POL (Polygon Ecosystem Token ) is designed to gradually replace the current Matic Token within 4 years of the Polygon 2.0 transition roadmap. With this release, Polygon will evolve into Polygon zkEVM validium, featuring an interoperable network of application-specific blockchains. POL will come with an add-on that includes reStaking, where validators can restake their POL to secure other chains in the Polygon supernet and earn additional rewards.
In a statement released on October 25, 2023, Polygon announced it had deployed the contract for POL Token on the Ethereum blockchain.
This is an important step towards a series of further developments in the Polygon 2.0 upgrade roadmap. The POL Token is set to power the complex ecosystem being designed by the Polygon development team and the community and will eventually replace Matic. So what is POL Token ?
Polygon Ecosystem Token (POL) is the new native Token of the Polygon ecosystem. By design, it is being integrated into the core operations of Polygon 's key products and applications within the ecosystem. POL will eventually replace the Matic Token , taking on governance and gas Vai , in addition to other utilities that will come with the expanding Polygon ecosystem.
Polygon claims POL is an economic, technical upgrade to Matic and is future-proofed, with the POL Token being (technically) adapted to be scalable along with the entire ecosystem. ecosystem as it develops. POL will improve the security and scalability of the ecosystem as the validator can secure multiple chains, providing support to the Polygon ecosystem as the industry grows.
According to POL's official Whitepaper, the initial POL supply will be 10 billion Token, exclusively for the conversion of Matic to POL. In the future, POL will be issued as a reward to validators at a predetermined rate, not increasing by more than 1%. However, supply may decrease after 10 years through governance as the Polygon ecosystem reaches maturity. As the Polygon ecosystem matures, the team believes that the transaction fees and other incentives guaranteed by validating the Polygon chain will generate profits for Polygon validators, so the final proposal is to reduce the rate. release.
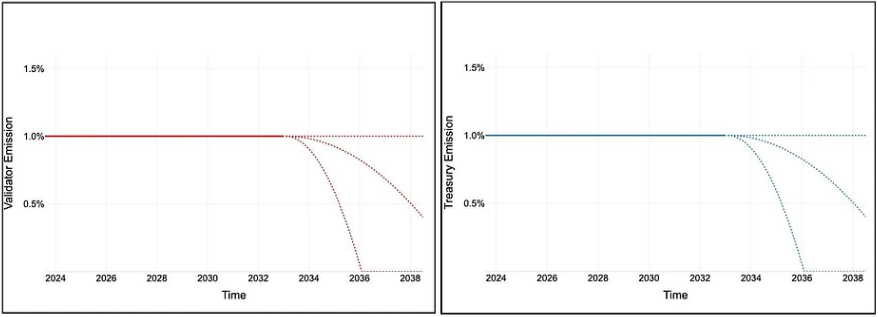
Next, let's XEM at what Vai POL will play in this expanding ecosystem.
Polygon has described the POL Token as a “super-yield” Token to reflect the expanded benefits it brings to holder. The POL Token will be the native Token of the Polygon ecosystem and act as the tax currency of the Polygon network or any other network in the ecosystem.
This means that for every network that chooses POL as its gas Token , fees for transactions on the network will be paid in POL Token .
Additionally, the POL Token will help maintain the security, economy, and governance of the Polygon ecosystem through:
reStaking is a fairly new cryptocurrency concept, popularized by EigenLayer, where ETH can be retaken to secure other protocols, saving them the trouble of setting up their own set of validators.
On Polygon, POL stakers will secure the network and receive rewards for their efforts. After Staking a specified threshold amount of POL Token to run a validator node, the consensus algorithm will have a basis to affirm the validator's commitment to protecting the network and also a way to “punish ” default authenticator. As an incentive system, validators are rewarded with POL Token for securing the network.
And this is where reStaking comes in. As the native Token for an expanding ecosystem, the POL Token will also enhance the security of other chains operating under the Polygon supernet structure. This means that validators on the Polygon network can also validate other chains. Validators will earn rewards from transaction fees generated on the secondary network they validate, and additional rewards may also be given to validators as specified by the network they validate.
