As an important innovation in the field of decentralized finance, decentralized derivatives protocols are gradually changing the operating model of the traditional financial derivatives market. Through blockchain technology and smart contracts, they eliminate the dependence on centralized intermediaries and provide users with a transparent, secure and globally accessible trading environment. This article will conduct an in-depth analysis of eight representative decentralized derivatives protocols - Hyperliquid, Jupiter, Drift, GMX, Vertex, Apex, SynFutures and dYdX, covering the definition and characteristics of decentralized derivatives protocols, operating mechanisms, introductions and features of each project, comparative analysis, and future prospects for this track. This article aims to provide readers with a comprehensive and objective perspective to help understand this rapidly developing crypto-financial track.
1. Understanding decentralized derivatives protocols
1.1 Definition
Decentralized derivatives protocols are financial instruments based on blockchain technology that allow users to trade derivatives without the need for traditional centralized intermediaries. Derivatives are financial contracts based on underlying assets (such as BTC), and their value is derived from the price fluctuations of the underlying assets. Decentralized derivatives protocols use smart contracts to automate the transaction execution, settlement and liquidation processes, running on a public blockchain network to ensure that the rules are transparent and cannot be tampered with.
Unlike centralized exchanges (such as Binance or Coinbase), decentralized derivatives protocols do not rely on a single entity to manage user funds or match transactions, but instead achieve decentralized market operations through distributed networks and algorithms. Perpetual Futures are the most popular product type in decentralized derivatives protocols, which allow users to bet on the rise and fall of crypto asset prices in a leveraged manner with no expiration date.
1.2 Features
The decentralized derivatives protocol has the following core features:
Decentralization : There is no centralized control body, and all transactions are completed directly on the blockchain, reducing single points of failure and censorship risks.
Transparency : Transaction records and contract terms are stored on the blockchain and are publicly accessible, so anyone can verify the fairness of the transaction.
Security : User funds and data are protected through smart contracts and encryption technology, reducing the risk of hacker attacks or internal fraud.
Accessibility : Global users only need a crypto wallet to participate, without the need for KYC (identity verification) or permission from the traditional financial system.
Innovation : Supports a variety of financial products, such as perpetual contracts, options, synthetic assets, etc., providing users with flexible trading strategies.
These characteristics make decentralized derivatives protocols not only attractive to retail traders, but also gradually become an area of focus for institutional investors.
2. The operating mechanism of decentralized derivatives protocols
The operation of decentralized derivatives protocols relies on blockchain technology and different market mechanism designs to achieve liquidity provision, price discovery, and trade execution. The following are several common operating mechanisms:
2.1 Automated Market Maker (AMM)
Automated Market Maker (AMM) replaces traditional buy and sell order matching through algorithms and liquidity pools. Users deposit assets into the liquidity pool, and the funds in the pool automatically adjust the price according to a preset mathematical formula (such as a constant product formula). The advantage of AMM is that it can complete transactions without waiting for the counterparty, and is suitable for markets with low liquidity.
Representative projects : Jupiter, GMX.
Advantages : Simple and efficient, suitable for small transactions and high volatility markets.
Disadvantages : There may be slippage, and price discovery is less efficient than an order book.
2.2 Order Book Model
The Order Book Model is similar to traditional financial exchanges, where buyers and sellers submit limit orders and the system matches transactions. This mechanism is widely used in centralized exchanges, but in a decentralized environment, the limitations of on-chain transaction speed and cost need to be addressed.
Representative project : Hyperliquid
Pros : Provides more accurate price discovery, suitable for professional traders.
Disadvantages : High on-chain performance requirements, which may lead to transaction delays or high fees.
2.3 Hybrid Model
The hybrid model combines the advantages of AMM and order book, trying to find a balance between liquidity and trading efficiency. For example, the protocol may use AMM to provide basic liquidity while optimizing price discovery through order book.
Representative project : Vertex.
Advantages : High flexibility and adaptability to various market conditions.
Disadvantages : The implementation is complex and the user experience may not be uniform.
2.4 On-chain/off-chain mixing
Some protocols place order matching off-chain for speed, while placing settlement and fund management on-chain for security. This approach takes advantage of the efficiency of centralized systems while retaining decentralized trust mechanisms.
Representative project : dYdX (V4).
Advantages : Fast transactions and low fees.
Disadvantages : The off-chain part may introduce a certain degree of centralization risk.
