The Bitcoin network, with its outstanding stability and security, has not only endowed BTC with lasting value, but has also accumulated impressive capital.
With the approval of the BTC spot ETF, a massive influx of traditional funds has pushed its market value to over $1.3 trillion.
However, the distinction between Bitcoin as a network and BTC as a digital asset is often overlooked. The key to realizing Bitcoin’s full potential is to leverage the network’s capabilities to transform Bitcoin from a mere store of value to the core infrastructure of the Bitcoin economy.
In December 2022, the emergence of the Ordinals protocol brought an unexpected innovation to the Bitcoin ecosystem.
The popularity of "Inscription" not only focused the attention of the public and developers on the Bitcoin ecosystem, but also allowed people to see the possibility of unleashing the huge potential of Bitcoin.
In just 12 months, the total market value of Bitcoin Inscription tokens based on Ordinals exceeded $3.5 billion, showing an astonishing growth rate. Even today, the daily NFT transaction volume on the Bitcoin network is greater than Solana.
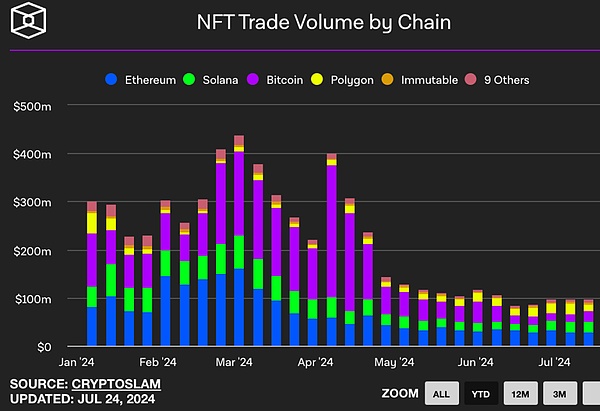
However, the market's high expectations for the Bitcoin ecosystem have also brought about subsequent setbacks.
The rapid cooling of the inscription craze, the performance of the much-anticipated Runes that fell short of expectations after its launch, and the dramatic turnaround of the Merlin project from its TVL peak to a sharp drop in price after its coin issuance have all made the market confused about the future of the Bitcoin ecosystem.
With the rise of Memecoin, market attention has also been greatly diverted.
This wave of ups and downs in the Bitcoin ecosystem is just like the "high temperature annealing" process in semiconductor technology. This process is designed to release the internal stress of the material and increase its ductility and toughness.
We believe that this principle also applies to the development of the Bitcoin ecosystem. After the FOMO sentiment fades, which projects are still being actively built? What is the development direction and trend of the Bitcoin ecosystem?
This article will be classified by track, and will deeply explore the development trends and representative projects of the Bitcoin ecosystem, analyze how they respond to challenges, and the role they play in the Bitcoin ecosystem.
BTC Layer
As the first successful cryptocurrency, Bitcoin's network design was originally designed with a focus on security and decentralization, which also brought inherent limitations in programmability and transaction speed.
Although upgrades such as SegWit and Taproot have improved these problems to some extent, the Ordinals asset issuance boom has clearly exposed the limitations of the network: severe network congestion, rising gas fees, and an urgent need for more powerful smart contract functions.
As users' demand for scalability and additional functions beyond Bitcoin's original functions grows, the Bitcoin ecosystem begins to explore various expansion solutions. Most of these solutions draw on the expansion experience of the Ethereum ecosystem and adopt a modular layered architecture, which gave birth to the concept of the "Bitcoin layer".
This architecture includes L2 layers (such as Lightning Network, sidechains, and Rollup solutions), which aim to increase transaction throughput by moving transactions off-chain while maintaining a secure connection to the main chain;
The settlement layer further optimizes the performance and functionality of specific application scenarios; the data layer provides data availability and storage solutions; and the application layer develops various decentralized applications based on the underlying infrastructure.
This multi-layer architecture improves programmability, making more complex smart contracts possible; significantly increases transaction processing speed; improves data availability; and expands ecological possibilities.
In the most competitive Bitcoin Layer2 track, most of them use the EVM technology stack and cooperate with cross-chain bridges to solve the Bitcoin expansion problem. Although this method can quickly build an ecosystem in the short term, these solutions lack a strong binding relationship with the Bitcoin main chain and are highly dependent on cross-chain bridges, which increases potential security risks.
At the same time, using Ethereum's account model and EVM to expand UTXO-based Bitcoin is, to some extent, inconsistent with the concept of "Bitcoin Native". There are roughly three types of L2 from a technical perspective:
Rollup system: This type of solution attaches great importance to the verifiability of Layer1 and is committed to extending the security of Layer1 to Layer2.
Sidechain system: The advantage of this type of solution lies in its relatively mature technology and ecosystem.
Client-side validation: This type of solution emphasizes the use of Layer 1 native data availability (DA).
While pursuing the verifiability of Layer 1, the Rollup solution controls the user's trust cost through a variety of modular designs. This approach not only ensures security, but also reduces the user's trust burden to a certain extent.
In contrast, although the sidechain system has advantages in technological maturity, it may face more challenges in inheriting Layer 1 security.
Although the client verification scheme can ensure that all ledger records are performed on Layer 1 to a large extent, it requires users to maintain a high degree of trust in the client. This trust cost is endogenous and difficult to completely eliminate.
