Introduction
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has entered a new stage, evolving from single-task models to intelligent agents - AI Agents - with autonomous decision-making and collaboration capabilities. This change is driven not only by advancements in algorithms and computing power, but also by the empowerment of blockchain technology in terms of decentralization, transparency, and immutability. AI Agents have not only had a profound impact on traditional industries, but also have shown strong potential in the fields of finance, Web3 ecosystem, automated services, and gaming.
As the core of the future intelligent economic system, the self-driving and cross-domain collaboration capabilities of AI Agents will redefine business models and social structures. With the continuous evolution of technology, AI Agents are expected to experience explosive growth by 2025, becoming the driving force behind the intelligent revolution. This report will provide a detailed analysis of the technical foundation, application scenarios, challenges, and future development trends of AI Agents, aiming to provide a comprehensive perspective for practitioners, investors, and researchers in the relevant fields.
I. What is an AI Agent?
1.1 Definition
An AI Agent is an intelligent entity with autonomy, environmental perception, and goal-oriented capabilities. It can make decisions based on external environments and internal goals, and achieve these goals by executing tasks. Compared to traditional AI systems, AI Agents have stronger self-driving capabilities and autonomous decision-making abilities, allowing them to think independently and make dynamic adjustments in complex environments. Its core characteristics include:
Autonomy: AI Agents can make decisions and execute tasks independently without human intervention.
Environmental Perception: By collecting external data, AI Agents can adjust their behavior in real-time to adapt to different changing situations.
Goal-Orientation: The actions of AI Agents are centered on achieving pre-defined goals, and they can optimize their decision-making paths to complete tasks efficiently.
1.2 Classification
Single Agent: This type of Agent completes relatively simple and independent tasks, and usually does not interact with other Agents. For example, the control system in an autonomous vehicle or the assistant in a smart home device.
Multi-Agent System (MAS): Multiple Agents collaborate to complete complex tasks, often used in distributed systems. The intelligent agents share information and coordinate with each other to handle more complex tasks, such as automated supply chain management.
Autonomous Agent: In addition to the traditional characteristics of intelligent agents, this type of Agent also has economic autonomy, allowing it to conduct on-chain transactions, token transfers, and other financial operations, playing an important role in the blockchain.
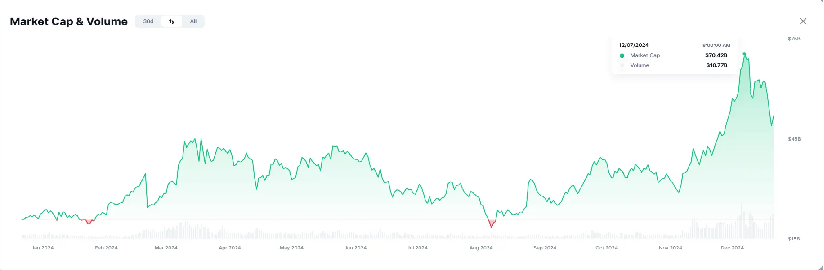
Figure: The market capitalization of AIxCrypto has grown significantly this year
II. Core Technologies and Architecture
2.1 Core Technologies
The implementation of AI Agents relies on the integration of several advanced technologies, mainly including:
Machine Learning and Deep Learning: These technologies enable AI Agents to extract knowledge from large amounts of data and continuously optimize their decision-making models. Through Reinforcement Learning, AI Agents can self-improve their strategies through multiple decision-making processes, thereby improving the quality of their decisions.
Reinforcement Learning: Reinforcement Learning allows AI Agents to constantly adjust their strategies through the reward and punishment mechanism during their interaction with the environment, thereby achieving their task goals. For example, DeepMind's AlphaZero has mastered the ultimate skills of Go through Reinforcement Learning.
Natural Language Processing (NLP): Based on large language models such as GPT, AI Agents can understand and generate natural language, enabling efficient interaction with users. For example, ChatGPT uses NLP technology to provide consulting services or execute tasks for users.
Blockchain and Smart Contracts: Blockchain provides a decentralized infrastructure, ensuring the transparency and security of AI Agents' task execution. Smart contracts provide an automated protocol execution environment for AI Agents, allowing them to conduct financial transactions without third-party intervention.
Distributed Computing: With the proliferation of Multi-Agent Systems, distributed computing has become a necessary supporting technology. Frameworks like Swarm can accelerate collaboration and data sharing among multiple Agents, improving task execution efficiency.
