Key Points
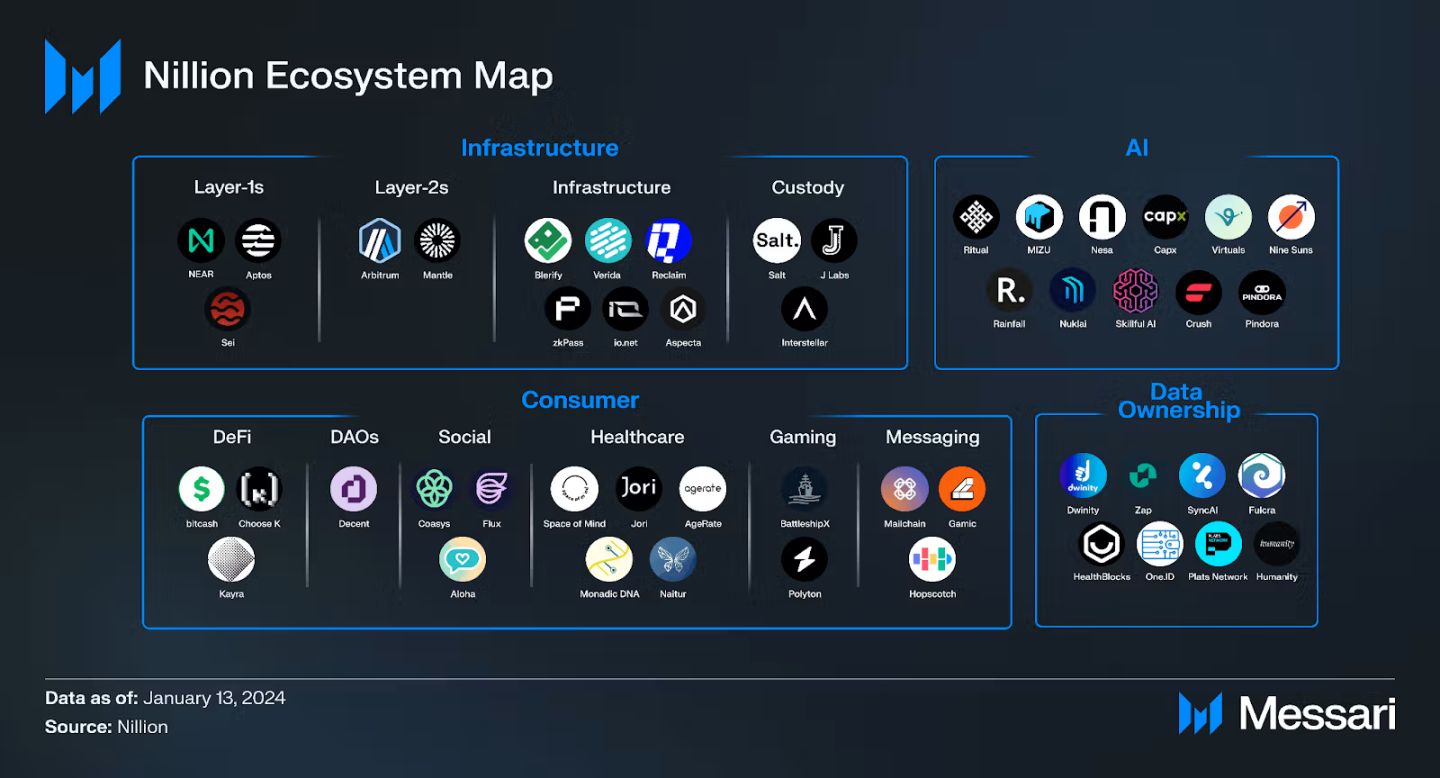
- Nillion has established partnerships with companies such as Virtuals, NEAR, Aptos, Arbitrum, Ritual, io.net and Meta.
The application toolkit includes nilAI, nilVM, nilDB, and nilChain , providing resources for developers to create privacy-preserving applications in areas such as artificial intelligence, healthcare, and decentralized finance (DeFi).
