Author | GaryMa
With the rapid development of blockchain technology, more and more projects are emerging on multiple chains. Whether it's the main chain, application-specific chain, or Layer-2 scaling solutions, the diversity and complexity of the blockchain ecosystem is constantly increasing. Although the multi-chain system provides users and developers with greater flexibility and choice, it also brings significant challenges, including liquidity fragmentation, the complexity of cross-chain operations, and the lack of user experience. This makes the operation process in the Web3 world more complex than in Web2.
Chain Abstraction has emerged as a key solution to this problem. By abstracting the differences of the underlying blockchains, chain abstraction technology can greatly simplify the user experience, allowing users to interact seamlessly across different chains without needing to worry about the underlying blockchain details. As an innovative representative of chain abstraction, XION is committed to providing a wallet-less experience through Generalized Abstraction, further lowering the threshold for users to use Web3 applications. By abstracting accounts, signatures, Gas fees, and interoperability at the protocol level, XION has enhanced the user experience (UX). In this process, XION has eliminated the barriers for new users to enter, while avoiding the fragmentation challenges faced by developers in other ecosystems. Through abstraction of interoperability, XION can also extend the seamless user experience to all integrated public chains and support many novel use cases.
This article will delve into the project background of XION, analyze its innovations in blockchain user experience, including how to solve the user experience challenges through Generalized Abstraction, and how to leverage abstraction of interoperability to enhance the cross-chain experience. In addition, the article will also analyze the token economic design of XION and interpret the competitive landscape of the chain abstraction track.
Project Background
XION was founded by Burnt Banksy, and the name is derived from the Banksy artwork "Morons" that he once burned. Through this event, Burnt Banksy demonstrated the concept of digital scarcity and the potential of blockchain technology. However, he also realized that ordinary blockchain users face many obstacles due to the complexity of the technology and the poor user experience. To this end, he founded XION, aiming to build a L1 blockchain for mainstream audiences, making digital ownership truly accessible through simple and easy-to-use dApps.
XION has received support from well-known investment institutions in multiple financing rounds:
● On May 6, 2021, XION completed a seed round of financing, raising $3 million from investors including Injective, Multicoin Capital, Mechanism Capital, Tribe Capital, Solana Foundation, and Alameda Research.
● On January 17, 2022, XION completed a Series A round of financing, raising $8 million, with major investors including Animoca Brands, Multicoin Capital, Mechanism Capital, Alliance DAO, Sonic, DeFiance Capital, Spartan Group, HashKey Capital, Figment Capital, Tribe Capital, Play Ventures, Valory, Terraform Labs, and Alameda Research.
● On October 5, 2023, XION received strategic financing from Circle Ventures, with the specific amount undisclosed.
● On April 1, 2024, XION completed a new round of financing of $25 million, with investors including Multicoin Capital, Animoca Brands, Arrington Capital, Sfermion, and Spartan Group.
These financing rounds demonstrate the widespread attention and support XION has received in the blockchain and cryptocurrency field, and have laid a solid capital foundation for its further development.
Generalized Abstraction: Encapsulating Complexity, Building a User-Friendly L1
The so-called complex blockchain operation threshold is usually concentrated in account management, signing, payment, and Gas fees. Traditional blockchain systems rely on private key management and address generation, and require private keys for transaction signing. Each public chain also requires the use of its own native token for Gas payment, and the fees are unstable. Furthermore, the volatile prices of cryptocurrencies can also lead to an unfriendly user experience if products and services are priced in cryptocurrencies. All these factors are barriers that keep outsiders and newcomers away.
To eliminate the cryptographic complexity that users face when using blockchains, XION has proposed a "Generalized Abstraction" solution, implementing abstraction at the protocol level for accounts, signatures, Gas, interoperability, pricing, devices, and payments.
Account and Signature Abstraction
XION has adopted a "meta-account" system, allowing users to log in through familiar methods (such as email or biometrics) and enabling secure cross-device access without having to deal with complex private keys. Meta-accounts support multiple login methods (such as social accounts, Face ID) and integrate flexible permission management features, such as private key rotation and custom rules, to enhance account security.
