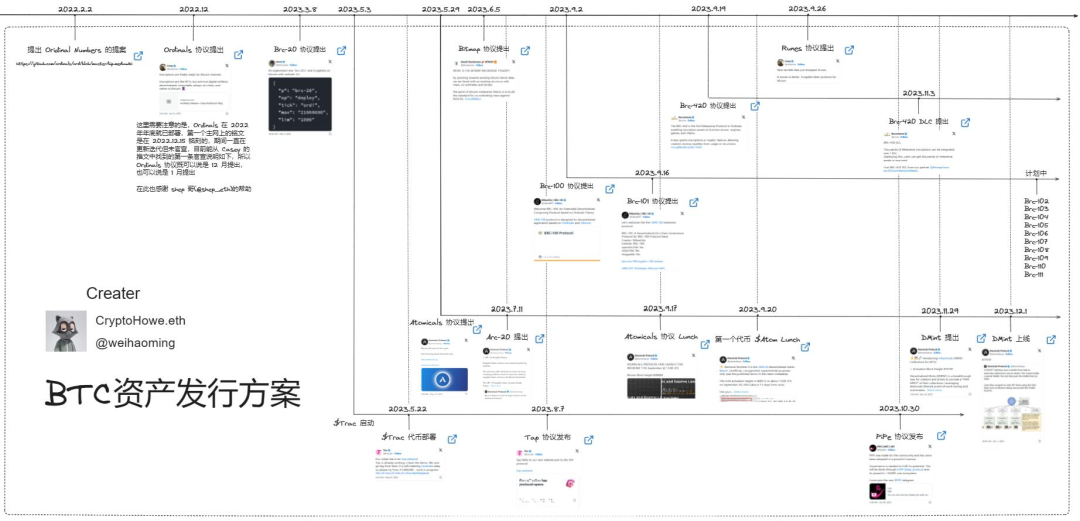
TL;DR
- With the recent popularity of the BTC ecosystem, we can see a variety of tokens issued on the Bitcoin mainnet. So what are these tokens and how do the protocols behind them operate?
- This article aims to let everyone understand the ins and outs of the BTC asset issuance plan through a timeline. What exactly triggered the popularity of Bitcoin Inscription, let us dive in and find out.
- At the same time, this article refers to many articles. During my reference and research, I found that some articles may have errors in the timing of some protocols/projects, so I have attached relevant materials to all timelines in this article. If there are any errors, please point them out to me. ,Thanks.
- Disclaimer: The tokens involved in this article are only for learning and exchange use, without any investment advice, DYOR
Agenda
Chapter Ⅰ — The gears of fate begin to turn
「1」Ordinal Numbers
「2」Ordinals Protocol
Chapter Ⅱ — A hundred flowers bloom in the issuance of BTC ecological assets
「1」Brc20 Protocol
「2」TRAC Systems
「3」Atomics Protocol
「4」Bitmap protocol
「5」BRC-100 protocol
「6」BRC-420 protocol
「7」Runes Protocol
Summarize
Reference
Chapter Ⅰ — The gears of fate begin to turn
「1」Ordinal Numbers
Many existing articles start from the Ordinals protocol, but in the official document of Ordinals, the first mention is the Ordinal Numbers theory. From this, it can be inferred that Casey should also get some inspiration from it and create Ordinals. protocol
As we all know, the smallest unit in the Bitcoin world is Satoshi (sat), and the Ordinal Numbers theory can be simply understood as artificially numbering these sats. From the motivation part of the BIP proposal, we can summarize that the theory wants to provide Bitcoin with a way to serve as a stable identifier to prevent ownership transfers or key rotations, without requiring any changes to the Bitcoin network.
Of course, there are some objections to this theory, such as reducing user privacy, increasing the size of UTXO sets, dust attacks, etc. For details, please refer to the BIP proposal.
「2」Ordinals Protocol
Agreement proposed
The Ordinals protocol was proposed and published by Casey, in which he proposed the following ideas:
"Can we arrange these Satoshis in a certain order, assign them an ordinal number between 0 and 2,100,000,000,000,000, and then connect them to other information: pictures, text, videos, or even a string of code. Each Satoshi thus becomes unique and irreplaceable. This is equivalent to giving Bitcoin the native ability to create NFTs. "
The Ordinals protocol was deployed at the end of 2022, and the first mainnet inscription was inscribed on 2022.12.14 UTC (https://ordinalswallet.com/inscription/6fb976ab49dcec017f1e201e84395983204ae1a7c2abf7ced0a85d692e442799i0), during which the protocol has been Update iteration but not For the official announcement, the first official announcement tweet that can be found from Casey’s Twitter is as follows, so the Ordinals agreement can be considered to be proposed in December or January: (Thanks also to Shep brother here clues provided)
Protocol features
The number of sat and the division of rarity
Humans are born collectors. Since Ordinal Numbers artificially numbers sats, why not classify these sats into high and low levels, so there is a distinction between rarities. There are currently 6 types of rarity:
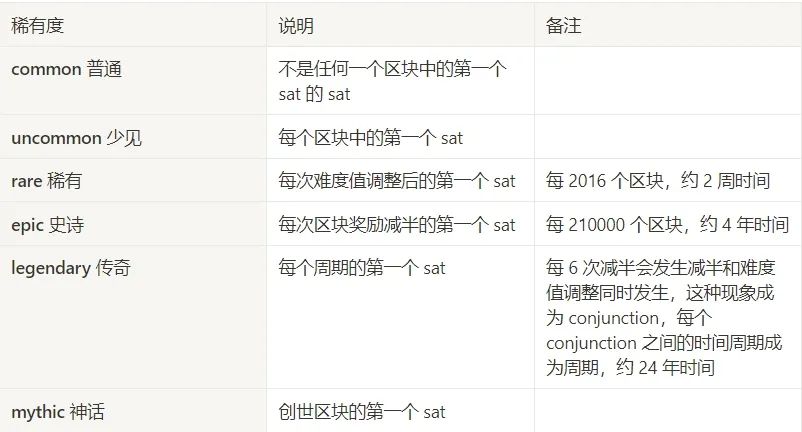 This rarity is similar to what we call "leopard banknotes", "serial banknotes", etc. when playing with banknotes in real life. They are essentially banknotes, and their actual value is the face value of the banknote. However, because people assign Because of its special meaning, it has a higher collection value and a premium, which is what we often call "consensus generates value."
This rarity is similar to what we call "leopard banknotes", "serial banknotes", etc. when playing with banknotes in real life. They are essentially banknotes, and their actual value is the face value of the banknote. However, because people assign Because of its special meaning, it has a higher collection value and a premium, which is what we often call "consensus generates value."
While assigning a specific rule number to each sat and tracking it in the transaction, the Ordinals protocol also allows anyone to attach additional data such as images, text, videos, and audio through the Ordinals protocol. Audio) and so on. At that time, early players were mostly creating NFTs on it. Founder Casey's initial positioning for it was also to let people store something eternal on Bitcoin, the oldest chain with the strongest consensus. Therefore, for a period of time, many people will equate Ordinals with "Bitcoin NFT". We can still see them in Unisat Wallet today.
 Transaction first in first out
Transaction first in first out
In order to ensure that the sats with serial numbers will not be out of order during the transaction, a first-in, first-out method of transaction is adopted. Here is an example from Teacher Wang Yishi’s article (https://yishi.io/a-beginner-guide-to-the-ordinals-protocol/) to explain the first-in-first-out feature:
In the picture below, there are two Inputs on the left. Address 1 and Address 2 have a total of 5 satoshis. In this transaction, 4 satoshis were sent to an address starting with 3oPz, and 1 satoshi was left as a miner fee to pay the miners.
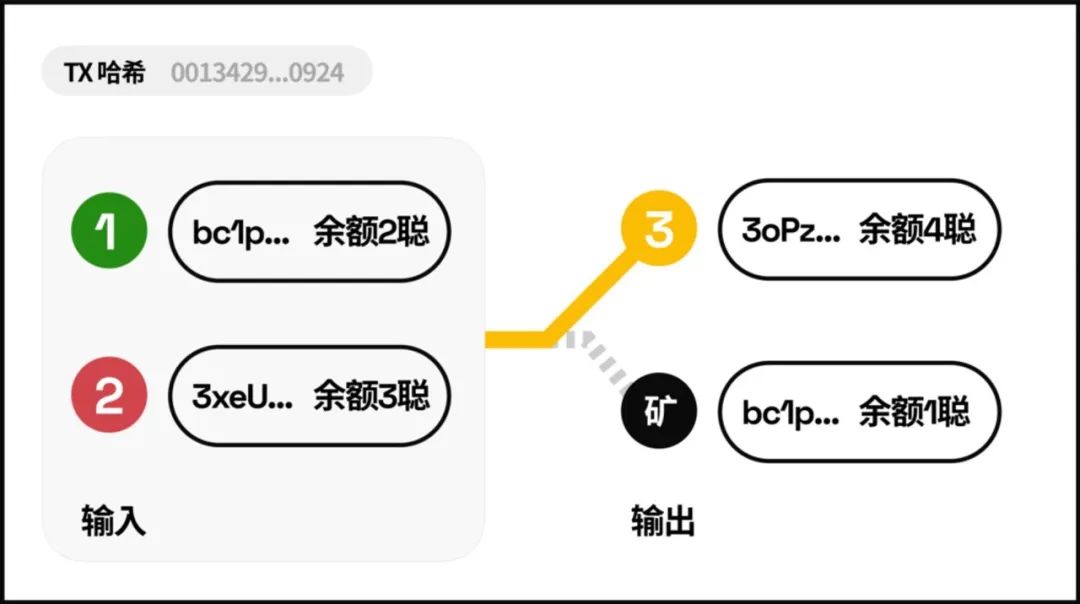 Assume that in the above transaction, we secretly use the Ord protocol to assign an identity (serial number) to each satoshi. Then after the transaction is completed, the four numbered satoshis Ord A->D at address 1 and address 2 will go to address 3. There, the last satoshi was given to the miners.
