In the digital age, protecting information and assets online is more important than ever. The two key factors that help ensure this security are the public key and the Private Key/Secret Key . They act as a pair of digital keys, opening the door to the world of online trading, cryptocurrency and many other applications.
What are Public Key & Private Key?
Public Key and Private Key are basically used to decrypt messages encrypted in a complex mathematical algorithm in cryptography. While public keys can be widely distributed, private keys used in the context of cryptocurrency are meant to be kept discreetly like a password to protect your digital assets.
- Public Key: Think of it as your home address. Anyone can know and use it to send you mail. In the digital world, public keys are used to encrypt information, which can only be decrypted by the corresponding private key.
- Private Key: This is your private key, similar to a house key. Only you have the right to access and use it. The private key is used to decrypt information encrypted by the corresponding public key and to create a digital signature, confirming your identity and ownership.
Cryptographic methods used in cryptocurrency
Hashing:
Like creating a “digital fingerprint” of information. It transforms data into a unique, irreversible chain of characters. Any change in the data will create a completely different “fingerprint”, helping us XEM whether the information has been tampered with or not. Hashing also helps create a shorter and easier to remember wallet address from a long and complex string of characters.

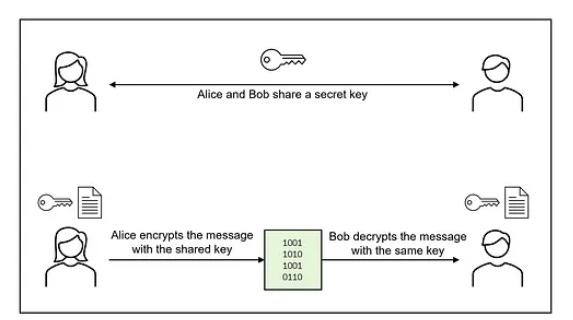
Symmetric encryption (Symmetric encryption):
This is one of the most popular, easiest yet effective encryption methods. Imagine you and your friend have the same special key. You use that key to "lock" the secret message before sending it to your friend, and only your friend, who has the same key, can "unlock" and read the content. This method is quick and effective, but make sure the key doesn't fall into the wrong hands.
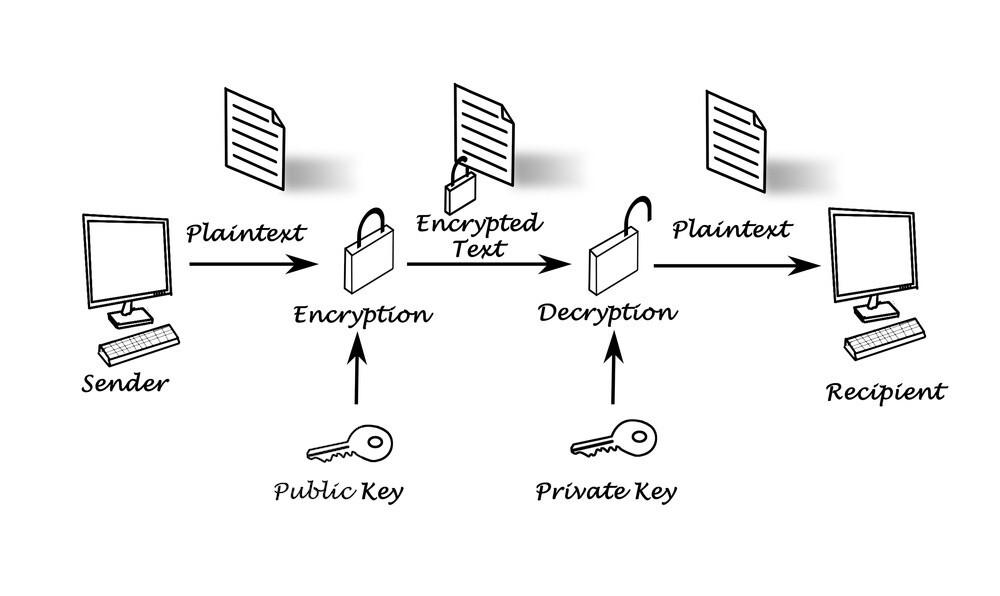
Asymmetric encryption:
Unlike symmetry, this time, you have two keys: a “public key” for everyone to send you information, and a “private key” that only you have to “unlock” the information. that news. The "public key" is like your home address, anyone can know it, while the "Private Key/Secret Key" is like a house key, only you can keep it. This method is more secure because you don't need to Chia the " Private Key/Secret Key" with anyone, but it is also slower than symmetric encryption. The coding process includes:
- The sender receives the Public key of the recipient address.
