Macroeconomic changes after rate cut
1. FOMC meeting minutes and rate cut outlook
At the September 2024 FOMC meeting, the Fed made a highly anticipated rate cut, lowering the federal funds rate range by 2 basis points to 4.75%~5.00%. This move shows that the Fed is beginning to pay more attention to signs of weakness in the job market. Although the overall economic situation is still stable, it has shown a slowing trend. This decision, combined with the gradual loss of strong growth momentum in the job market and slowing inflation, makes future policy changes crucial to the market.
Key changes
- Slowing job market: Job growth has gradually shifted from "moderate" to "slowing", and the unemployment rate, while still at a historical low, has begun to rise slightly. This may indicate a longer-term labor market adjustment.
- Inflation continues to progress: The Federal Reserve has increased its confidence in reaching its 2% inflation target, and inflation is expected to continue to fall this year, indicating that inflationary pressure has been effectively alleviated.
- Clear employment goals: The Federal Reserve further emphasized the policy goal of "maximum employment", sending a mildly dovish signal and demonstrating its firm commitment to supporting employment stability.
Interest rate outlook
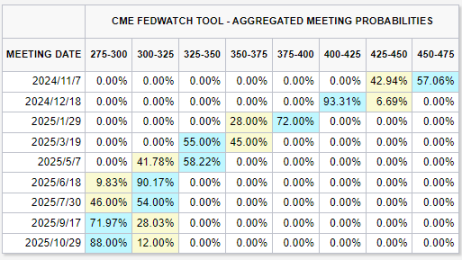
Distribution of Fed rate cut expectations - Source: @10xWolfDAO
According to the latest interest rate dot plot, the expectation of interest rate cuts in 2024 has been raised from 1 basis point to 4 basis points, and it is expected that there will be room for two more interest rate cuts this year. In addition, there may be another 4 basis points cut in 2025 and a further 2 basis points cut in 2026. This forecast shows that the Federal Reserve has a strong intention to maintain economic growth, promote labor market stability and prevent a further economic slowdown by cutting interest rates in the next two years.
 Expected Fed rate cuts in November and December 2024 - Source: @10xWolfDAO
Expected Fed rate cuts in November and December 2024 - Source: @10xWolfDAO
Although the rate cut was slightly lower than market expectations, the Fed made it clear that future policies will depend on the latest economic data. This will prompt market participants to re-examine the Fed's policy pace and adjust the impact of interest rate adjustments on different asset classes.
1.2 Economic and inflation forecasts
According to the latest economic forecast, the Federal Reserve slightly lowered its GDP growth forecast for 2024 to 2.0%, and expects the growth rate to remain near this level in the next few years. In addition, the unemployment rate is expected to rise to 4.3%~4.4% between 2024 and 2026, reflecting that the job market still needs to be rebalanced against the backdrop of a gradual economic slowdown.
At the same time, PCE inflation and core PCE inflation are expected to fall to 2.3% and 2.6%, respectively, which shows the Fed's optimistic expectations for future inflation easing. This also provides room for further interest rate cuts, allowing the Fed to flexibly respond to economic risks without having to worry too much about inflationary pressures.