Assume that in the above transaction, we secretly use the Ord protocol to assign an identity (serial number) to each satoshi. Then after the transaction is completed, the four numbered satoshis Ord A->D at address 1 and address 2 will go to address 3. There, the last satoshi was given to the miners.
The so-called "first in, first out" means that the number ordering of each Satoshi is determined according to its index in the transaction output. For example, in the transaction output (Output) in the figure below, address 3 is ranked in front of the miner's address, so the satoshi transferred from address 1 and address 2 will be inherited by address 3 first, and then the miner's address.
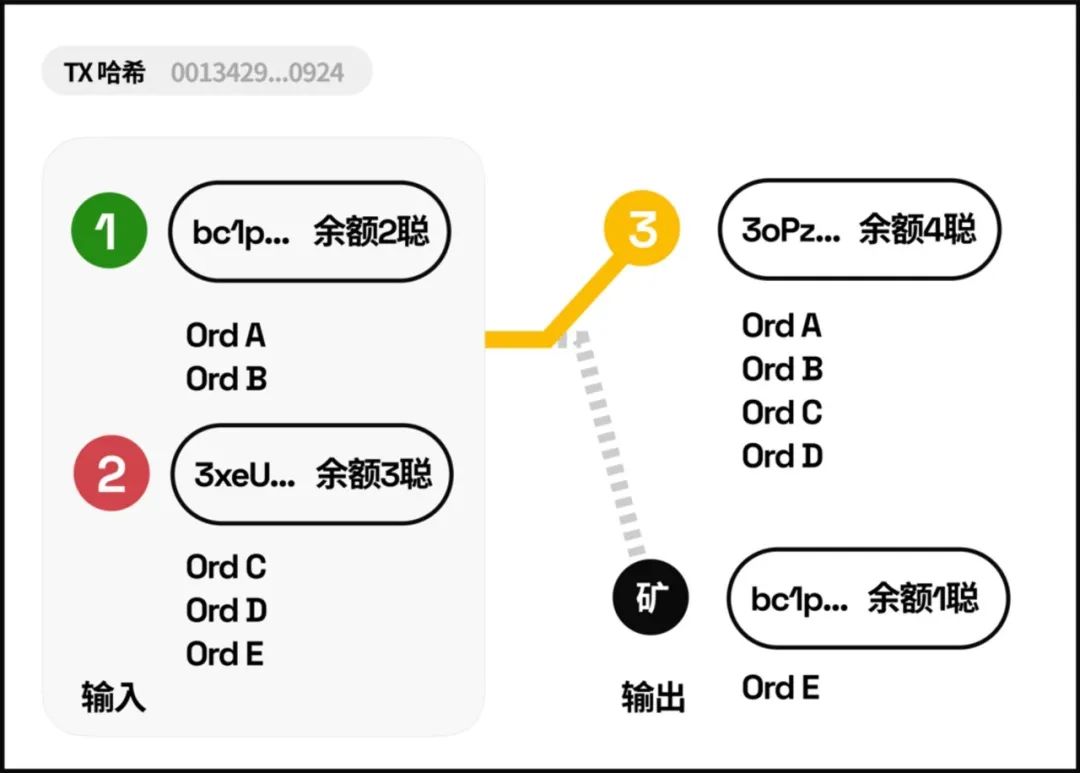 Agreement principle
Agreement principle
Friends who know Bitcoin well know that Bitcoin has existed as a peer-to-peer electronic currency system since its birth. The programming language it uses is a non-Turing complete scripting language, so it is almost impossible to implement some complex functions. The two major updates of BTC in 2017 and 21 allowed us to implement some functions containing complex logic on BTC.
 Based on the above development premise, the Ordinals protocol achieves viewing and transfer effects by writing its inscription content into the Taproot script and using UTXO. Since Taproot script consumption can only be performed from existing Taproot Outputs, the two phases of commit/reveal (commit/reveal) are used to implement engraving. First, in the submission transaction, we need to create a Taproot Output containing the script of the inscription content. Secondly, in the reveal transaction, spend the previously created submission transaction to reveal the content of the inscription on the chain. In this process, we also need Perform a series of serializations on the contents of the inscription:
Based on the above development premise, the Ordinals protocol achieves viewing and transfer effects by writing its inscription content into the Taproot script and using UTXO. Since Taproot script consumption can only be performed from existing Taproot Outputs, the two phases of commit/reveal (commit/reveal) are used to implement engraving. First, in the submission transaction, we need to create a Taproot Output containing the script of the inscription content. Secondly, in the reveal transaction, spend the previously created submission transaction to reveal the content of the inscription on the chain. In this process, we also need Perform a series of serializations on the contents of the inscription:
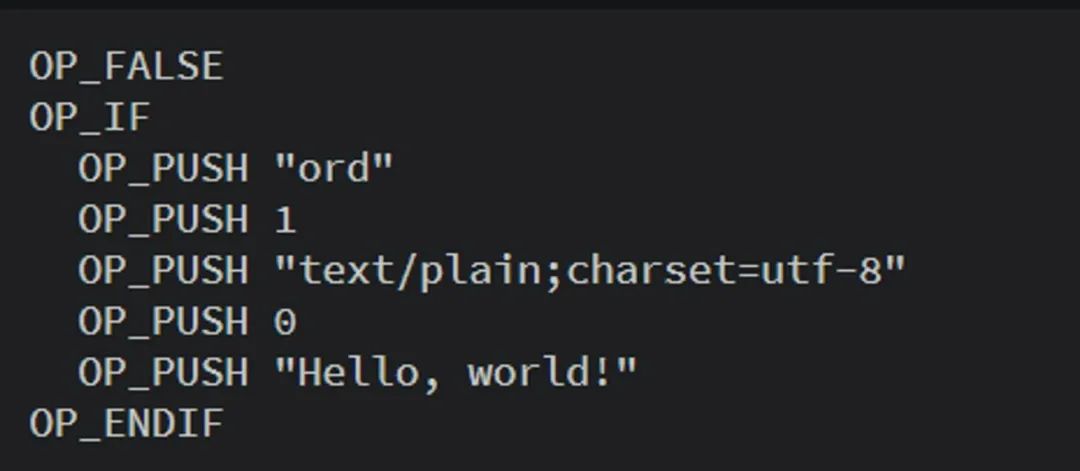
So to explain it in plain English, it is equivalent to you initiating a WeChat transfer. During the transfer process, we need to write the content of the inscription you created in the note (Taproot Output), and then send the transfer. Go out (spend and submit the transaction), then after the sending is completed, we can let the other party see what you wrote in the note in the chat box (reveal the transaction). If there is no note written on this transfer or the transaction is canceled, the content of this inscription will not be uploaded to the chain.
Chapter Ⅱ — A hundred flowers bloom in the issuance of BTC ecological assets
「1」Brc20 Protocol
Agreement proposed
After the Ordinals protocol came out, early players were playing with NFT, and the anonymous developer domo released an experimental standard on March 8, 2023 - the BRC-20 protocol improved based on the Ordinals protocol and officially deployed the first BRC20 $ordi. The protocol enables anyone to issue tokens on the Bitcoin network, similar to how ERC-20 tokens work on Ethereum.
Notice:
1. Domo’s earliest tweet about BRC-20 was 2023.3.9, but judging from the deployment time of $meme and $ordi, it should have been launched on 2023.3.8
2. $meme is the first BRC20 deployed, while $ordi is the first officially released BRC20, which can be inferred by looking at their deployment times.
As for the development of $ordi, everyone should have some experience. I won’t mention it here. For details, please refer to the tweet below:
Agreement principle
The BRC-20 protocol develops a series of standards to deploy, mint, and transfer BRC20 tokens based on the Ordinal theory. The format standard of this protocol is derived from the format of the Sats Name project (the first DID project based on the Ordinals protocol):

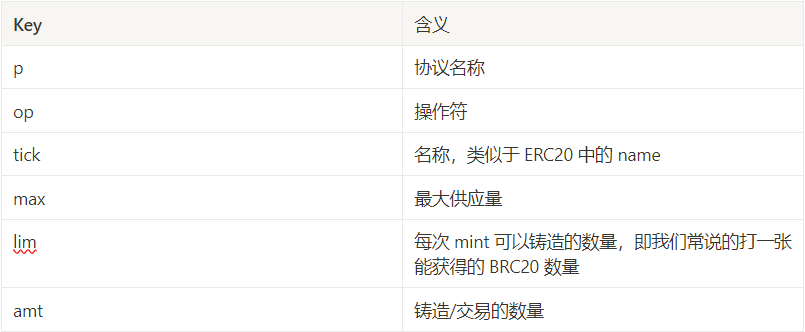 Similarly, if explained in plain language here, it is the same as the Ordinals protocol when you initiate a WeChat transfer, but the content of the remark is different.
Similarly, if explained in plain language here, it is the same as the Ordinals protocol when you initiate a WeChat transfer, but the content of the remark is different.