Gas Abstraction
XION has fully abstracted the Gas fees, allowing users to pay transaction fees with any token. XION will automatically convert these fees into platform tokens, realizing a transparent fee settlement process for users. Furthermore, through the PlatformSend mechanism and FeeGrant feature, XION allows developers to pay transaction fees on behalf of users, reducing the fee burden on users in blockchain operations.
Device Abstraction
XION has eliminated the need for users to store and manage private keys, which also indirectly eliminates the security risks and complexity that traditionally arise when users use their accounts on multiple devices. XION users can interact with their meta-accounts seamlessly across various devices (including PCs, smartphones, or tablets). This multi-device architecture significantly simplifies the user experience, promoting mass adoption of new users by reducing entry barriers and improving the usability of all applications accessed through XION.
When interacting with applications through XION, users will see various login methods, including email, social accounts, Face ID, or the option to log in with a Web3 wallet (such as Keplr or MetaMask). Therefore, XION can meet the needs of all audiences, while preserving a very simple user experience for non-crypto users.
Pricing and Payment Abstraction
XION's abstraction makes it a blockchain that supports payments in stablecoins like USDC. Users can directly complete payments using stablecoins without worrying about token fluctuations or tedious exchanges. This design enhances the user experience and makes blockchain applications more aligned with mainstream payment habits, facilitating their promotion to a wider user base.
Through the design of these abstraction layers, XION provides users with an intuitive experience close to traditional applications, significantly lowering the threshold for users to enter the Web3 world.
Interoperability Abstraction: Solving the Liquidity Fragmentation Dilemma
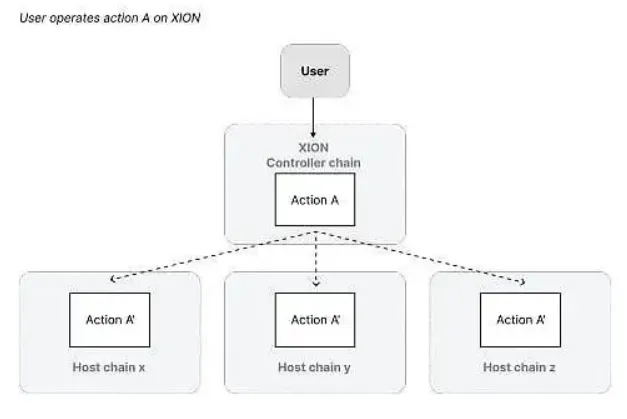
In addition to providing users with a smooth blockchain operation experience on the current chain, XION is also committed to the abstraction of cross-chain interoperability. XION mainly achieves this through the "Package Forwarding Middleware", allowing users to operate on any other public chain from the control chain (such as XION). With the integration of this middleware and the Generalized Abstraction framework, XION provides a simplified protocol-level interface. As shown in the figure below, XION allows users to seamlessly execute operations on any chain integrated with XION, with a consistent and smooth experience.

XION's interoperability abstraction effectively solves the problem of user account fragmentation in the current multi-chain environment. Users can link their accounts on different blockchains to the XION meta-account, managing all on-chain assets through a "central account".
To achieve this goal, XION has adopted various symmetric communication methods, building reliable, ordered, and authenticated communication channels between different blockchains. This interoperability abstraction provides possibilities for new cross-chain application innovations, allowing multi-chain users to enjoy a smooth and integrated operation experience.
Token Economic Design
XION is a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) blockchain based on the Cosmos SDK, and its native token $XION has multiple uses, endowing the ecosystem with broader utility:
● Network Fees: Transactions on the XION network require the payment of fees, and these fees are innovatively used to offset the minting of new tokens. As the network usage increases, this mechanism may even achieve token deflation.
● Security of Proof-of-Stake (PoS): As a PoS network, XION relies on validators to maintain the network's security. $XION holders can delegate their tokens to validators or stake tokens to run their own validator nodes. Furthermore, XION's inflation is based solely on staked tokens, significantly reducing the overall inflation rate of the tokens and ensuring the sustainability of the network economy.
● Governance: $XION holders can participate in network governance through proposals and voting, influencing important decisions in the ecosystem.
● Medium of Exchange and Collateral: Within the XION ecosystem, $XION can be used as native liquidity and collateral, supporting peer-to-peer transactions between different applications and accounts.
