Over the past six months, a concept named DePIN has gradually emerged in the public eye. DePIN, short for Decentralised Physical Infrastructure Networks, was first introduced by Messari at the end of 2022.
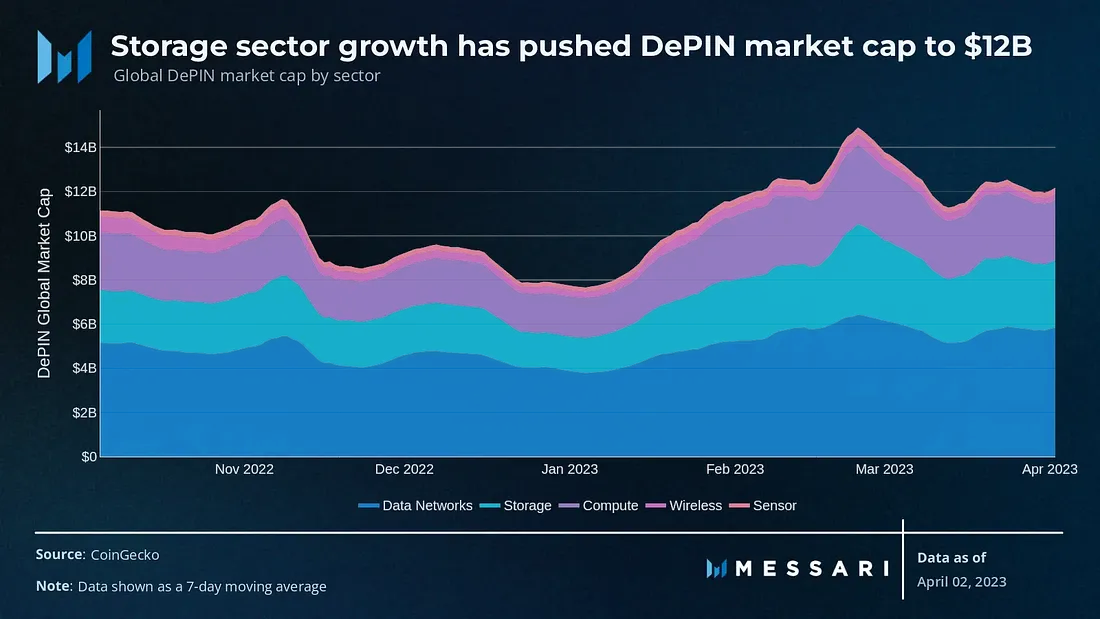
As a nascent concept, DePIN has quickly garnered market attention and demonstrated robust growth momentum. Currently, the total market capitalization of the DePIN protocol has exceeded $12 billion, with a year-to-date (YTD) growth rate reaching 42%.
The rise of the DePIN network represents people's expectations for a more decentralized and efficient future. Individuals hope that blockchain technology will play a crucial role in shaping the foundational aspects of our physical world.
Introduction to DePIN Concept: Incentivizing users to deploy hardware devices and share network resources using digital tokens
DePIN, as an emerging technology, revolves around incentivizing users to deploy hardware devices through token rewards, thereby providing real-world goods and services or digital resources. The DePIN concept can be divided into two main parts: Physical Resource Networks (PRN) and Digital Resource Networks (DRN).
Physical Resource Networks (PRN) encourage participants to use location-based hardware to provide unique goods and services in the real world. These services include, but are not limited to, WIFI, 5G, VPN, energy information sharing, and geographic spatial data. By deploying these facilities, participants contribute tangible value to the surrounding environment while earning token incentives.
Digital Resource Networks (DRN) involve the provision of digital resources through the physical infrastructure network of hardware facilities. These networks include broadband networks, storage networks, and computing power networks, essential components of the digital era.
To operate efficiently, DePIN's structure consists of the following four basic components:1.Physical Infrastructure: DePIN's operation relies on various physical infrastructure, including mobile networks, base stations, wireless network routers, and cloud network servers.
