In 2014, 850,000 bitcoins were stolen from Mentougou (MT. Gox), the world's largest crypto exchange, and went bankrupt.
On the day the crisis broke out, the price of Bitcoin plummeted 25%, from $535 to $400.
Bitcoin China (BTC China), Coinbase, Bitstamp and other six large institutions urgently issued a joint statement to draw a clear line with Mentougou.
While trying to save the image of the industry, all exchanges are doing their best to carve up the lost territory of Mentougou.
This unprecedented crisis is also regarded by many people as a good opportunity to Bottom Fishing.
Among the Bottom Fishing hunters is CZ (Changpeng Zhao), the founder of the world's largest crypto exchange in the future.
This year, CZ sold his house in Shanghai and studded Bitcoin for $600. In less than a year, the house price in Shanghai doubled, and the price of Bitcoin fell to one-third of its original value.

When CZ was busy stud Bitcoin, the United States on the other side of the ocean, Coinbase, an exchange founded by Brian Armstrong for two years, finally ushered in the 1 millionth user, a young man named SBF, who just graduated from MIT and is investing on Wall Street CV.
Many years later, as the founders of the three major crypto exchanges, they will gather in the 2022 Forbes Crypto Rich List and occupy the top three.
Of course, this did not become the end of the crypto exchange industry.
Just one year later, Brian's net worth has shrunk by 75%, SBF is in prison, and CZ is facing the siege and interception of US regulators, causing true and false news about CZ to fly everywhere, and "CZ was shot dead by the FBI" once rushed into the hot search.

Exchanges are undoubtedly one of the most profitable businesses in the encryption industry, and one of the most competitive businesses.
From the birth of the first encrypted exchange to the present, the exchange industry has been changing, and the ups and downs are in the blink of an eye.
Platform coins, trading mining, exchange alliances... the gameplay has been refurbished, futures, options, stocks... targets emerge in endlessly, coin theft, shady, guarding and stealing... security and compliance issues are lingering.
Almost every day, we can see negative news about exchanges. Unfortunately, many negative news have become true. The world of encrypted exchanges is full of bones, except for the well-known Mentougou, the short-lived FCoin, the rapid rise and fall FTX, and countless smaller exchanges that are gradually being forgotten.
To this day, although Binance and Coinbase occupy the leading positions and hold most of the market share, the structure of the exchange industry is still undecided.
This article will review the development history of encrypted exchanges in detail, focusing on the four aspects of gameplay, target, security compliance, and form. While reviewing this history, consider how these factors determine the changes in the landscape of encrypted exchanges.
1. 2010-2013: Mentougou Era
After the birth of Bitcoin, there were no exchanges for a long time, and people mainly traded Bitcoin on the Bitcoin Talk forum.
In October 2009, the New Liberty Standard began to publish the price of bitcoin calculated based on power consumption. The quotation on October 5, 2009 was 1 US dollar to 1309.03 bitcoins, which is equivalent to a price of 0.00076 US dollars per bitcoin.

Since then, several centralized exchanges have been established one after another.
On January 5, 2010, the first anniversary of the birth of Bitcoin, Bitcoin Talk forum user dwdollar posted: "I am building an exchange, which will be a real trading market."
In March 2010, Bitcoin Market was born.
But during this period, the Bitcoin exchange market was clearly still very primitive, and the Bitcoin Market often needed to be tinkered with based on feedback from forum members.
In July 2010, Jed McCaleb, the famous father of eMule, founded Mentougou Exchange, which will dominate the currency circle in the future.
By chance, Jed met Mark Karpeles on the Bitcoin Talk forum.
Capules, born in France, settled in Japan in 2009, known as "Fat Fat".

