"Bitcoin Layers: Tapestry in the Era of Trustless Finance" is a research report on the development of the entire Bitcoin ecosystem. The report was written by Spartan Group team member Kyle Ellicott and multiple experts who provided feedback and insights and generously took their time to review the final version you are reading today. This part is the second in a series of four in this report.
Author/Contributor
Kyle Ellicott, Yan Ma, Darius Tan, Melody He
Evolving Bitcoin Issues
Since Bitcoin's inception in January 2009, its role and potential have evolved significantly. Many initially viewed Bitcoin as a beacon of hope for an inflation hedge, store of value, and democratization of the financial system. Its role in shaping the future of decentralized applications (dApps) has only recently come into focus. By 2023, nearly 14 years after launch, this evolution has become evident as Ethereum enjoys increasing success with applications and Bitcoin continues to grow and dominate as an asset on Ethereum status, developers have introduced numerous infrastructure “layers” (Layer-1 or L1) on top of the Bitcoin Core network. ). These Bitcoin layers enhance scalability and programmability, leveraging Bitcoin's stability and security while leveraging its over 850B+ value and increasing unproductive capital without changing L1. We are now seeing significant advancements in Bitcoin’s layers, allowing them to act on BTC assets and inherit Bitcoin’s restructured security and finality while overcoming its programmability and performance limitations. Going forward, these additional layers of infrastructure unique to the Bitcoin ecosystem will become the building blocks for many people to build applications.
Despite these advances, much of the necessary infrastructure remains in the development and experimental stages . This journey is not without precedent. In 2017, early NFT and token projects flooded the Ethereum network, resulting in slow transactions and high transaction fees. This has reignited the ambition of the developer community to build more robust infrastructure, providing the network with the necessary scalability and flexibility to support the needs of even a small subset of potential applications. The Ethereum community debated and experimented with multiple approaches, ultimately settling on a layered approach to improve performance and scalability, resulting in a well-utilized Ethereum (Layer 2 or L2) with billions in total value locked USD (TVL). Ethereum’s experience provides Bitcoin with valuable insights into the scaling, growth, and decentralization of applications and its underlying network.
Similar to Ethereum, Bitcoin went through a pivotal moment with the introduction of ordinal numbers and the shift to “building on Bitcoin.” Nearly six years later, Bitcoin has been experiencing a similar moment recently, thanks to the release of ordinal numbers (based on ordinal theory and the ability to burn data on the Bitcoin chain) and a new cultural shift toward "building on Bitcoin." This shift triggered a revolution in the development of infrastructure and scaling layers on top of Bitcoin L1. Not only are we now seeing new protocols and token standards (BRC-20, etc.), we are also seeing the development of new Bitcoin L2s that have begun to unlock the Bitcoin economy and give us a glimpse into unlocking the $850B+ dormant potential. Capital and the industry’s most stable and proven technology to date. As a result, Bitcoin theory is being redefined: Bitcoin is no longer just a store of value or asset, but is becoming a fundamental infrastructure in its own ever-expanding economy. Similar to Ethereum’s growth trajectory, the Bitcoin ecosystem may experience a surge in user adoption driven by viral use cases, kicking off the flywheel. In turn, this will attract more developers and increase the ecosystem’s application TVL. Considering that Bitcoin’s $850B market capitalization is approximately 3.1 times that of Ethereum’s $270B, and its application TVL is currently only a fraction of Ethereum’s $76B, at around $320 million, this scenario provides a great opportunity for the Bitcoin ecosystem The potential 740x growth opportunity to reach similar maturity to Ethereum in terms of applications does not include additional liquidity inflows as the ecosystem gains momentum.