- The sender uses this key to encrypt the information.
- The sender sends encrypted information to the receiver.
- The recipient uses his Private key to decrypt the data.
Suppose, A (sender) wants to send 1 BTC to B (receiver). A knows B's Public key and uses it to encrypt the transaction. B receives the transaction and decrypts A's 1 BTC transfer using the Private key. B should be the only one who can authorize the transaction because no one else knows B's private key.
When it comes to cryptocurrency, a private key is something you physically own. It proves your authority to manage digital assets and authorize any transaction. Anyone who knows this key can use the related funds.
Detailed comparison between Public key and Private key
| Characteristic | Public Key (Public Key) | Private Key (Private Key/Secret Key) |
| Nature | Public, can be Chia freely | Secret, absolutely not Chia |
| Form | Long, complex chain of characters, often represented as hexadecimal (e.g. 0x…) | Similar to Public Key, it is a long and complex chain of characters |
| Main function | Encrypt information; Verify digital signatures | Decode information; Create digital signatures |
| How to create | Generated along with the Private Key in a key pair through a cryptographic algorithm | Generated along with the Public Key in a key pair through a cryptographic algorithm |
| Storage | Can be stored anywhere, as long as it is easily accessible when needed | Must be stored securely and confidentially, e.g. hardware wallet, wallet application with strong password |
| Chia | Can be Chia publicly, e.g. posted on a website, sent via email | Do not Chia with anyone, including relatives or friends |
| Risk | If you lose the Public Key, you can still access the data if you have the Private Key | If you lose your Private Key, you will lose access to your data and digital assets |
| Application | Cryptocurrency: Wallet address to receive cryptocurrency Email decryption: PGP key to encrypt and decrypt emails SSH: Key to authenticate remote access to computer systems | Cryptocurrency: Key to spend cryptocurrency Digital signature: Key to create a digital signature that verifies the identity and authenticity of the document SSL/TLS: Key to establish a secure connection between client and server |
What are addresses and mnemonics keys (seeds)?
What is address (wallet address)?
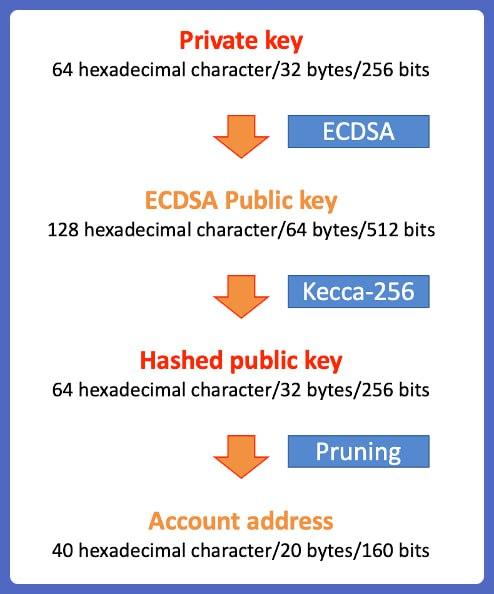
Many people often mistake that the wallet address (address) is the Public key but it is not. Address is a key code created from the Public key through a series of complex cryptographic algorithms such as Hashing. Address is used to represent the Public key in a concise way with fewer characters for easier use. An Address has a form similar to: 0xe1fb525a8944bfcf1e64a3f165bcb7e2338d5ccd. Basically, you can deduce the wallet address from the Public key but cannot deduce the Public key from the wallet address.
