Author: Marcel Pechman, CoinTelegraph; Translated by: Bai Shui, Jinse Finance
On February 20, the S&P 500 index fell 1%, and the US dollar weakened against a basket of foreign currencies, falling to its lowest level in 70 days. Over the past six months, Bitcoin has shown a positive correlation with the US Dollar Index (DXY), leading traders to suspect an impending correction.
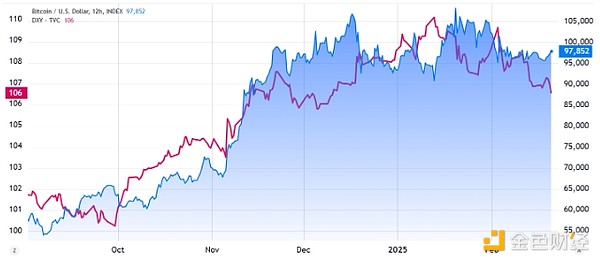
DXY index (left) and Bitcoin/USD (right). Source: TradingView / Cointelegraph
While it is difficult to directly link the causality between the US dollar index and Bitcoin prices, both have risen from September 2024 to January 2025, and then faced challenges in maintaining their bullish momentum.
Some analysts believe that the election of US President Donald Trump has promoted fiscal policy, which may have led to a strengthening of the domestic currency. However, recent data (whether or not attributed to the previous administration) show that US inflation remains persistent, and retail sales are weak, suggesting the possibility of "stagflation" in the future.
It is still too early to fully assess the impact of recent import tariffs and government budget cuts, but in a report released on February 14, Chief Investment Officer Larry Adam of Raymond James warned that this could have a 0.6% negative impact on US GDP growth, and warned that inflation could rise by 0.5%. While this scenario is not necessarily favorable for Bitcoin, it may dampen investors' risk appetite.
The DXY index puts pressure on Bitcoin prices, but the trend may weaken
On February 20, US Treasury Secretary Scott Bassentt stated that the government has not yet moved towards issuing more long-term bonds. "There's a long way to go," Bassentt commented. Although there had been previous criticism of Janet Yellen's preference for short-term debt, the previous administration's approach has not changed.
Bassentt explained that any move towards longer-term bonds would depend on market conditions and inflation trends, and attributed the current situation to "Biden inflation." However, more worryingly, Bassentt pointed out that "when I'm not competing with the Fed, I'll be more inclined to extend maturities," as the Fed has been a "big seller" of government bonds.
The positive correlation with the DXY index has put downward pressure on Bitcoin's price. However, as investors shift Bitcoin from a risk asset to a scarce hedge asset similar to "digital gold," this trend may weaken. Part of the reason for this shift is that several US states have passed legislation allowing Bitcoin to be held as a reserve asset.
On February 19, the Montana Business and Labor Committee passed a bill establishing a special revenue account to invest in precious metals and Bitcoin. Other states, including Utah, Arizona, Oklahoma, Illinois, Kentucky, Maryland, New Hampshire, New Mexico, North Dakota, Ohio, Pennsylvania, South Dakota, and Texas, have also introduced Bitcoin reserve bills.
On February 20, the Bitcoin price broke through $98,000, indicating that investors are increasingly recognizing its sound monetary policy. This is particularly important given the high risk of the US government pursuing expansionary monetary policies (for example, if Elon Musk's government efficiency department achieves its spending reduction targets).
Investors' cautious sentiment is also reflected in the price of gold, as this precious metal hit a new all-time high on February 19. Traders should not only focus on the US dollar's performance relative to other currencies, but also on how nation-states assess Bitcoin. Czech National Bank Governor Aleš Michl emphasized the importance of evaluating Bitcoin's potential as a reserve asset.
Ultimately, the path to Bitcoin's new all-time high largely depends on inflows into spot Bitcoin exchange-traded funds (ETFs), the preferred tool for institutional investors - according to data from Farside Investors, this has not been the case over the past two days, with a cumulative net outflow of $125 million.