At the time, Fatty's startup business was dying and looking around for new opportunities. He vaguely felt that Bitcoin trading might be a lucrative business.
And Jed didn't have much interest in continuing to be a bitcoin exchange, so in March 2011, Fatty bought Mentougou, Jed kept 12% of the shares, and then joined Ripple.
Up to that time, none of them would have thought that Mentougou could reach its later scale.
In February 2011, the transaction volume of Mentougou was only 360,000 bitcoins, which was only 329,000 US dollars based on the price at that time.
After taking over, Fapang immediately remodeled Mentougou, including changing the supported currency from only US dollars to more than ten currencies such as US dollars, Euros, and Australian dollars, and redesigned the new website pages. These updates probably cost 4 months.
During this period of time, the launch of the dark web black market Silk Road provided a usage scenario for Bitcoin, and the price of Bitcoin rose rapidly. On February 9, the price of Bitcoin reached $1. By June 8, the price of Bitcoin on Mentougou The price reached $32.
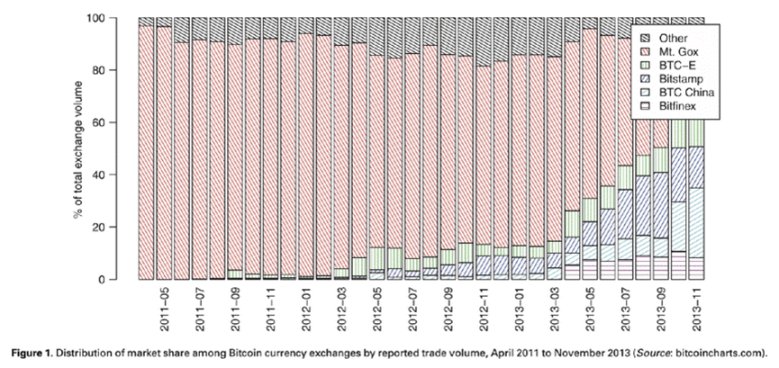
The 32-fold increase in 4 months has attracted more new entrants, and Mentougou has received the largest traffic bonus. In April 2011, Mentougou accounted for more than 90% of Bitcoin transactions.
With the skyrocketing price of bitcoin, hackers have targeted bitcoin exchanges including Mentougou.
In mid-June 2011, the price of Bitcoin on Mentougou fell from $17 to 1 cent in just a few minutes, because hackers obtained a large amount of user data in Mentougou, and then sold the bitcoins in other people's accounts at a price of 1 cent. Bitcoin, use your own account to "accept orders".
After discovering the problem, Fa Fatty hurriedly suspended the transaction.
Fortunately, Mentougou only lost 2,000 bitcoins in the end. In contrast, other exchanges were not so lucky, such as MyBitcoin in August 2011 when more than 78,000 bitcoins were stolen and went bankrupt; in September 2012, Bitfloor was closed after being stolen with 24,000 bitcoins; It went bankrupt after being attacked twice in a month.

https://en.bitcoin.it/wiki/File:MyBitCoin08042011.png
https://bitcointalk.org/index.php?topic=81045.0
After the accident, Fatty urgently upgraded the security system, and did not suffer from large-scale hacking attacks until 2013.
During the period when Mentougou was hacked, several new exchanges quietly appeared. In June 2011, China’s first exchange, Bitcoin China, was established. In July, Kraken was established. In August, Bitstamp was established.
These newly established small exchanges are not enough to threaten the dominance of Mentougou. In the ensuing bull market, the price of Bitcoin skyrocketed. Became the biggest beneficiary of the bull market.
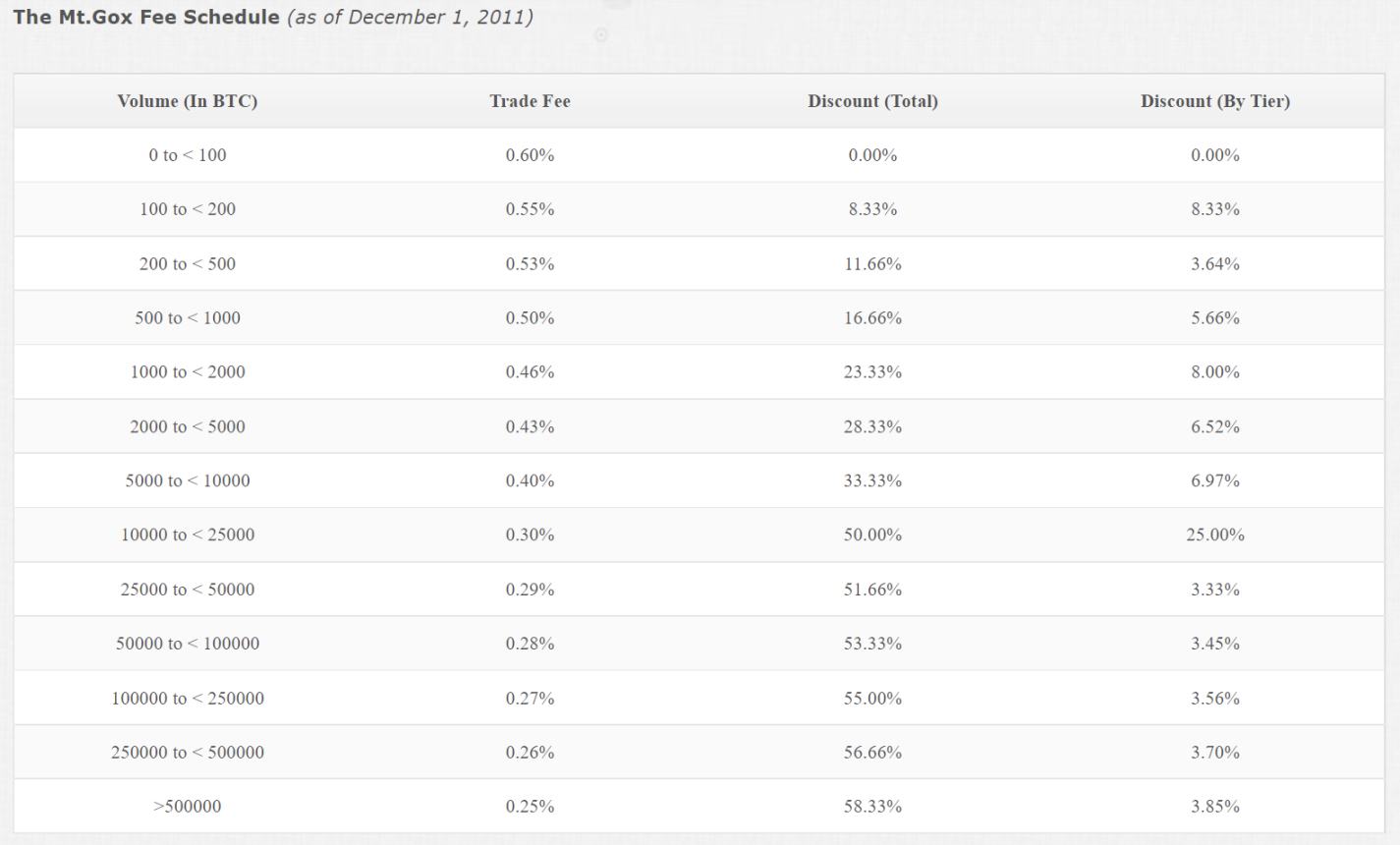
In July 2013, the registered users of Mentougou had reached 500,000. By charging a handling fee ranging from 0.6% to 0.25% for each transaction, Fa Fatty has also become a wealthy local tyrant.
By the end of 2013, Fatty had earned an estimated $8 million plus 345,000 bitcoins, enjoying his new title:
King of Bitcoin.
In the face of the media, Fa Fat talked about the reasons for the success of Mentougou: Mentougou is one of the earliest bitcoin trading platforms; the security measures upgraded after being attacked by hackers look good; he has been seeking the legitimacy of transactions; currency payment range.
Such a scene is easily reminiscent of the "savior of the currency circle" in 2022-SBF.

