Original author: Jtsong.eth (Ø,G) (X: @Jtsong2)
Recently, the crypto investment research think tank @MessariCrypto released a comprehensive and in-depth research report on 0G. This article is a summary of the key points in Chinese:
[Core Summary]
With the explosive growth of the decentralized artificial intelligence (DeAI) sector in 2026, 0G (Zero Gravity) , with its disruptive technical architecture, has completely ended the historical problem of Web3's inability to support large-scale AI models. Its core killer features can be summarized as follows:
High-speed performance engine (50 Gbps throughput) : Through logical decoupling and multi-level parallel sharding, 0G achieves a performance leap of over 600,000 times compared to traditional DA layers (such as Ethereum and Celestia), becoming the only protocol in the world that can support real-time distribution of ultra-large-scale models such as DeepSeek V3.
dAIOS Modular Architecture : It pioneered a four-layer collaborative operating system paradigm of "settlement, storage, data availability (DA), and computing", breaking the "storage deficit" and "computing lag" of traditional blockchain and realizing an efficient closed loop of AI data flow and execution flow.
AI Native Trusted Environment (TEE + PoRA) : Through the deep integration of Trusted Execution Environment (TEE) and Proof of Random Access (PoRA), 0G not only solves the need for "hot storage" of massive amounts of data, but also builds a trustless and privacy-protected AI inference and training environment, realizing a leap from "ledger" to "digital life foundation".
Chapter 1 Macro Background: The "Decoupling and Reconstruction" of AI and Web3
With artificial intelligence entering the era of large-scale models, data, algorithms, and computing power have become core production factors. However, existing traditional blockchain infrastructures (such as Ethereum and Solana) are facing a severe "performance mismatch" when supporting AI applications.
1. Limitations of traditional blockchain: bottlenecks in throughput and storage.
Traditional Layer 1 blockchains were originally designed to handle financial ledger transactions, rather than to handle terabyte-scale AI training datasets or high-frequency model inference tasks.
Storage deficit : Data storage costs on chains like Ethereum are extremely high, and there is a lack of native support for unstructured big data (such as model weight files and video datasets).
Throughput bottleneck : Ethereum's DA (Data Availability) bandwidth is only about 80KB/s, which, even after the EIP-4844 upgrade, is far from meeting the GB-level throughput requirements of real-time inference for large language models (LLM).
Computational lag : AI inference requires extremely low latency (milliseconds), while blockchain consensus mechanisms are often measured in seconds, making "on-chain AI" almost impossible under the current architecture.
2.0G's core mission: Breaking down the "data silos"
The AI industry is currently monopolized by centralized giants, forming a de facto "data wall," which leads to limited data privacy, unverifiable model outputs, and high rental costs. The emergence of 0G (Zero Gravity) marks a profound restructuring of AI and Web3. It no longer views blockchain merely as a ledger storing hash values, but rather decouples the "data flow, storage flow, and computation flow" required for AI through a modular architecture . 0G's core mission is to break down the centralized black box, enabling AI assets (data and models) to become sovereign, owned public goods through decentralized technology.
Having understood this macro-level misalignment, we need to delve into how 0G, through a rigorous four-layer architecture, addresses these fragmented pain points one by one.
Chapter 2 Core Architecture: Four-Layer Collaboration of a Modular 0G Stack
0G is not simply a single blockchain, but is defined as dAIOS (Decentralized AI Operating System) . The core of this concept is that it provides AI developers with a complete protocol stack similar to an operating system, achieving an exponential leap in performance through deep collaboration of a four-layer architecture.
1. Analysis of dAIOS's four-layer architecture
0G Stack ensures that each layer can scale independently by decoupling execution, consensus, storage, and computation.