Rollup
The emergence of Ordinals makes the Bitcoin network a highly secure database capable of storing various data, including Rollup proof data.
However, simply uploading the Rollup's proof data to the BTC network is not enough to ensure the validity and correctness of transactions within the Rollup. The core problem facing BTC Rollup lies in verification.
At present, most BTC Rollups may choose the sovereign rollup (client-side verification) method, in which the validator synchronizes all the Rollup data off-chain and checks it by itself.
The limitation of this method is that it cannot fully utilize the most powerful feature of the Bitcoin network - the POW consensus of hundreds of thousands of nodes to ensure the security of rollup.
The ideal state is to allow the BTC network to actively verify Rollup proofs, similar to Ethereum, and have the ability to reject invalid block data.
At the same time, it is also necessary to ensure that the assets in the Rollup can still be trustlessly withdrawn to the BTC network through a safe escape channel in extreme circumstances (such as the Rollup's nodes or sorters being down for a long time or refusing to accept transactions).
Bitlayer
Bitlayer is the first Bitcoin Layer 2 network based on the BitVM solution, aiming to provide the same security as Bitcoin while supporting Turing-complete computing power.
The core technical innovation of the project lies in the adoption of the latest BitVM computing paradigm and OP-DLC bridge, which solves the three main challenges facing Layer 2:
Trustless two-way anchoring: Combining OP-DLC with the BitVM bridge to achieve trustless two-way flow of assets between the Bitcoin main chain and Bitlayer
Layer 1 Verification: Inheriting Bitcoin’s Security via BitVM
Turing completeness: supports multiple virtual machines and achieves an environment that is 100% compatible with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM)
Bitlayer launched a $50 million ecological incentive plan on March 29 this year to attract early builders and contributors. Currently, many native projects have joined the ecological construction, including DEX, permissionless lending protocol and MEME.
Recently, Bitlayer announced the completion of a $11 million Series A financing round, led by Franklin Templeton and other institutions, becoming the first Bitcoin infrastructure project to obtain institutional investment in an ETF license.
The project has been launched in the user center, which includes three modules: novice tasks, advanced tasks, and daily tasks. Users can earn Bitlayer points by completing tasks and get exclusive racing cars as racers. In the future, Bitlayer plans to distribute $BTR airdrops based on user points and racing car levels.
Bitlayer's innovative technical solutions and proactive ecosystem building strategies make it one of the Bitcoin Layer 2 projects worth paying attention to.
https://www.bitlayer.org/ready-player-one/dapps-center
B² Network
B² Network is an EVM-compatible Layer2 on BTC. It provides an off-chain trading platform that supports Turing-complete smart contracts, improving transaction efficiency and reducing costs.
By integrating zero-knowledge proof (ZKP) technology with Bitcoin's Taproot, B² Network ensures enhanced privacy and security of transactions. The network aims to develop Bitcoin into a dynamic platform, setting the stage for innovative applications such as DeFi and NFT, applicable to traditional Bitcoin assets and emerging Bitcoin derivative assets.
B² Network's technical architecture consists of two layers:
1. Rollup layer: uses ZK-Rollup and zkEVM solutions, responsible for executing user transactions and outputting related proofs.
2. Data Availability (DA) Layer: includes distributed storage, B² nodes, and the Bitcoin network, responsible for permanently storing Rollup data, verifying zero-knowledge proofs, and performing final confirmation on Bitcoin.
Distributed storage is a key component of the B² Network and serves as a repository for ZK-Rollup user transactions and proofs, improving network security, reducing single points of failure, and ensuring data immutability.
Currently, B² Buzz has entered the third phase and launched Buzz Farming, cooperating with well-known BTCFi projects such as Babylon, Unirouter, Lombard, Bedrock, etc. to provide diversified income strategies.
Buzz Farming benefits include:
14,580 B² tokens are acquired from the B² network every day.
Rewards from BTCFi partner chains and important partners, including Babylon, Aptos, Bedrock, Lombard and many other projects.
As the native revenue aggregator of B² Network, Buzz Farming will continue to bring more revenue and paths to users, reflecting the project’s innovation in the DeFi field.

https://buzz.bsquared.network/farming
QED
QED Protocol is a ZK rollup on BTC, running on zkevm. Unlike other zk rollups, QED does not choose to generate zk proofs for the entire Rollup transaction, but only creates ZK proofs for withdrawal transactions from rollup to BTC L1, and verifies these proofs on BTC L1 by composing scripts into logic circuits.
Each user's public key acts as a custom ZK circuit with a "smart signature" capability similar to a smart contract.
Similar to the idea of BitVM, QED Protocol organizes scripts into logic circuits to verify the ZK proof of withdrawal transactions on BTC L1. This type of logic circuit will contain 1,000 UTXOs. Although direct verification is achieved, the cost is huge.
Decentralized applications built on QED can locally prove transactions, providing users with unlimited computation with fixed gas fees.
Founder Carter Feldman said that QED can process more than 150,000 transactions per second and plans to launch a test network in the next 3-4 months. The mainnet will be launched after the community reaches a consensus, and native tokens will be launched to incentivize the operation of high-performance infrastructure.
QED has completed a $6 million seed round of financing, with Blockchain Capital as the only investor, with a valuation of at least $100 million. It has also previously received $3.25 million in pre-seed rounds and $1.35 million in angel rounds of financing.