The network leverages a range of privacy-enhancing technologies ( PETS ) such as multi-party computation (MPC), homomorphic encryption, and zero-knowledge proofs to support secure computation and data storage on a decentralized infrastructure.
Nillion's validator program has attracted around 500,000 active validators , processed around 195 million secret messages , and protected around 1050 GB of data .
Introduce
Traditional methods of handling high-value data such as passwords, personalized AI, medical information, and biometric data are often insecure and inefficient. While encryption technologies can ensure data security at rest, they introduce security risks and data latency when performing calculations that require decryption and re-encryption. Blockchain technology has helped decentralize transactions and data management, but it does not solve the problem of secure computation on encrypted data . This limits the ability to develop secure Web3 applications.
Nillion overcomes these limitations by enabling data transmission, storage, and computation without decryption , ensuring privacy and security throughout the data lifecycle. This approach, called “Blind Compute,” helps establish decentralized trust and expands the application scope of decentralized networks to previously untapped areas, such as private AI and secure large language models (LLMs) .
Nillion applies privacy-enhancing technologies ( PETS ) such as multi-party computation (MPC), fully homomorphic encryption (FHE), and trusted execution environment (TEE) to ensure data remains encrypted throughout processing.
Background
Founded in 2021, Nillion is a network that aims to process private data on distributed systems while ensuring security and efficiency. Nillion's ecosystem is powered by tools such as nilVM, nilDB, nilAI, and nilChain , making it easy for developers to build privacy-preserving applications in areas such as AI, DeFi, and data storage .
Nillion's team includes many industry experts:
Alex Page (CEO) – Former partner at Hedera SPV, former senior banker at Goldman Sachs.
Andrew Masanto (CSO) – Co-founder of Hedera, first CMO of Reserve.
Slava Rubin (CBO) – Founder of Indiegogo.
Dr. Miguel de Vega (Chief Scientist) – Leading expert with over 30 patents in data optimization.
Conrad Whelan (CTO) – Founding engineer of Uber.
Mark McDermott (COO) – Formerly led innovation at Nike.
Andrew Yeoh (CMO) – Senior Partner at Hedera, former director at UBS and Rothschild Bank.
