ZKF Fair Launch
In the current Ethereum ecosystem, zk-rollup technology is widely recognized by the industry for its significant advantages in network expansion and transaction cost reduction. This technology greatly improves the throughput of the network by packaging a large number of transactions and processing them off-chain, while reducing user transaction fees, making the application of blockchain technology more practical and economical.
Against this background, ZKFair, the first EVM-compatible Layer 2 (L2) platform developed based on Polygon's CDK and Celestia database, launched a 48-hour Fair Launch event on Christmas Eve 2023. The purpose of the event is to issue its new token ZKF. ZKFair plans to issue a total of 10 billion ZKF tokens. Participants can obtain air investment qualifications by performing transfer operations on the ZKF chain and consuming gas. This mechanism ensures fairness in token distribution, as the number of tokens obtained will be proportional to the amount of gas consumed. In addition, 25% of ZKF tokens will be airdropped to members who have contributed to the community after the event, while the remaining 75% will be fairly distributed to participants of this Fair Launch.
Token issuance model
1. Traditional Token Issuance
The traditional token issuance method usually refers to the project party issuing tokens directly to investors through private sales, pre-mining or public sales. This approach may not have clear specifications and processes, and may lack the participation of exchanges or other third-party platforms. It may include early-stage private investment rounds, distribution of tokens to early backers, development teams or consultants, etc. This issuance method may be less transparent and less secure because it is completely controlled by the project party.
2. ICO (Initial coin offering)
An ICO is an early form of token sale, similar to an initial public offering (IPO) in traditional finance. In an ICO, a project sells newly created tokens to the public, usually to raise funds for the development and operation of the project. Investors usually purchase tokens with the expectation that the tokens will increase in value in the market in the future. ICO led the bull market from 2017 to 2018, but its reputation has been damaged due to regulatory issues and fraudulent behavior by some project parties, and it is now rarely used.
3. IEO (Initial Exchange Offering)
IEO is a method of issuing tokens through a cryptocurrency exchange. In an IEO, the exchange conducts due diligence on the token project and provides a venue for the token sale on its platform. Investors need to register an account on the exchange and purchase new tokens through the platform. IEOs are generally considered safer than ICOs because the participation of an exchange provides a level of trust and verification to investors.
4. IDO (Initial DEX Offering)
IDO is conducted on a decentralized exchange (DEX). It does not rely on traditional centralized exchanges, but directly issues and sells tokens on DEX through smart contracts. The advantages of IDO include higher transparency and lower participation threshold, making it a fairer and more in line with the characteristics of the web3 industry. IDO helps projects quickly obtain liquidity because tokens can be traded on DEX immediately upon issuance. However, in actual applications, IDO is mostly used as an auxiliary issuance means, and its proportion in the total issuance is not high.
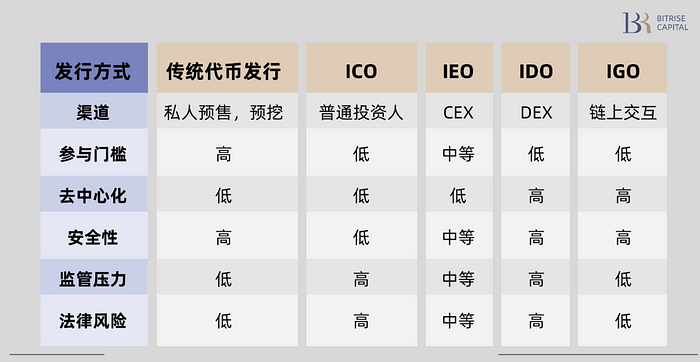 IGO (Initial Gas Offering)
IGO (Initial Gas Offering)
This ZKFair Fair Launch can be considered a revolution in token distribution. His form does not fit any previous mold. Participants receive token airdrops in proportion to the gas burned through their on-chain transfer behavior; the issuer uses the gas paid by participants as the income of this token issuance. This is innovative in terms of airdrop rules and financing forms. After internal discussions, Bitrise Capital believes that this new form of token issuance can be called IGO (Initial Gas Offering), and the biggest features of IGO can be summarized as the following two points:
