Cryptocurrency Transfer Fees: The So-Called "Gas Fee"
In the traditional financial system, when we transfer cash from a bank account to another account or withdraw cash, we are usually charged a fee of around $15. This fee is used to cover the "operating costs" of the entire transfer process.
In the world of cryptocurrencies, the so-called transfer fee is the "Gas Fee" that users need to pay to the miners and validators on the blockchain network to reward them for helping to process and confirm the transaction.
Cryptocurrency Transfer Fees are Dynamic
The difference is that in the traditional financial system, the fees are usually fixed. But on the blockchain, the level of the Gas Fee is closely related to the usage of the blockchain. When the transaction volume surges and the blockchain system is congested, the Gas Fee will rise significantly, and users will need to pay a higher fee to complete the transaction; conversely, when there are fewer ongoing transactions, the fee will also decrease relatively.
Gas Fee is like the "fuel" for the operation of the blockchain, so by understanding the usage of the blockchain, you can predict the changes in the cryptocurrency transfer fees, and users can choose the right time to transfer more wisely, thereby reducing their transfer costs!
Different Blockchains Have Different Cryptocurrency Transfer Fees
However, in addition to the "timing" factor, the choice of "which blockchain to use" will also directly affect the amount of the fees.
Because each blockchain has different designs and operating methods, from the consensus mechanism to the transaction processing capacity, these factors will directly affect the level of the fees.
For example, the Gas Fees on Bitcoin and Ethereum, which many people are often concerned about, can be staggeringly high when the network is congested, sometimes even exceeding the transfer amount itself! In comparison, the fees on blockchains like Binance Chain and Solana are relatively cheaper, attracting many users who need to make small or frequent transactions.
Therefore, choosing the appropriate blockchain according to different needs can not only save on fees, but also complete transactions more efficiently.
Common Cryptocurrency Transfer Fees: Bitcoin, Ethereum, Solana, BNB, TRON, Polygon, Avalanche
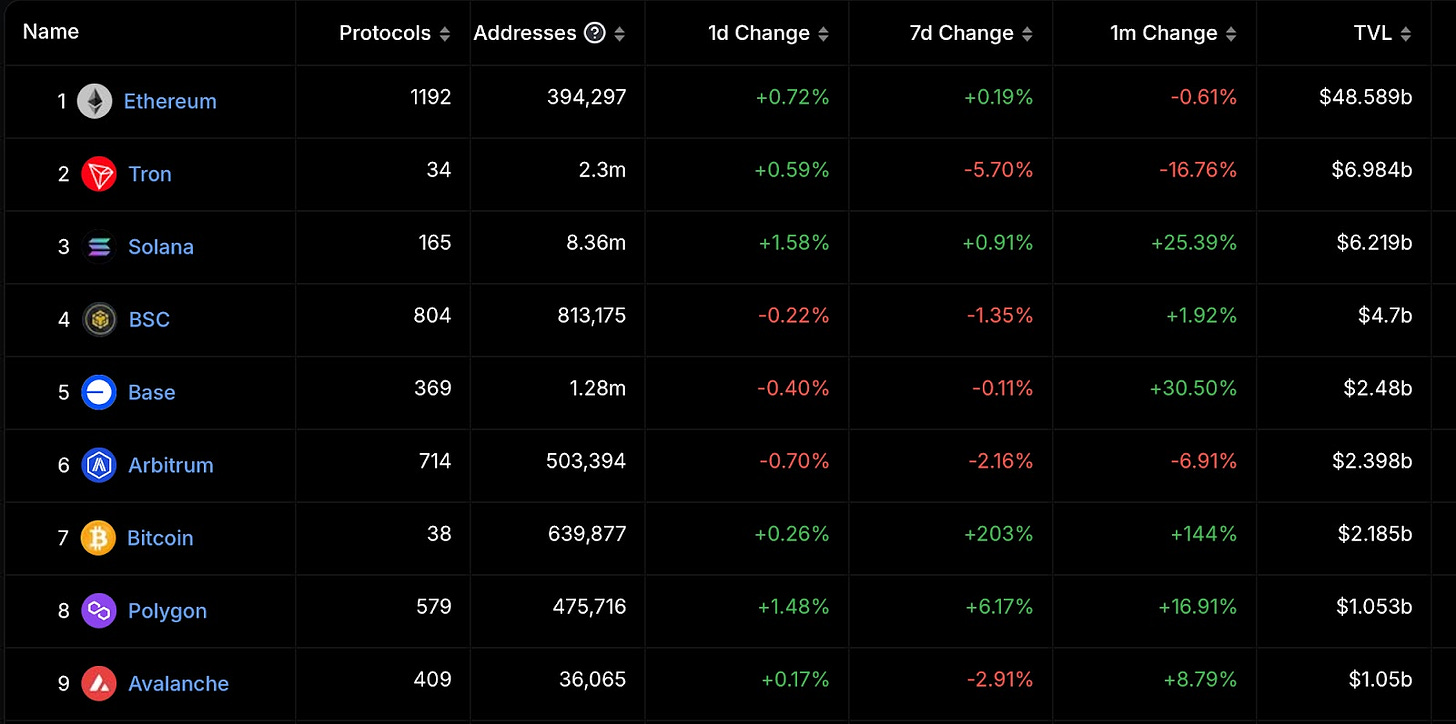
According to data from Defillma, excluding Ethereum's Layer 2, the chains most commonly used by on-chain users are probably Bitcoin, Ethereum, Solana, BNB, Tron, Polygon, Avalanche, and Ton. Although we mentioned earlier that the Gas Fee is constantly changing, the following is a simple list to give you a preliminary idea of which chain is more expensive and which is cheaper.