Knowledge Graph: Knowledge graphs provide AI Agents with background knowledge and reasoning capabilities, allowing them to make more accurate judgments by combining multiple knowledge sources in complex decision-making processes.
2.2 Architectural Design
The architectural design of AI Agents typically includes the following core modules:
Perception Module: Responsible for collecting information from the external environment, including data input and sensor feedback. For example, in the financial field, the perception module can collect real-time market data to support investment decision-making.
Decision Module: Based on goals and environmental data, it generates action plans and determines priorities. The decision module analyzes algorithms and models to automatically select the best course of action.
Execution Module: Responsible for putting the strategies generated by the decision module into practice and executing actual operations. The execution module often needs to interact with external systems (such as blockchain, trading platforms, etc.).
Learning Module: During the task execution process, AI Agents continuously optimize their decision-making strategies through feedback mechanisms. By learning from historical data, AI Agents can improve their execution efficiency and accuracy.
III. Application Scenarios
3.1 Finance
The application of AI Agents in the financial industry has gradually become a norm, especially in the following areas:
Intelligent Investment: AI Agents can analyze market data globally and adjust investment portfolios in real-time to maximize investment returns. For example, investment management platforms can deploy AI Agents to execute asset allocation based on big data analysis.
Automated Trading: Through high-frequency trading algorithms, AI Agents can capture profit opportunities from market fluctuations in a very short period of time. By combining with blockchain technology, the trading process can be decentralized and automated.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi): In the DeFi field, AI Agents can act as liquidity providers, optimizing the asset allocation in liquidity pools to improve user yield rates.
3.2 Web3 Ecosystem
NFT Market: AI Agents can autonomously manage the minting, trading, and auctioning of digital assets. By combining with smart contracts and blockchain technology, Agents can ensure the transparency and security of each transaction.
DAO Governance: In decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs), AI Agents can provide decision-making suggestions and execute governance operations, such as voting and asset allocation. Through blockchain technology, the operations executed by Agents can be traced and verified, ensuring the transparency and fairness of the DAO.
3.3 Automated Services
Customer Support: AI Agents, such as ChatGPT, can provide 24/7 customer support, automatically handling customer inquiries and complaints, reducing human intervention, and improving customer experience.
Logistics and Supply Chain: AI Agents play an important role in automated logistics, as they can optimize transportation routes, inventory management, and ensure the efficient operation of the supply chain.
3.4 Gaming and Virtual Worlds
In the gaming industry, AI Agents are playing an increasingly important role:
AI NPCs: In the metaverse and GameFi ecosystems, AI-driven non-player characters (NPCs) provide dynamic interactive experiences, allowing players to engage in more natural and in-depth exchanges with virtual intelligent entities.
Figure: Investment and financing in AI-related projects have surpassed other tracks this year
IV. Business Models
As AI Agent technology continues to evolve, business models are gradually expanding towards diversification and decentralization. The business potential of AI Agents is not only reflected in their application in traditional industries, but also in the unprecedented opportunities in the Web3 and decentralized economic ecosystems. The following are the main business models that can drive the practical application of AI Agents and their related technologies, and create value for innovative economic activities.
4.1 Tokenomics
Tokenomics is an economic model that operates based on blockchain and digital token systems. AI Agents in decentralized application scenarios often rely on tokens as a medium of exchange to participate in economic activities. Autonomous Agents can perform various functions on the platform and create business value by issuing or using tokens. The key components of their business model are as follows:
Here is the English translation of the text, with the specified terms translated as instructed:Token Incentive Mechanism: Many AI Agents issue tokens to incentivize user participation in various platform activities. For example, on decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms, AI Agents act as liquidity providers, earning token rewards by providing liquidity to the platform and executing trading strategies.
4.2 Data Economy
Data is one of the most valuable resources in the modern economy, and its economic value has been further amplified by technologies such as artificial intelligence and blockchain. AI Agents can collect and process various data through efficient computation and information processing capabilities, thereby establishing the foundation of the data economy. Specifically, the roles of AI Agents in the data economy are as follows:
4.3 Infrastructure Services
As AI Agents' technology matures, more and more companies are starting to focus on providing technology and computing infrastructure services for AI Agents. Such service models include, but are not limited to, computing power, storage resources, and API interfaces. The business models of infrastructure service providers are mainly reflected in the following aspects:
4.4 Smart Contracts and Decentralized Marketplaces
AI Agents can automatically execute transactions and business activities through smart contracts, reducing human intervention and improving efficiency. In decentralized marketplaces, smart contracts can provide a more reliable execution environment for AI Agents:
Decentralized Marketplace Platforms: AI Agents can directly conduct transactions on decentralized marketplaces without the need for third-party intermediaries. Smart contracts ensure the transparency and fairness of transactions, and the entire transaction process can be fully automated. For example, in the Non-Fungible Token (NFT) market, AI Agents can independently handle the creation, trading, and auctioning of digital assets, thereby realizing self-governance and decentralized market activities.