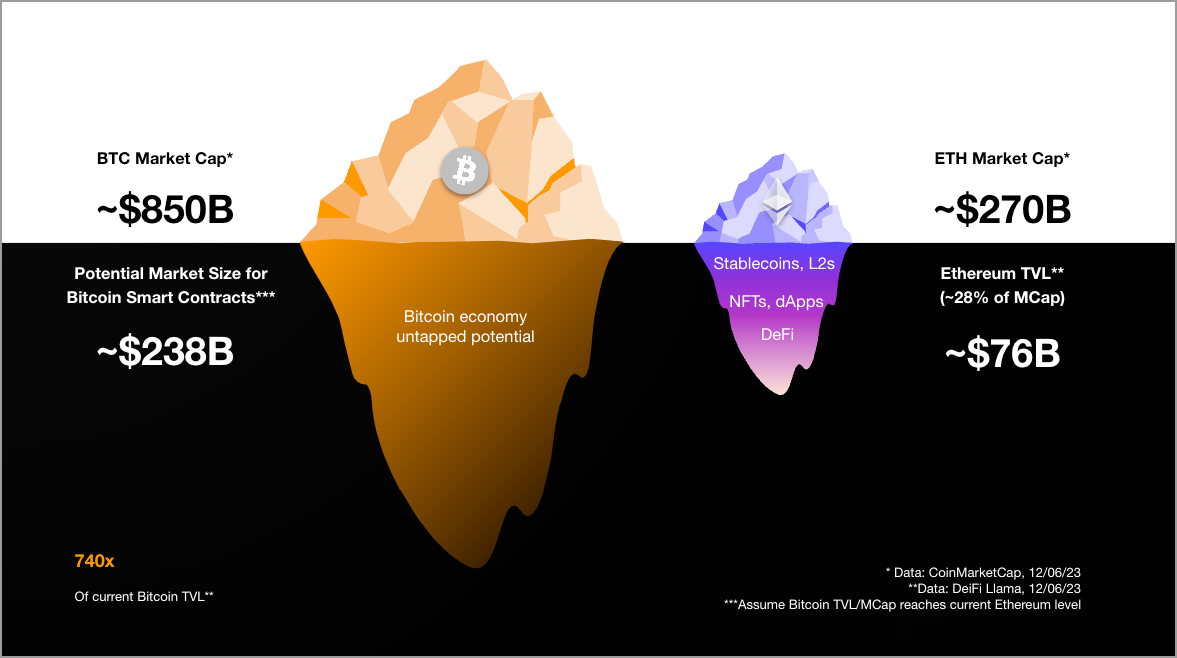 The huge market potential of Bitcoin smart contracts
The huge market potential of Bitcoin smart contracts
Network and assets
In order to understand the changing narrative, one needs to distinguish between Bitcoin, the network (i.e. Bitcoin Core, Bitcoin L1, the Bitcoin blockchain) and BTC (the digital asset). Many people have been confused because the word "Bitcoin" itself can refer to both, which although very different, are closely related. To avoid confusion, this report adopts the standard of capitalizing Bitcoin when referring to the network, and uses BTC as the token or digital asset.
- On October 31, 2008, shortly after the release of the famous white paper introducing a peer-to-peer electronic cash system, the Bitcoin network went online. Its Genesis Block was mined on January 3, 2009. Since its launch, the network has remained stable while other networks have experienced outages, attacks, and more, proving its viability as the ultimate L1. Bitcoin has shown that it can provide trust without centralized intermediaries and serve as the ultimate decentralized settlement layer for transactions, assets, and future applications. However, developing applications on Bitcoin other than the BTC asset itself has been difficult due to Bitcoin's lack of flexible programmability and the inability to be trusted to write to the network from outside. Bitcoin differs from Ethereum in one important way: it does not natively support smart contracts, which enable decentralized applications to use BTC as an asset or settle transactions on Bitcoin L1.
- The digital asset Bitcoin has traditionally been considered a store of value and an inflation hedge against volatile global financial markets. Its creation provides for the first time a digital, permissionless, censorship-resistant, and scarce global asset. It remains the top crypto asset with a market cap of over $850B, reaching $1.25 trillion at its peak in November 2021. However, even today, more than a decade later, BTC is still very much a SoV with little other utility or capabilities. Go beyond this without further development.
The Bitcoin layer provides a solution to this problem. BTC, the asset, is the original use case of Bitcoin L1. If a Bitcoin layer (e.g. Bitcoin L2) could run smart contracts that could use BTC as an asset, then Bitcoin L1 could retain its key advantages of security, durability, and decentralization while allowing on other Bitcoin layers Unlimited experimentation. Applications using BTC as an asset can run L2 tracks and settle transactions on L1. These L2 rails can also inherit more and more security from L1 while providing faster and more scalable transactions. This enables “Bitcoin-based” and redefines Bitcoin theory as an asset and infrastructure for the ever-expanding Bitcoin economy.