Blockchain | Instant Transfer/Transaction Fee Gas Fee (10.23) |
Bitcoin | $3.05 USD |
Ethereum | $1.03 USD |
Solana | $0.003 USD |
BNB | $0.089 USD |
Tron | $2.15 USD |
Polygon | $0.002 USD |
Avalanche | $0.058 USD |
Ton | $0.076 USD |
How to Check Cryptocurrency Instant Transfer Fees: Blockchain Explorer Tutorial
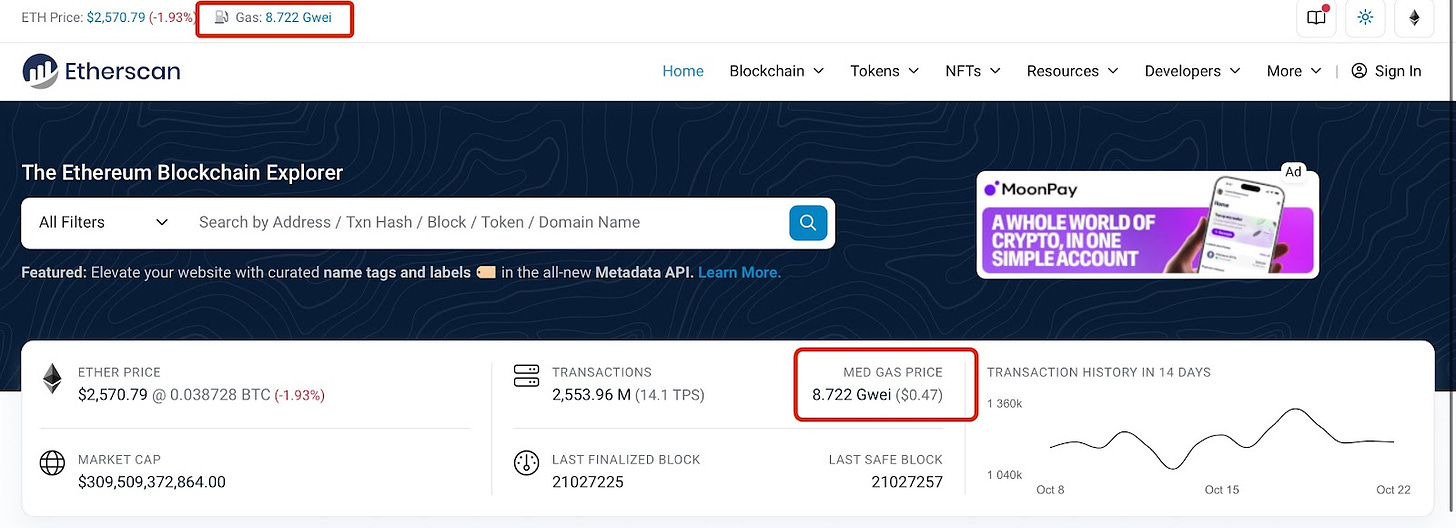
To check the instant transfer fees of cryptocurrencies, using the blockchain explorer of each blockchain is the most direct and safest method. Let's take Ethereum's Etherscan as an example.
💡Blockchain Explorer: A tool specifically designed to query the transaction information on the blockchain network, used to view all the public data on the blockchain, including transaction history, block information, address balances, and fees.
Go to the Etherscan website, and you can see the current Gas Fee at the top of the page or in the red box, which is the average fee required for a single transaction. You can see that the current Ethereum transfer or transaction fee is about $0.47.
We also provide the links to the blockchain explorers of other commonly used blockchains for your quick reference.
Blockchain | Blockchain Explorer Link |
Bitcoin | |
Ethereum | |
Solana | |
BNB | |
Tron | |
Polygon | |
Avalanche | |
Ton |
How to Save on Cryptocurrency Transfer Fees: Choose the Right Time, Blockchain, and Transfer Tool
In summary, we can simply conclude the following methods that can help you save on cryptocurrency transfer fees.
• Choose a low-fee blockchain: Use blockchains with extremely low fees, such as Solana, Polygon, or Avalanche, to make transfers, which is more cost-effective than using high-fee blockchains (such as Ethereum).
・Choose the right time to transfer funds: Avoid transferring funds during peak network hours, and instead choose times when blockchain transaction volume is lower, as this will result in lower fees.
・Combine multiple small transactions into one larger transaction: Avoid fragmented operations, and instead combine multiple small transactions into one larger transaction. This can reduce the need to pay multiple transaction fees, and is particularly suitable for blockchains like Bit and Ether that charge fees based on transaction size.
・Use wallets with built-in fee recommendation features: Wallets like MetaMask and Trust Wallet display the current fee status and provide recommendations, which can help you choose the most suitable fee to complete the transaction.
・Use Layer 2 solutions: If your assets are on the Ether network, use Layer 2 blockchains (such as Arbitrum or Optimism) to conduct transactions. These solutions can significantly reduce Gas fees by bundling a large number of transactions and submitting them to the main chain.
What is the lowest fee chain for transferring cryptocurrencies to a wallet or another exchange?
💡Before carefully calculating the fees, make sure that the destination wallet or exchange supports the chain you want to use. The blockchain for sending and receiving cryptocurrencies must be the same, otherwise transferring to the wrong chain will result in the loss of your assets, and they cannot be recovered.
Although the TRON chain itself does not have very high fees, if you want to withdraw stablecoins like USDC from an exchange to another exchange, there are actually cheaper options:
・Transfer USDC, you can choose the Solana or Polygon chain
・Transfer USDT, you can choose the BNB chain