The irony is that they have countless halos on their heads and pretend to represent the industry, but it turns out that they themselves are the biggest thunder in the industry.
It was from 2013 that Mentougou's business began to decline.
In May 2013, Mentougou's American partner, CoinLab, accused Mentougou of breach of contract and claimed USD 75 million.
Originally, the two parties reached an agreement that CoinLab would be responsible for the operations in North America and Canada, but Mentougou has not fulfilled the agreement for some reason.
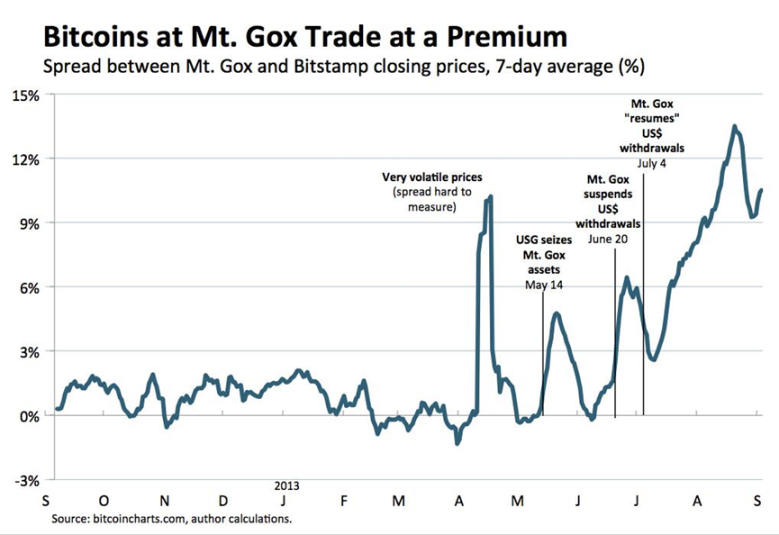
From May to July, the U.S. Department of Homeland Security seized Mentougou's US$5 million in funds on the grounds that Mentougou had not obtained an operating license, and Mentougou had to suspend US dollar withdrawals.
On June 28, Mentougou finally obtained a license from the US Financial Crimes Enforcement Agency, and announced on July 4 that withdrawals will be fully resumed. However, until September, there were very few successful dollar withdrawals.