Based on Bitcoin
Building on the Bitcoin blockchain has presented unique opportunities and challenges over the years. Unlike other blockchains, Bitcoin started out as an asset or "currency" rather than as an application platform, whereas other blockchains started explicitly as application platforms. In order to understand why Bitcoin has been relatively late to develop into a mature ecosystem relative to other ecosystems, it is necessary to look back at its origins:
- The Bitcoin network welcomes everyone, regardless of background or technical knowledge . Bitcoin's code is open source and can be copied and modified. This openness fosters a culture of experimentation, with no single group or individual deciding the direction of blockchain.
- The network's limited interoperability results in unique derivatives. Bitcoin derivatives are completely independent networks, with their own independent assets, and lack "backward compatibility" with the original Bitcoin network. Therefore, in its current state, BTC assets are limited to the Bitcoin network and cannot be directly removed or transferred to other blockchain networks.
- The lack of programmability presents a significant obstacle to building. Bitcoin does not have flexible programmability , because it does not provide smart contracts, which hinders its use as an application development platform. This and its severe performance limitations are a key challenge when considering Bitcoin as the platform on which it is built.
- Bitcoin L1 needs help with speed and scale. The Bitcoin network is very limited in its ability to confirm transactions quickly or process large amounts of transaction data on its platform in a short period of time. Due to the desperate desire to remain decentralized, the records in the Bitcoin blockchain (called blocks) are necessarily limited in size and frequency. The Bitcoin network's on-chain transaction processing capabilities are limited by an average block creation time of 10 minutes and a raw block size limit of 1 megabyte. The average transaction confirmation time is between 10 and 30+ minutes, neither of which is close to sufficient. most applications.
Addressing these characteristics requires understanding the blockchain trilemma . Applying this to Bitcoin's L1 reveals a network that is decentralized (a) and secure (b) but lacks direct scalability (c), processing only about 3 to 7.8 transactions per second (TPS). This limitation highlights the need for alternative solutions or additional layers to compensate for the sacrifices inherent in the network.
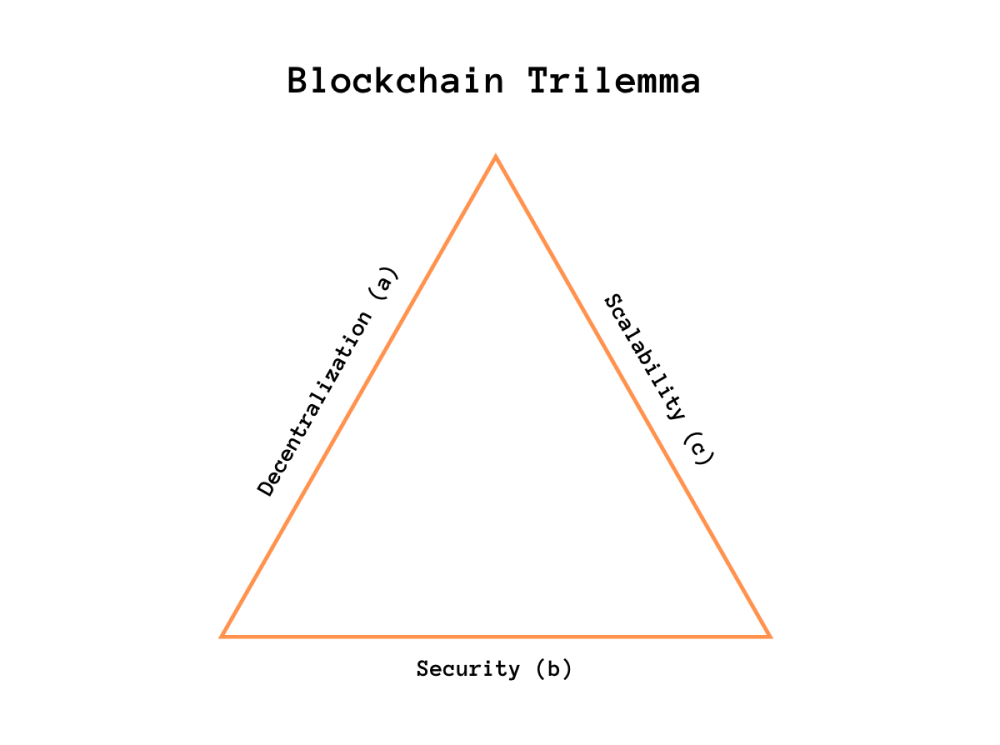 The urgency for scalable solutions led to the early creation of the Ethereum network , which despite lacking the security and decentralization of Bitcoin, was developed for applications such as L2 (i.e. Arbitrum, OP mainnet, etc.), subnets, etc. Providing the necessary scalability solutions to achieve significant growth (i.e. Avalanche's Evergreen ) and more. Similar trade-offs have been made across the industry, leading to a wave of development focused on scaling solutions such as sharding, nested blockchains, state channels, supernets (i.e. Polygon Edge ), application chains, and L2 (or sidechains) , as some prefer).