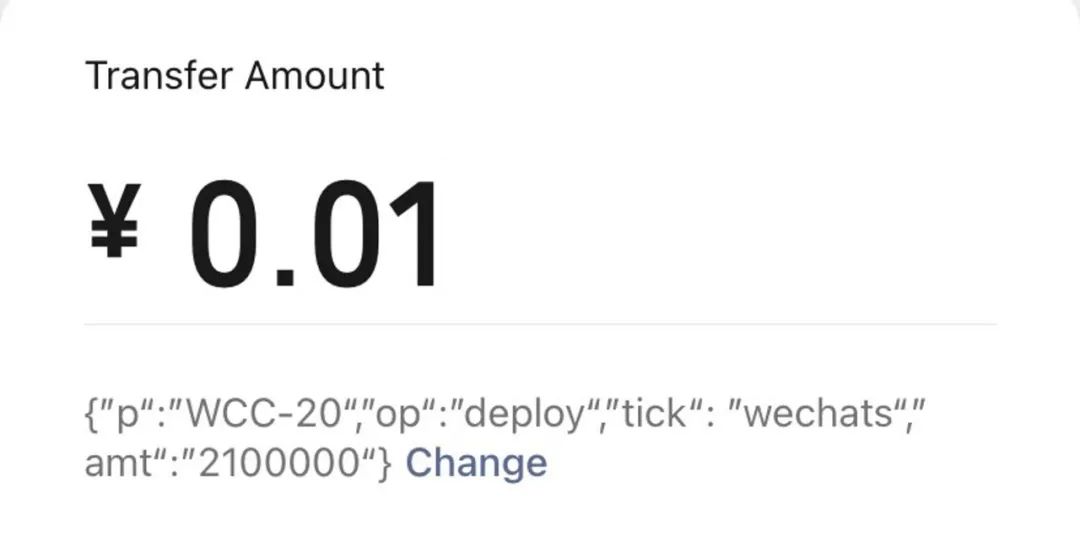 extend
extend
Although this method of the BRC-20 protocol enables the free issuance of homogeneous tokens on the Bitcoin chain, because Bitcoin does not have an account model and the content of BRC-20 is placed in the Taproot script of Segwit, we cannot directly issue it on the chain. Calculate the BRC20 balance for each account. Therefore, the current method is to build an index server off-chain to achieve BRC20 token information acquisition, balance calculation, transaction transfer, etc., but this method will have the risk of centralization.
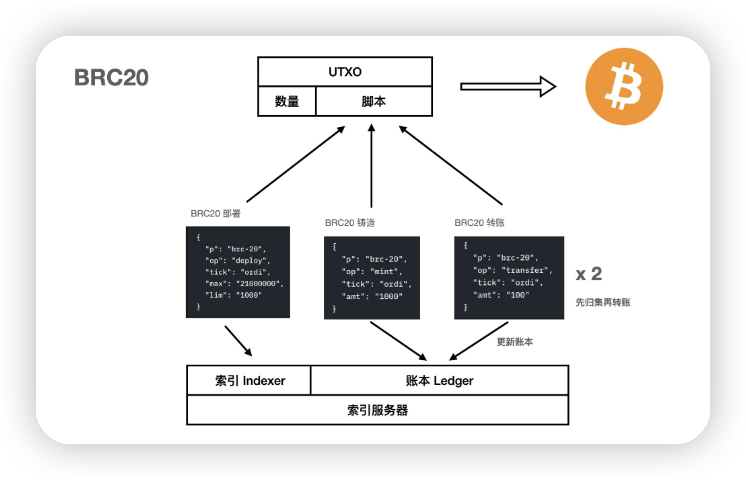 First of all, you can first understand the three major parts of the BTC layer protocol: the protocol stipulates the rules for writing data on Bitcoin, the indexer provides the ability to query and parse these data, and the ledger records the token balance and handles transfers .
First of all, you can first understand the three major parts of the BTC layer protocol: the protocol stipulates the rules for writing data on Bitcoin, the indexer provides the ability to query and parse these data, and the ledger records the token balance and handles transfers .
For BRC20, the index server first needs to identify each BRC20 deployment to read the token information. This part is called the "index".
At the same time, since the balance of BRC20 is engraved into the script and cannot be recognized by the BTC network itself, the index server of BRC20 must build a local ledger to record the balance of BRC20. Every time a transfer occurs, whether the transaction can be carried out (there are enough coins), the local ledger needs to be checked and updated.
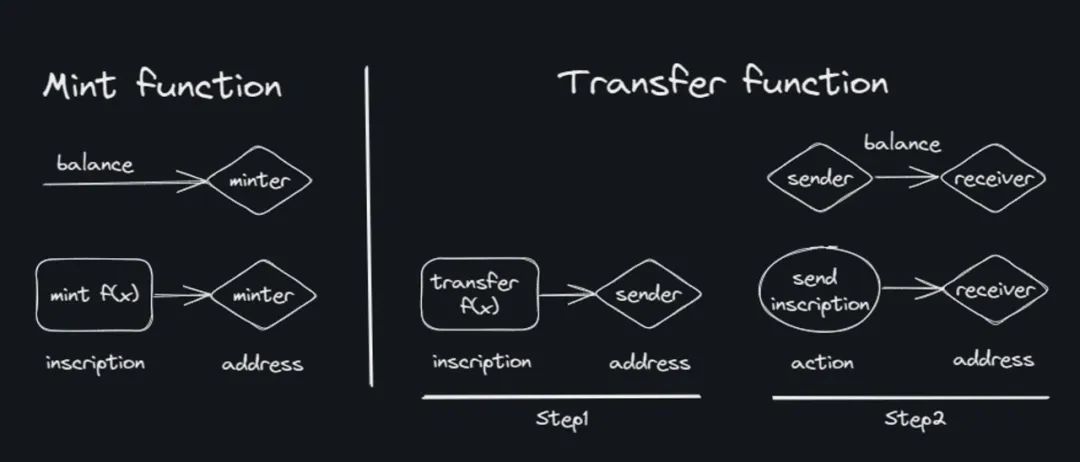 So BRC20 needs to send two transactions when trading:
So BRC20 needs to send two transactions when trading:
1. The first transaction reads the latest ledger data in the local ledger and calculates the balance.
2. Transfer the second transaction.
The Ordinals protocol is essentially designed for NFTs. Based on its improved BRC20, the transfer complexity increases recursively. The BRC20 indexer also takes on the work of the ledger, which exists completely off-chain without Bitcoin. The indexer must accurately record every balance change to ensure the integrity of the ledger.
Therefore, as time accumulates, the indexer ledger will accumulate, and the pressure on the nodes will increase. If the indexer is not continuously incentivized, it will be difficult to sustain. If the indexer ledger ceases to provide services, BRC20 will become completely unusable.
「2」TRAC Systems
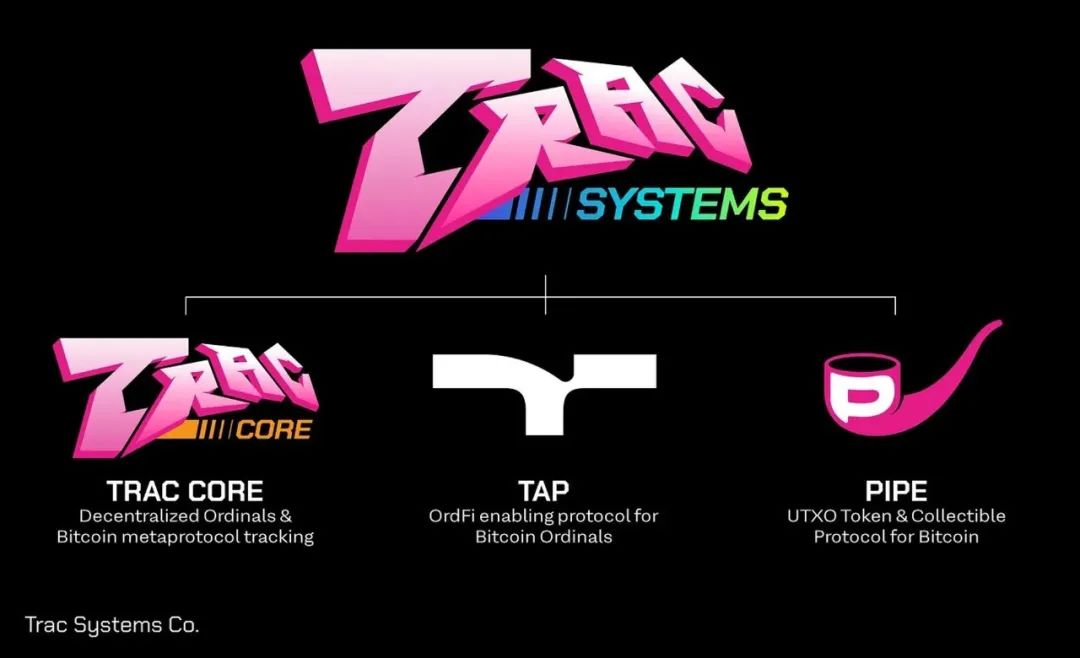 $TRAC
$TRAC
$TRAC is a BRC20 Token launched by Benny on 2023.5.3 and officially deployed on 2023.5.22.
Trac Core
Trac core is the oracle and decentralized indexer of Bitcoin inscriptions, solving problems such as inscription ecological data indexing, retrieval, and price feeding.