1.3 Balance Sheet Reduction Progress and Market Liquidity
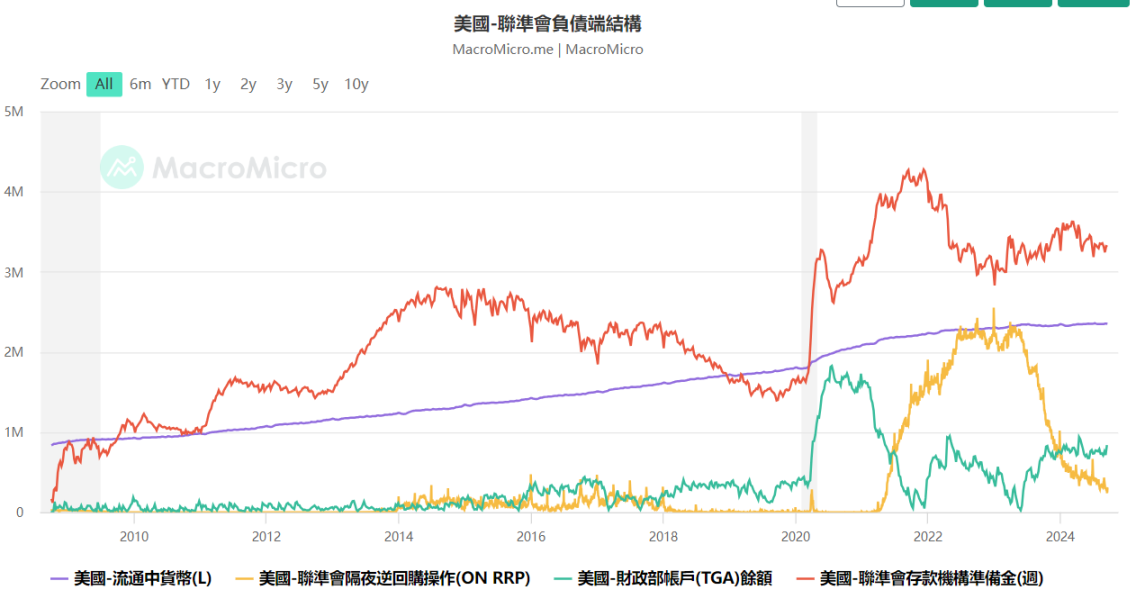 Source: Macromicro - @10xWolfDAO
Source: Macromicro - @10xWolfDAO
Since May 2024, the Fed has slowed its balance sheet reduction, with the current rate of reduction being $25 billion in Treasury bonds and $35 billion in MBS maturities per month. By September, the Fed's balance sheet had fallen to $7.12 trillion. However, market liquidity remains ample, and outflows from the reverse repurchase facility (ON RRP) have maintained liquidity stability. As the Fed continues to reduce its balance sheet, the market's reaction will be closely watched, especially for liquidity spillovers and their impact on asset prices.
1.4 Highlights from Powell’s Press Conference
Fed Chairman Jerome Powell reiterated the Fed's commitment to economic stability at a press conference. He pointed out that although the unemployment rate has risen, this is more due to an increase in the labor supply rather than a sign of economic recession. He also emphasized the Fed's confidence in cooling inflation and said that the pace of future interest rate cuts will be adjusted according to data. Such remarks mean that the Fed's flexibility will become a core feature of future policy direction, and the market will continue to pay attention to changes in economic data to predict its policy response.
Rate cut outlook
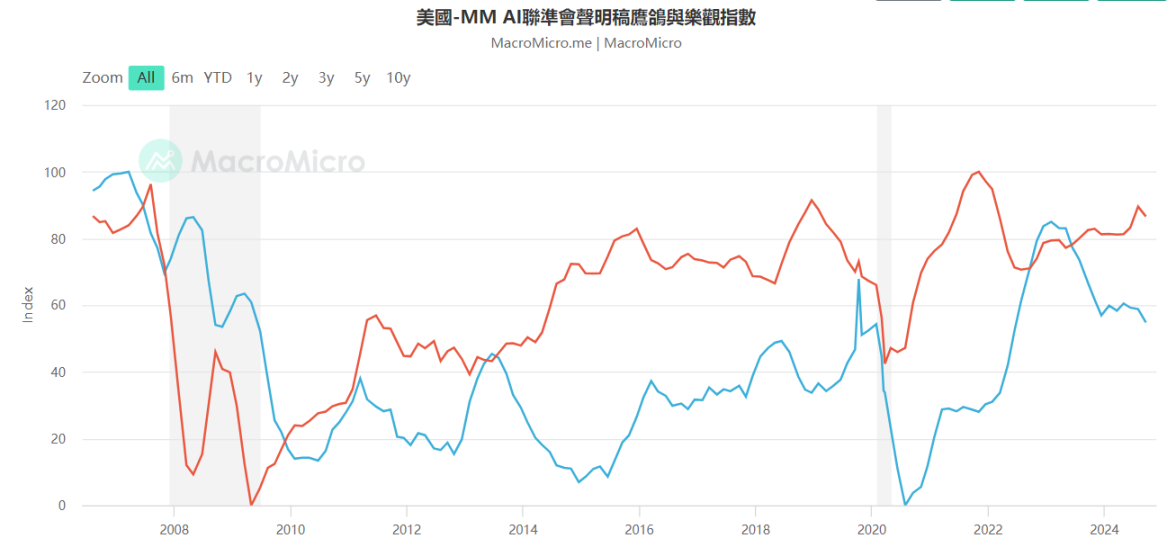
Source: Macromicro - @10xWolfDAO
The September FOMC meeting officially kicked off a preventive rate cut cycle, aimed at responding to the risk of a slowing job market and supporting continued economic growth. Although this rate cut was lower than some market expectations, the Fed's policy path of continued rate cuts still shows its willingness to respond to economic challenges by adjusting interest rates. In the future, monetary policy will be mainly driven by changes in the job market, oil prices and inflation.