Polygon also expands the role of authenticators. In addition to the normal transaction validation process, validators in Polygon can also take on other Vai such as becoming members of the Data Availability Committee (DAC) and generating zero-knowledge credentials. -ZK). Validators can perform these Vai in a single chain or multiple chains in the supernet.
Polygon also announced that the POL Token gives governance rights to holder . This means that every Token holder will be able to decide on community proposals. Although Polygon has not yet published the full design of the governance system at the time of writing, the governance system is expected to operate in a similar model to most DAOs.
POL Token will be accepted in the project's voting portals and each holder will be able to vote for or against proposed developments related to the project. These developments may be in fields related to technology, management or finance. The community voting system also means that the majority vote confirms the community's choice and becomes the recognized decision. This will become clearer when the project releases the full design of its governance structure.
On June 20, 2023, the Polygon Labs team announced a proposal to convert the Polygon PoS chain into a completely zkEVM validium network. Polygon PoS Chain is one of the most used EVM networks, having over 482 protocols and a TVL of over $750 million according to defillama .
Polygon XEM the upgrade to the existing Polygon PoS as a way to improve the security model, as by exploiting zkEVM technology, Polygon will be able to inherit the higher security of Ethereum. The proposal also claims the move will bring the project closer to resolving current consensus issues and fluctuations in the gas efficiency estimation model that cause transaction fees to occasionally spike and allow for forecasting. project in pursuit of an overall improved user experience.
ZkEVM validium is an alternative to rollups when deploying Layer 2 (L2) that supports ZK. L2s support ZK sending valid proofs to Layer 1 (Ethereum), providing security guarantees for all its transactions. However, unlike rollups that send compressed transaction data to Ethereum, validiums do not publish transaction data to Ethereum, instead ensuring the availability of this data in a different way.
This allows zkEVM validium to offer lower fees, as it does not require Block space on Ethereum to store transaction data, and also improves scalability as rollup throughput is limited by the amount of data. transactions that Ethereum can store.
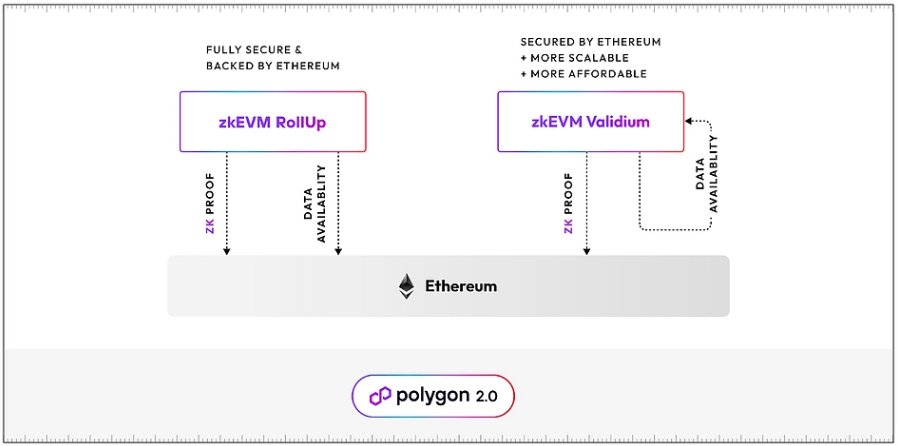
Since Polygon already has a $2 billion decentralized validator with Polygon PoS, it can Vai as a very reliable transaction data availability layer.
The proposal also claims the move from PoS to zkEVM validium is a preparation for the Polygon 2.0 upgrade. As a zkEVM validium network, the Polygon PoS chain will be compatible with the supernet structure being developed. This will allow it to enjoy the benefits of being part of the centre.