Among these, the mechanisms of "offsetting network fees against new inflationary tokens" and "only staked tokens counted towards inflation" in the first two functions represent XION's innovative adjustments to optimize inflation. In the past few years, many new public chains and their ecosystems have tried to attract validators and stakers through exceptionally high staking rewards. However, this practice often leads to hyperinflation, causing the tokens to depreciate rapidly and ultimately affecting the network's stability and security. Therefore, XION has made the following two important adjustments by extending the Cosmos mint module to alleviate inflation:
● Fees Offset Inflation: XION uses the fees collected in each Block to offset the minting of new tokens. For example, if the inflation demand is 1,000 tokens, and the Block fees have accumulated 600 tokens, only 400 new tokens need to be minted, reducing the pressure on the total supply. As user activity increases, this mechanism is expected to further alleviate inflationary pressure and may even lead to a deflationary effect.
● Only Staked Tokens Counted Towards Inflation: Unlike the inflation model of the Cosmos Hub, XION calculates inflation based solely on staked tokens. This approach makes the stakers' annual percentage yield (APY) more stable, unaffected by fluctuations in the number of unstaked tokens, thereby attracting participants focused on long-term returns and effectively reducing short-term arbitrage behavior.
Furthermore, XION recently announced that it will use the USDC stablecoin issued by Circle as the primary trading currency, becoming the first blockchain to be priced in USDC. All products built on XION will be priced in USDC, and all transactions will be free of gas fees. This design significantly reduces market volatility risk and provides users with a more predictable and secure trading experience, not only reducing users' concerns about crypto market fluctuations but also simplifying the trading experience, making XION more accessible and usable for the mainstream market.
Competitive Landscape of the Chain Abstraction Track
Chain abstraction aims to solve two key problems in the blockchain industry. First, the user experience is not user-friendly, and the threshold for understanding blockchain-related usage is relatively high. Externally Owned Account (EOA) wallets, Gas, and various crypto concepts are all barriers that deter new users, making it difficult to achieve the seamless interaction of Web2 applications. Secondly, the current multi-chain situation inevitably leads to the dispersion of liquidity and users, forming mutually isolated ecosystems.
Of course, different projects have different understandings and entry points for chain abstraction.
From the perspective of simplifying user operations and encapsulating operational complexity, projects like CoWSwap, UniswapX, and smart contract wallets can all be included in the category of chain abstraction.
From the perspective of cross-chain interoperability, early industry universal interoperability protocols like Cosmos and Polkadot can also be considered as track OGs, and more recent cross-chain communication protocols like Layerzero, Wormhole, and Axelar, as well as specific ecosystem-level interoperability protocols like OP superchain, can all be considered as track players.
Although these solutions can still be included in the concept of chain abstraction, they are limited by the stage of development in the industry, and the problems they are committed to solving are limited. At the current stage, track players have generally been able to well integrate solutions for both user experience and interoperability, with a focus on one or the other. Here, we mainly select Particle Network, NEAR, and ZetaChain for comparison with XION.
NEAR Protocol: Chain Abstraction Solution Centered on Account Aggregation and Multi-Chain Signing
As a sharded Proof-of-Stake Layer 1 blockchain, NEAR's core chain abstraction features are:
● Account Aggregation: Allows users to integrate multiple operations in a single account, simplifying the management of cross-chain, wallets, and Gas fees. Additionally, NEAR supports user-friendly account names (e.g., wu.near), providing a more intuitive account management approach than traditional blockchains. NEAR's FastAuth system further reduces the user's entry barrier, allowing users to register with email and use biometrics instead of complex private key management, significantly enhancing the fluency of the user experience.
● Multi-Chain Signing Support: Through the NEAR MPC (Multi-Party Computation) network, NEAR allows accounts to have corresponding remote addresses on other chains and to sign transactions and perform operations from these addresses. The signing nodes in the MPC network do not rely on explicit private keys but use a threshold signature protocol, supporting key sharing and dynamic node changes, enabling continuous access in a cross-chain environment.
● Meta Transactions (NEP-366): NEAR implements meta transactions (NEP-366), allowing users to execute transactions without pre-holding Gas tokens.