Market participants should adopt flexible strategies and pay close attention to key data, especially in the context of increasing global economic risks, as flexibility in asset allocation is crucial.
Countermeasures and data focus after interest rate cut
2.1 Background and economic situation analysis
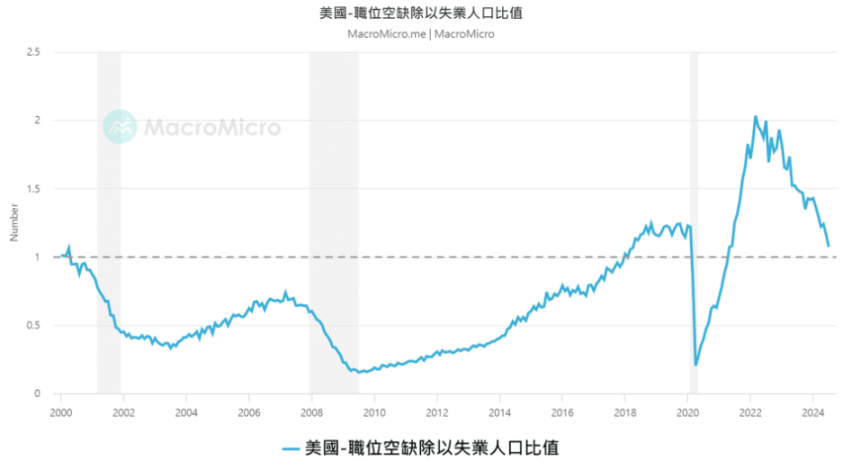
Source: Macromicro - @10xWolfDAO
The August 2024 non-farm payrolls report showed that the supply and demand of the U.S. job market has basically reached a balance, with the ratio of job vacancies to unemployed people at 1.07. This shows that there is almost one job vacancy for every job seeker, and the overheating of the labor market in the past few years has weakened. At the same time, the Federal Reserve has taken interest rate cuts to alleviate potential weakness in the job market.
Job Market Dynamics
- The disappearance of the employment umbrella: As market supply and demand balance and corporate hiring shows signs of slowing down, the unemployment rate may gradually rise, especially after the non-farm payrolls data was significantly revised down, revealing previously overestimated employment growth.
- Employment fragility is evident: the monthly non-farm employment growth rate showed weakness, with the three-month average increase falling to 116,000. The unemployment rate in many states is also rising, indicating that the job market may face greater challenges.
2.2 Reasons for interest rate cuts and market impact
The rate cut is aimed at reducing corporate borrowing costs to prevent a further slowdown in the job market and stimulate the economy. By boosting companies' willingness to raise funds, the rate cut is expected to boost hiring and help stabilize the consumer market.