https://www.wsj.com/articles/BL-MBB-4101
The two incidents brought Mentougou notoriety, and users began to panic and flee due to the difficulty of withdrawing US dollars.
Because the U.S. dollar cannot be withdrawn, but the bitcoin can circulate freely, so some people choose to buy the U.S. dollar in the Mentougou account into bitcoin and then transfer it out of the platform.
This flight behavior has led to a 12% premium in the price of Bitcoin in Mentougou compared to other platforms. The price of Bitcoin on Bitstamp is 129 US dollars, and it reaches 145 US dollars in Mentougou.
While Mentougou was busy with compliance, litigation, and improving service quality, competitors Bitstamp, BTC-E, and Bitcoin China took the opportunity to erode its market share.
By October 2013, Bitcoin China had a market share of nearly 33%, Bitstamp 25%, and Mentougou only 23%.
In February 2014, 850,000 bitcoins were stolen, which dealt a fatal blow to Mentougou
It will not be until 2023 that the nine-year Mentougou incident will finally come to an end.
Fatty was sentenced to 30 months in prison for inflating assets only, suspended for 4 years, and escaped from prison.
The victims of the Mentougou coin theft incident, "passively locked" for 9 years, compared with the currency price at that time, can also get a "window income".
The market has been worrying about how the 140,000 bitcoins in Mentougou will have an impact on bitcoin.
In hindsight, the Mentougou coin theft incident was not without warning. As early as March 2011, when Fa Pang bought Mentougou, there was a shortfall of 80,000 bitcoins, and Mentougou was attacked by hackers on a large scale. It has already started, but it was only in the middle of 2013 that the internal and external troubles broke out completely.
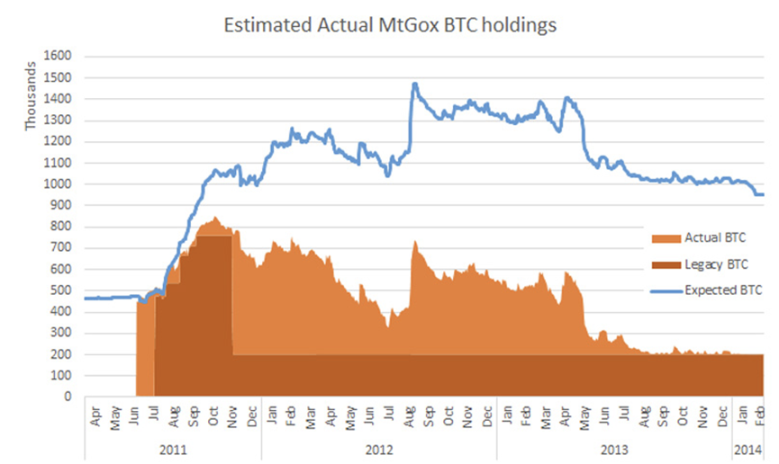
Looking back on this period, the encryption trading industry is still in its early stages, the target is concentrated in Bitcoin, the gameplay is limited, and security compliance is the key to the life and death of the exchange.
Compliance issues have dealt a heavy blow to Mentougou. Exchanges have gone bankrupt due to hackers stealing coins, losing coins and other reasons. However, even if such a large-scale crisis breaks out, similar incidents will continue to occur many times, constantly threatening encrypted transactions. So, and even the entire industry.
Two 2014-2016: Chinese market
When Mentougou gradually fell into the abyss in Japan, the pattern of Bitcoin exchanges in China was also quietly changing.
China, the earliest established bitcoin company, dominates, but under the hot bitcoin market in 2013, more and more gold diggers came after hearing the news.
In June 2013, Xu Mingxing founded OKCoin, and in September, Li Lin founded Huobi.com.
Xu Mingxing and Li Lin are both "other people's children" in the parents' mouth, and their experiences have many similarities.

Li Lin graduated from Tsinghua University. After Xu Mingxing was admitted to the National People’s University as a graduate student, he decided to drop out of school and start a business after listening to an exciting speech by Mr. Ma Yun. In 2010, they both joined the “Hundred Regiments War” and reunited in 2013. in the blockchain world.
Both Huobi and OKCoin were born with golden keys in their mouths.
Two months after its establishment, Huobi received angel investment from Zhen Fund and Dai Zhikang, and in April 2014, it received investment from Sequoia Capital. OKCoin, on the other hand, has raised USD 10 million in Series A financing only 3 months after its launch.
As soon as Huobi.com went online, it played the banner of "free transaction fees", attracting a large number of users, and a bunch of unaffordable exchanges closed their doors. OKCoin took the lead in launching Litecoin transactions in September 2013, making a comeback. .
Although Li Qiyuan, the founder of Bitcoin China, and Li Qiwei, the founder of Litecoin, are brothers, it was not until March 2014 that Bitcoin China launched Litecoin.

Another reason for OKCoin's rapid expansion is that the team at that time gathered many bigwigs who will dominate the currency circle in the future.
In 2014, CZ joined OKCoin as CTO. Together with CEO Xu Mingxing and He Yi, who is known as "the first sister of the currency circle", he formed the famous "iron triangle" of the currency circle.

Facts have proved that this iron triangle is not very strong. Just one year later, CZ left and became OKCoin’s opponent in the future, and similar things will happen many times. OKCoin has become what people call the “Whampoa Military Academy in the currency circle”.
At the same time that CZ became the CTO of OKCoin, Huobi acquired the blockchain data query network qukuai.com created by Zhang Jian, and Zhang Jian joined Huobi as CTO.