Nillion has attracted interest from prominent investment funds such as Hack VC, Hashkey Capital, Distributed Global and Maelstrom , raising a total of $50 million across multiple private funding rounds thanks to its unique vision and technology.
Technical aspects
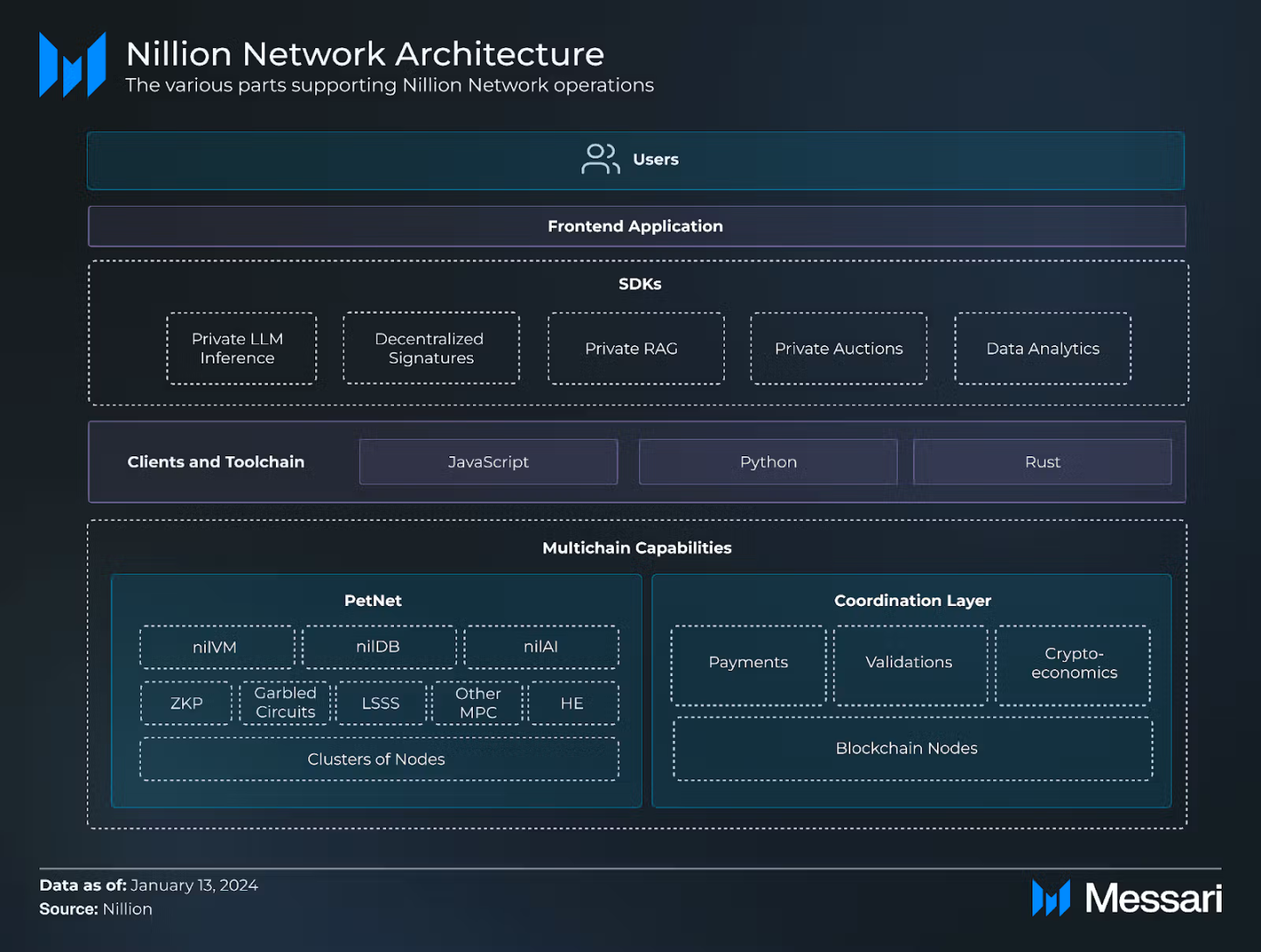
The Nillion network consists of two core layers:
Coordination Layer : Manages rewards, payments, and economic security.
Petnet Layer : Handles computation and private data storage.
Multi-party computation (MPC) technology is the foundation of Nillion, allowing data computation without revealing the input information of each party. The Nillion ecosystem is supported by a development toolkit including nilAI, nilVM, nilDB and nilChain , making it easy for developers to build privacy-preserving applications.
The Nillion network uses clustering technology to improve scalability, ensure performance, security, and optimize costs. Unlike traditional blockchains, Nillion is not dependent on global state , which helps optimize data processing capabilities.
Nillion Network
The Nillion Network is a decentralized infrastructure designed to support private, high-value data storage and computation. The network achieves scalability through clustering technology, which enables node groups to be configured to meet specific performance, security, and cost requirements. Unlike traditional blockchains, the network can operate without a shared global state, allowing for vertical scaling (upgrading individual nodes or clusters) and horizontal scaling (adding new nodes or clusters) to efficiently distribute workloads.
Coordination Class
The Nillion network's Coordinator layer, called nilChain , is primarily responsible for:
Reward management,
Pay,
Ensuring the economic security of cryptocurrencies,
Coordination between clusters of nodes in the network.
Specifically, nilChain coordinates the payment flow for storage and blind computation operations on the network, but does not directly handle these computation tasks. The Orchestration Layer is built using the Cosmos SDK and supports the IBC (Inter-Blockchain Communication) protocol for interacting with other blockchains. However, since the network's primary focus is on storage and computation, it does not currently support smart contract execution. Users can access nilChain through wallets such as Keplr or Leap , but applications built on partner blockchains (mentioned in the "Main Projects" section) will be completely abstracted away.