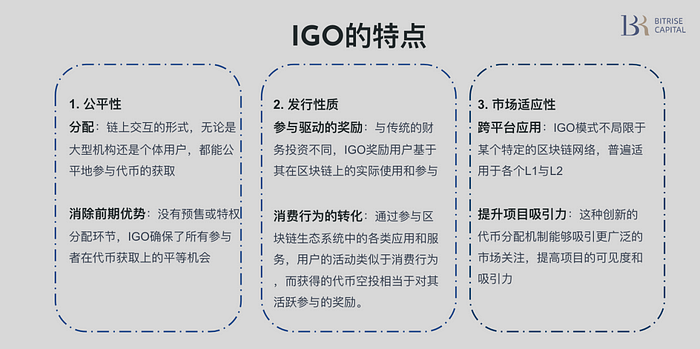
 1. Issuance standards
1. Issuance standards
ZKFair’s Fair Launch demonstrates its fairness in the token issuance mechanism. The key is that this mechanism has no restrictions on the identity of the participants: whether they are large institutions or individual retail investors, as long as they perform corresponding operations on the ZKFair chain during the event, they will automatically be eligible for the ZKF airdrop. In addition, there is no whitelist or pre-sale process during the ZKF issuance process, ensuring equal participation opportunities. Of the total 10 billion tokens, in addition to 2.5 billion distributed to community contributors, the remaining 7.5 billion tokens are fairly distributed to all event participants through airdrops. The entire release activity is divided into four phases, each lasting 12 hours. The project party has set a total GAS consumption limit of 3 million USDC, and an average distribution of 1.875 billion ZKF worth 750,000 USDC in each stage. In each stage, if the gas consumption exceeds the predetermined limit of 750,000 USDC, the project team will calculate the number of airdrops the user should receive based on the proportion of the gas consumed by the user in that stage to the total gas consumption in that stage. For the excess gas consumed, the project party promises to return it in proportion after the event.
For example, if a total of 1 million USDC gas is consumed in the first phase, user A who consumed 10,000 USDC will receive an airdrop of approximately 18.75 million ZKF after the event ends, and 2,500 USDC will also be returned. This mechanism ensures that ordinary participants will not lose their participation opportunities due to fierce competition from big-fund players. At the same time, by returning excess gas costs proportionally, this mechanism also solves the problem of unnecessary burning of gas costs in previous airdrop activities. Such rule design not only reflects careful consideration in fair issuance, but also demonstrates ZKFair's commitment to fairness in action.
2. Nature of issuance
Under the Initial Gas Offering (IGO) framework, the roles and motivations of participants are significantly different from the traditional token issuance model. This new issuance mechanism is not based on direct financial investment, but on active participation and contribution to the ecosystem. In this framework, participants obtain air investment qualifications through interaction and transaction activities on the ZKFair chain, which includes using various applications on the chain and thus consuming gas. This type of participation is closer to consumption behavior, where users actively participate by using services and applications in the ecosystem, and in return, they receive token airdrops as additional rewards.
This model can be compared to traditional business promotions. For example, in a shopping mall's anniversary event, consumers can receive additional gifts after spending a certain amount in the shopping mall. Here, the mall (i.e., the ZKFair ecosystem) provides a variety of goods and services for consumers to choose from, and the gifts are equivalent to the token airdrops that users receive by participating in ecosystem activities. This model not only encourages users to participate more deeply in the ecosystem, but may also reduce the legal risks associated with traditional token issuance to a certain extent, as it places more emphasis on participation and consumption rather than direct financial investment.
In addition, this design of the IGO model also reflects the emphasis on user participation in the field of blockchain technology and cryptocurrency, emphasizing the establishment of a more inclusive and dynamic ecosystem. This model encourages users to experience and support blockchain projects through actual use of applications and services, thereby promoting the popularization and innovation of technology. In the long run, the IGO model can not only bring a broader user base to the project, but also help form a more active and healthy blockchain ecosystem.