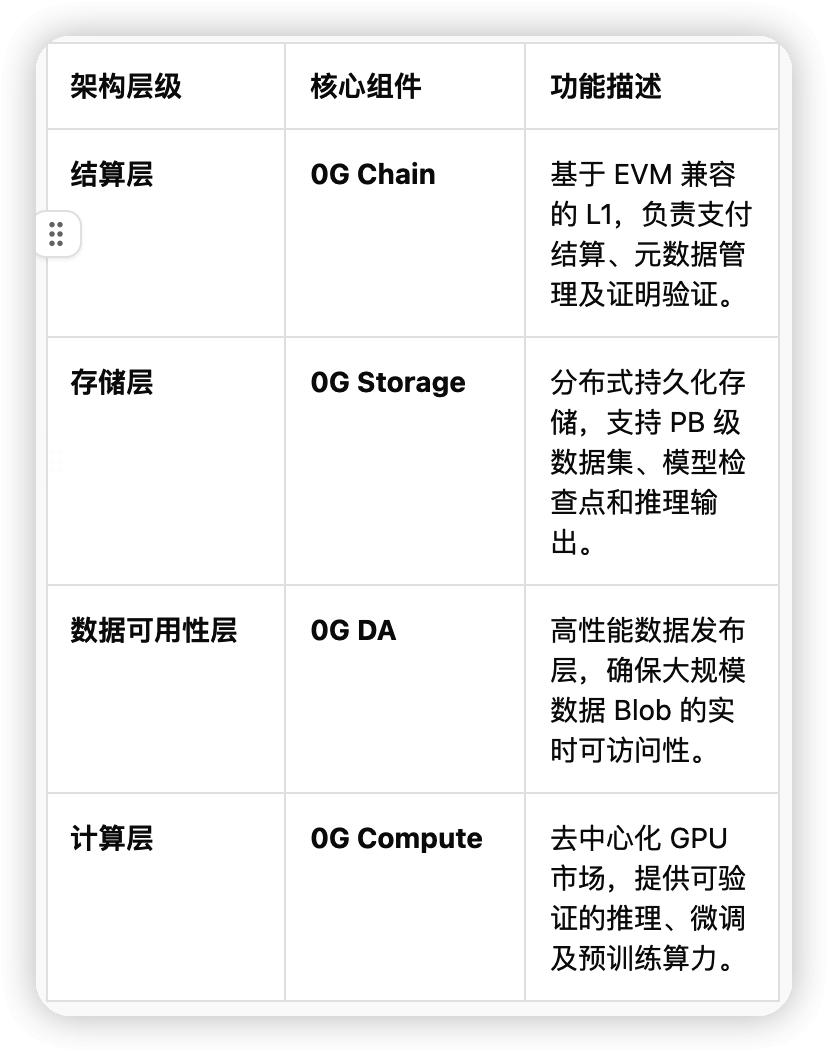
2. 0G Chain: A performance foundation based on CometBFT
As the nerve center of dAIOS, 0G Chain employs a highly optimized CometBFT consensus mechanism. Its innovation lies in separating the execution layer from the consensus layer and significantly reducing block production latency through pipelined parallel processing and ABCI modular design. Performance metrics : According to the latest benchmarks, 0G Chain achieves a throughput of 11,000+ TPS on a single shard and boasts sub-second finality. This extremely high performance ensures that on-chain settlement will not become a bottleneck during high-frequency interactions by large-scale AI agents.
3. Decoupling and Collaboration of 0G Storage and 0G DA
0G's technological moat lies in its "dual-channel" design, which separates data publishing from persistent storage:
0G DA : Focuses on fast broadcasting and sampling verification of blob data. It supports single blobs up to approximately 32.5 MB and ensures data availability even when some nodes are offline through erasure coding technology.
0G Storage : Handles immutable data through the "Log Layer" and dynamic states through the "Key-Value Layer".
This four-layer collaborative architecture provides fertile ground for the growth of high-performance DA layers. Next, we will delve into the most impressive part of the 0G core engine—high-performance DA technology.
Chapter 3: The Technical Depths of High-Performance DA Layer (0G DA)
In the decentralized AI ecosystem of 2026, data availability (DA) is not just about "issuing proofs," but must be a real-time pipeline that carries petabytes of AI weight files and training sets.
3.1 Logical Decoupling and Physical Synergy: Generational Evolution of the "Dual-Channel" Architecture
The core advantage of 0G DA stems from its unique "dual-channel" architecture: it logically decouples data publishing from data storage, but achieves efficient collaboration at the physical node level.
Logical decoupling : Unlike traditional DA layers that conflate data publishing with long-term storage, 0G DA is only responsible for verifying the accessibility of data blocks in a short period of time, while leaving the persistence of massive amounts of data to 0G Storage.
Physical collaboration : Storage nodes use Proof of Random Access (PoRA) to ensure the authenticity of data, while DA nodes ensure transparency through a shard-based consensus network , achieving "instant verification and integrated storage and verification".