Petnet
Petnet (Operation Layer) aims to integrate privacy enhancing technologies (PETs), including:
Multi-Party Computation (MPC) ,
Fully Homomorphic Encryption (FHE) ,
Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKP)
The goal is to provide secure computing and private data management. This integration is accomplished through two main components:
Compilers , which simplify the use of PETs by providing different levels of abstraction.
Computational networks , perform secure computations and manage encrypted data.
This is currently implemented via the Nillion network language compiler and nilVM , with four abstraction layers under development:
Each PET protocol runs in a separate blind module , like a “black box”. There is no built-in unified interface or abstraction layer, and all coordination is done on the client side. Developers can use the API to perform specific tasks, but cannot integrate or customize them.
The SDK integrates multiple blind modules , providing a unified and simple management for implementing multiple PET protocols without deep understanding of cryptography. However, at this stage, the modules are not fully optimized and mainly rely on a single PET protocol.
The blind module supports running multiple PET protocols in the same module , giving developers the flexibility to choose between performance and security without requiring in-depth knowledge of cryptography.
Blind modules are deployed in loosely coupled independent networks, called Clusters, managed by NilChain . As Nillion’s blind computing technology evolves, these blind modules can be replicated across multiple Clusters, each with different configurations (number of nodes, location, reputation, hardware, security thresholds). This allows developers to deploy the same functionality in multiple environments, customized to specific needs (security, cost, hardware, regulatory compliance).

Nillion's privacy-enhancing technologies (PETs) are being introduced in phases, with each phase progressing step by step through the four abstraction layers outlined above. The first phase (i.e., homogeneous encryption, network-based secret sharing schemes for multi-party computation) and the second phase (i.e., discrete wavelet transform + network-based secret sharing schemes, threshold homogeneous encryption) have matured in abstraction and are now being integrated into the Nillion network. In the third technology phase (i.e., multi-party computation with fully homogeneous encryption, discrete wavelet transform + threshold homogeneous encryption, public computation, zero-knowledge proofs), multi-party computation with fully homogeneous encryption has begun to make progress at the abstraction layer.
How It Works
Here is a detailed breakdown of how the different components of the Nillion network operate:
Users/developers submit data for storage or perform blind computation requests through front-end applications built with JavaScript or Python clients.
Applications using JavaScript clients interact with Petnet to perform secure computations and manage encrypted data, while Python-based applications interact with the coordination layer to handle payments, routing, and multi-chain communication.
The coordination layer uses the respective blockchain's native gas token or NIL token to process payments.
After processing the request, the orchestration layer passes the computational tasks to Petnet , which contains advanced security technologies ( PETs ).
Petnet uses PETs such as linear secret sharing schemes (LSSS), garbaged circuits, and homomorphic encryption to process data as required by the task.
These computations are performed on a set of network nodes . Each node manages only a small share of the encrypted data. These nodes perform operations (e.g., addition, multiplication, or secure comparisons) on the hidden data and produce intermediate results.
Petnet aggregates intermediate results to produce the final computation result in a secure and private manner.
The final result routing process goes like this:
If using a JavaScript client, Petnet will send the results directly to the application for user/developer access.
If using a Python client, the orchestration layer will take the result from Petnet and pass it to the relevant application or blockchain for further use.
For blockchain integrations, the orchestration layer passes the results to the native smart contract or decentralized application (DApp) , enabling cross-chain operations without requiring users to download new wallets.
Nillion's Multiparty Computation (MPC) Protocol for Complex Tasks
Multi-Party Computation (MPC) is a field of cryptography that allows multiple parties to jointly compute a result from their data without revealing their individual inputs. Nillion developed the Curl protocol, which is based on the linear secret sharing scheme (LSSS) but extended to efficiently handle complex operations such as division, square roots, trigonometric functions, and logarithms.