For example, in terms of indexers, although inscription data is stored on the Bitcoin chain, this is only information about related inscriptions, and data updates and audits need to rely on third-party centralized indexers, and security will always be criticized (for example, at the end of November The market's accounting error for Binance's ordi index), so Trac can allow the Inscription ecosystem to inherit the security of Bitcoin to a greater extent, collect, organize and sort all data on Bitcoin, and plans to introduce hundreds of indexer nodes in the future.
At the same time, with the increase of nodes, Trac Core also integrates the role of oracles, obtaining necessary reliable data from external sources to input into the blockchain, which is the basis for subsequent construction of upper-layer protocols such as Inscription native DeFi, and the API of Trac oracles is Can be called for free.
Therefore, Trac core’s ecological position of having both a decentralized indexer and a Bitcoin oracle can be said to be ahead of most Inscription projects.
Tap Protocol
Tap Protocol is an improved protocol based on Ordinals released by the $TRAC team on 2023.8.7. We can regard it as an upgraded version of the mirror BRC20 protocol. It is a protocol that is compatible and upgraded to BRC20. It has the following four characteristics:
- OrdFi protocol with unique token standards
- Compatible with BRC20 tokens, easy for market integration, and breaks through the name length limit of BRC20. The length of BRC-20 tokens is fixed at 4 digits, while the length of Tap tokens is 3 or 5-32 digits (cannot be 4 digits)
- Supports batch transfers, pledged assets, token swap and other functions. Improve transaction efficiency without relying on L2 chain
- The first protocol to support cursed inscriptions
Use the previously deployed $TRAC as the governance token of its protocol (it is not a feature, but it is explained here)
Currently, the two tokens $TAP and $-TAP are officially issued in Tap Protocol. Among them, $TAP was minted by BennyTheDev on 2023.8.6 but has not been circulated; $-TAP is open to the community mint , with a total amount of 21,000,000 (that is, 21,000 pieces). According to Shep's research, $-TAP was deployed 30 minutes earlier than $TAP, and is the real first native token in the protocol.
Pipe
The Pipe protocol was proposed by Benny, the author of $TRAC. This protocol was improved by Benny on the Runes protocol. The Pipe protocol can be said to have preempted the Runes protocol in a corner, because the Runes protocol was proposed by Casey, the founder of the Ordinals protocol, but its main focus is on the Ordinals protocol, so the development progress of the Runes protocol has been relatively slow, and Benny is finishing learning the Runes protocol. After thinking about it, the Pipe protocol was launched in just about a month.
The connection between the three
At this point we can see that Benny has launched 3 projects in succession in less than half a year, and these 3 projects are also layered with each other, the ultimate matryoshka doll. Let us use the picture below to explore them. relationship between.
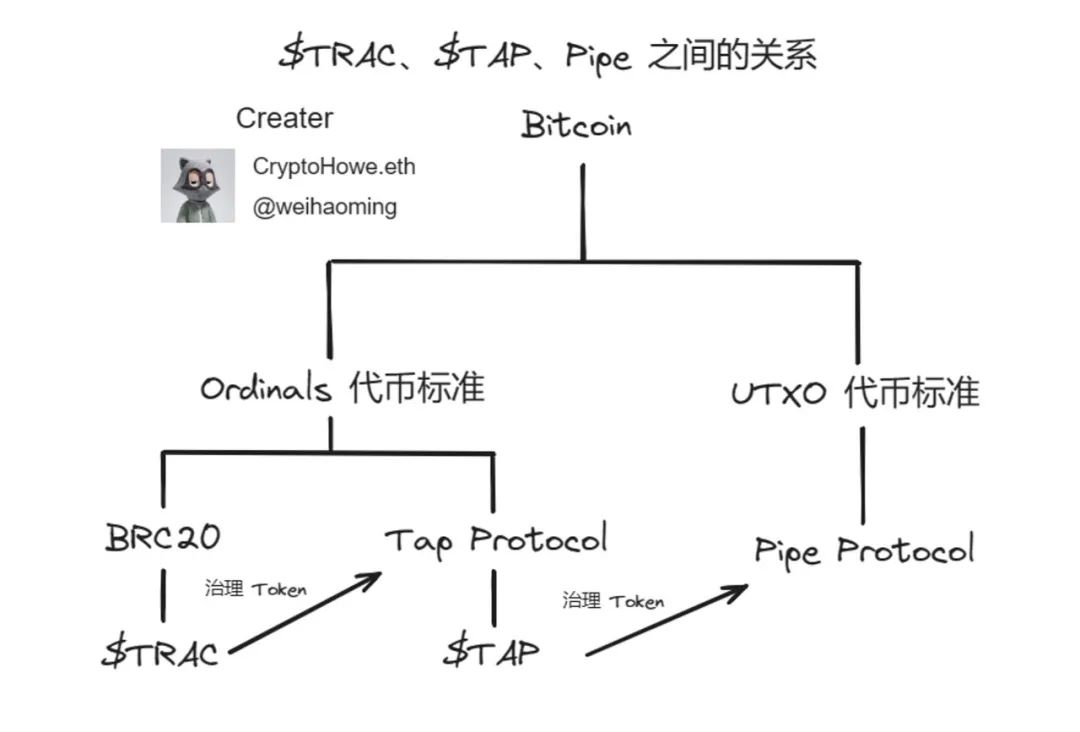 Generally speaking, the governance token of a project is chosen to be the native token of its protocol. However, Benny uses this governance token method to achieve that three projects can promote and restrict each other, which is extremely rare. At present, the specific functions of these governance tokens have not been officially announced, so in the next development, we can see whether this will produce some different exciting collisions.
Generally speaking, the governance token of a project is chosen to be the native token of its protocol. However, Benny uses this governance token method to achieve that three projects can promote and restrict each other, which is extremely rare. At present, the specific functions of these governance tokens have not been officially announced, so in the next development, we can see whether this will produce some different exciting collisions.
「3」Atomics Protocol
Agreement proposed
The founder of the Atomics protocol tried to develop a DID project on the Ordinals protocol in February. However, during the development process, he found that the limitations of the Ordinals protocol made it impossible or awkward to implement some of the functions he wanted, making it easier for 2023.5. 29 posted the first idea about the Atomics protocol on Twitter, and finally launched the protocol on September 17, 2023 after several months of development.
The initial launch of the Atomics protocol did not stir up much excitement in the Bitcoin ecosystem, because at that time due to the launch of the Ordinals protocol and the BRC-20 protocol, a large number of improved protocols based on them emerged on different chains. However, when we look at When looking at the documentation for the Atomics protocol, we will find that it is a completely different protocol.
Theoretical basis—Digital Matter Theory (DMT)
DMT theory (Digital Matter Theory) refers to digital matter theory, which means that digital information is not just random numbers and letters. In fact, it can also be regarded as its own "matter", such as wood or metal. DMT in blockchain data can be transactions, bytes, or any other pattern of blockchain data that can be turned into a valuable digital item or asset.
Here is also a quote from Dr. Jingle’s content to facilitate everyone’s better understanding:
- Some physicists claim that information is a new form of matter that may eventually dominate everything on Earth (also highly controversial). According to current growth trends, in about 350 years, the amount of digital information used on Earth may be greater than the number of physical atoms, which also highlights the exponential growth and importance of digital information.
- The physicist's idea encouraged many people to turn it into an executable protocol, parsing valuable information from the Bitcoin blockchain to create "non-arbitrary tokens." Utilizing digital matter theory has the potential to revolutionize the creation of digital value, making it more non-arbitrary and meaningful. By leveraging data in the context of digital matter theory, new mechanisms can be created to identify and derive new sequences of value in the data, opening up possibilities for new forms of tokens.
- For example, some people even compare Bitcoin to an application of DMT. Bitcoin is also a non-arbitrary token and has its own specifications, such as 21 million coins, one block every 10 minutes, etc. Through the exchange of digital information on the Bitcoin network, value can be transferred and stored. Although Bitcoin only exists in the digital world, its value and influence can have significant real-world impacts, just like traditional physical currency.
- However, DMT is not without controversy. Some critics argue that digital information cannot be compared with basic physical entities such as matter and energy because digital information itself cannot directly change the real world. However, DMT advocates believe that although digital information cannot directly change the real world. However, digital information can change the world indirectly through human actions and decisions, such as the application of cryptocurrency.
Problems faced by existing Bitcoin builders
- Various problems caused by proprietary APIs:
- Service lock-in, high interaction costs, the same on-chain data will have different manifestations, and competition among developers
- Unreliable indexer:
- Asset security issues, frequent changes, positive and negative numbers of Ordinals
- Lack of top-level design:
- Difficulty combining protocols and developing proprietary facilities
- Limitations of on-chain metadata:
- Example: Collections must be manually uploaded to Github repositories, and they must be manually updated on dozens of marketplaces, with no consensus on on-chain responses
- Errors cannot be fixed or are expensive to fix
- The data structure of the Ordinals protocol relies heavily on the use of individual files, which means there are off-chain conventions and proprietary indexes in different markets
- Lack of control:
- Without access to powerful, high-performance decentralized indexers and more service/indexer lock-ins, data portability becomes an issue
- Lack of benefits:
- Reliance on these specific services and marketplaces and their proprietary services such as indexers, APIs, etc. results in reduced profits
The first three points are for developers, and the last three points are for creators.
atomic theory
The Atomics Protocol is a simple and flexible protocol for minting, transferring, and updating digital objects (traditionally known as NFTs) for Unspent Transaction Output (UTXO) blockchains like Bitcoin.