The ZK technology used by QED is STARK technology, which is a pioneer project of Starkware<>BTC and has received early investment and support from Starkware.
GOAT Network
GOAT Network is a BTC Rollup Layer2 launched by ZKM, a project incubated by MetisDAO. It is the first decentralized Bitcoin L2 with shared network ownership.
Technically, the Optimistic Challenge Protocol (GOAT-OCP) was introduced, and the BTC script provided locked the native security mechanism to ensure security. ZKM Entangled Rollup was used as the general settlement layer to improve transaction inclusiveness and finality.
GOAT Network can support direct deposit of assets without introducing additional cross-chain bridges and protect assets in the decentralized Sequencer network.
The development team comes from MetisDAO. Metis is currently the only Ethereum Layer 2 project that implements a decentralized sequencer. They have also brought this technical advantage to BTC Layer2. The decentralized Sequencer network allows any Bitcoin holder to lock in a node or delegate to an existing node.
GOAT has received commitments of 5,000 BTC from five institutional node operators. It plans to start with seven node operators and expand to dozens in the future.
Potential benefits of participating in the GOAT Network include:
Gas fees in BTC
GOAT Token Mining Rewards
Returns generated by yBTC (receipt token after locking BTC on the GOAT network)
yBTC Unlocks More Yield Opportunities in the GOAT Network Ecosystem
The first phase of the decentralized sequencer activity has been launched. Users can bind their wallets (need to hold 0.001 BTC), social information, and complete social tasks.

https://club.goat.network/goatlist
Mezo
Mezo is a Bitcoin Layer 2 network that aims to drive Bitcoin's transformation from a "savings technology" to a circular economy.
The project uses a unique Proof of HODL mechanism, where users protect the network by locking BTC and MEZO tokens and verifying transactions.
Mezo uses the CometBFT consensus mechanism, combined with the innovative concept of proof of holding. Users can lock BTC on Mezo, and the longer the lock-up period, the higher the HODL score, so that they can contribute to network security and earn income when the mainnet is launched.
The project was launched by the startup studio Thesis, whose team has extensive experience in BTC ecosystem development and has developed the tBTC project.
According to data from Mezo’s official website, the current number of users is close to 12,000, and the total number of staked BTC has reached 2,333.
Mezo recently announced the completion of a new round of funding of $7.5 million, bringing the total funding to $30 million. The new funds will be used to expand network adoption, including integrating more products such as Bitcoin staking platform Acre.
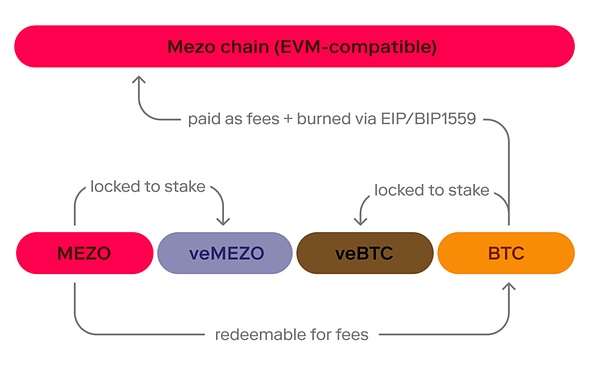
https://mezo.org/hodl
Bitfinity Network
Bitfinity Network EVM is an Ethereum-compatible blockchain created based on Internet Computer (IC) and developed using the Solidity language. Developers can deploy Bitcoin, Ordinals, and BRC-20 smart contracts written in Solidity through Bitfinity, which is expected to enhance the practicality of Bitcoin.
Thanks to the unique architecture of IC and Chain Key technology, Bitfinity Network EVM is more efficient than traditional EVM implementations, with on-chain storage capacity and processing speed comparable to traditional network services, without the need to pay gas fees.
Bitfinity plans to integrate Ethereum and other EVM-compatible chains by running light clients on the IC, which requires adjusting the network protocol to interface with full nodes of other chains and sync the entire blockchain.
The project supports connecting ICRC-1 tokens and ERC777/ERC20 tokens, as well as Bitcoin as an ICRC-1 token.
At the beginning of this year, it completed a $7 million financing with a valuation of $130 million.
Token Economy: BITFINITY is the official project governance token approved by Bitfinity DAO and the native token of Bitfinity EVM. It has a total supply of 1 billion and is an ERC-20 token.
Arch Network
Arch Network is an innovative Bitcoin-native programmability solution that, unlike traditional L2, aims to introduce programmable capabilities directly into the Bitcoin network.
Arch is a parallelized PoS network that uses ZK proofs to enhance Bitcoin's native programmability. The network consists of a Rust-based zkVM (ArchVM) and a decentralized validator network.
The project draws inspiration from Solana and SVM (Solana Virtual Machine) and does not rely on any bridge or L2. Arch has three characteristics: programmability, parallel execution speed, and trustless interoperability and composability.
In the Arch network, asset transfers and state changes on the Bitcoin chain all occur on Bitcoin L1. Arch utilizes ordinals through the state chain to commit state changes in a single transaction, thereby reducing fees and ensuring atomic execution.
Arch's charging model includes infrastructure processing fees and dynamic pricing mechanisms. Infrastructure processing fees are charged for each BTC transaction, including operations such as deploying smart contracts, trading, and minting NFTs. The dynamic pricing mechanism is similar to fast-track tips, which are adjusted according to network congestion and transaction complexity.