At this time, the two CTOs did not expect that their experience is establishing the style of the next generation of exchanges, and the exchanges they created will become the protagonists of the next cycle.
Another key word in crypto trading in 2014 is Derivatives.
Bitcoin futures have appeared as early as 2012, but did not attract much attention.
In June 2013, the 796 Exchange, which positioned leveraged trading and futures, was established. Since Bitcoin was in a unilateral rise at that time, spot trading was sought after, and futures had not yet attracted widespread attention. Until 2014, when Bitcoin fell all the way, futures began to be used. Players pay attention to it, and the 796 exchange has only begun to emerge.
As for the Big Three in the Chinese mainland market, Huobi and OKCoin all support "financing and financing", and only Bitcoin China has not set foot in it.
796, which deployed Derivatives earlier, together with Huobi and OKCoin, became the three major Bitcoin Derivatives exchanges. In order to compete for limited customers, the first bloody battle in the field of Derivatives was launched.
With the help of its unique platform lending model, Huobi ascended to the dominant position in March 2014.
On March 4, 2014, the daily trading volume of Huobi Bitcoin exceeded 350,000, and the transaction amount reached 1.5 billion RMB, creating the highest record of the global Bitcoin trading platform and accounting for 50% of the global Bitcoin trading market.
But the good times didn't last long. On March 21, the "Huobi.com 3.21 Plunge of 1 Yuan Incident" broke out, which shocked the industry.

Latecomers who want to ascend to the dominant position, in addition to their own efforts, sometimes have to rely on their peers to make fatal mistakes.
In this incident, Litecoin, whose price on Huobi was close to 100 yuan, fell to an incredible 1 yuan in an instant.
Nine years later, on March 10, 2023, a similar scene repeated itself. What's more, this time it happened on Huobi's platform currency HT . In just half an hour, the price of HT dropped from $4.7 to $0.3 Dollar.
When the "1 yuan event" broke out on Huobi, although there were no major problems with Litecoin on OKCoin, the price of Bitcoin fell from close to 3600 yuan to around 2680 in an instant.
The free fall of currency prices on the two platforms has caused countless players to suffer huge losses. In contrast, the price performance on the 796 platform is relatively stable and has won the trust of many customers.
However, with the outbreak of risk events and the downturn in the market, investors have become more and more suspicious of the exchange’s short-selling mechanism and financing.
Under pressure, on May 6, the five major Bitcoin trading platforms, Bitcoin China, Huobi, OKCoin, CHBTC, and BtcTrade, jointly issued a self-discipline statement, announcing that in order to avoid excessive speculation, they would no longer carry out leveraged transactions and unified transaction rates.

http://tech.sina.com.cn/i/2014-05-06/15169361845.shtml
However, 796 Exchange is a maverick and did not join this joint statement
When other exchanges closed their financing and coin financing business one after another, 796 Exchange became the overlord in the midst of abuse and controversy. After other platforms gave up lending, their market share was much smaller.
Facts have proved that in the face of commercial competition and interests, the shelf life of the self-discipline statement is only one month.
Only one month later, Huobi and OKCoin successively restarted their financing and coin financing business, and launched futures trading with 10 times leverage, and a new round of Derivatives war started.
The three exchanges fought a price war on handling fees. 796’s contract handling fee was reduced from 0.3% to 0.03%. OKCoin’s futures opening handling fee is 0.03%, and there is no handling fee for closing positions. The BitVC futures service fee under Huobi is 0.025%. Later, the V point privilege function was launched, which can further reduce the service fee.
The glory that belongs to 796 is very short-lived. 796 Exchange reached the top due to risk events of other platforms, but quickly fell due to its own risk events. On November 3rd, 796 was unable to log in and gradually lost customer trust. Huobi took the opportunity to catch up, but failed to last. OKCoin became the biggest winner in this round of futures war.
From 2014 to 2016, the rise of the Chinese mainland market brought about earth-shaking changes to the exchange landscape. Huobi, OKCoin, and Bitcoin China are three pillars, taking the top spot in turn, and the volume of other exchanges is far from being comparable to the Big Three.
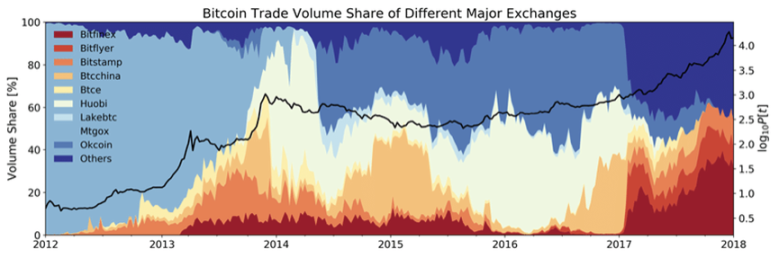
The former industry leader, Bitcoin China, lost its first-mover advantage and lost a large number of customers due to its insistence on not getting involved in the Derivatives business, so it began to deploy mining pool business.
BitMEX, which was established in Hong Kong in 2014, emerged from Derivatives during the bear market.
Although BitMEX will become a player that cannot be ignored in the field of Derivatives in the future, at that time, it was just a small and unknown exchange.