Decentralized Autonomous Governance: Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) can use AI Agents to automatically execute governance tasks, reducing the dependence on human intervention in the decision-making process. The combination of smart contracts and AI Agents can help DAOs improve decision-making efficiency, increase community participation, and drive the self-development and continuous innovation of the platform.
Five. Challenges Faced
5.1 Technical Challenges
Performance Bottleneck: As the number of AI Agents increases, how to improve the computational efficiency of the system, especially when multiple Agents are collaborating, is a current technical bottleneck, as the demand for computing power will rise sharply.
Data Privacy: In a decentralized environment, how to balance data privacy protection and transparency is an important challenge faced by AI Agents. Particularly in the financial and medical fields, protecting personal data is crucial.
5.2 Regulation and Legal
Legal Liability: The autonomous capabilities of AI Agents make their behavior unpredictable, which poses challenges in determining legal liability. Currently, there is no clear legal framework to define the responsibility of AI Agents when executing tasks.
Economic Autonomy and Regulation: AI Agents have economic autonomy, which may lead to regulatory issues, especially in cross-border payments and digital currency transactions.
5.3 Community and Ecosystem
User Education and Adoption Rate: Although AI Agents have shown potential in multiple fields, user education remains a significant challenge. Many potential users lack understanding of the working principles of Agents, which directly affects their mainstream market application.
Competition and Collaboration: As more AI Agent projects and platforms emerge, how to achieve a balance between cooperation and competition in the open ecosystem will be a key to future development.
Six. Case Studies
With the integration of artificial intelligence and blockchain technology, AI Agents have made significant progress in various fields and application scenarios. Through the analysis of specific cases, we can better understand how this technology is applied in practice and how it drives industry transformation. The following are several representative cases that not only demonstrate the powerful capabilities of AI Agents but also reveal how technology can be combined with different industries, bringing far-reaching impacts to the entire ecosystem.
6.1 TruthGPT Agent
TruthGPT is a fully autonomous AI Agent based on blockchain technology, specifically designed to execute automated investment and arbitrage strategies in the decentralized finance (DeFi) domain. Its core advantage lies in its complete decentralization and lack of human intervention, allowing it to independently assess market trends and execute on-chain transactions. The launch of this project marks a new stage in the application of AI Agents in the DeFi field.
Core Functions and Applications
Automated Arbitrage: The TruthGPT Agent can utilize its algorithms to identify arbitrage opportunities in the market, whether it's price differences across exchanges or yield differences based on different DeFi protocols. It can quickly make decisions and execute transactions. By reacting quickly, the TruthGPT Agent can maximize its earnings in the DeFi ecosystem while reducing the emotional volatility associated with human decision-making.
Intelligent Risk Management: To avoid excessive risk, TruthGPT also integrates smart risk control functions. The AI Agent monitors market fluctuations, analyzes historical data, and adjusts investment strategies to ensure the safety of funds and the stability of returns.
Decentralized Execution: By integrating blockchain and smart contracts, the TruthGPT Agent can directly execute operations specified in smart contracts without the need for human intervention. This decentralized execution model ensures the transparency, security, and immutability of transactions, while also eliminating the costs and risks associated with intermediary institutions.
Token Economic Incentives: TruthGPT adopts a token incentive mechanism, where users can obtain proxy services by holding the platform's native tokens, and can also earn token rewards by providing liquidity and participating in governance.
6.2 Swarm Framework
Swarm Framework is an open-source distributed computing framework that aims to achieve efficient processing of complex tasks through the collaborative work of multiple AI Agents. It is not only a platform for building AI systems but also an ecosystem focused on multi-agent system (MAS) collaboration. The launch of this framework marks a further expansion of AI Agents in the field of collaboration and distributed computing.