2.Off-Chain Computing Infrastructure: DePIN utilizes off-chain computing infrastructure to connect the real world with blockchain technology. Users' real-world activities are recorded, and fees paid are allocated to hardware providers. This data can be integrated and analyzed for different blockchain applications.
3.Token Incentives: Participants building the DePIN network receive incentives through token rewards, providing motivation until the network generates sustainable income from user demand.
4.End Users: Once the network is established, end users can begin paying fees to access services provided by DePIN.
The Significance of DePIN: Sharing computing and storage resources to achieve cost reduction and efficiency in the network world
DePIN coordinates and optimizes the use of data storage and computing resources through blockchain technology. Its decentralized approach aims not only to enhance security but also to leverage the success of decentralized protocols to expand the physical infrastructure of the real world, significantly reducing costs.
In the DePIN field, three key challenges include improving economic efficiency, lowering market entry barriers, and strengthening governance and security. Firstly, DePIN's economic advantage stems from the ability to utilize globally idle resources, such as underutilized servers, GPUs, and CPUs. The monetization of these resources, combined with the DePIN protocol's ability to aggregate these computing resources globally at a lower cost and offer them to users at a reduced price, means that computing power and bandwidth resources can be more unified and efficiently utilized.
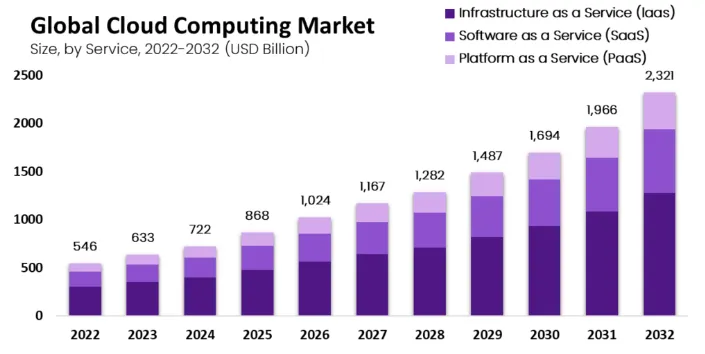
According to Grand View Research data, the global cloud computing market is massive, with an expected compound annual growth rate of 16% from 2023 to 2032, indicating significant market potential. Akash, as an example, demonstrates the possibility of aggregating cloud computing resources through a decentralized network and providing them to developers at a lower cost, approximately 80% lower than traditional centralized service providers such as AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure.
DePIN is also committed to lowering the market entry barriers for resource providers and new projects by simplifying the joining process, attracting more suppliers, as illustrated by the case of Storj. At the same time, DePIN can flexibly expand across different regions, utilizing its decentralized structure to provide customized resource solutions in various geographical and demographic communities.
In terms of governance and security, decentralized networks can implement better governance systems, allowing stakeholders to participate in the decision-making process through voting and governance proposals. Additionally, DePIN offers higher resilience and security guarantees compared to centralized systems. For instance, centralized providers like Google Cloud and AWS have experienced service interruptions, while DePIN's decentralized nature enables it to maintain continuous service even if some nodes go offline.
Overall, DePIN is creating value for resource providers, project developers, and end-users by enhancing economic efficiency, lowering market entry barriers, and strengthening governance and security. It is driving the entire industry towards a more efficient, inclusive, and secure direction.