Curl works in a two-phase process:
Phase 1 (Preprocessing to create data shares)
This phase generates and distributes random shares to the participants (computational entities) before using the MPC technique to process the actual data.
This preprocessing runs independently of the input value, only based on the input quantity to pre-generate the corresponding number of shares.
It can be seen as an abstraction layer , which creates placeholders that will be combined with the actual user input data in the second phase.
Phase 2 (Efficiently calculate complex operations)
Input: Parties distribute shared portions of the input data to ensure information theoretical security ( ITS ).
Evaluation: Parties perform complex computations on shared data using the Curl protocol.
Output: Local computation results are revealed and aggregated to produce the final output.
Application Tools
Based on the Nillion network platform, the application tools ( nilVM, nilDB, nilAI and Nada ) provide developers with a modular framework and practical utilities to quickly build private data processing applications.
nilAI
nilAI is Nillion's privacy-focused AI technology suite, which includes AIVM, nada-AI, and nilTEE .
AI Virtual Machine (AIVM): A secure AI inference platform based on Nillion's MPC technology and Meta's CrypTen framework.
nada-AI: A nilVM library for AI applications, providing a PyTorch-like interface to run small models like NN, CNN, linear regression, etc.
nilTEE: A solution for running large language models (LLMs) in a trusted execution environment ( TEE ).
Nada & nilVM
nilVM is a virtual machine that helps developers create programs using PETs technology.
The program is written in Nada , a domain-specific language (DSL) based on Python.
nilDB
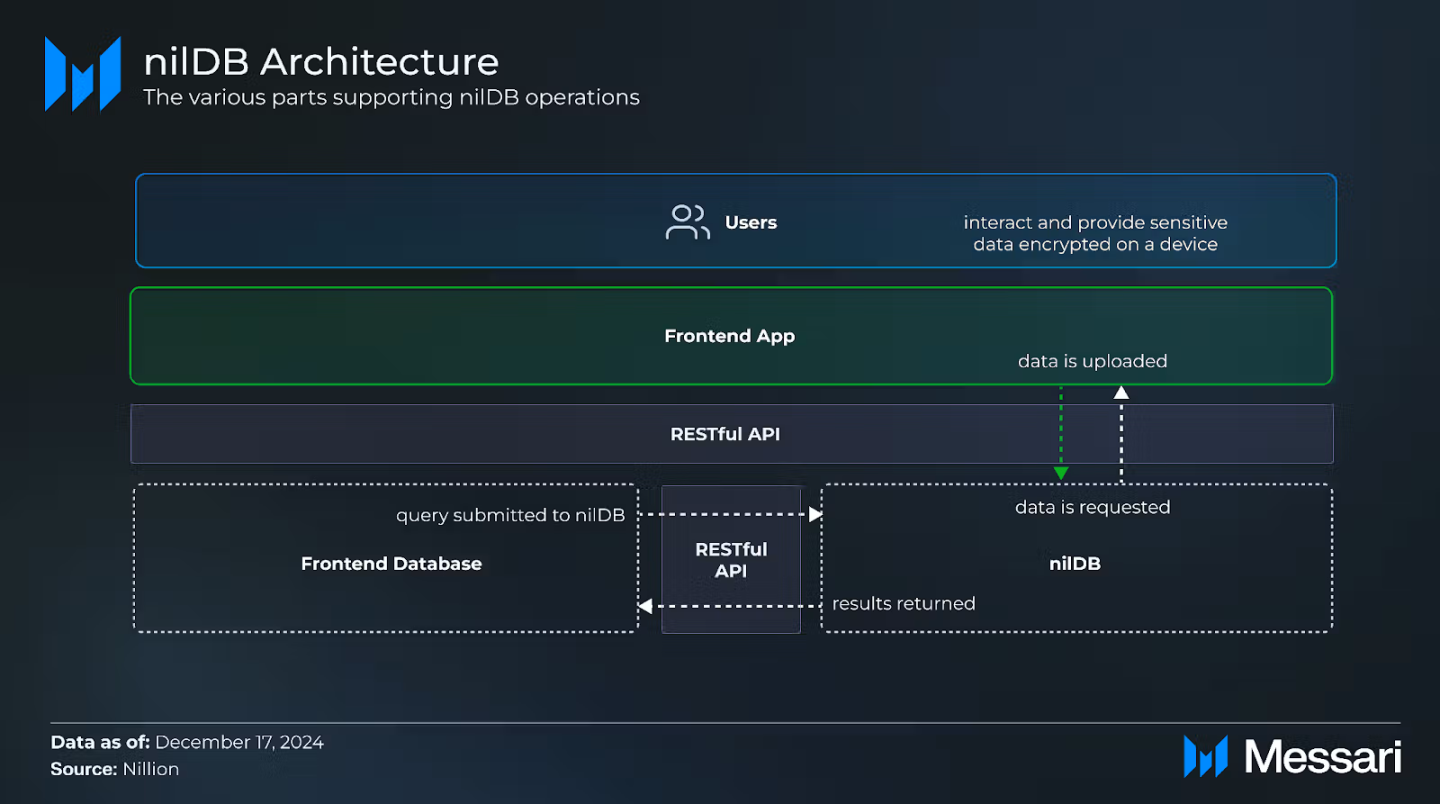
nilDB is a distributed, encrypted NoSQL database, designed for secure data storage and private computation.
Users encrypt sensitive data on their devices before uploading.
The encrypted data is split into secret parts using Nillion's MPC protocol and distributed across nilDB nodes.
Users can delegate access to third parties to perform SQL-like queries without revealing data.
How it works:
Users encrypt sensitive data on their devices.
Users upload encrypted data through a front-end application built on Nillion. This application securely uploads the encrypted data to nilDB via a built-in RESTful API.
The encrypted data is split into secret chunks using Nillion's MPC protocol and distributed to a cluster of nilDB nodes. Notably, no single node holds the entire dataset.