1️⃣ Digital objects — “atom” NFTs
Atomic (or “atomic”) is a new type of NFT that can be minted, transferred, and updated on Bitcoin. The main difference is that there is no need to use a centralized service or a trusted third-party indexer. It does not require any changes to Bitcoin to run, nor does it require sidechains or any L2. It’s time to take back control of our digital lives for good.
 2️⃣BitWork — Proof of micro-workload PoW
2️⃣BitWork — Proof of micro-workload PoW
The most interesting improvement of the Atomics protocol is that the CPU computing link is added to the token minting process. This link is called BitWork. The caster needs to exhaustively calculate the hash value matching the specific prefix characters before casting.
PoW can make token minting relatively fair, with both the value injection of energy and time and the presence of random luck.
Unlike the traditional PoW algorithm, which is computationally difficult, Bitwork achieves fine-grained adjustment of mining difficulty by changing the prefix matching method. It can add a number between 1 and 15 after the prefix, such as: "7777.1" or "7777.15" or any number in between that represents the range of variation allowed for that character.
How it works is that the number after "." is called a semi-wildcard and is used to match any 5th character starting from that number. Take "7777.10" as an example: the first 4 txid characters (hexadecimal) must be "7777", and the fifth character can be the number 10 (hexadecimal) and above.
So the 5 digit number can be a, b, c, d, e or f. This allows the entire system to not only have 16x to choose from each time the difficulty increases, but to have a range of 2x to 16x to choose from.
At the same time, BitWork also brings some novel use cases:
- Add a random element of luck to the casting process
- Organizing communities around vanity TXIDs and REFs
- When you have a really cool reference or prefix, organize a related community through consensus
- Content ranking based on expensive signaling theory
- This way we can rank content based on energy consumption such as electricity
- Throttle and limit token minting — spam filter
3️⃣Container NFTs — NFT standard
Container is a collection standard for representing NFT and metadata. It can be used to add/modify/delete the content of any protocol such as Atomicals, Ordinals, Bitmaps, etc. You can also choose to permanently "seal" the content, that is, lock the content into a container and then destroy the "key" that can open the container, thereby The purpose is to maintain the sealed state and cannot be modified.
Container name service:
- Container names begin with the hashtag # symbol, and each name is unique and non-repeatable, and is minted on a first-come, first-served basis.
- The length of the name is between 3-64 characters, and Bitwork is used to slow down the registration of container names.
- Examples of container names: #bitcoin-funks, #gemini-warriors,…
4️⃣ARC20 — Colored Coin
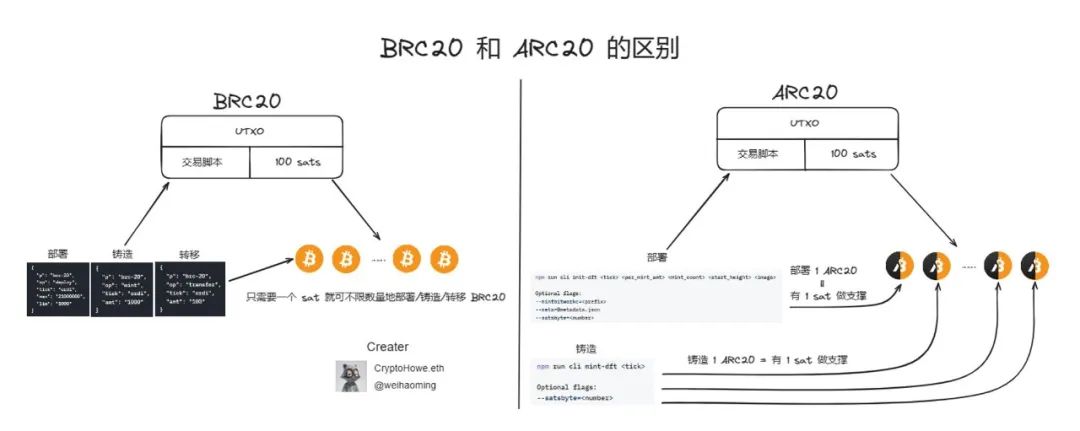
The Atomics protocol uses sat, the smallest unit of Bitcoin, as the basic "atom". The UTXO of each sat is used to represent the Token itself, that is, the balance of ARC20 is the number of sat, 1 token = 1 sat.
ARC20 is a colored coin model, and the registration information is recorded in the transaction script. By binding information with UTXO, the programmability and decentralization of the token can be improved. At the same time, the security of the transaction is guaranteed by the BTC mainnet. In terms of tracking transactions, calculating balances, etc., no off-chain system is required. , to calculate the balance of ARC20 tokens, because the token balance is consistent with the number of sat in UTXO. This is the biggest difference from the BRC-20 protocol.
-
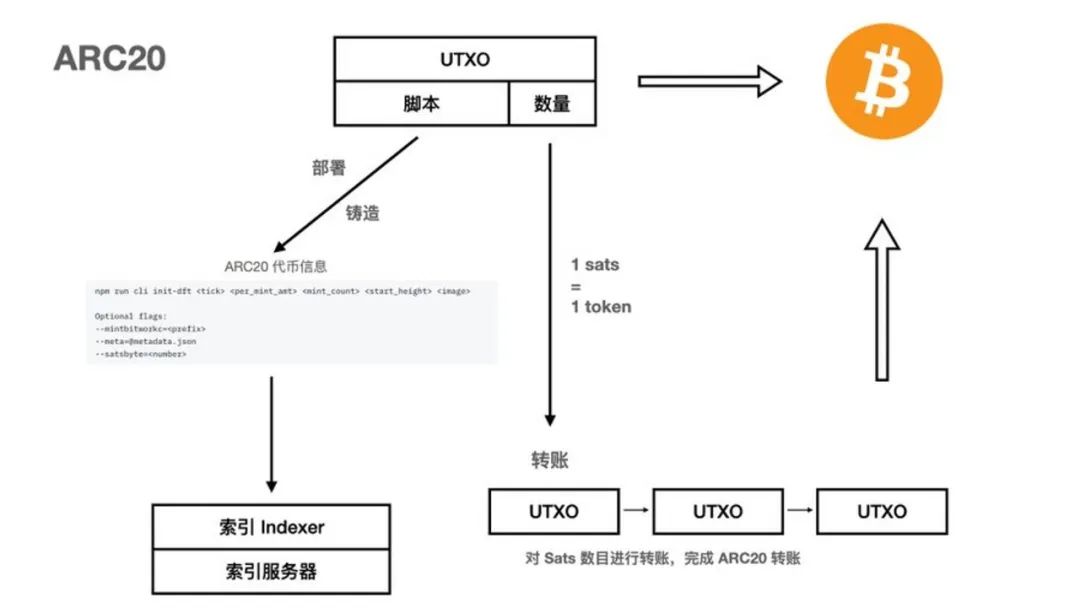 When deploying ARC20, the token name, total amount, quantity limit, difficulty setting, starting block, image and other information.
When deploying ARC20, the token name, total amount, quantity limit, difficulty setting, starting block, image and other information. - When users mint ARC20, they write the name of the token into the UTXO script. The amount is directly determined by the number of sats in the UTXO, 1 sat = 1 token.
- To transfer ARC20, users no longer need to deposit any data into BTC. They only need to use the UXTO that continues to hold the token as transaction input and output it to other addresses.
For ARC20, we only need an index to help us read the token registration information and identify mint transactions to confirm and verify which UTXO is ARC20.
The benefits of this are:
- The cost of the index server is greatly reduced. Almost anyone can make an index server by themselves. The system is highly decentralized.
- The transfer completely relies on the BTC network and will not repeatedly create junk transactions. The security of the ARC20 transfer itself is guaranteed by BTC.
- The atomicity of ARC20 is consistent with the atomicity of BTC and is suitable for implementing many native applications.
Of course, the design of colored coins also brings some disadvantages, because the balance is not written in the data, but is bound to sat, so the minimum split precision of the ARC20 balance is 1.
This also makes it impossible for users to conduct fine-grained transactions under the fact that the BTC mainnet itself has set a minimum transaction limit of 546 sat to prevent dust attacks. However, the Atomics protocol has currently provided a specific split plan and is actively developing it.
Here is a picture to show the most essential difference between BRC20 and ARC20:
 5️⃣Realm Name System (RNS) — Realm Domain Name System
5️⃣Realm Name System (RNS) — Realm Domain Name System
RNS claims to be the true rival of the DNS domain name system and aims to become a global alternative to DNS and other blockchain domain name systems.
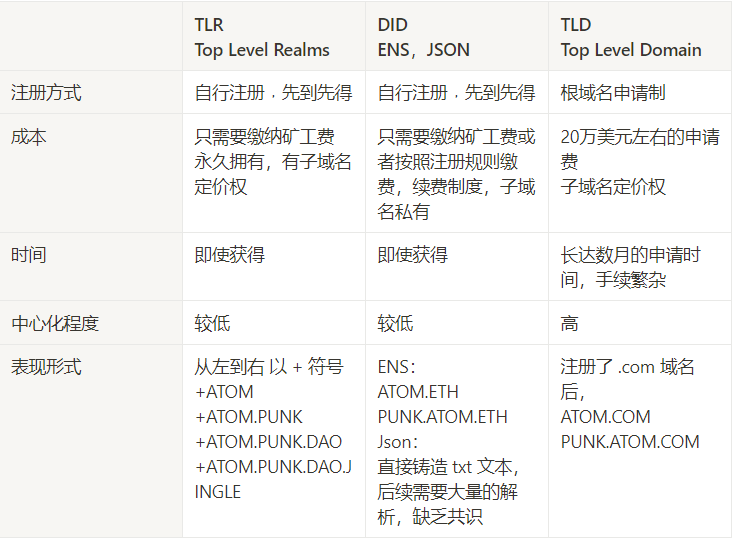
Realm Name is a human-readable identifier that can be used to associate network addresses with resource information. Realm names start with the plus sign + and have at least one alphabetic character, such as +alice and +agent007 , which are both valid names (top-level—realm or TLR in the Realm Domain Name System (RNS)).