Arch Network completed a $7 million seed round of financing, led by Multicoin Capital, with participation from OKX Ventures, CMS Holdings and others.
Currently, Arch's products and roadmap are still under development, and no specific launch schedule has been announced.
BTC Sidechain
The concept of sidechain originated from the paper "Enabling Blockchain Innovations with Pegged Sidechains" published by Adam Back et al. in 2014. The concept aims to enhance the service capabilities of Bitcoin by allowing assets to be transferred between multiple blockchains.
A sidechain is essentially an independent blockchain network that runs in parallel with the main chain and has the following characteristics:
Strong customization: Specific rules and functions can be designed to improve scalability and flexibility.
Independent security mechanism: Maintain its own security mechanism and consensus protocol. Security depends on the sidechain design.
High degree of autonomy: It has greater design freedom than the main chain.
Interoperability: Interoperability with the main chain may be low, but cross-chain asset transfer is supported.
The core function of the sidechain is to realize the transfer and use of assets from the main chain to the sidechain, which usually involves operations such as cross-chain transfers and asset locking. This design brings new possibilities to the Bitcoin ecosystem. The advantage is that the Ethereum network can be quickly linked to Bitcoin, but it also brings challenges in terms of security and interoperability.
Merlin
Merlin Chain is a Bitcoin sidechain released by Brc420. As one of the earliest Bitcoin Layer2s, Merlin has long occupied a huge TVL. Even if the price of the coin is lower than expected after the coin is issued, according to BTCEden data, Merlin still leads other BTC L2 projects by a TVL of 1.28 billion US dollars.
Merlin Chain is based on the native assets, protocols and products of Bitcoin Layer 1. Its goal is to empower Layer 1 assets, protocols and user ecosystems on Layer 2, such as building a user-friendly metaverse based on Bitmap and building DeFi protocols using BRC-420.
Merlin uses the MPC solution of cobo wallet to implement BTC cross-chain. There is still some gap in security compared with the BTC multi-signature after Taproot upgrade, but MPC has been verified for a long time. Using ParticleNtwrk's account abstraction technology, users are allowed to continue to use Bitcoin wallets and addresses to interact with side chains, maintaining user habits. This design is more user-friendly than requiring Bitcoin users to use Metamask for interaction.
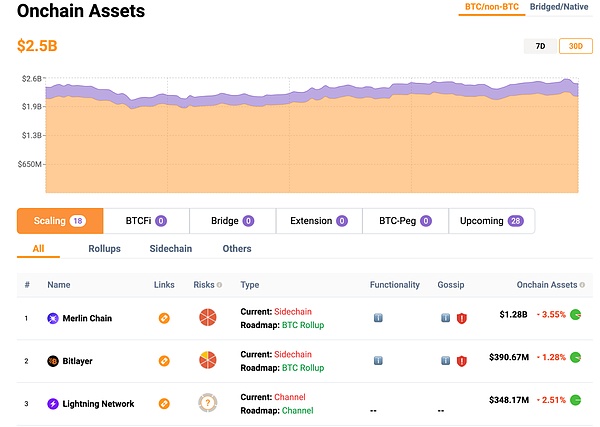
https://www.btceden.org/?type=all
Stacks
Stacks is a sidechain that is closely integrated with Bitcoin, with a unique consensus mechanism and smart contract capabilities. The project uses an innovative proof-of-transfer (PoX) consensus mechanism, in which miners participating in the consensus no longer destroy Bitcoin, but instead distribute it to a group of participants who maintain network security.
Stacks plans to launch the Nakamoto upgrade this year, which will make it a true Layer 2 solution. The upgrade code has been completed and will be deployed to the mainnet soon. The upgrade aims to significantly increase transaction throughput, achieve 100% finality of Bitcoin transaction confirmation, and reduce transaction confirmation time from 10 minutes to about 10 seconds.
The Nakamoto upgrade will also enhance the security of Stacks, bringing it in line with the Bitcoin network. Even in the event of a Bitcoin network reorganization, most Stacks transactions will remain valid, improving overall network reliability.
In addition to the Nakamoto upgrade, Stacks will also launch sBTC, a decentralized, programmable 1:1 Bitcoin-backed asset that can deploy and transfer BTC between Bitcoin and Stacks (L2).
sBTC enables smart contracts to write transactions to the Bitcoin blockchain, while in terms of security, transfers are secured by the entire Bitcoin hashing power.
Stacks currently has a relatively rich ecological project, and the current on-chain TVL has reached 200 million US dollars.
For example, Alex is the DEX of the Stacks ecosystem, which also includes the Launchpad function. It currently has a TVL of 30 million US dollars; the liquidity staking project StackingDAO has locked in 100 million US dollars of liquidity.
The STX token also has the highest market value in the current Bitcoin sidechain ecosystem and is the only token to enter the top 100 on Coinmarketcap.