 Market prospects of IGO
Market prospects of IGO
The Mint project has played a vital role in the current bull market. Its success lies not only in effectively solving the asset issuance problem in the BTC ecosystem, but also in that the "fair mint" principle it adopts has become a key narrative for the project's success. The core of this principle is to create a fair and open market environment driven by a wide range of retail investors, ensuring that everyone has the opportunity to participate. The openness and inclusiveness of this market environment is one of the main reasons why the market gives high recognition to the inscription project.
On this basis, the emergence of the IGO (Initial Gas Offering) model can be said to be a successful reference to the core concept of the Inscription project. The IGO model emphasizes openness in the early stages of the project and allows a wider range of ordinary investors to participate. This not only enhances the attractiveness and visibility of the project, but also effectively meets the financing needs of the project party and brings benefits to actively participating users. substantial returns. IGO is designed with both flexibility and universal applicability in mind, allowing it to be widely used in a variety of Layer 1 (L1) and Layer 2 (L2) blockchain networks.
Both the Inscription project and the IGO model reflect the current high emphasis on innovation and fairness in the cryptocurrency market. They not only provide new opportunities for participants, but also promote the healthy development of the entire blockchain ecosystem. With the application and development of these models, we have reason to believe that they will continue to have a profound impact in the field of cryptocurrency, stimulate market vitality, and promote the attention and activity of more public chains. Just like the Inscription project has brought major breakthroughs to the BTC ecosystem, the IGO model is also expected to trigger a series of new innovations and active trends in the cryptocurrency field.
 Industry evaluation
Industry evaluation
iZUMI Jimmy:
"ZKFair is the first Ethereum second-layer module blockchain to be launched fairly using the IGO model. iZUMi cooperates with ZKFair. What values is the team's long-term accumulated technical strength, and more importantly, respect for the community, user-friendliness, low valuation, and transparency. A fair and innovative token distribution model. As the earliest ecological supporter of multi-chain protocols and ZKFair, iZUMi expects more public chain partners to learn from ZKFair’s successful experience and achieve success. iZUMi will also launch iZUMi Layer2 Fund in 2023 to provide The cooperative public chain provides sufficient on-chain liquidity on Day 1."
Bitrise Capital Kevin:
“ZKFair is a very successful and high-profile project case recently. I think its case can be called a textbook level. I find this to be an innovation and try to use the IGO method to define this new way of issuing tokens. From this project, we have seen that innovation in web3 can come from self-drive and from bottom-level innovation in the community. This reminds me of the term "self-finance". In the case of ZKFair, we see that it is not just about the business model. Breakthrough, and pays great attention to de-financialization. The IGO model allows us to see a new way of starting projects and downplays the financial attributes. Just like when you go to a supermarket to shop, you consume and get basic services, and then the supermarket I’ve given you points again. For the cold start of the project, this not only attracts users, but also solves the problem of early start-up funds for the project. Of course, the current economic model of ZKFair still needs to be improved, but I am impressed by the self-iteration ability of the ZKFair team Very promising, especially when problems are encountered during the project start-up process, it can quickly adjust to adapt to market changes."
Lumoz Alvaro:
“Lumoz is committed to developing and promoting advanced applications of blockchain technology. The project we are collaborating on, ZKFair, is a Layer-2 solution based on ZK-Rollup technology, which integrates Polygon’s Co-Development Kit (CDK) and Celestia’s Data Availability Layer (DA), designed to improve transaction processing efficiency and maintain full compatibility with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM). ZKFair chose the USDC stablecoin as a means of payment for transaction fees to reduce network congestion and increase transaction speed. In addition, ZKFair's architectural design supports a decentralized prover network, which reflects our commitment to network autonomy and sustainable development. This decentralized network structure is designed to increase network participation and achieve greater success through a community governance model. Transparent and fair operations.
The launch of Fair-L2 LaunchBase marks Lumoz’s solid step in supporting emerging ZK-L2 projects. This platform is designed to provide key technical support for subsequent new projects and promote their smooth launch. The partnership with Polygon also takes advantage of ZK-Rollup to improve transaction efficiency and network security. "