Realm names are self-owned and self-managed directly on the Bitcoin blockchain using the atomic digital object format, which basically means there are no middlemen or centralized registrars.
 6️⃣Subrealm Minting — Subrealm Mining
6️⃣Subrealm Minting — Subrealm Mining
The community is managed and tokenized by issuing subrealms under any Realm. The specific rules are as follows:
- Any domain or sub-domain can publish sub-domains
- All subdomains can inherit the same characteristics and publish their subdomains based on the subdomain
- Everyone is a registrant in the field they own, and there is no centralized organization
To give a simple example:
- First we registered a domain + ATOM
- When we want to form a community about Punk NFT in this field, we can create a sub-field +ATOM.PUNK based on the +ATOM field
- After we want to form a DAO in the Punk community, we can create a sub-domain +ATOM.PUNK.DAO
- If everyone in DAO is assigned a DID, you can create a subdomain name +ATOM.PUNK.DAO.JINGLE
In addition to this, Subrealm can be used for social media organization, identity verification, loyalty rewards, and more.
Protocol features
Through the atomic theory above, we can know that the main features of the Atomics protocol include:
- Using satoshis as the base unit to represent tokens
- Allows the creation, transfer and update of digital objects on Bitcoin
- Providing a decentralized and Bitcoin culturally compliant approach to tokenization
- Leveraging Proof of Work (POW) to increase fairness and decentralization of the minting process
- Designed to expand the functionality of Bitcoin and support a wider range of applications
Main differences from other protocols
The best way to understand the differences in the Atomics protocol is to compare it to other popular NFT protocols:

「4」Bitmap protocol
Agreement proposed
Bitmap.land is the first Metaverse project in the Bitcoin ecosystem. It is based on Ordinals theory and Bitmap theory.
Bitmap theory was proposed by Twitter user @blockamoto on June 5, 2023.
This theory maps each transaction input in the Bitcoin block into a parcel (Parcel), forming a block or district (District). The difference in size of different transaction inputs results in different sizes of mapped plots.
Agreement concept
Buyers of Bitmap.land were influenced by Decentraland and The Sandbox and adopted a method of dividing land and drawing patterns on the map, which is similar to the logic of buying land on these two platforms. Users write data into Satoshi through inscriptions and obtain ownership of specific Bitcoin blocks, similar to free minting.
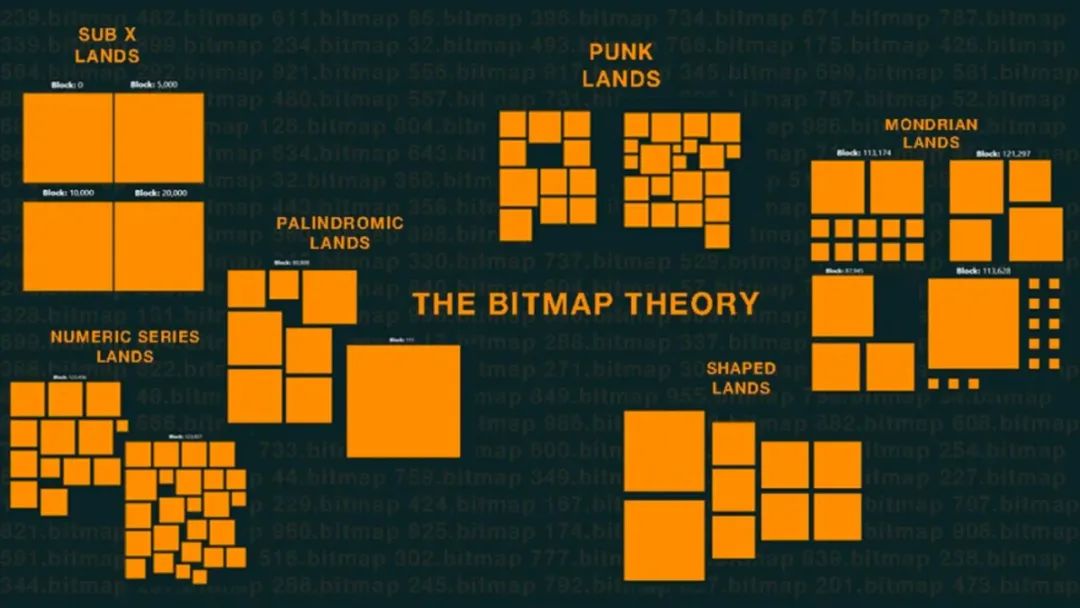 On the Bitcoin blockchain, each block is divided into four parts to represent different halving cycles. Users can check the number and color of each block on the Bitmap.land website. Different colors represent different selling statuses.
On the Bitcoin blockchain, each block is divided into four parts to represent different halving cycles. Users can check the number and color of each block on the Bitmap.land website. Different colors represent different selling statuses.
The sale of Bitmap.land is closely related to ordinal theory, similar to the virtual land sale of Decentraland and The Sandbox, which relies on the ERC-721 standard. Ordinal theory is similar to the principle of early colored coins, but in the context of Bitcoin’s current narrative, consensus, ecology, and infrastructure, the two are different. While ordinal theory is not as innovative as ERC-721, BRC-20's approach is more original.
Bitmap theory adds a new interpretation to Bitcoin blocks, providing a topicality despite lacking practicality. It changes the connection between Bitcoin and the Metaverse, giving each block of the Bitcoin blockchain a new dimension and making it part of the Metaverse by allowing users to own and record individual blocks.
Bitmap theory attracted the attention of the Ordinals community and inspired the inscription craze. Any block on the Bitcoin blockchain can become part of the Metaverse through Bitmap, bringing new creation and ownership opportunities to the community.
Bitmap.land blurs the lines between Bitcoin and the Metaverse through bitmap theory, paving the way for ownership, creativity, and community development. As the inscription craze continues, it means huge potential for those looking to carve out a niche in the digital realm.
Interested students can also go to the official browser to view various Bitmaps: https://bitmap.game/
「5」BRC-100 protocol
Agreement proposed
As we all know, Bitcoin-based protocols such as the Ordinals protocol and BRC-20 have brought a lot of imagination to the development of the Bitcoin ecosystem through the "on-chain declaration, off-chain analysis" mechanism. And a large number of Bitcoin NFTs and tokens have been issued, but the development of decentralized applications such as DeFi is still lagging behind. Therefore, Mikael.btc released a protocol to support decentralized computing on September 2, 2023: BRC-100.
Protocol introduction
BRC-100 is an extension protocol based on the Ordinals theory, specifically designed to implement various decentralized applications on Bitcoin Layer 1. This protocol not only takes over the basic functions of BRC-20 on Bitcoin, such as creation, minting and transactions, but also introduces the concept of decentralized computing.
This means that based on the BRC-100 protocol stack, various decentralized applications such as DeFi, SocialFi and GameFi can be developed, bringing true decentralization, trustlessness, censorship resistance and permissionless to the first layer of Bitcoin. Application scenarios.
A major feature of the BRC-100 protocol is its interoperability, which not only allows all protocols and applications within its protocol stack to be compatible with each other, but also supports interoperability with BTC, BRC-20 or other layer 1 chains such as Ethereum and Stacks to interact with. In addition, the protocol also introduces the UTXO model and state machine model to enhance its security and computing capabilities.
Protocol features
Because the BRC-100 protocol is an extension of the Ordinals theory, BRC-100 itself has all the features of BRC-20, and also introduces some innovative features:
Saving money: It is based on the BRC-100 protocol to carry out various extensions such as airdrop protocol, governance protocol, relay protocol, etc. We can understand that Mikael wants to introduce various DeFi gameplay into BTC
Protocol inheritance
The BRC-100 protocol introduces the concept of inheritance. The protocol that directly or indirectly inherits from BRC-100 is called BRC-100 extended protocol. BRC-100 extension protocols must inherit from only one protocol. An extended protocol will inherit the properties, operations, and calculation operations of the parent protocol, and can only extend properties and calculation operations.
This is similar to when we make ceramics. It is just a clay embryo at the beginning. Slowly, by polishing and shaping it, it gradually has more expanded functions such as decoration, holding things, etc.
BRC-100 protocol stack
The BRC-100 protocol and all its extensions and improvements are collectively called the BRC-100 protocol stack. Based on this protocol stack, all tokens/applications are compatible with each other, which means that one token/application can be used anywhere by other app.
Protocols and Applications
In the BRC-100 protocol stack, a protocol is a standard that describes the properties, operations, and calculation operations of an application. Applications are instances of the protocol that are created after being deployed to the Bitcoin network via Inscription.
An application is essentially a token with computing power and state. The computing capabilities of the application are detailed in the agreement. Without adding sub-applications, applications cannot have computing capabilities not described in the protocol. The added sub-application can only have the computing power of the protocol, otherwise the public indexer cannot verify the status of the application, resulting in inconsistent status between users and applications.