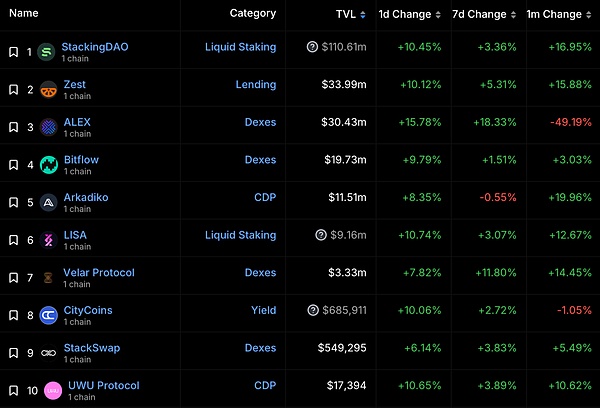
https://defillama.com/chain/Stacks?pool2=false&staking=false
Citrea
Citrea is an innovative Bitcoin expansion solution that achieves expansion within the Bitcoin network through zero-knowledge proof technology, ensuring on-chain verifiability and data availability. The core advantage of the project is its ability to support more complex applications without compromising Bitcoin’s security or changing its consensus rules.
Citrea’s technical features include:
Batching large numbers of transactions and generating succinct validity proofs in zkVM
First implementation of burning and local verification of validity proofs in the Bitcoin blockchain
A native ZK proof validator smart contract on Bitcoin L1 built into BitVM
Unlike traditional sidechains, Citrea creates a modular ecosystem for Bitcoin by implementing sharding, keeping settlement and data availability on the Bitcoin main chain.
The project announced in February this year that it had completed a $2.7 million seed round of financing led by Galaxy.
Currently, Citrea’s public developer network is online. There will be three one-week testing tasks from July to August. Users can participate in the testing and obtain NFT rewards in Galaxy.

Fractal Bitcoin
Fractal BTC is a Bitcoin Layer 2 solution developed by the Unisats team. It is the only solution that uses Bitcoin Core code to recursively expand infinite layers on top of the Bitcoin blockchain, using the BRC20 token Sats as Gas fees.
Fractal forked the Bitcoin core code and made some key adjustments. The main features include shortening the block confirmation time to 30 seconds. The project plans to implement "controversial" opcode proposals such as OP_CAT and ZK native verification OPCode faster than the Bitcoin mainnet, and smart contracts can be implemented through scripts in the future.
The consensus mechanism uses the same proof-of-work (PoW) as Bitcoin, and miners can use existing ASIC, GPU and other hardware equipment for mining.
Fractal has introduced an innovative Cadence Mining method, where two out of every three blocks are mined in a permissionless manner and one is mined through merged mining, balancing decentralization and security.
As a native scaling solution, Fractal supports cross-layer secure asset transfers starting from the Bitcoin mainchain, including decentralized bridging of assets such as BRC-20 and Ordinals.
The main applications include Fractal swap (flexible BRC20 exchange mechanism), Asset bridge (asset bridge between the mainnet and Fractal network) and UniWorlds (application that introduces real-world transactions).
Unisats completed its Pre-A round of financing in May this year, led by Binance. The specific amount of financing was not disclosed.
Unisats is one of the most reliable infrastructures in this round of Ordinals. Wallets and trading platforms have also occupied the minds of users to a large extent. With a good user base and trading foundation, it would not be surprising for Unisat to develop such a shadow chain. The new round of financing also demonstrates stronger resource capabilities. We look forward to more pioneering applications.
https://unisat-wallet.medium.com/2024-07-unisat-swap-product-important-update-e974084074a1
Botanix
Botanix Labs is building the first fully decentralized EVM-equivalent L2 on Bitcoin, combining the ease of use and versatility of the EVM with the decentralization and security of Bitcoin.
The project uses Bitcoin's Proof of Work (PoW) as the basic settlement and decentralized layer 1, while adopting a Proof of Stake consensus model. Stake (represented in Bitcoin) is securely stored on the distributed network Spiderchain and protected by a randomly selected subset of participants through decentralized multi-signatures.
Botanix allows users to stake Bitcoin directly on the Bitcoin network. After the user connects to MetaMask, a special Bitcoin deposit address is generated, which encodes the user's EVM address in Taproot.
This innovative mechanism allows users to send Bitcoin directly from major exchanges to this deposit address, and then use Bitcoin in MetaMask. The user experience is similar to Ethereum, but in fact all operations are performed using Bitcoin. This innovative method of combining Bitcoin with EVM compatibility is expected to bring more application scenarios and user-friendly experience to the Bitcoin ecosystem.
Botanix announced in May this year that it had completed an $8.5 million seed round of financing.
The Botanix testnet was launched on November 30, 2023. As of June, the testnet has connected more than 300,000 wallet addresses and launched two applications, AvocadoSwap and Bitzy, for interaction.

https://botanixlabs.xyz/en/ecosystem
Client Verification RGB++
Nervos
Nervos Network is one of the Bitcoin scalability solutions, which adopts a more native approach and modifies the UTXO model that supports Bitcoin. It adopts a layered architecture, including an L1 blockchain (Common Knowledge Base, CKB) that can be expanded through payment channels and RGB++.
CKB takes advantage of its natural structural advantages of being POW+UTXO like BTC, and combines it with innovative "isomorphic mapping" technology to "seamlessly migrate" RGB's client verification paradigm to CKB, naming it RGB++. This approach sacrifices a little privacy in exchange for great functionality and flexibility expansion, and its security is strongly bound to BTC L1.