Polygon claims to be making every effort to create an efficient value layer through decentralized technologies over the past decade on the Polygon 2.0 upgrade. They hope to reflect these developments in Polygon 2.0 to define a new structure for the project.
With the Polygon 2.0 upgrade, Polygon will transform into a supernet of ZK networks operating in a system capable of efficient interoperability and Chia of valuable resources between them. It defines a unified security system and end-to-end solution on the Ethereum blockchain using the ZK prover to determine the validity of transactions and achieve near-instant transaction processing time. .
Next, let's XEM what features Polygon 2.0 has?
Supernet is a network of networks. Polygon hopes to build the “value layer of the Internet”. The basis of the design is to achieve a push system for multiple Layer 2 ZK networks and achieve near-instant processing times on the Ethereum network. This is the basic structure of Polygon 2.0.
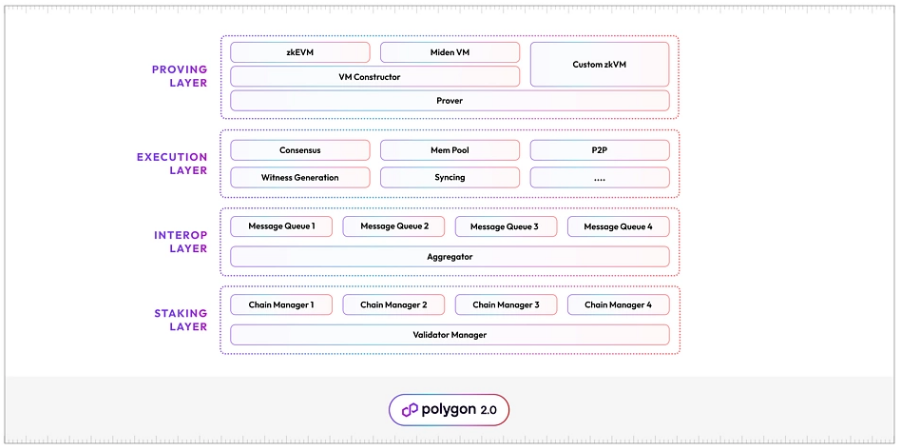
Polygon 2.0 is made up of 4 layers that work together to provide a compact network for communication, including: Staking layer, interaction layer, execution layer, proof layer.
Polygon 2.0 applies the PoS consensus algorithm. Layer Staking is the core of the network security system. It handles the core aspects of validator Staking and validator management of the network. Polygon 2.0 validators are required to Stake the network's native Token to run a validator node on the network. Polygon claims the Staking layer will be optimized for the regular Staking model as well as the reStaking model. The Staking layer is controlled by two smart contracts. These two contracts are deployed on the Ethereum network: Validator Manager and Chain Manager.
The Validator Manager smart contract handles the “inventory” aspect of the validator. It processes Staking and unstaking requests and keeps track of the number of validators on the network. Validator Manager handles the reStaking process and also handles Slashing events when they arise. Through this gateway, the authenticator can choose a secondary network for authentication.
Chain Manager is a smart contract governance. It determines the number of validators the network needs for decentralization and describes the conditions for running a node on the network, while also defining penalties for violating validators.
This layer handles communication between networks in the supernet. Polygon claims to be developing a dedicated communication system powered by a modified version of the Message Queue algorithm currently used by the Polygon zkEVM rollup. Using Message Queue and ZK proofs, Polygon ZkEVM can send messages across the network seamlessly. Polygon claims the interaction layer enhances this design through the Aggregator. Aggregator mediates between the Ethereum network and the networks in the Polygon 2.0 supernet. It compiles ZK Proofs from these chains and posts them to the Ethereum network.
By sending proof to Ethereum, messages in the queue will be transmitted as soon as the batch is verified on Ethereum. In this way, Aggregator can establish an efficient communication path between chains and the Ethereum network. Native assets on the Ethereum network can be transferred to the Polygon chain seamlessly. Validators in the Staking layer also take on the task of securing the interoperability layer.