DePIN Track Analysis + Overview of Representative Projects: From Helium, Filecoin to Render and Akash
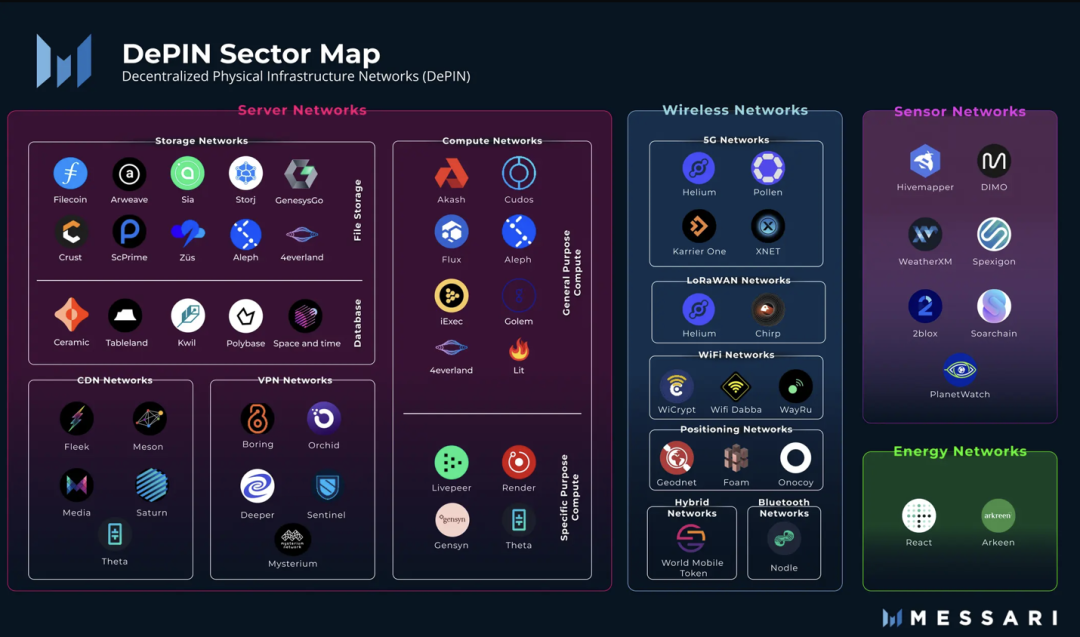
The DePIN track is a unique and expansive field that encompasses various similar or related projects. According to Messari's DePIN Sector Map, we can understand this track more clearly from several different dimensions.
DePIN can be classified along two main dimensions: as part of the blockchain network itself and as businesses utilizing blockchain technology for new ventures. Within the blockchain network, DePIN can optimize data storage, retrieval, archiving, and the possibility of L3 scaling. For example, independent storage layers like Filecoin and Arweave have become mainstream, while projects enhancing L3 layer efficiency by leasing external communication networks or GPU networks can also be categorized as DePIN. Another dimension is new businesses based on blockchain, such as the Internet of Things, cloud computing, energy storage, etc. These projects coordinate the provision and demand of hardware infrastructure through blockchain.
In terms of devices, DePIN involves various hardware components such as PCs, mobile phones, servers, communication signals, and GPUs. While customized hardware, as seen in the case of Helium, was once popular, it faces challenges in market acceptance and economic feasibility. Helium attempted to establish a "network of networks" compatible with third-party networks, but its effectiveness remains unclear. Helium's experience suggests that caution is needed in the development pace of customized hardware to avoid market imbalance.
The DePIN track can also be analyzed based on specific service areas, such as IoT and wireless communication, GPU rendering, real-life data, and image collection. Projects like Hivemapper, Spexigon, and DIMO demonstrate the application of different hardware devices in building specific services. However, their common challenge lies in the uncertainty of demand. In the existing web2 ecosystem, many services can be replaced, and DePIN projects' advantage lies in token incentives. However, token incentives are not the entirety of web3; DePIN's true significance is in connecting real-life with web3 through hardware infrastructure to better integrate into people's lives.
1.Helium: Building a Network of Networks
Helium, a pioneer in the DePIN field, has been leading the development of Decentralized Wireless Networks (DeWi) since launching its LoRaWAN network in July 2019. Initially targeting low-power wide-area networking (LoRaWAN) for IoT device connectivity, Helium gained a first-mover advantage in the IoT space. It collaborated with various projects involving weather tracking, air quality monitoring, and GPS integration.
