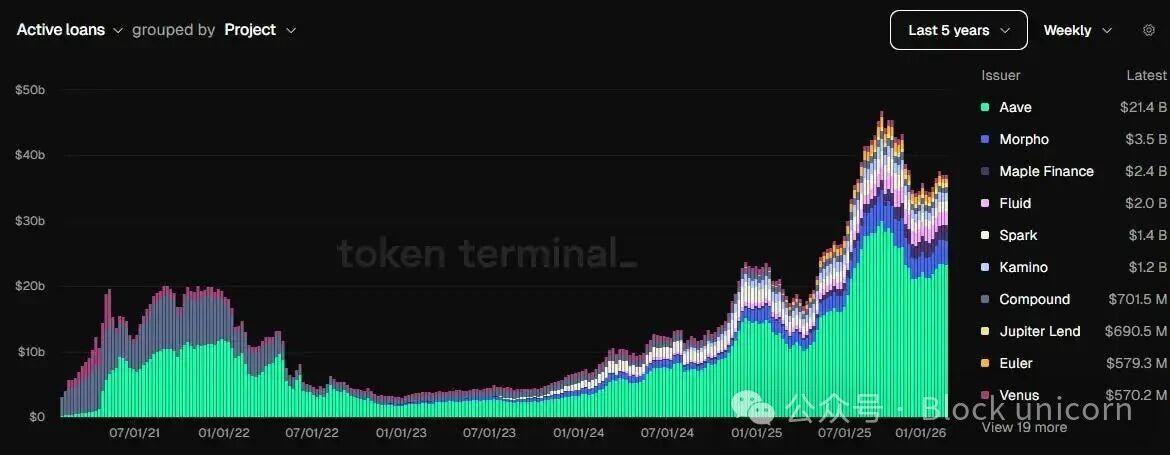
The dashboard shows that the foundation laid by leading protocols such as Aave and Morpho is very solid, with active lending exceeding $40 billion in recent months, more than double the peak in 2022.
The dashboard shows that existing institutions, including Aave and Morpho, have laid a solid foundation, with active lending exceeding $40 billion in the past few months, more than double the peak level in 2022.
Today, both Aave and Morpho earn six times more than they did two years ago.
While these charts demonstrate investor confidence in loan agreements, I believe the growth of gold treasury deposits over time is more compelling.
In October 2025, the total deposits in the vault will surpass the $6 billion mark for the first time. Currently, the deposits have reached $5.7 billion, more than double the amount in the same period last year ($2.34 billion).
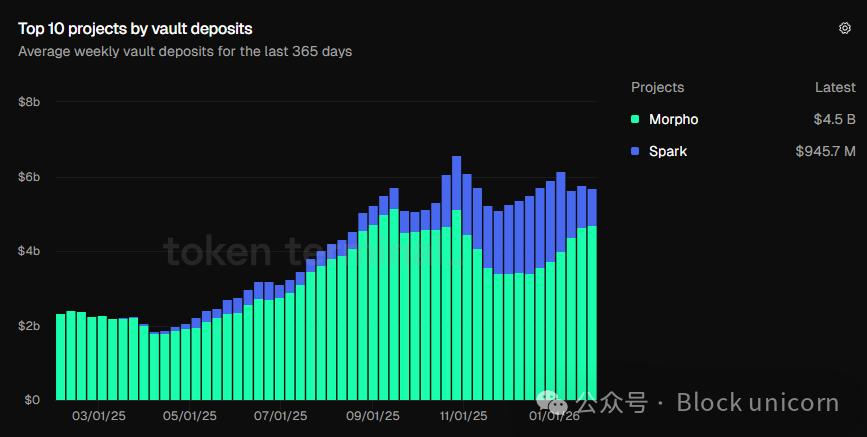
These charts show that users are choosing products that offer a comprehensive ecosystem, including vaults, yield optimization strategies, risk allocation , and professional managers .
This is the evolution I'm optimistic about, completely different from what we observed during the DeFi summer.