Apply nesting
Applications deployed based on BRC-100 and its extension protocols can be nested, that is, another application can be created under one application, called a sub-application.
The ticker of a sub-application starts with "parent application ticker:". Multiple applications can be created under one application to complete multiple independent calculation logics. For example, in the classic AMM DEX scenario, multiple LP sub-applications/tokens need to be created in one DEX application, such as "amm_dex:LP_BRC100_BTC".
Application status and address
In addition to the UTXO model, the BRC-100 protocol also introduces a state machine model to expand the computing capabilities of the protocol.
Applications, sub-applications, and addresses can all have state. For example, applications can hold tokens and addresses can have balances within the application. UTXO and state conversion are completed through the burn2/burn3 and mint2/mint3 instructions.
Calculation operations (COP) are used to represent specific calculation logic, that is, the conversion logic of application and address states.
For example, address A destroys 10 token1 to the application through the burn3 inscription. At this point the application owns this UTXO and 10 token1. The application can allocate these 10 tokens by changing any address or the internal state of the application through its computational logic. Then the address or application in the application that owns token1 can mint it through the mint3 command.
Permissions
The BRC-100 protocol introduces two roles: owner and administrator.
The address with the application deployment inscription is called the owner. Owners can track UTXO transfers deploying inscriptions. The owner of all child applications is the owner of the parent application.
Administrators are managed by owners, and administrators cannot manage other administrators. Owner and administrator permissions are strictly limited. They cannot censor users, they can only do: manage applications that have not started DAO, and complete mint2/burn2 calculation operations.
Administrators can be addresses, applications, or subapplications. Applications and sub-applications are mutual administrators by default and no additional settings are required, but sub-applications are not mutual administrators.
Inscriptions for burn2/burn3 need to be sent to the deployer of the application to be processed correctly.
The "mint2" directive requires that a portion of the tokens minted can only be allocated by the application/sub-application logic, and the application/sub-application needs to be the administrator of the tokens. The "burn2" directive has similar logic.
The inscriptions for burn2/burn3 need to be sent to the deployer of the application in order to be processed correctly according to the logic of the computational operation.
Decentralized governance of applications
The BRC-100 protocol stack introduces a governance protocol: BRC-101, which can govern applications that implement the BRC-100 or its extended protocol standards. After the application starts the DAO, it needs to complete governance through decentralized voting.
Application management includes updating application and sub-application properties, deploying sub-applications, and stopping applications. Application governance is on-chain governance. After the on-chain vote is passed, the application should be notified through the calculation operation:egov, and then the application will automatically perform governance after the time lock.
Deploy application/Token
In the BRC-100 protocol, there are two ways to deploy applications: one is to deploy directly using deployment instructions, and the other is to deploy through the governance protocol: BRC-101.
The first one is used to deploy the parent application and child applications whose configuration does not require governance, and the other is used to deploy the child applications that require governance.
minting tokens
The BRC-100 protocol provides three mint instructions: mint, mint2, and mint3, which are used to mint tokens in different scenarios.
When deploying your application, you need to set the number of tokens a user can mint (using the "mint" command). The remaining tokens will also be minted using the "mint" command.
"mint": User minting, fair minting, anyone can mint tokens for users, but the total amount minted by the "mint" operator cannot exceed the settings of the application's "max" and "mma" attributes. After minting, the circulating supply of the token will increase.
"mint2": Whitelist minting, the application records the number of users or applications that can mint, anyone can mint2 tokens for users or applications under the application rules. After mint2, the circulating supply of the token will also increase.
"mint3": Treasury mint, mint3 is the balance of users or applications in other applications, anyone can mint3 tokens for users or applications under the application rules. After mint3, the circulating supply of the token will not increase.
Burn tokens
Destruction is a newly introduced operation in the BRC-100 protocol. Users can inscribe a destroy operation and then transfer the inscription to the deployer of the application, similar to the semantics of a transfer operation. The burned tokens will then be destroyed or transferred to the application's balance.
Similar to the definition of the mint operation, there are three burn operators: burn, burn2, and burn3, which logically correspond to mint, mint2, and mint3 respectively. No additional configuration is required, all applications/tokens support these three burn instructions.
"burn": Public destruction, everyone can use instructions to destroy tokens. After the token is successfully destroyed, the circulation will be reduced, and the destroyed token cannot be minted again.
"burn2": whitelist destruction, according to the application's preset rules, after burn2 tokens are transferred to the application, the user's balance will be reduced, the status of the application will be updated accordingly, and the circulation will be reduced. In practice, logic such as liquidity removal in AMM DEX can be implemented through burn2.
"burn3": The treasury is destroyed. burn3 will reduce the user's token balance and increase the balance of the "to" application. In practical applications, mint3 can be used to complete the logic of exchanging tokens and increasing liquidity in AMM DEX.
Transaction taxes and deflation
The BRC-100 protocol introduces a new token trading mechanism: transaction tax and deflation. The application can set the transaction tax percentage, tax recipient and transaction black hole percentage. These settings only take effect when trading on AMM-based decentralized exchanges. Normal transfer, minting and burning operations will not trigger transaction taxes and deflation.
Computational operations
Computing operations are extended computing behaviors of the BRC-100 protocol. It is represented by the cop attribute, which is the smallest unit of the protocol's computing power. When used with the op operator: burn2/burn3/mint2/mint3, it can be understood as a state transition function, which defines how the status of the application and the user is updated under the corresponding op operator.
Oracle oracle
Oracle is a common requirement for blockchains to interact with off-chain parties, and has been well implemented and applied on blockchains such as Ethereum. Without oracles, smart contracts on the blockchain would be completely limited to on-chain data. But compared with blockchain, the BRC-100 protocol has very special characteristics.
It not only has the computing power of the blockchain, but also relies on off-chain indexers to complete the calculations. At the same time, off-chain indexers are able to communicate directly with other blockchains or meta-protocols, but blockchains cannot do this, which means that the indexer can verify any data off-chain or on-chain with enough attestation data Meets the requirements of Oracle's BRC-100 protocol.
For example: verifying the transfer of BTC or BRC-20 assets, verifying the ETH price on a certain block of Ethereum, etc.
In other words, in the BRC-100 protocol, oracles have a new paradigm: proof and verification, in which users submit proof data, and the indexer serves as an Oracle Verifier to verify the user-submitted proof data outside the protocol, without the need for an independent Oracle service .
In the BRC-100 protocol, the burn2/burn3/mint2/mint3 instructions natively support the proof attribute, which is used to submit proof data outside the protocol. The indexer can verify the proof data to ensure the consistency and correctness of the state. The proof can be a transfer proof, a Merkel tree proof, a zero-knowledge proof, a price proof, etc. It can be used in scenarios such as bridging assets, airdrops, and Bitcoin layer 2 , loan settlement, etc.
relay protocol
The meta-protocols on Bitcoin are heterogeneous and cannot communicate with each other. Different protocols are similar to different blockchains, they share the security of the Bitcoin blockchain and have different computing power. Additionally, the meta-protocol cannot communicate directly with other blockchains: such as Ethereum, nor can it use assets on other blockchains.
Therefore, the BRC-100 protocol stack requires a relay protocol to complete the communication between Bitcoin, meta-protocol, blockchain and BRC-100 protocol, bridge assets on other protocols or blockchains to BRC-100, and participate in Decentralized applications such as DeFi. At the same time, BRC-100 will have multiple relay protocols due to the diversity of protocols and blockchains.
First, we will release: BRC-103, responsible for bridging assets between Bitcoin, BRC-20, and BRC-100.
When bridging an asset from a meta-protocol or blockchain (source) to the BRC-100 protocol (destination), in order for the indexer to verify the correctness of the transfer, proof data needs to be submitted using the "mint2" instruction, which is called a proof of transfer.
Transfer proof means that when minting anchor assets on the target protocol (BRC-100), you need to submit the transfer data on the source side (such as Bitcoin, BRC-20 or other blockchains) as proof at the same time, which can be a transaction hash. Or inscription ID.
So that all BRC-100 indexers can verify the correctness of the minting of the anchored assets.
Transfer Proof is a very important application of Oracle BRC-100 protocol.
Protocol use cases
Since BRC-100 is extended from BRC-20, it essentially has all the application scenarios of BRC-20, but the application scenarios of BRC-100 are far more than that. We can still expand on the basis of the BRC-100 protocol. Here are some officially listed extension protocols, some of which are already under development:
BRC-101 (released)
The decentralized on-chain governance protocol of the BRC-100 protocol stack defines how to update properties of parent/child applications/tokens, stop applications, and add child applications.
In addition, BRC-101 can also complete off-chain governance through decentralized voting.
BRC-102 (under development)
The automated liquidity protocol defines how to exchange tokens of the BRC-100 protocol stack through the automated market maker (AMM) algorithm. The calculation logic will be similar to Uniswap on Ethereum.
BRC-103 (under development)
Relay protocol between BTC, BRC-20 and BRC-100. Meta-protocols on Bitcoin are heterogeneous and cannot communicate with each other. Different protocols are similar to different chains. They share the security of the Bitcoin blockchain and have different computing capabilities.
Therefore, the BRC-100 protocol stack will release multiple relay protocols to complete communication between meta-protocols, different chains and BRC-100, and bridge other protocols and assets on the chain to BRC-100 to participate in DApps such as DeFi.
BRC-104
The liquidity mining protocol defines how to obtain token rewards after staking tokens.