The urgency for scalable solutions led to the early creation of the Ethereum network , which despite lacking the security and decentralization of Bitcoin, was developed for applications such as L2 (i.e. Arbitrum, OP mainnet, etc.), subnets, etc. Providing the necessary scalability solutions to achieve significant growth (i.e. Avalanche's Evergreen ) and more. Similar trade-offs have been made across the industry, leading to a wave of development focused on scaling solutions such as sharding, nested blockchains, state channels, supernets (i.e. Polygon Edge ), application chains, and L2 (or sidechains) , as some prefer).
For years, the focus has been primarily on Ethereum and the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM)-compatible ecosystem. However, as of 2023, there has been a clear shift with the recent upgrades to Bitcoin L1 and Ordinals. Developers are increasingly turning their attention back to Bitcoin, specifically addressing its scalability – an important part of Bitcoin’s L1-specific triangle dilemma.
Scaling Bitcoin: Critical L1 Upgrade
Major advancements in Bitcoin’s scalability began withthe Segregated Witness (SegWit) update in July 2017. The upgrade marks a key change that separates the unlocking code into a dedicated section for each Bitcoin transaction. This reduces transaction times and increases block capacity beyond the original 1MB limit set by Satoshi Nakamoto in 2010 .
SegWit introduced a revised block size measurement using weight units (wu) , later called vsize/vbyte, allowing up to 4M weight units (4wu) per block, effectively extending the block size to approximately 4MB. This change is designed to be backwards compatible with all previous Bitcoin Core versions, significantly improving transaction efficiency.
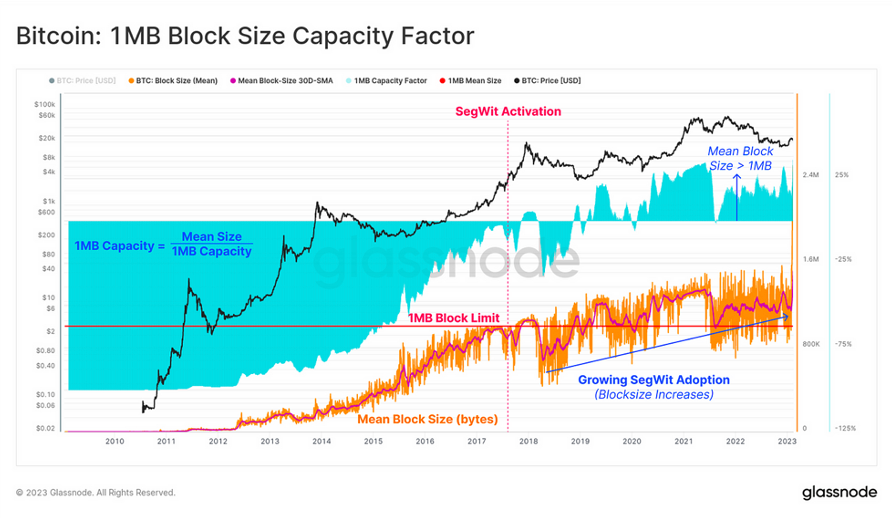 Bitcoin: 1MB block size capacity factor. Source: Glassnode
Bitcoin: 1MB block size capacity factor. Source: Glassnode
SegWit achieves this by splitting the data structure, separating the "witness" data in the transaction (including signatures and scripts) into an entirely new part of the Bitcoin block called "transaction data", which contains the details of the sender, receiver, etc. Information The introduction of this structure splits the new 4wu block size into:
- Witness data has a count per vbyte of 1wu or 25% of the weight per vbyte compared to transaction data.