What are Mnemonics keys (seeds)?
Mnemonics the Public-Private key is not as easy as remembering the regular security ID and password we are using. If you lose these keys, especially the Private key, you will lose access to your account forever. To overcome this, most Blockchains use Mnemonic keys – Mnemonics keys (or seeds – Mnemonics phrases). They are often meaningful phrases and are easier to remember than any series of characters.
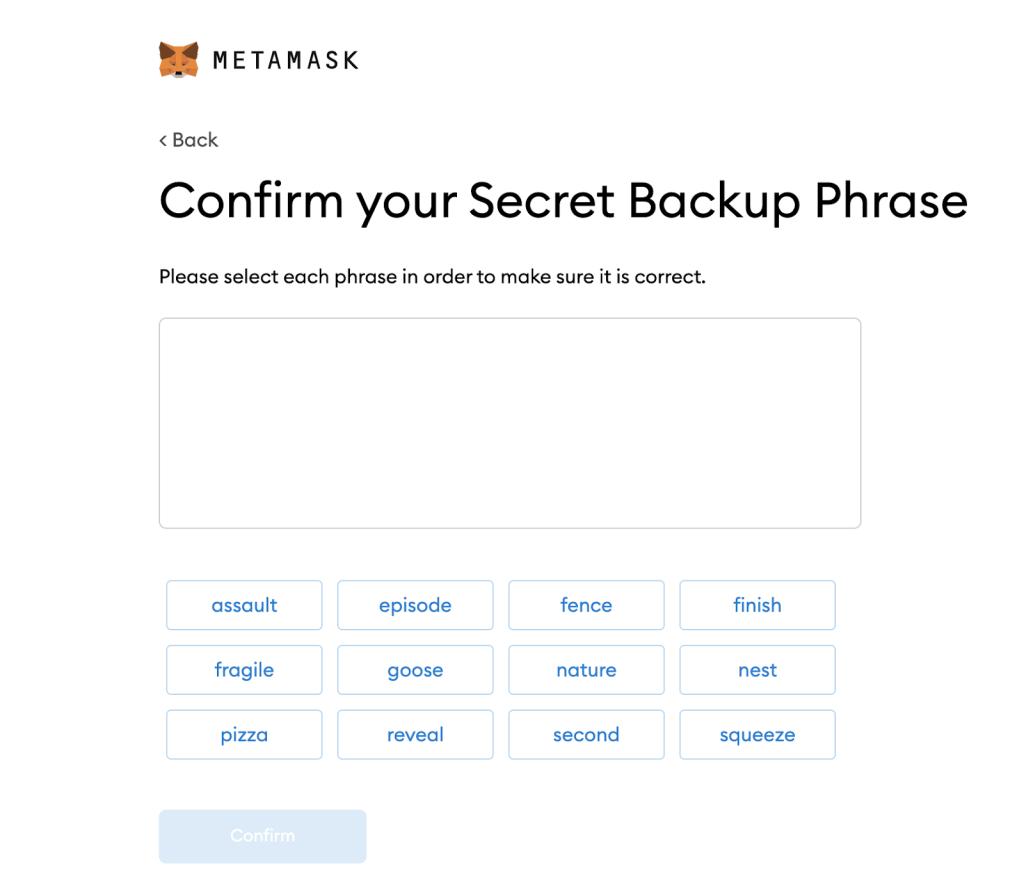
Examples of Mnemonics phrases (Seeds/Mnemonic key):
- Assault
- Episode
- Fence
- …
Mnemonic/Seed keys consist of 12,18 or 24 easy-to-remember words associated with a certain private key. They are created using a mathematical method called BIP 39 that encodes 128-256 Bit of random data into 12-24 phrases.