The pledged token can be any BRC-100 based token, such as the BRC-103 protocol’s liquidity pool token, or it can be the same token as the reward token. Additionally, BRC-104 will support lock-up periods to lock staked tokens.
BRC-105
The airdrop protocol defines how to efficiently airdrop tokens to multiple addresses.
The protocol will use a Merkle Tree to complete airdrops to save transaction fees since all original airdrop data does not need to be made public on Bitcoin. Users only need to submit Merkle Proof to prove that they have airdrops during "mint2", and then all indexers can verify the correctness to complete the airdrop.
BRC-106
The decentralized stablecoin pool protocol defines how to generate stablecoins through collateral.
The calculation logic will be similar to MakerDAO3’s DAI on Ethereum.
BRC-107
The lending pool protocol defines how to borrow assets through collateral.
The computing logic will be similar to Aave on Ethereum.
BRC-108
Automated liquidity protocol for stablecoins.
BRC-109
A decentralized trading protocol for perpetual futures.
BRC-110
The relay protocol between the EVM compatible blockchain and BRC-100 defines how to bridge assets on the EVM compatible blockchain to BRC-100.
BRC-111
The Bitcoin Layer 2 Verification Protocol defines how to verify Bitcoin Layer 2 proof data like Layer 2 smart contracts on Ethereum.
「6」BRC-420 protocol
Agreement proposed
After the BRC-20 protocol was proposed, another new experimental protocol BRC-420 appeared on 2023.9.19, also known as the Metaverse protocol.
Agreement concept
BRC-420 is an interesting experiment. It is the first metaverse protocol in the Ordinals protocol and is an asset protocol based on the Bitmap protocol.
By combining multiple inscriptions into a complex asset, such as a game item, animations and effects, or a game module in the Metaverse. Created assets ranging from small characters and pets to full game scripts and virtual machines.
Due to the open source nature of these assets on the chain, any client can run or verify them, fully embodying the "Client Agnostic" spirit of the full-chain game.
 The BRC-420 agreement contains two parts, one is the Metaverse Standard, and the other is the Royalty Standard. The former defines an open format for assets in the Metaverse, while the latter sets economic standards for creators. On-chain protocol.
The BRC-420 agreement contains two parts, one is the Metaverse Standard, and the other is the Royalty Standard. The former defines an open format for assets in the Metaverse, while the latter sets economic standards for creators. On-chain protocol.
 BRC-420 opens up possibilities for Ordinals’ on-chain gaming and modular blockchains. Different creators can contribute different modules, and new creators can innovate based on the innovations of their predecessors. This has led to a proliferation of various innovations within the Ordinals ecosystem, benefiting all participants.
BRC-420 opens up possibilities for Ordinals’ on-chain gaming and modular blockchains. Different creators can contribute different modules, and new creators can innovate based on the innovations of their predecessors. This has led to a proliferation of various innovations within the Ordinals ecosystem, benefiting all participants.
Protocol development
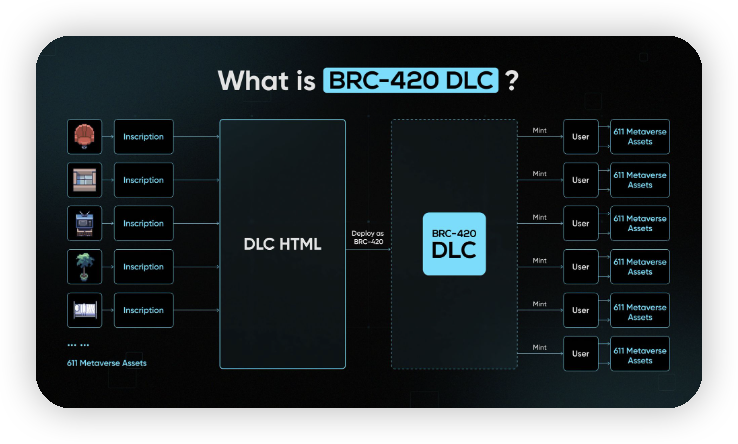
Currently, BRC-420 released the BRC-420 DLC on 2023.11.3, which can integrate thousands of meta-inscriptions into 1 DLC. After deployment, users can earn thousands of meta-assets in a single minting.
「7」Runes Protocol
Agreement proposed
After the BRC20 protocol came out, Casey felt that it was not a good idea to create fungible tokens on Bitcoin. 99% of fungible tokens were scams and would not disappear in the short term. Creating a good fungible token protocol for Bitcoin could bring significant transaction fee revenue, developer attention, and users to Bitcoin.
Therefore, Casey proposed the Runes protocol based on UTXO technology on September 26, 2023.
The design of the Runes protocol may also be influenced by ARC20. It chooses to write Token data directly in the UTXO script, which includes the Token ID, output and quantity.
Obviously, the implementation of Runes is very similar to ARC20, and the token transfer is directly handed over to the BTC mainnet for processing. The difference is that Runes writes the number of Tokens in the script data, which gives it higher accuracy than ARC20.
But at the same time, the complexity has become higher, making it difficult to directly utilize the combinatorial nature of BTC UTXO like ARC20.
Protocol development
After the launch of the Runes protocol, since Casey's development energy was mainly on the Ordinals protocol, the development of the Runes protocol has been relatively slow. This is why Benny quickly overtook the development of the Pipe protocol after the release of the Runes protocol.
During the Taiwan Blockchain Week in December, Casey also announced the time when the Runes protocol will be launched on the mainnet at the Taipei event. It will be at block height 840,000, which is the time of the next BTC halving, probably at the end of April 2014. .
Summarize
After investigating BTC asset issuance plans, I fully felt their charm, so I also expressed some of my own subjective opinions:
- The issuance of BTC assets has ignited the explosive development of the BTC ecosystem this year, although everyone has mixed opinions about them. But when we look at the development of the BTC ecosystem in the abstract, it is actually inseparable from an important thing - "narrative."
- As I mentioned in my previous thoughts, the product needs to be supported by a good narrative, otherwise it will be easy to face the embarrassing situation of only having the product but no users. The various major asset issuance plans also prove this, such as first is first, the various imaginations that the agreement brings to the ecology, official endorsement, etc., these are all concrete manifestations of the narrative.
- Similarly, we cannot deny the contribution this wave of asset issuance has made to the BTC ecosystem. Although from a technical perspective, most asset issuance solutions may not have any substantial breakthroughs in the limitations of Bitcoin, they not only provide a rare stress test for major public chains, but also bring some possible routes for Bitcoin's future development.
- Through these waves of inscription craze this year, the long-tail effect brought by inscriptions has gradually expanded from the initial Bitcoin to inscriptions on other public chains. With the popularity of inscriptions among the people, we have also felt some shortcomings of the current Bitcoin mainnet, such as high gas fees, slow transaction speed, etc., which also shows the necessity of BTC expansion plan.
- Even though the expansion plan has been planned by project parties a long time ago, it has always been tepid. Now more and more users are paying attention to the BTC ecosystem under the craze of Inscription, and this has also accelerated the development of the BTC expansion plan in disguise. develop.
- Currently, the existing expansion solutions are mainly divided into three categories: side chain/lightning network/native L2. However, their leading advantages have not yet been determined in a certain direction, and they are still in the stage of competition with each other. As for whether there will be more blooms in the future or There will be a certain direction that will be a blockbuster, we can look forward to it, and this is also the direction that can be focused on next.
- In the research on asset issuance solutions, there is a clear trend, from the initial launch of the Ordinals protocol, to the subsequent BRC-20 improved protocol based on Ordinals, to the BRC-100 decentralized computing protocol (wanted to Based on this, we will continue to expand and introduce the gameplay of the DeFi ecosystem into Bitcoin), BRC-420 Metaverse Protocol (bringing the possibility of introducing games, music, etc. into Bitcoin), ARC-20 (new asset issuance parallel to BRC-20) plan) and so on.
- The asset issuance plan has evolved from making some basic improvements to the existing asset issuance protocol to making some large-scale ecological layout based on a certain asset issuance protocol in response to the needs of the BTC ecosystem (such as oracles, DeFi, games, etc.) Even publish a new type of asset issuance protocol to formulate rules.
- The ecological development of BTC is still in its early stages. Whether it is in Web2 or Web3, there is a phenomenon that whoever masters the power to formulate rules first can have users. Therefore, there are still many wealth opportunities. We must take a comprehensive look at the development of the BTC ecosystem. The craze for inscriptions will eventually cool down. We cannot just focus on the tail of asset issuance, but we should also look at how to use asset issuance. Accelerate the development of the entire BTC ecosystem in other aspects.
- Of course, there are also some different opinions on this aspect, such as teacher NingNing’s views on BTC L2 https://twitter.com/0xNing0x/status/1737010523374563744, rational discussion.
- Although it is still in the stage of rushing first and then researching, everyone’s butt determines their head. But I still want to remind everyone to pay attention to risks when investing, and write down your own investment logic clearly. Whether you are pursuing the short term or looking at the long term, different logics and different strategies. In terms of investment, we should try our best to integrate knowledge and action. I believe in the saying "You will never make money beyond your knowledge, even if you make it now, you will spit it out later."
Finally, thank you all for reading this. The original intention of the article is to let you have a better and more comprehensive understanding of the development of the BTC ecosystem. You are also welcome to come to me to communicate. In the coming time, I will express some opinions from time to time, and I will also write another article on the expansion plan, so stay tuned.