- Compared to witness data, transaction data per vbyte is 4wu, which is four times the weight per vbyte.
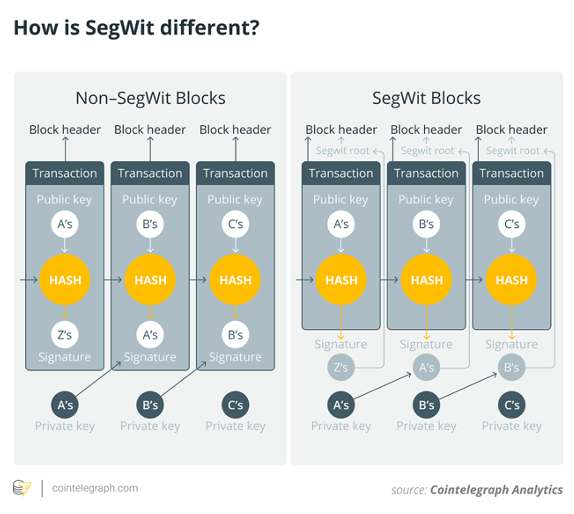 How is SegWit different? Source: Cointelegraph
How is SegWit different? Source: Cointelegraph
After SegWit, the next major upgrade activated in November 2021 is called Taproot . It is a soft fork that removes the limit on the maximum number of witness data footprints per transaction, resulting in faster transactions, enhanced privacy with Merkelized Alternative Script Trees (MAST), and more efficient keys using Schnorr sign. Taproot also facilitates asset transactions on Bitcoin L1, introducing protocols such as Pay-to-Taproot (P2TR) and Taproot Asset Representation Overlay (Taro).
- Taro powered by Taproot is a proposed protocol for issuing, sending and receiving assets on Bitcoin L1 and the Lightning Network, which launched its mainnet alpha launch in October 2023.
- Schnorr signatures unlock key aggregation by introducing the ability to combine multiple public keys and signatures into one. In short, combining multiple signatures for verification rather than aggregating them individually can provide greater transaction efficiency.
- MAST hides any preset conditions associated with the transaction. Unused results are not published on-chain, increasing privacy and compressing transaction sizes, thereby reducing data usage.
- P2TR has added a new way to spend Bitcoin using Taproot addresses.
These L1 upgrades lay the foundation for further development of the Bitcoin layer, which has been quietly happening in the background. It wasn't until the release of Ordinals that Bitcoin-based builds returned to the spotlight, marking a new era of Bitcoin scalability and functionality.
Ordinals revive Bitcoin builder culture
Despite the L1 upgrade, Bitcoin development activity experienced a period of lull until 2022 following the conservative outcome of the 2017 “block size war”. This relatively slow pace of development can largely be attributed to a primary focus on maintaining Bitcoin Core L1 and less attention on developing the broader infrastructure required for the vast ecosystem. Of Bitcoin's limited development activity, work has been concentrated in emerging ecosystems such as Stacks (more than 175 monthly active developers) and Lightning, the latter of which accounts for only a small portion of the industry's developers.
With the emergence of Ordinals in December 2022, the development landscape of Bitcoin has undergone a major shift . Ordinals' ability to create immutable on-chain digital artifacts has not only reinvigorated the Bitcoin developer community but is expected to grow into a $4.5B market by 2025. More and more developers are looking beyond their sole focus on Ethereum. These developers are constantly expanding their scope to incorporate Bitcoin L2’s framework. This key development signals a resurgence of engagement and innovation within the Bitcoin ecosystem, setting the stage for a new era of growth and technological advancement.