The RGB++ protocol is an improvement and extension of the original RGB protocol. The original RGB protocol is an L2 solution designed to implement smart contracts and asset issuance without changing the Bitcoin mainnet. It implements asset transfer by binding assets to specific Bitcoin UTXOs, mainly relying on client verification, and transactions are processed and verified off-chain.
Nervos Network solves the limitations of the original RGB through the RGB++ protocol. RGB++ uses CKB as Bitcoin's data availability and execution layer, and maps Bitcoin UTXO to CKB's Cell through isomorphic binding technology, achieving seamless integration with CKB's Turing-complete smart contracts.
RGB++ introduces on-chain verification of key transaction elements, improving security and data availability. It also enables transaction folding, masterless contracts with shared states, and non-interactive transfers, and cross-chain transfers of Bitcoin without the need for a cross-chain bridge.
As an asset issuance protocol, RGB++ enables BTC L1 to issue new RGB assets. RGB++ asset transactions on CKB are completely Turing-complete and programmable. Not only RGB++ assets can be mapped to CKB, but also Atomical, Rune and other assets with UTXO characteristics can be mapped to CKB for Turing-complete transactions.
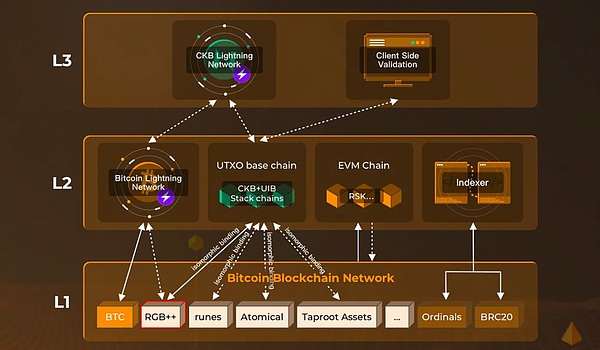
UTXO Stack
UTXO Stack is a modular Bitcoin second-layer chain issuance platform, which can be understood as a "one-click chain issuance" platform. It focuses on issuing Bitcoin second-layer chains based on the UTXO isomorphic model.
The project was developed by the CELL Studio team, a blockchain software company incubated by the Nervos Ecosystem Fund. The company's founder, Cipher, is also the originator of the RGB++ protocol, and its purpose is to promote the development and prosperity of the Nervos ecosystem.
UTXO Stack is actually the strategic layout of the Nervos project in the Bitcoin ecosystem. Its positioning is to provide technical support and modular services for projects that want to develop UTXO model second-layer chains on Bitcoin.
UTXO Stack can be compared to Op Stack in the Ethereum ecosystem. Just like Base is Ethereum Layer 2 built on the OP Stack toolkit, UTXO Stack provides similar functions for the Bitcoin ecosystem.
The Bitcoin Layer2 built through UTXO Stack can natively integrate the capabilities of the RGB++ protocol and use CKB as the data availability layer. This makes UTXO Stack equivalent to the OP Stack + EigenLaye of the Bitcoin ecosystem.
These UTXO Stack-based Layer2s can adopt the POS consensus mechanism to ensure the security of the second-layer chain by staking BTC, CKB, and BTC L1 assets.
Restaking
The security of many emerging PoS chains is limited by the size of the on-chain economy, which poses a risk of being controlled. The Bitcoin pledge and re-pledge protocol provides security for the PoS network by introducing the Bitcoin asset with the strongest consensus.
Especially under the education of EigenLayer and a number of re-staking projects, the concept of re-staking has been deeply rooted in people's minds, and it is more natural to derive this concept from the Bitcoin ecosystem.
The advantages of Bitcoin re-staking include:
Bitcoin is the most secure blockchain in existence, with an unparalleled foundation of trust.
Activate Bitcoin, which has a market value of approximately $1.3 trillion, to create sustainable profit opportunities for holders.
Bridging the gap between PoW and PoS blockchain systems, leveraging the security advantages of Bitcoin.
Bitcoin-collateralized derivative assets have huge market prospects, including building diversified ecological applications such as collateralized stablecoins, lending, and derivative revolving loans and structured products.
Babylon
Babylon is a Bitcoin staking protocol that allows Bitcoin holders to stake BTC on the PoS chain and earn returns while protecting the security of the PoS chain, applications, and application chains.
Unlike traditional methods, Babylon uses remote staking, without the need to bridge, wrap or host Bitcoin to the PoS chain. This method allows Bitcoin holders to earn income from idle BTC while enhancing the security of the PoS chain and application chain.
Babylon's core functions expand the application scenarios of Bitcoin, making it not only limited to value storage and exchange, but also extend Bitcoin's security capabilities to more blockchains.
The project introduced the Bitcoin Timestamp Protocol, which places event timestamps from other blockchains on Bitcoin, allowing these events to enjoy the same timestamp security as Bitcoin transactions. This enables features such as fast pledge unbinding, reduced security costs, and cross-chain security.
From a technical perspective, Babylon consists of two main protocols:
Bitcoin Timestamp: Concisely verifiable timestamp of any data (like PoS blockchain) sent to Bitcoin.
Bitcoin staking: Allowing Bitcoin assets to provide economic security for any decentralized system in a trustless and self-custodial manner.
In May this year, Babylon announced the completion of a US$70 million financing round led by Paradigm.
Project development stage: Bitcoin Staking Testnet-4 has been completed. When the subsequent testnet is opened, it is recommended to actively participate in the staking test and complete the corresponding Galaxy tasks.