ZetaChain: Cross-Chain Asset Management through Omnichain Smart Contracts
ZetaChain focuses on cross-chain asset and transaction management, using Omnichain Smart Contracts to solve asset flow and contract operations between different chains. Users can directly call other chains' smart contracts on ZetaChain, making cross-chain transactions and asset management more convenient.
In the ZetaChain 2.0 upgrade plan, the team also proposed a series of potential upgrades to achieve the first universal Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) and full-chain abstraction, including full-chain accounts that allow contracts on ZetaChain to interact with native contracts on the connected chains.
Particle Network: Cross-Chain Account and Liquidity Integration Based on Universal Accounts
Particle Network, through its Universal Accounts and Universal Gas features, allows users to manage assets on multiple blockchains with a single account, avoiding the fragmentation of accounts and balances across multiple chains. Universal Gas also allows users to pay cross-chain transaction fees with any supported token, greatly reducing the operational difficulty of Gas fees for users.
Overall, Particle's solution focuses on the interoperability and liquidity integration of multiple chains. Universal Accounts act like a multi-chain wallet account, hiding the complex cross-chain operations, thereby optimizing the user experience.
Based on the available documentation, Particle Network's Layer 1 is more focused on serving as a cross-chain transaction coordination and settlement layer, acting as a cross-chain middleware, rather than being a ecosystem-type Layer 1 like NEAR or XION that supports diverse application development and ecosystem expansion. This middleware solution allows Particle Network to focus on improving the accessibility and interoperability of multiple chains, rather than building a complete ecosystem, which is a significant difference from the positioning of other ecosystem-type Layer 1 public chains.
XION's Differentiation
Comparing XION with the above three projects, we can clearly feel the differences between XION and them: XION places more emphasis on the user experience of its own Layer 1 blockchain, and it can even be said that it is specifically designed as a Layer 1 blockchain to solve the problem of the difficulty of Web3 application adoption. Its goal is to eliminate the technical barriers in the user experience, allowing non-technical users to directly participate in Web3 applications. Through universal abstraction, XION has implemented the abstraction of accounts, signatures, fees, and interoperability at the protocol layer, allowing users to no longer need to understand complex concepts like private keys and Gas fees.
XION is positioned as a Layer 1 public chain designed specifically for consumers. In addition to the current crypto industry users, XION's goal is to attract a large number of new users from outside the industry, so its ecosystem will not be dominated by DeFi financial applications like the current public chains, but will cover areas such as consumption, gaming, social finance, crowdfunding, and payment, and has realized new use cases that were previously difficult to achieve. A typical example is the EarnOS application built on XION. EarnOS, using blockchain technology, is committed to disrupting the advertising market worth over a trillion dollars. In the second quarter of 2024, EarnOS launched a test version, which has received over $12 million in committed spending, attracted more than 500 creators to participate, and reached cooperation with more than 40 global brands and institutions. After the launch of the test version, EarnOS has partnered with well-known brands such as UberEats, Baskin Robbins, Sunglass Hut, and The North Face, and achieved over 950,000 task completions.
Summary
As a seed player in the layer abstraction track, XION has achieved substantial breakthroughs in account management, signing, payment, and interoperability through its simplified user experience abstraction technology. XION's design goal is to break down the high threshold of blockchain user experience, and provide users with a smooth experience similar to Web2, attracting not only the existing Web3 users, but also clearing the obstacles for mainstream users to join the Web3 ecosystem.
However, while the layer abstraction track is advancing rapidly, it also faces the challenges of "air infrastructure" dominated by basic infrastructure and uncertain market demand. Currently, most layer abstraction projects focus on building universal protocols, but there is a gap in practicality and market fit, and the need for compatibility has even led to new fragmentation phenomena. In addition, layer abstraction technology may also exacerbate the imbalance of resources between mainstream public chains and long-tail public chains, affecting the development of the decentralized ecosystem. Therefore, while leading the innovation of layer abstraction, XION also needs to continue exploring how to balance the relationship between user experience, market demand, and technical expansion in the future, in order to consolidate its long-term value in the layer abstraction track. All of this also points to a new direction for the development of the layer abstraction field: not only to improve technological sophistication, but also to truly popularize blockchain around user needs.