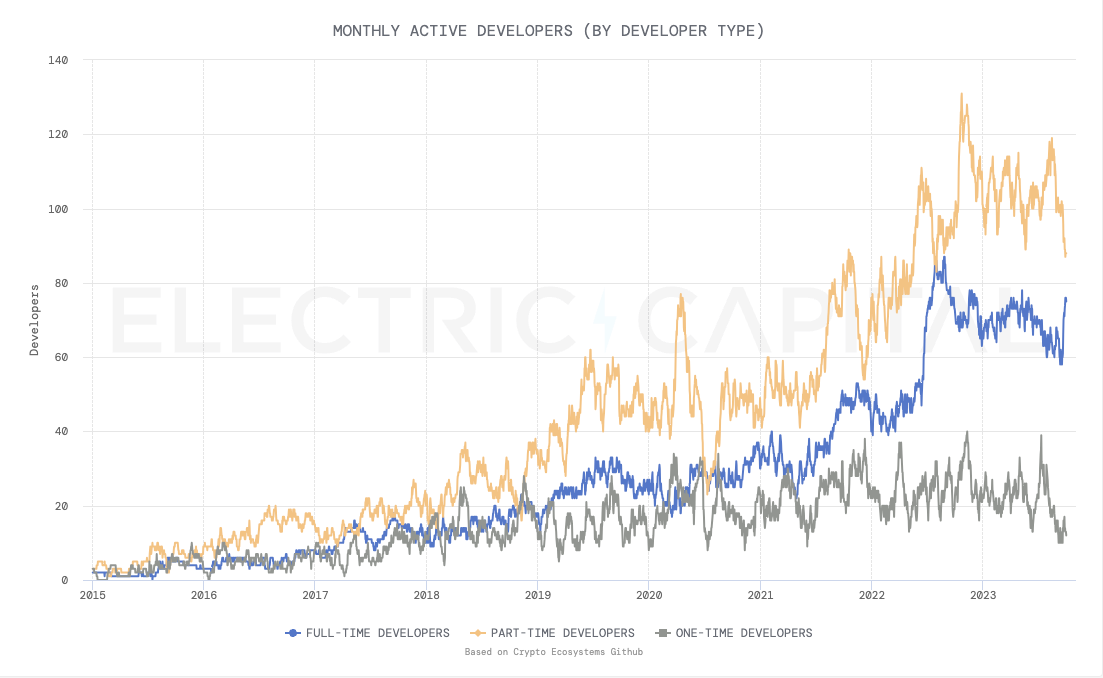 Bitcoin monthly active developers. Source: Power Capital
Bitcoin monthly active developers. Source: Power Capital
The introduction of Ordinals has had a profound impact on the Bitcoin network, especially the increase in transaction fees . In stark contrast to relatively modest fees of 1-3 sats/vB in 2022, fees quickly rose to 20x to 500x in May 2023 when Ordinals first hit the scene. As of December 2023, fees continue to rise by up to 280%. The rise in fees is a clear indication of increased activity and interest in the Bitcoin network, playing a vital role in revitalizing the culture and ecosystem of Bitcoin builders. While higher fees contribute positively to Bitcoin’s long-term security budget beyond current standards, they also reflect growing demand for Bitcoin block space.
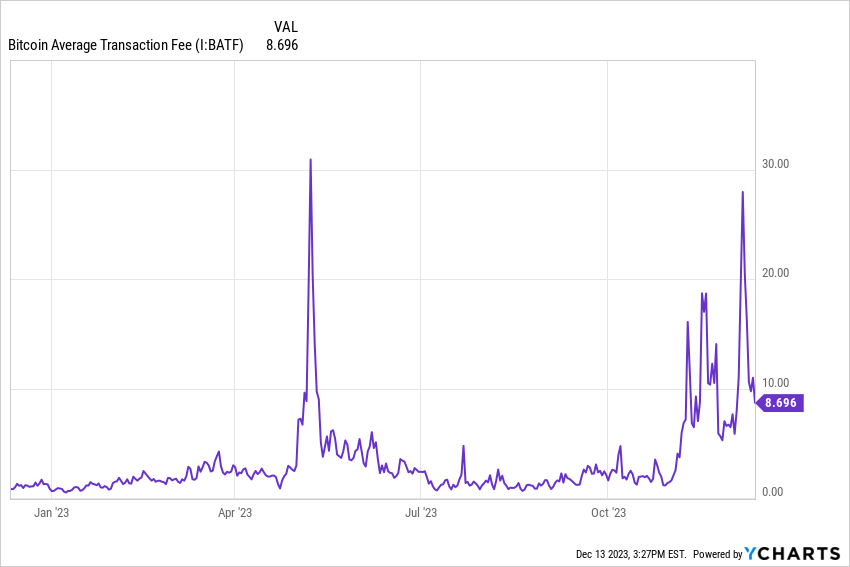 Due to ordinal numbers, average Bitcoin transaction fees peaked in May 2023. Source: ycharts
Due to ordinal numbers, average Bitcoin transaction fees peaked in May 2023. Source: ycharts
The surge in usage of the Bitcoin network has led to increased pressure on its infrastructure , manifesting in higher transaction costs and posing challenges to affordability and practicality. This trend is especially evident when users face disproportionately high fees relative to transaction amounts. For example, a Bitcoin transaction worth $100 may incur fees of up to $50, significantly reducing its economic viability. This scenario extends to Lightning Network channels, where closing channels with similar transaction values becomes impractical due to prohibitive costs. If transaction fees reach excessive levels of up to 1,000 sats/vB, the network risks further complication. This situation highlights the urgent need for scalable solutions in the Bitcoin ecosystem to accommodate growing demand while maintaining transaction viability.