https://babylonchain.io/
Lorenzo
Lorenzo Protocol is a liquidity re-staking protocol built on Babylon, which aims to improve the application capabilities of Bitcoin by introducing liquidity staking and privacy enhancements. The project allows Bitcoin holders to convert BTC to stBTC, participate in Bitcoin staking and receive rewards without locking up funds.
Lorenzo innovatively divides the Liquidity Re-Pledge Token (LRT) into Liquidity Principal Token (LPT) and Yield Accumulation Token (YAT), which is similar to Pendle's PT and YT. This separation mechanism provides a flexible solution for liquidity re-pledge, enhancing the liquidity and accessibility of Bitcoin re-pledge.
An important feature of the project is that there is no minimum staking time requirement and no "unbinding" time. This means that investors can avoid the risk of being locked in the staking and maintain flexibility when the market fluctuates.
Lorenzo provides an EVM-compatible Cosmos chain secured by Babylon BTC shared security for issuing and settling BTC liquid recollateralized tokens. This provides the basis for cross-chain operations and broader DeFi applications.
In the future, Lorenzo plans to build a series of financial products, including interest rate swaps, lending agreements, structured BTC income products and stablecoins, etc. The project focuses on building an efficient Bitcoin liquidity allocation market and liquidity assetization.
Although the specific financing information has not been disclosed, it has received support from Binance Labs.
The Beta mainnet is now online.

https://www.lorenzo-protocol.xyz/
Chakra
Chakra is an innovative Bitcoin re-staking protocol driven by ZK technology. It introduces the concept of SCS (Settlement Consumer Service) and integrates Bitcoin re-staking into the PoS system.
The core technical features of the project include:
Lock BTC using time lock
Proof of staking events generated through ZK-STARK technology
Off-chain verification mechanism, no need to directly connect to the BTC network
Leverages STARK technology to ensure high security without the need for trusted setup
Chakra's ZK Proofs design has the potential for multi-scenario applications, including artificial intelligence, DeFi, and games. Users only need to stake once, and through authorization, they can expand to multiple application scenarios and obtain multiple staking benefits.
The project has the potential to build an L2 network based on proof of stake, allowing stakers to participate in the consensus and governance of L2. These L2s will share the security of Bitcoin while providing data availability services and execution environments maintained by stakeholders.
Chakra plans to integrate with Babylon to expand its application scope in the Bitcoin ecosystem.
In April 2024, the project announced its investment institutions, mainly including STARKWARE, ABCDE and some Asian miners.
Project development progress:
The testnet has been launched and participated in Babylon testnet-4
Chakra becomes the top finality provider in Babylon Testnet-4
Confirmed TVL of 258 Signet BTC, representing 36% of Babylon’s total TVL, showing strong early performance
https://btcstaking.testnet.chakrachain.io/
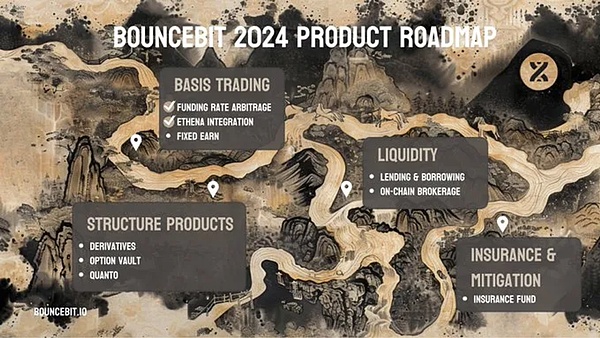
BounceBit
BounceBit is an innovative BTC re-pledge infrastructure that provides a base layer for a variety of re-pledge products. The project adopts a CeFi + DeFi hybrid framework, allowing BTC holders to obtain returns from multiple channels.
The core idea is to advance Bitcoin by using assets rather than changing the Bitcoin blockchain. The main strategies include funding rate arbitrage and creating on-chain certificates for re-staking and mining.
Layer 1 of BounceBit consists of two key components:
Dual-Coin PoS: A hybrid consensus mechanism where validators can accept both BBTC and BB tokens
Native LSD module: allows you to delegate staking to validators and receive LST certificates in return
The project’s CeFi layer includes:
Compliance custody: Ensure user funds security through MPC wallet
OTC Settlement: Safely utilize CEX liquidity and settle transactions over the counter
BTC re-staking: Ensure the safety of funds through regulated custody services, and users will receive bounceBTC (BBTC) as a pledge certificate
BounceClub: A platform for creating no-code DeFi experiences
Liquid Custody: Introducing the concept of Liquid Custody Tokens (LCT) to maintain the liquidity of collateral assets
BounceBit completes $6 million in seed round financing, co-led by Blockchain Capital and Breyer Capital.
The project plans to launch the on-chain brokerage business Superfast in the third quarter of 2024, aiming to solve the liquidity problems of BBTC and BBUSD and launch a large-scale BB reward activity.
Superfast will combine the concepts of LCT and CEX to achieve fast settlement and high liquidity of on-chain transactions, and support ultra-liquid exchange of BB, BBUSD and BBTC.