By 2022, Helium shifted its focus to becoming a "network of networks," supporting other DePIN projects in addition to providing services for IoT. Nearly one million hotspots have connected to the Helium network to date.
However, Helium has faced criticism, with commentators suggesting its actual use cases may be overstated. The majority of Helium's revenue reportedly comes from selling hardware to new network providers rather than its services. This model could lead to supply-demand imbalances, raising questions about the project's long-term sustainability.
2.Filecoin: Decentralized Cloud Storage Solution
Filecoin, a significant DePIN project launched in 2020, aims to provide decentralized cloud storage services similar to centralized providers like Google Cloud and Amazon Web Services. Filecoin's unique aspect is its distributed storage solution, utilizing cryptographic economic incentives to secure services. Users needing storage space are connected with those having spare disk space, with the latter being paid in FIL tokens.
Despite initial success, Filecoin experienced a significant drop in monthly revenue during the bear market. To address this, Filecoin introduced Filecoin Plus, offering free storage space to verified users and attracting a substantial user base.
Filecoin's case prompts deeper considerations about DePIN: Is it a new concept speculation driving the IoT economy, or a genuine force propelling development? Currently, while there is significant market potential, barriers between DePIN services still exist. The challenge is to align cryptographic technology and incentive models with real-world use cases.
3.Render Network: Decentralized GPU Rendering Service Platform
Render Network is a revolutionary decentralized GPU rendering service platform, connecting users needing rendering jobs with those having idle GPU resources. The platform's core is a token incentive mechanism designed to optimize and incentivize GPU rendering processes.
To ensure efficiency and fairness, Render Network uses OctaneBench (OB) standards to measure rendering power, categorizing idle GPU users into three tiers based on rendering speed. The unique Burn-and Mint Equilibrium (BME) token incentive model ensures the value of RNDR tokens throughout the economy. Tasks are measured not only by completion standards but also by factors like customer satisfaction, rewarding high-quality service.
Render Network's business model evolved from an initial simple C2C model to a more managed and controlled B2C model. This innovative incentive mechanism enhances rendering service efficiency and quality, unlocking new development opportunities for the rendering industry by activating underutilized GPU resources globally.
4.Akash Network: Enabling Users to Enjoy 80% Cost Savings
Akash Network is an innovative decentralized cloud service network composed of various cloud service providers. Its core functionality lies in aggregating the cloud computing resources of these providers and offering the required cloud computing capabilities to developers at a lower cost. This decentralized approach not only makes the service more efficient but also significantly reduces costs.
Compared to traditional centralized cloud service providers such as AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure, the services provided by Akash Network allow users to benefit from approximately 80% cost savings. This substantial cost advantage makes Akash an ideal choice for developers and small businesses, especially those seeking high-quality and cost-effective cloud computing resources.
The decentralized model of Akash Network not only optimizes resource allocation but also enhances the efficiency of the entire network by allowing multiple service providers to share their underutilized computing resources. The successful implementation of this model demonstrates the potential application of decentralized technology in traditional industries, particularly in the highly concentrated and cost-intensive field of cloud computing.
Through observation, we have witnessed various projects such as Helium, Filecoin, Render Network, and Akash Network innovating in decentralized infrastructure and services. These projects not only showcase the potential application of blockchain technology in traditional industries but also provide us with a glimpse into the possible future directions of the digital economy.
DePIN's future remains uncertain, and its prospects await validation from the market as the developments are yet to be determined
Despite the challenges in the DePIN (Decentralized Private Information Network) field, such as the imbalance of supply and demand, market acceptance, technological complexity, and sustainability issues, these projects have been advancing the industry towards a more decentralized, efficient, and economical direction. We look forward to seeing more innovators join this field, bringing forth breakthrough technologies and business models.
As an emerging domain, the true potential and impact of DePIN are yet to be tested by the market and time. However, regardless of the outcome, DePIN has already proven itself as a significant force driving technological and business innovation. It not only provides alternative solutions to existing economic models but also demonstrates a more decentralized and democratic future possibility.