Core Functions and Applications
Multi-Agent Collaboration: Swarm Framework can combine multiple AI Agents into a collective, using distributed computing to jointly complete complex tasks. These tasks can involve data processing, information sharing, collaborative decision-making, and other domains, significantly improving the efficiency and accuracy of task execution.
Task Allocation and Optimization: Swarm Framework allows users to assign different tasks to different AI Agents based on their specific capabilities and strengths.
Fault Tolerance and Adaptability: Swarm Framework has strong fault tolerance, where if any AI Agent in the system fails or is unable to complete a task, other Agents will automatically take over the task to ensure the system continues to run without interruption.
Blockchain Integration: Swarm Framework integrates with blockchain technology to provide AI Agents with an immutable record and a decentralized execution environment.
Through the application of Swarm Framework, we can see the advantages of AI Agents in multi-agent systems, particularly in terms of their strong capabilities in collaboration, fault tolerance, and adaptability. It not only promotes efficient cooperation between intelligent agents but also provides a new direction for distributed computing.
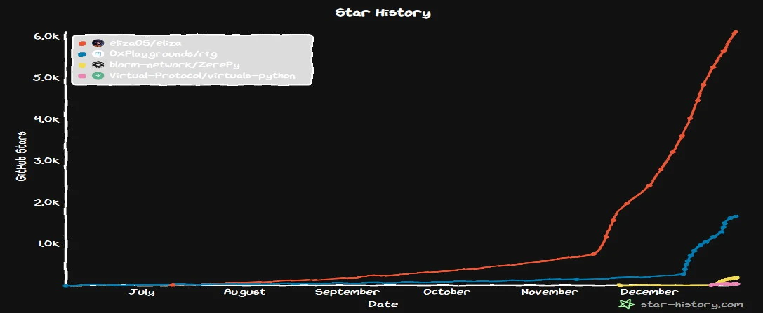
Figure: Changes in GitHub star data for mainstream projects since their launch
6.3 AI NPCs in GameFi
The application of AI Agents in the gaming industry is becoming increasingly common, especially in the convergence of GameFi (Game Finance) and virtual worlds, where AI Non-Player Characters (NPCs) have become an important component in enhancing the gaming experience. GameFi platforms not only provide gaming experiences for players but also integrate blockchain technology, endowing virtual world economic activities with capabilities, and AI NPCs provide intelligent and automated support for these virtual economic activities.
Dynamic Interaction and Intelligent Behavior: Traditional game NPCs mainly interact with players through pre-set scripts, while AI NPCs have the ability to learn and make decisions autonomously. They can respond dynamically based on player behavior, environmental changes, task requirements, and other dynamic factors.
Virtual Economy and Transactions: In GameFi platforms, AI NPCs can participate in the construction of the virtual economy, for example, through automated trading, asset management, and resource allocation, to provide players with real-time market interactions.
Here is the English translation:Metaverse and Social Interaction: With the rise of the metaverse concept, AI NPCs are gradually entering virtual social scenarios. For example, in the virtual reality world, AI NPCs can become virtual social partners for players, providing entertainment, education or collaboration services. Decentralized Game Governance: In GameFi platforms, AI NPCs can participate in game governance and decision-making through decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs). These AI Agents can automatically adjust game rules, task rewards and resource allocation based on player feedback and participation, promoting the healthy development of the game community.
VII. Future Development: Future Development
The combination of AI Agents and crypto-assets will see critical breakthroughs in the coming years. With the continuous advancement of technology and changes in market demand, AI Agents will help the crypto-asset field achieve innovation at multiple levels, including cross-chain collaboration, resource sharing, and efficient computing methods. In the future development, the combination of AI Agents and crypto-assets will focus more on intelligence, automation and security, bringing a more efficient and flexible ecosystem.
7.1 Technical Direction
7.1.1 Cross-chain Collaboration
The heterogeneity of blockchain technology means that there are technical barriers between different blockchains, and resources and information are difficult to flow across multiple blockchain platforms. The cross-chain collaboration capability of AI Agents will be a key technical direction in their future development. Through cross-chain bridge technology, AI Agents will be able to overcome the limitations of different blockchains, utilize the advantages of different chains, and enhance their applications in multiple crypto-asset networks.
Asset Management and Optimization: AI Agents can intelligently allocate assets on different chains, flow between chains, to maximize returns or reduce transaction costs.
Cross-chain Data Collaboration: Different blockchain platforms often have different consensus mechanisms, data structures and transaction models. AI Agents will act as an intermediary to facilitate the processing and interaction of cross-chain data.