The ordinal phenomenon, while reigniting developer interest in Bitcoin, also amplifies these limitations. Notably, Ordinals lacks support for fully expressed smart contracts, which has turned developers' attention to other platforms. This highlights the need for more sophisticated scaling solutions within the Bitcoin ecosystem to ensure its utility and relevance within the wider blockchain and financial landscape.
Strategic imperatives for L2 solutions
As a result, L2 solutions are becoming increasingly important to the functionality and success of the Bitcoin network. L2 runs on top of L1, enhancing scalability and reducing transaction costs by facilitating off-chain transaction channels. Unlike Ethereum's L1, which independently supports smart contracts, Bitcoin's L1 relies on L2 to implement this functionality because its original design prioritized security and decentralization. This reliance highlights the critical role of L2 solutions in extending Bitcoin’s utility beyond basic transactions, thereby enhancing its efficiency, scalability and overall appeal in the digital asset space.
Bitcoin's L2 solutions, while still in the early stages of development, are poised for significant growth. Currently, Bitcoin L2 does not show the same maturity as established alternative L1 networks such as Ethereum and scaling solutions for L2 networks such as Polygon. These networks have benefited from extensive development efforts since 2017, equipping their platforms with advanced tools (i.e. Starknet, ZKSync, etc.) and features, which is reflected in their TVL figures, which are approximately 9.0% to 12.5% of their market capitalization. The expectation is that over time, through continued innovation, Bitcoin's L2 solutions will reach a similar level of development, unlocking a comparable or larger L2 economy. It is estimated that Bitcoin L2 will manage a significant portion of all BTC transactions in the foreseeable future, potentially handling over 25% of all BTC transactions, a significant increase from its current minimal share compared to Bitcoin L1 usage .
contact us
If you are in construction or involved in the industry, we would love to hear your feedback and contact you! If your project is not mentioned in the report or included market map, but would like to be included in a future edition, please contact any of us; Twitter/X DM and email are open.
Author's note (February 8, 2024):
Some recent developments in Bitcoin's L1 infrastructure aim to emulate smart contract functionality without the need to build a dedicated smart contract layer. Innovations such as Recursive Inscription (BRC-420) and OrdiFi, as well as discussions of restoring “OP_CAT” functionality through soft forks, exemplify efforts to bypass traditional smart contracts and facilitate complex transactions similar to DeFi.
Compared to the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), the cornerstone of EVM-compatible chains that promotes composability through a general-purpose VM, Bitcoin's framework lacks such a mechanism. This fundamental difference requires the deployment of additional tools and more complex integration strategies to provide an equivalent user experience, which can lead to scalability challenges similar to those faced by underlying networks. The ecosystem has already seen the emergence of smart contract integration to varying degrees and is looking to expand further.
To highlight these advancements, the team behind BRC-420 recently launched Merlin Chain , a Bitcoin-native L2 solution designed to alleviate scalability issues. Additionally, Ordz Games launched its first Bitcoin-based game utilizing the BRC-20 token $OG, which had an Initial DEX Offering (IDO) on ALEX Lab’s $ORDG launchpad, achieving an 81x oversubscription Subscription. In subsequent parts of this series, we will explore more of these innovations in detail, outlining the evolving landscape of the Bitcoin ecosystem.