Until October 2015, BitMEX increased the trading leverage from 3 times to 100 times, and users began to flock in large numbers. In 2016, BitMEX launched perpetual contracts, gradually gaining a foothold in the market.
During this period of time, cryptocurrency exchanges still frequently broke out security issues.
In January 2015, Bitstamp was hacked, 19,000 bitcoins were stolen, and a large number of users were lost.

In May 2015, 1,200 bitcoins were stolen from Bitfinex.
But a bigger disaster is yet to come. In August 2016, Bitfinex was hacked and 120,000 bitcoins (worth $72 million) were stolen.

This became the second largest Bitcoin theft case after the Mentougou theft case, and Bitcoin plummeted 20% on the day.
However, compared with Mentougou, which has been recorded in history, Bitfinex, which has been hit hard, is still active today
After the theft happened, Bitfinex announced that the stolen loss would be shared equally among all users, and the user account funds would be reduced by 36%, but they would receive a corresponding amount of BFX tokens, each BFX token representing a loss of $1.
Users can hold BFX and wait for redemption, or convert it to iFinex, the parent company of Bitfinex 1:1. About 54.4 million BFX tokens were converted into stocks. It is rumored that Zhao Dong, the founder of DGroup, became Bitfinex’s small shareholder.
By April 2017, Bitfinex had successfully redeemed all BFX tokens.
Moreover, 94,000 of the stolen 120,000 bitcoins were recovered in February 2022, but they are still lying at the address of the US Department of Justice.
Looking back, this is not the only time that Bitfinex turned a bad luck into a fortune. In 2019, Bitfinex’s US$850 million in funds was frozen by the US Department of Justice. Bitfinex repeated the same trick and raised US$1 billion through the issuance of LEO.

Looking back at this stage, the gameplay and targets of encrypted exchanges are very different from before.
In terms of gameplay, Huobi launched a price war at the beginning of its entry into the game, and rose rapidly. In the subsequent Derivatives war, the price war continued.
In terms of bids, OKCoin was the first to enjoy the bonus of the listing of Litecoin. In the bull market of 2017, with the arrival of the copycat season, the competition around listing coins will become more intense.
At that time, as the market entered a bear market, Derivatives began to rise, Bitcoin China missed this wave and lost its dominant position, 796 exchanges were short-lived, BitMEX gained a foothold with perpetual contracts, and OKCoin became a Derivatives war In the Derivatives war, various exchanges have also exposed technical problems to varying degrees, and product quality has become the key to determining the outcome.
In terms of security compliance, following the theft of Mentougou, Bitfinex broke out the second largest coin theft case in history, but Bitfinex deftly resolved the crisis by issuing coins.
With the expansion of the influence of Bitcoin and the outbreak of cases such as the theft of Mentougou, Japan began to study the issue of cryptocurrency regulation, banks in mainland China were banned from engaging in cryptocurrency business, and countries such as Thailand and Russia completely banned Bitcoin.
During this period, exchanges in mainland China and Hong Kong dominated the encryption world, and a large number of heavyweight players including OKCoin, Huobi, BitMEX, Bitfinex, etc. were born.
At the beginning of 2023, when Hong Kong planned a new cryptocurrency policy to shake the currency circle, BitMEX founder Hayes commented:
“Deribit is the only non-Asian exchange that has made major innovations to the cryptocurrency market. The US-based centralized exchange has not brought any innovation to the cryptocurrency market at all.”
Three 2017: The Rise of Binance
At the beginning of 2017, the price of Bitcoin broke through the high point of the previous round, the market heat was rekindled, and the amount of ICO funds raised hit new highs again and again.
It has been two years since CZ left OKCoin.
In 2015, CZ and Xu Mingxing broke up unhappy, and the mutual hatred between the two became a big drama in the currency circle. He Yi also left OKCoin soon after.
It was this experience at that time that laid the foundation for CZ and He Yi to do Binance later.
After leaving OKCoin, CZ founded Bijie Tech to provide exchange-as-a-service platform for other exchanges. According to CZ himself, at that time Bijie had more than 30 customers, and the business was very good, but in early 2017, due to regulatory reasons, all of CZ's customers closed down.
On June 14, 2017, CZ heard about ICO for the first time at a banquet. Within 3 days, he wrote a Whitepaper in both Chinese and English.
The subsequent ICO was completed within a week, selling 100 million BNB and raising $15 million.
Then, in just 6 months, Binance became the world's largest exchange.