The execution layer is just like any other execution layer. It includes a consensus system operated by validators to screen transactions before adding them to the Block. The validator obtains detailed information about the transactions from the mempool and reaches an agreement on the validity of the transaction. Once consensus is reached, the transaction's data will be stored and this layer also generates proof data for use by ZK provers.
The proof layer creates evidence for transactions executed on the network. It is made up of a generic prover, a state machine, and an optional state machine constructor. The state machine constructor is a framework for building state machines that allows networks on the supernet to design their own state machines to suit their needs. It is a modular framework and thus offers some flexibility. The network can choose the components of the proof machine as desired. The state machine then handles generating transaction proofs for the network.
The generic prover is designed to be easily adapted to any state machine defined by the networks in the supernet. It uses a unique proof system to query the accuracy of transaction data before sending it to the Primary Network. The general proofer completes the system and proves the existence of different types of ZK networks in a supernet. The ability to scale to transaction types and custom state machines ensures every network's transaction data is properly analyzed.
Developing a Layer 2 ZK network is certainly a complex and technical undertaking. To reduce these complexities and ensure developers launch the ZK network in accordance with the design of the Polygon supernet, Polygon is introducing the Polygon CDK (Chain Development Kit). CDK is the code base for launching L2 ZK on Supernet. This is an open source framework that can be adopted by developers who want to deploy networks on supernets. Networks developed using CDK are in fact Ethereum L2 networks with Polygon 2.0 principles. Polygon claims these networks inherit the security and decentralization provisions of Polygon 2.0 and automatically become members of this super network. They benefit from system interoperability and resource Chia (including the liquidation layer).
Polygon CDK is modular, meaning developers have a high degree of freedom in choosing their network components.
In short, the POL Token will replace the Matic Token . Matic has been the project's native Token since its inception and has undergone several rebrands over these years. It is also widely owned by Polygon and the projects are enthusiastically received. According to on-chain data, Matic Token are held by more than 600,000 investors. However, the upgrade to the POL Token is the biggest update ever since it was launched. This upgrade will move the entire Polygon Token Economy to another smart contract to allow the Token to operate within the new desired scope. Like Matic, the total POL Token supply is 10 billion. The initial circulating supply is expected to be equal to the circulating supply of Matic Token by the time the phase-out process begins.
During the Matic Token phasing process, holder will need to perform a swap transaction to transfer their old Matic Token to the upgraded smart contract. Matic will be swapped into POL Token at a 1:1 ratio. According to Polygon, the phase-out process lasts over 4 years, which should provide enough time for every holder to transfer their Token to the new contract. Once this is done, the Matic Token will no longer exist. Therefore, Matic holder should stay updated on new developments related to this issue and complete their Token swap within the specified time period.
Polygon is moving deeply into ZK and Layer 2 technology. It's quite easy to understand why they used technology in this way. This is also in line with their original goal of expanding the Ethereum network. Polygon PoS Chain has been in operation for a while and has seen quite significant adoption during this time, becoming one of the most used POS EVM networks. This new development is one to watch out for as it will likely be a game-changer for other decentralized applications and smart contract projects in the Polygon ecosystem. Not only the technical aspect, the economic aspect of the project also needs change, especially reStaking. The new POL Token will include everything built on the expanding ecosystem, not just the utility of the original Matic Token .
Polygon tilt towards ZK technology is also an important factor for the ZK model and the development of this technology. Over time, we will see how the system evolves and affects blockchain enthusiasts and investors. It is important to note the technical volatility associated with new systems and apply caution when necessary. Also, please note this article is for educational purposes only and should not be considered financial advice. Always do your own research before investing in any Token or protocol.
Join Bitcoin Magazine's Telegram: https://t.me/tapchibitcoinvn
Follow Twitter: https://twitter.com/tapchibtc_io
Follow Tiktok: https://www.tiktok.com/@tapchibitcoin
Minh Anh
According to Coingecko