BounceBit's innovative model is expected to provide Bitcoin holders with more re-staking options and profit opportunities, while promoting the expansion of Bitcoin's application in the DeFi field. The project's hybrid architecture and diversified product line show its potential in Bitcoin financial innovation.
https://bouncebit.io/
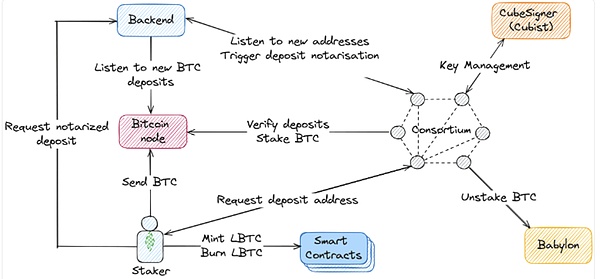
Lombard
Lombard is a Bitcoin staking protocol that aims to enable Bitcoin staking and liquidity release through the Babylon platform.
The core product, LBTC, is a cross-chain liquidity Bitcoin token with yield, backed by BTC at a 1:1 ratio. When users stake Bitcoin through Babylon, Lombard uses LBTC tokens to represent the liquidity and yield of staked Bitcoin.
The main innovation of the project is to allow BTC with yield to move across chains without dispersing liquidity, which may become an important catalyst for introducing large amounts of new capital into the DeFi ecosystem.
Lombard plans to integrate LBTC into Ethereum’s DeFi protocol later in 2024, which will greatly expand the scope and potential of Bitcoin in the DeFi field.
Lombard recently announced the completion of a $16 million seed round led by Polychain
Currently, Lombard is still in the development stage and the test network has not yet been launched.
DA Layer
There are significant differences between Bitcoin and Ethereum in terms of ecological maturity, technical genes and mainnet characteristics. Ethereum's data availability (DA) layer is a further enhancement of its already relatively rich mainnet functions. In contrast, the transaction processing capacity of the Bitcoin mainnet is extremely limited, and can only process about 4 transactions per second.
Therefore, for Bitcoin, developing the DA layer is more like solving an urgent need rather than simply enhancing functionality. There is less competition in this field, and currently only Nubit has taken shape.
Nubit
Nubit has built a highly scalable and secure Data Availability Layer based on the economic security of Bitcoin. It is committed to significantly increasing the data capacity of Bitcoin without sacrificing security, and providing support for applications such as Ordinals, second-layer expansion solutions, price oracles and indexers.
Nubit integrates Babylon's POS staking solution to ensure that the economic security of the entire DA ecosystem is determined by Bitcoin-native stakers, which enables Bitcoin holders to participate in and strengthen the Nubit system to create the most secure and scalable data availability layer.
In addition to the DA layer, Nubit will also develop an execution layer based on the Nubit DA framework, which is stateless and efficient, allowing users to reliably verify calculation results, which will be widely used by Bitcoin wallets and users.
In terms of financing, in June this year, it was announced that Polychain had invested US$8 million in a seed round of financing (total financing of US$12 million).
Currently, the Alpha testnet is open, and activities that can be participated in include: Community Assemble, Light Node Quest, and Testnet Adventure, which will be opened later.
Summarize
This article only briefly introduces the progress of some ecological projects from the perspective of the Bitcoin layer. In fact, the Bitcoin ecosystem also includes more infrastructure, such as cross-chain bridges, wallets, oracles, various asset protocols and DeFi projects, and the scope is too wide to mention.
Our discussion is only intended to serve as a starting point, and aims to give us a glimpse of the characteristics of the development of the Bitcoin ecosystem through these cases.
The development of the Bitcoin ecosystem is facing the challenge of balancing technological nativeness and user needs. This challenge is reflected in the gradual formation of two forces in ecological development.
The native technology group is committed to exploring the potential based on Bitcoin's unique UTXO model and scripting language, and developing projects that truly conform to Bitcoin's design philosophy.
Although this approach is more technically challenging, it can better maintain consistency with the core values of Bitcoin. Through the analysis of a large number of projects, we found that native technology projects generally have a strong academic background, which reflects the high difficulty of developing Bitcoin ecological infrastructure.
Due to the limitations of the Bitcoin network itself, these projects need to use new technologies such as advanced cryptography to solve challenges, so they require a very strong academic foundation.
Relatively speaking, user-oriented companies focus more on quickly responding to market demands and using existing mature technologies to quickly develop and deploy products to serve existing user groups.
These projects adopt more of Ethereum's experience, and the advantage is that it reduces the cost of user education. However, the disadvantage of this approach is the lack of innovation on the application side, and most of the landing projects are basically copying Ethereum's solutions on the side chain.
Innovation is an indispensable key element for every cycle. In the BTC ecosystem, technological innovation should be more reflected in breaking through its original limitations.
The Babylon project is a great example of how Bitcoin’s utility can be enhanced through native technological innovation. By using innovative technologies such as Bitcoin timestamping, Babylon allows users to earn additional benefits while retaining ownership of their BTC.
This BTC interest-earning method not only minimizes additional asset security risks, but also creates new value for users, making it very attractive to market users. Based on these observations, we believe that the future development path of the BTC ecosystem may be:
Through continuous native technology innovation and improvement, we develop emerging protocols and projects to improve the capital utilization of BTC.
This approach not only breaks through the original technical limitations of Bitcoin, but also meets market demand while maintaining its core value, laying a solid foundation for the long-term healthy development of the Bitcoin ecosystem.