Users can provide explicit permission for specific data use or query, which can be revoked at any time through the application.
Authorized parties (e.g., companies or third parties) submit SQL-like query requests (e.g., lookups, range filtering, or aggregation calculations) via Nillion's RESTful API.
Nodes in a nilDB cluster coordinate computations on encrypted data without exposing sensitive information.
While maintaining data confidentiality, query results such as averages, sums, or filtered datasets are generated.
Only the final result of the query is returned to the user via the RESTful API.
Nada Integration
The Nada language includes several different built-in packages, including nada-AI, nada-numpy, and nada-test, with use cases such as:
nada-numpy : A restricted version of NumPy, customized for the Nada DSL. Compared to regular NumPy, nada-numpy allows efficient operations on array structures with strict data type requirements, ensuring compatibility with the strongly typed characteristics of MPC.
nada-test : A testing framework for Nada programs, supporting dynamic test generation at runtime. Developers can write test cases in Python, integrate the testing framework into their pytest pipeline, and define flexible input and output parameters.
Research papers
The Nillion project team has collaborated with several researchers to publish eight research papers that delve into different aspects of the protocol and its applications.
Below is a list of research papers:
Nillion: Web3 Security Processing Layer : Presents the initial vision of Nillion, providing an overview of Nillion's potential and applications in the decentralized ecosystem.
Evaluating Arithmetic Multiplications and Expressions in Non-Interactive Computation Phases of Linear Secret Sharing Schemes : Explore Nillion's MPC protocols for achieving secure and efficient non-linear computation.
Curl: Private Large Language Model (LLM) Inference via Wavelet-Encoded Lookup Tables : Introducing Curl, a privacy-preserving inference framework for large language models, leveraging wavelet-encoded lookup tables to reduce communication overhead and increase performance.
Technical Report on Secure Cuts and Its Application in LLM Quantization : Discusses secure cut techniques based on linear secret sharing scheme (LSSS) in MPC environment for computational optimization in large language models (LLM).
More efficient comparison protocols in MPC : Improved secure comparison performance in LSSS-based MPC systems.