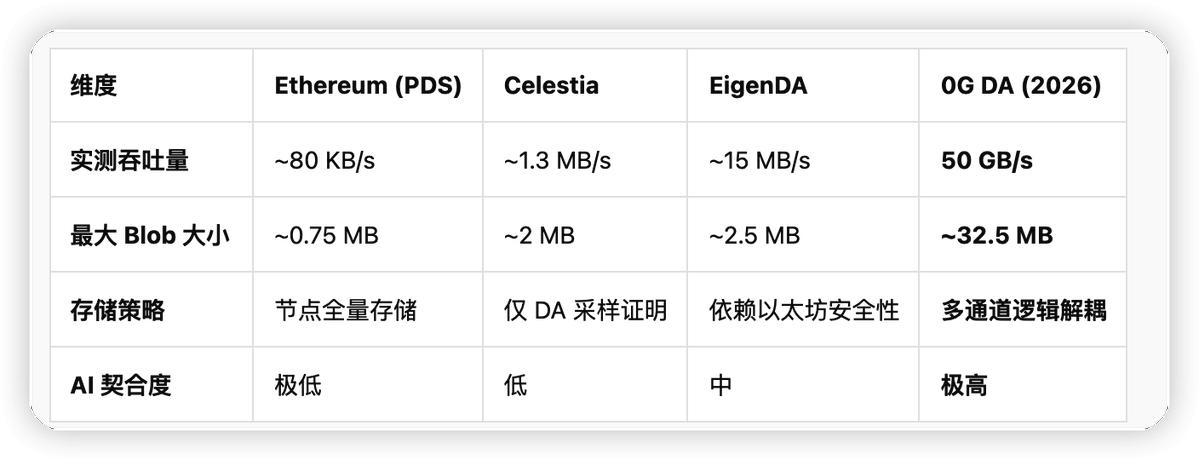
3.2 Performance Benchmark: A Data Showdown with Leading Scale
The breakthrough in throughput achieved by 0G DA directly defines the performance boundaries of decentralized AI operating systems. The table below compares the technical parameters of 0G with mainstream DA solutions:
3.3 Technical Foundation for Real-Time Availability: Erasure Coding and Multi-Consensus Sharding
To support massive amounts of AI data, 0G introduced erasure coding and multi-sharding :
Erasure coding optimization : By adding redundant proofs, complete information can still be recovered by sampling a very small data fragment even if a large number of nodes in the network are offline.
Multi-consensus sharding : 0G abandons the linear logic of a single chain handling all DAs. By horizontally scaling the consensus network, the total throughput increases linearly with the number of nodes. In real-world testing in 2026, it supported tens of thousands of Blob verification requests per second, ensuring the continuity of the AI training stream.
High-speed data channels alone are not enough; AI also needs a low-latency "brain storage" and a secure and private "execution space," which leads to the development of AI-specific optimization layers.
Chapter 4 AI-Specific Optimization and Enhanced Security Computing Power
4.1 Addressing Latency Anxiety in AI Agents
For AI agents that execute strategies in real time, data read latency is a matter of life and death.
Hot and cold data separation architecture : 0G Storage is internally divided into an immutable log layer and a mutable key-value layer . Hot data is stored in the high-performance key-value layer, supporting sub-second random access.
High-performance indexing protocol : Utilizing distributed hash tables (DHT) and dedicated metadata index nodes, the AI agent can locate the required model parameters in milliseconds.
4.2 TEE Enhancement: The Final Piece of the Puzzle for Trustless AI
In 2026, 0G fully introduced a TEE (Trusted Execution Environment) security upgrade.
Computational privacy : Model weights and user input are processed in an "isolated zone" within the TEE. Even node operators cannot observe the computation process.
Verifiability of results : The remote attestation generated by the TEE is submitted to the 0G Chain along with the computation results, ensuring that the results are generated by a specific, tamper-proof model.
4.3 Vision Realization: The Leap from Storage to Operating System
AI agents are no longer isolated scripts, but digital life entities with sovereign identities (iNFT standard) , protected memories (0G Storage) , and verifiable logic (TEE Compute). This closed loop eliminates the centralized cloud vendors' monopoly on AI, marking the beginning of the era of large-scale commercial use of decentralized AI.
However, to support these "digital lives," the underlying distributed storage must undergo a performance revolution, moving from "cold" to "hot."
Chapter 5 Innovation in Distributed Storage Layers—A Paradigm Revolution from "Cold Archiving" to "Hot Performance"
0G Storage’s core innovation lies in breaking the performance limitations of traditional distributed storage.
1. Two-layer architecture: Decoupling of Log Layer and Key Value Layer
Log Layer (Streaming Data Processing) : Designed specifically for unstructured data (such as training logs and datasets). Through append-only mode, it ensures millisecond-level synchronization of massive amounts of data across distributed nodes.
Key-Value Layer (Indexing and State Management) : Provides high-performance indexing support for structured data. Reduces response latency to milliseconds when retrieving model parameter weights.
2. PoRA (Proof of Random Access): A Sybil-resistant verification system
To ensure the authenticity of storage, 0G introduced PoRA (Proof of Random Access) .
Anti-Symanian attack : PoRA directly links mining difficulty to the actual physical storage space used.
Verifiability : Allows the network to randomly "check" nodes, ensuring that data is not only stored, but also in a "ready-to-use" hot-activated state.
3. Performance Leap: Engineering Implementation of Second-Level Search
0G achieves a leap from "minute-level" to "second-level" retrieval by combining erasure coding with high-bandwidth DA channels. This "hot storage" capability delivers performance comparable to centralized cloud services.