At the time, the lending market appeared to be a closed loop . Users exploited this loop by depositing collateral, lending money , using the proceeds to buy more collateral, and then depositing it again to earn higher returns . Even when collateral prices fell, these users could still receive rewards from the platform for using its lending protocols. But when those rewards disappeared, the loop broke.
Even in the current cycle, the underlying element remains the same—over-collateralized lending—but it's built on a significantly different and more robust foundation. Today's vault has evolved into a wrapper for transforming agreements into automated asset management tools . Risk managers play a central role, responsible for setting up safeguards.
This shift has changed the attractiveness of on-chain lending to both investors and lenders.
During the DeFi summer, lending protocols were simply another way to make quick money. This model worked until the incentives wore off. Users registered for an Aave account, deposited funds, and borrowed against collateral, repeating this process until the incentives disappeared. We saw this in Aave's Avalanche deployment: the incentives attracted deposits and initially kept the cycle running. But as the subsidies diminished, the cycle collapsed. As a result, Avalanche's outstanding debt decreased by 73% quarter-over-quarter in Q3 2022.
Today , the lending business has evolved into a complete ecosystem with specialized participants responsible for risk management, return optimization, and liquidity management, respectively.
Here is how I assemble the entire stack.
At the very bottom are settlement funds, which exist in the form of stablecoins. These can be transferred instantly, stored anywhere, deployed at any time, and, crucially, are easy to measure.
Above that are the money markets we are familiar with, such as Aave, where lending is enforced by software code and collateral.
Next comes the world of wrappers and routers, which aggregate funds and route them from lenders to borrowers. Vaults act as wrappers, packaging the entire lending product in a way that is easy for retail investors to understand. For example, it could be presented as "Deposit X dollars to earn up to Y% yield," just like the Veda wallet does on Kraken's Earn platform.
Custodians override these agreements, deciding which collateral is allowed, liquidation thresholds , risk exposure concentration, and when to liquidate positions as collateral value declines. Consider Steakhouse Financial's approach on the Morpho platform, or how asset managers like Bitwise embed their judgment directly into vault rules .
Behind the scenes, AI systems operate 24/7, managing on-chain credit risk and acting as the nervous system of the lending ecosystem when humans are absent. Human risk management is difficult to scale. Limited risk management increases credit risk during market volatility. The best-case scenario is below-standard returns, and the worst-case scenario is liquidation .
The AI-powered optimization engine tracks borrowing demand, oracle bias, and liquidity depth to trigger timely withdrawals . It also issues alerts when vault risk exposure exceeds preset thresholds. Furthermore, it provides recommendations on risk mitigation measures and assists the risk team in decision-making.
It is this round-the-clock optimization, risk mitigation, audited treasury, meticulously planned strategies, institutional endorsement , and professional risk management that makes the current market feel safer and less risky.
However, none of these measures can completely eliminate the risks. Among them, liquidity risk is one of the most easily overlooked risks.
While vaults offer superior liquidity compared to isolated protocols, they still operate within the same market as those protocols. In markets with low trading volume, vaults increase the cost of liquidating funds, making it difficult to exit the market.
In addition, there is the risk of curators having excessive discretion.
When users deposit funds into a vault, they are essentially trusting that certain institutions can make investment decisions based on market conditions, select suitable collateral, and set appropriate redemption thresholds. Credit operations vary widely, but lending institutions should understand that non-custodial lending does not necessarily mean zero risk.
Despite these challenges, on-chain lending is changing the cryptocurrency landscape and, consequently, the economic landscape.
The operating costs of the credit market depend on time and operating costs.
Traditional lending costs heavily due to the significant investments in verifying, monitoring, reporting, settling, and executing transactions. A large portion of the interest they charge borrowers is avoidable and not necessarily related to the "time value of money."
On-chain lending saves time and reduces operating costs.
Stablecoins minimize settlement time, smart contracts reduce execution time, transparent ledgers reduce auditing and reporting time, and vaults simplify user complexity . These cost savings will be even more significant when addressing the credit gap for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs).
On-chain lending won't fill the credit gap overnight, but lower credit costs will make verification easier and credit access more inclusive. This could reshape the economic landscape.
That concludes this analysis. See you in the next article.