In a January 2018 interview with Bloomberg, CZ said it was adding "millions" of users every week.
Behind this incredible speed, on the one hand, CZ and his team have been engaged in cryptocurrency trading-related businesses for many years and have accumulated considerable accumulation; on the other hand, they are due to the frenzy during the bull market and the ban in mainland China.
In 2017, ICO exploded, and the funds raised through ICO were almost 40 times that of 2016.
Madness breeds chaos, ICO has become a scam tool for many people, and half of the projects die within 4 months after ICO.

Under the wave of ICO, competition among cryptocurrency exchanges has also launched. Whoever can list the most popular currency first and fastest can get more traffic, and get more traffic. It can make the exchange the most attractive place to list coins.
Under such circumstances, exchanges, project parties, and evaluation and ranking websites can easily collude with each other to jointly harvest retail investors and trigger risk events. ICOs and cryptocurrency transactions were quickly hit by regulatory authorities in various countries.
On September 4, 2017, the People's Bank of China and other departments issued the "Announcement on Preventing Financing Risks of Token Issuance", requiring the cessation of all ICO activities, and local regulatory authorities issued notices to clear cryptocurrency exchanges.

For a time, the cryptocurrency market fell in an all-round way, and the currency circle in mainland China was panicked, and exchanges "go to sea" one after another.
When the ban hit the industry hard, Binance, which only provides currency transactions, took advantage of the situation and took over customers lost by other platforms.
After this regulatory storm, Bitcoin China declined, and Huobi and OKCoin moved their servers overseas and "transformed" into Huobi PRO and OKEX respectively, but they are still open to registration and trading for users in mainland China. Bitcoin has become the new "Big Three".
Since its establishment, Binance has demonstrated its superb "regulatory arbitrage" capabilities. After reaping the "dividend" of supervision in mainland China, Binance tried to land in Japan, but quickly withdrew after Japanese regulations tightened. In 2019, Binance An also established Binance.US for US users to avoid US regulatory risks, but even so, Binance has not been able to avoid the siege and interception of US regulators after many years.
In addition to the regulatory "dividend", the development of Binance also benefits from the innovation of the platform currency BNB .
Back then, Huobi rose rapidly through the free service fee, while Binance issued BNB and continued to empower, and shared development dividends with BNB holders through a series of measures such as fee reduction, repurchase and destruction, and IEO.
The rapid development of Binance has driven the skyrocketing value of CZ.
In 2018, Forbes launched the first cryptocurrency rich list, and CZ ranked third on the rich list.