DeFi Interoperability: Currently, different platforms and protocols in the DeFi ecosystem are largely isolated. The cross-chain capability of AI Agents can enable them to perform automated asset management and decision execution across multiple DeFi protocols, thereby optimizing the interoperability and user experience of DeFi services.
7.1.2 More Efficient Swarm Computing
As blockchain networks continue to grow and task complexity increases, traditional computing methods are struggling to meet increasingly complex demands. Swarm computing, as a distributed computing method, can process large-scale data and execute complex tasks through the coordinated collaboration of multiple AI Agents. In the crypto-asset field, Swarm computing will have great potential, especially in data analysis, smart contract execution, and trading decisions.
The advantage of Swarm computing lies in its ability to accelerate the computing process, improve efficiency, and reduce costs through the cooperation of multiple intelligent agents (AI Agents).
Smart Contract Execution and Optimization: Swarm computing can distribute the execution tasks of smart contracts, with multiple intelligent agents collaborating to complete the verification, calculation, and transaction execution of contract terms.
Distributed Risk Assessment: AI Agents can make predictions and risk assessments on market trends based on distributed computing. Multiple intelligent agents can jointly process a large amount of market data, thereby reducing the risk of a single prediction model and improving the overall accuracy and reliability.
Decentralized Data Analysis: AI Agents will be able to efficiently obtain and analyze data between multiple decentralized data sources through distributed computing methods, providing rapid and accurate market insights to help users make smarter investment decisions.
7.2 Emerging Fields
7.2.1 Agent x IoT (Fusion of IoT and Crypto-assets)
The combination of Internet of Things (IoT) technology and crypto-assets, especially in the application of smart contracts and blockchain, will open up more innovative application areas for AI Agents. AI Agents can drive the application of crypto-assets in the IoT ecosystem through seamless connection with IoT devices.
Smart Contracts and Automated Payments: AI Agents can work in coordination with IoT devices to realize automated payments and smart contract execution based on IoT data.
Decentralized Trading and Settlement System: In the crypto-asset market, IoT devices can become the entry point for transactions, and AI Agents are responsible for automatically executing and settling transactions based on device data, enhancing the practicality and flexibility of decentralized trading platforms.
Tokenization of IoT Devices: IoT devices themselves will become part of crypto-assets, and AI Agents can help convert the usage rights or data flows of these devices into digital assets, promoting the digitalization and liquidity of IoT assets.
7.2.2 Agent x Social Networks (Fusion of Social Networks and Crypto-assets)
Social networks have become an indispensable part of people's daily life, and in this field, the combination of AI Agents and crypto-assets will also open up new development opportunities. By closely integrating crypto-assets with social networks, AI Agents will be able to provide users with more personalized, secure and intelligent services.
Privacy Protection and Data Management: AI Agents can assist users in managing personal data on social network platforms, ensuring the protection of privacy and the compliant use of data.
Decentralized Market Based on Social Networks: AI Agents can identify potential crypto-asset investment opportunities by analyzing content and user behavior on social platforms.
Social Tokenization and Reward Mechanism: AI Agents can automatically generate cryptocurrencies or social tokens based on user interactions and content creation on social platforms.
Decentralized Identity Management: AI Agents will be able to assist users in managing their digital identities, ensuring the security and privacy protection of user identity information on social platforms through decentralized identity authentication systems.
VIII. Conclusion and Recommendations
The future development of AI Agents is full of potential. From more intelligent autonomous decision-making to deep integration with multiple industries, and to cross-domain intelligent collaboration, AI Agents will undoubtedly become a key force driving transformations in various aspects of society. With continuous technological breakthroughs and the gradual improvement of ethics and governance, the widespread application of AI Agents will bring unprecedented innovation opportunities to human society. However, how to strike a balance between technological progress and ethics/regulations will be the most critical challenge in future development.
AI Agents represent the fusion of artificial intelligence and decentralized technologies, and are an important component of the Web3 ecosystem. Although the technology faces many challenges, its potential revolutionary impact cannot be ignored. In the future, with technological breakthroughs, the improvement of regulatory frameworks, and the advancement of user education, AI Agents are expected to experience rapid growth.
It is recommended that developers, enterprises and investors in related fields closely follow the development of AI Agent technology, and actively participate in this intelligent revolution to promote its widespread application and innovation across industries.