This leap in storage performance provides a solid decentralized foundation for supporting models with billions of parameters.
Chapter Six: Native AI Support—The Decentralized Foundation for Models with Billions of Parameters
1. AI Alignment Nodes: Guardians of AI Workflows
AI Alignment Nodes are responsible for monitoring the collaboration between storage nodes and service nodes. By verifying the authenticity of training tasks, they ensure that the AI model does not deviate from the preset logic.
2. Supports massively parallel I/O
Processing models with tens or hundreds of billions of parameters (such as Llama 3 or DeepSeek-V3) requires extremely high parallel I/O. 0G, through data slicing and multi-consensus sharding technology, allows thousands of nodes to simultaneously process large-scale dataset reads.
3. Collaboration between checkpoints and high-bandwidth DA
Fault recovery : 0G can quickly persist checkpoint files of hundreds of gigabytes in size.
Seamless recovery : Thanks to the 50 Gbps throughput limit, new nodes can instantly synchronize the latest checkpoint snapshot from the DA layer, solving the pain point that it is difficult to maintain the training of decentralized large models for a long time.
Beyond the technical details, we must broaden our perspective to the entire industry and see how 0G is sweeping through the existing market.
Chapter Seven: Competitive Landscape – 0G's Overwhelming Dimensions and Differentiated Advantages
7.1 Horizontal Evaluation of Mainstream DA Solutions
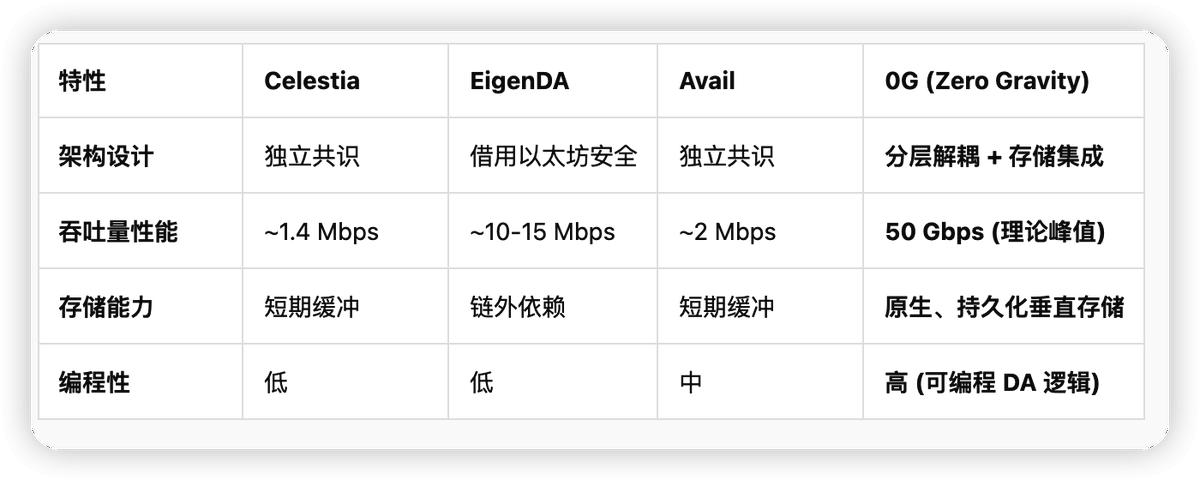
7.2 Core Competencies: Programmable DA and Vertically Integrated Storage
Eliminate transmission bottlenecks : The native converged storage layer enables AI nodes to retrieve historical data directly from the DA layer.
A leap in throughput of 50Gbps : several orders of magnitude faster than competitors, supporting real-time inference.
Programmable Data Allocation (DA) : Allows developers to customize data allocation strategies and dynamically adjust data redundancy.
This overwhelming dominance foreshadows the rise of a massive economy, fueled by token economics.
Chapter 8 2026 Ecological Outlook and Token Economics
With the mainnet running smoothly in 2025, 2026 will be a key year for the explosive growth of the 0G ecosystem.
8.1 $0G Token: A Multi-Dimensional Value Capture Path
Work Token : The sole medium for accessing high-performance Data Access (DA) and storage space.
Staking : Validators and storage providers must stake $0G to provide network revenue sharing.
Priority allocation : During busy periods, the amount of tokens held determines the priority of computation tasks.
8.2 Ecological Incentives and Challenges in 2026
0G plans to launch the "Gravity Foundation 2026" special fund to focus on supporting DeAI inference frameworks and data crowdfunding platforms. Despite its technological leadership, 0G still faces challenges such as high hardware barriers for nodes , a cold start for its ecosystem , and compliance issues .