During this period, Sequoia Capital, which once invested in Huobi, took a fancy to Binance. As a result, Sequoia Capital and Binance turned against each other and sued Binance in court. In the end, they failed to take the express train of Binance.
Two years later, Sequoia Capital got on the black car of another popular encryption exchange, but ended up with a tragic loss of more than 200 million US dollars.
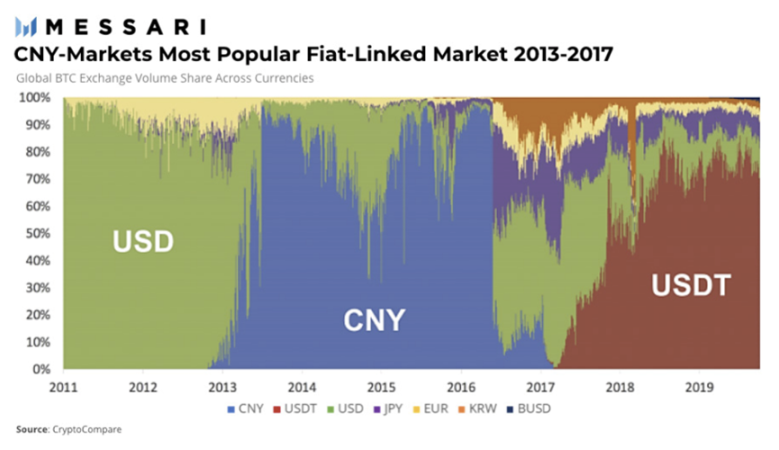
The regulatory turmoil in mainland China also contributed to the success of another exchange, Bitfinex, which was hacked in 2016.
It was from 2017 that due to the supervision of mainland China, the renminbi withdrew from the stage of cryptocurrency trading and was replaced by USDT, which is inextricably linked with Bitfinex.
The frenzy of the market in 2017 has also created a large number of Korean exchanges.
In 2017, the capital volume of South Korean crypto exchanges increased by 64 times compared to 2016. By the beginning of 2018, the South Korean won was already the legal currency in cryptocurrency transactions, second only to the US dollar. The bitcoin trading volume of South Korean exchange Upbit also entered the global top ten.
The madness of Korean leeks, coupled with the heavy restrictions on currency speculation, has given birth to a premium for kimchi - the currency price on Korean exchanges is often more than 20% higher than that in other countries.
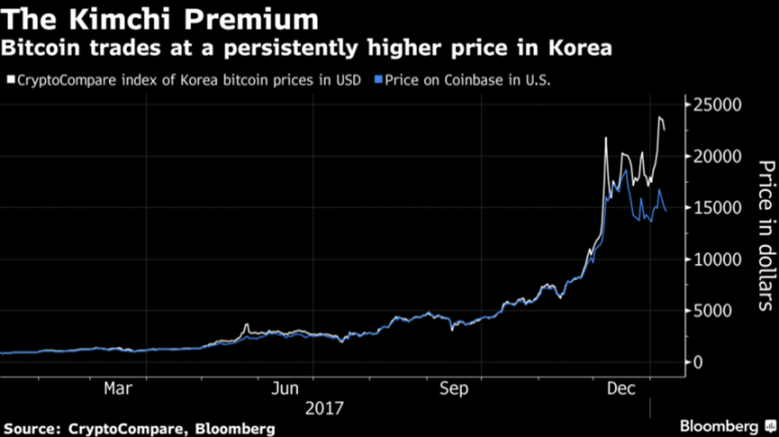
As a result, South Korea has become the most popular place to move bricks. Arbitrageurs buy coins from international exchanges and move them to Korean exchanges to sell, earning a lot of money.
In 2017, this set of processes has been industrialized, and some websites have even appeared to help brick movers arbitrage. On these websites, you can see which exchanges you can move from to which Korean exchanges can be profitable, and you can also see Which coins are most profitable to move.
Among these arbitrageurs, SBF is included.
In October 2017, SBF left Wall Street and founded Alameda, an encrypted quantitative trading company, to conduct arbitrage in the Japanese and Korean markets.
After this period of accumulation, 2 years later, SBF will establish FTX, which will become the world's third largest crypto exchange in the future, and compete with Binance.
The madness of the encryption market in 2017 also attracted the attention of traditional financial giants. The two futures industry giants, CME and CBOE, competed around Bitcoin futures.
At the beginning of December 2017, CME announced that it would launch bitcoin futures, but CBOE launched bitcoin futures first, and the encryption market entered the most frenzied stage. In just one week, the price of bitcoin rose from 12,000 US dollars It soared to nearly $20,000 before entering a year-and-a-half-long bear market.
Although CBOE was the first to launch Bitcoin futures, it reached its peak when it went online. After that, the trading volume continued to decline, and finally closed Bitcoin futures trading a year later.
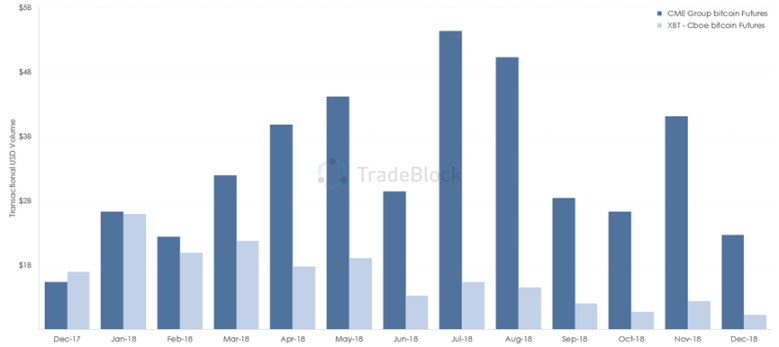
Looking back at this stage, Binance is undoubtedly the biggest winner. The success of Binance is inseparable from the regulatory dividends in mainland China. Although Bitfinex was hit by bankruptcy, with the disappearance of RMB and the rise of USDT, it has realized dislocation competition. Another exchange, BTC-e, which we did not introduce, was imprisoned for money laundering and the exchange closed down.
From the birth of crypto exchanges to today, regulation has been a key factor affecting changes in the crypto trading landscape, and the rise of Coinbase in the United States and the four major exchanges in South Korea will prove this point repeatedly.
In terms of gameplay, Binance created the platform currency for the first time, binding the development of the exchange with the holders.
On the target, the arrival of the copycat season has led to various exchanges launching a competition to list coins, but the crazy harvest is not without cost, and users will eventually vote with their feet, forcing exchanges to take users seriously.
As the market enters a bear market, the traffic dividend is no longer there, and the exchange industry has entered a cold winter without exception, while the battle among exchanges has become more intense.
In this long winter, in order to compete for traffic, encrypted exchanges started a new round of Derivatives wars, and at the same time started competitions around platform coins, transaction mining, IEO, etc., as traditional exchanges entered the encryption field and decentralized transactions With the explosive growth of exchanges, centralized exchanges have ushered in a new crisis, while security and compliance issues are still lingering, plaguing the entire industry.
These contents, we will continue to review with you in the next issue.