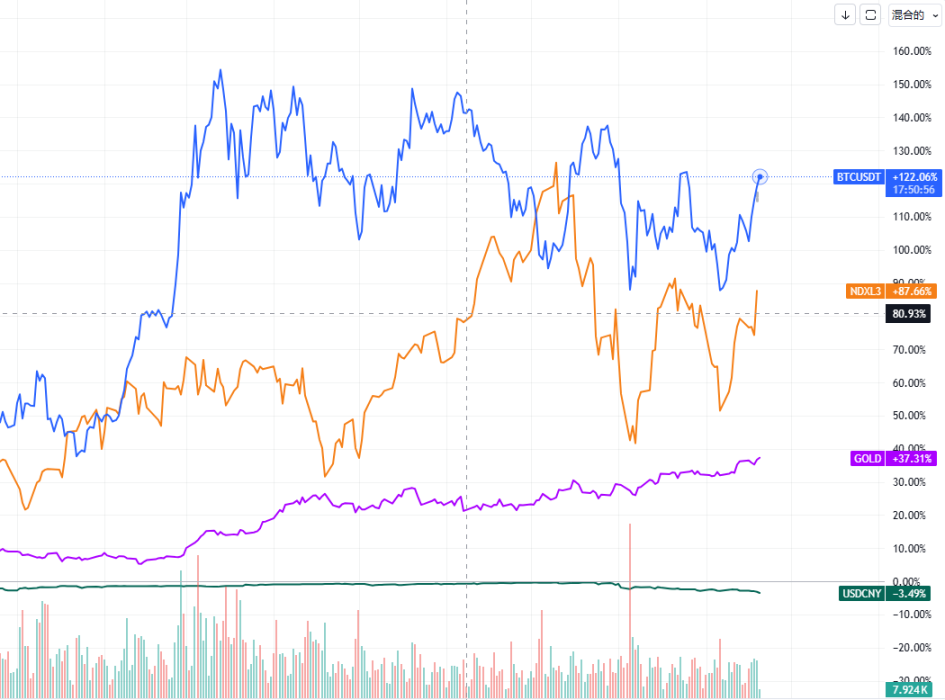
Comparison of market fluctuations in different financial markets after the Fed’s rate cut Source: @10xWolfDAO
Market Outlook
- Short-term effects: After the rate cut, the market is expected to experience short-term volatility, but safe-haven assets such as gold and bonds will benefit. Gold prices have risen significantly, indicating that they have benefited significantly from the rate cut. The U.S. dollar may depreciate under pressure due to the rate cut, pushing up the prices of other currencies and assets such as Bitcoin. The chart shows that the price of Bitcoin has rebounded, which also reflects the market's preference for safe-haven assets.
- Medium- and long-term impact: The interest rate cut will reduce corporate financing costs and is expected to boost growth stocks such as technology stocks. Although the Nasdaq index (NDXL3) has fluctuated, it has begun to rise overall, reflecting the positive impact of the interest rate cut on technology stocks. In addition, funds will further flow back to the cryptocurrency market, and the significant increase in Bitcoin prices is verifying this. However, the volatility shown in the chart also reminds us that whether the job market can grow steadily still needs further observation.
2.3 Economic vulnerability and response strategies
As the ratio of job vacancies to unemployed people decreases, the US economy becomes more vulnerable and the risk of recession increases. If the ratio continues to be below 1, historical data shows that the possibility of recession will increase. For this reason, market participants need to adopt diversified investment strategies to spread risks.
Coping strategies:
- Diversify your portfolio: Increase holdings of government bonds, gold, and cryptocurrencies (such as BTC) to cope with economic uncertainty.
- Closely monitor data: Pay attention to the development of the job market, especially the changes in the ratio of job vacancies to unemployed people. At the same time, the monthly increase in non-agricultural employment needs to be maintained at 150,000 to 200,000 to ensure that the economy does not enter a recession.
- Balanced allocation: Reduce the proportion of high-risk assets and increase the proportion of cash and low-volatility assets to cope with possible economic shocks.
Future Outlook: Market Response and Policy Sustainability
- Market reaction to rate cuts: As expectations of rate cuts are gradually realized, the market will experience short-term volatility. However, if rate cuts successfully stabilize employment and consumption, the market is expected to gradually stabilize, and the stock market may usher in new growth opportunities.
- Sustainability of policy support: The Fed will flexibly adjust its policies based on future economic data. If employment continues to be weak, further interest rate cuts may be made in the future.
- Global impact: The Fed’s policies have a significant impact on global markets, especially in terms of capital flows and exchange rates. Global investors need to pay close attention to US economic trends to guard against potential market risks.
The U.S. economy faces high uncertainty, and interest rate cuts will become a key tool for the Federal Reserve to deal with the weak job market. Investors should adopt a diversified strategy, pay close attention to employment data, balance risk asset allocation, and increase safe-haven asset holdings to cope with future economic fluctuations.