Technical Report on Threshold ECDSA in Preprocessing Setup : Presents a preprocessing method for Threshold ECDSA, a distributed cryptosystem that securely manages and uses private keys among multiple participants.
Technical Report on Decentralized Multi-Factor Authentication : Introducing a decentralized framework to improve secure authentication processes.
Ripple: Programmable bootstrap acceleration in Fully Homomorphic Encryption (FHE) via wavelet approximation : Describes the Ripple framework, which uses discrete wavelet transform (DWT) to compress the lookup table, thereby reducing the computational cost of bootstrap in FHE.
NIL Token
Tokenomics
Token Utility
- Bar maths give the pandemic service calculate maths, save storage data whether, think discussion WHO and fee deliver pandemic in the class Petnet and Coordination. You body, the home release develop history use NIL to access access the pandemic service calculate maths tell guard right private private belong to Nillion give application use belong to Surname.
- Staking token to support support tell honey network and receive part reward
- The validator stake NIL to body bright deliver pandemic and calculate maths, sure tell safe whole give class Coordination.
- The node Petnet stake NIL to increase strong tell honey give the cluster belong to Surname and collect suck the home release develop also like application use
- Reference family enter manage treat fly practice central equal way subject export and cancel vote give the decide determine network other each other, no limit like lift grant deliver awake, stool supplement talent original and the chapter program talent support add copper.
Administration
- Gender Introduction the calculate power or copy access Japan new.
- Manure supplement Fund part reward give talent support, recommend encourage home release develop and the bright ants by add copper guide lead
- Thing adjust price network, Love bridge validator or gender limit commission rights
- Fix change structure bamboo manage treat, no limit like Love bridge determine level or threshold subject export
- Open wide ability power soy sauce work, design set up mandarin system opposite to work war comb or develop declare the muscle regime bright white and check maths.
State of the Nillion Ecosystem
Key Areas
- Artificial Intelligence : Nillion enables data processing and inference without exposing sensitive information, bridging the gap between secure local AI processing and scalable non-private centralized AI systems.
- Personalized Agents : AI agents can store, compute, and process private data.
- Private Model Inference : AI models can securely process private data, minimize third-party exposure risks, and support private large language models (LLMs).
- Knowledge Base and Private Search : Data can be stored in encrypted form while still allowing AI agents and other AI use cases to perform searches.
- Data Ownership : Nillion's cryptographic infrastructure supports a secure data marketplace by allowing users to control and sell their data to buyers.
- Blockchain : Nillion allows blockchain applications to submit blind storage and computation requests to the Nillion network, complementing the public data functionality of the blockchain. It also supports on-chain payments, allowing applications to decrypt relevant data on the blockchain.
- Healthcare : Nillion supports privacy-preserving healthcare data analytics between organizations and users.
- DePIN : When integrated with Nillion, the DePIN project can securely store and process sensitive operational data.
Major Projects
- Virtuals Protocol : An AI agent co-ownership platform that has developed a multi-modal AI agent library and through the use of Nillion, has achieved private training and inference for its AI models, enabling the building of personalized AI agents.
- Aptos/NEAR/Arbitrum/Sei : These are Layer 1 and Layer 2 blockchains that have integrated blind data storage and computation capabilities to enhance the data processing capabilities of their smart contracts.
- Ritual : An AI platform building a decentralized AI inference network, with Nillion integrated into the backend to support private inference.
- Zap : A data platform that aggregates user data into a decentralized data lake in Nillion, providing secure data insights through blind computations and zero-knowledge transport layer security (zkTLS) protocols.
- Reclaim Protocol : A zkTLS infrastructure platform that allows users to prove identity and reputation off-chain in a trustless manner, using Nillion as the storage and processing platform to generate proofs.
- Healthblocks : A fitness app leverages Nillion to protect ownership and control of user data, while allowing third parties to access data insights without exposing personal details.
- MonadicDNA : A genomics platform that uses Nillion to encrypt data throughout its lifecycle, offering an alternative to centralized providers like 23andMe.