3. Current status of decentralized derivatives protocol track

Source: https://dune.com/uwusanauwu/perps
Centralized trading platforms have always dominated the perpetual contract trading market with high liquidity and stable trading experience. As an early leader in decentralized perpetual contract trading platforms, dYdX has occupied a certain share in the decentralized perpetual contract market with its innovative order book model, becoming a market pioneer.
With the popularity of decentralized finance, users' demand for decentralized transactions has gradually increased. Emerging platforms such as GMX provide simple and efficient trading experience through AMM models and liquidity pool mechanisms, attracting a large number of users and funds. Jupiter has emerged as an important decentralized derivatives protocol in the Solana ecosystem. In 2023, market competition has further intensified. The emerging platform Hyperliquid has emerged with high performance and low-latency trading experience, attracting a large number of professional traders and gradually becoming a market leader. At the same time, dYdX's market share began to decline, partly due to the rapid rise of competitors and the challenges it encountered in migrating to the Cosmos ecosystem.
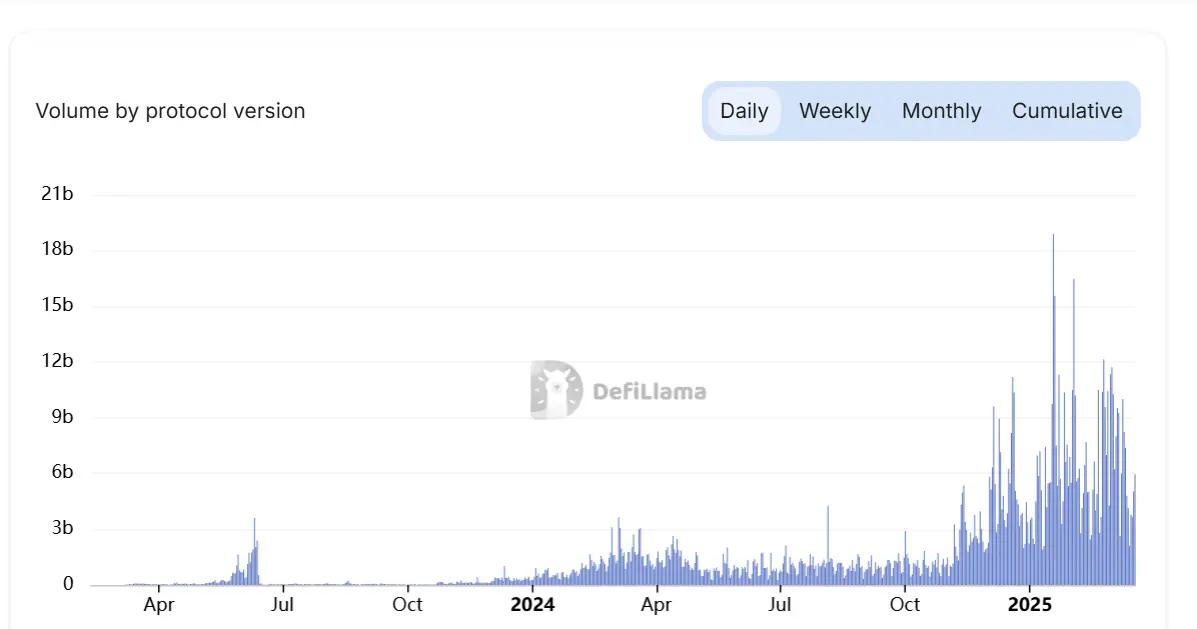
Source: https://defillama.com/perps/hyperliquid
As of March 20, the 24-hour trading volume of decentralized perpetual contracts reached US$9.4 billion, of which Hyperliquid's market share in decentralized derivatives protocols has reached 63%, and its trading volume ranks 15th among centralized exchanges.

Source: https://defillama.com/perps
4. Inventory and analysis of representative projects
4.1 Hyperliquid
Introduction : Hyperliquid is based on its own Layer 1 blockchain, runs completely on-chain, and uses an order book model. It provides liquidity and clearing support through the official HLP vault. Users can deposit funds into HLP and share the profits from transaction fees, funding fees, and clearing fees. HLP essentially acts as the counterparty to some transactions. Hyperliquid's TPS (200,000) and low latency (0.2 seconds) processing capabilities are close to CEX levels. The highest leverage supported by Hyperliquid is 50 times, but due to the mysterious whale's arbitrage operation on March 12, HLP suffered a loss of about US$4 million. Hyperliquid announced that the maximum leverage of BTC and ETH will be reduced to 40 times and 25 times, respectively.
Features :
Gas fee-free transactions reduce user costs.
Exclusive blockchain design, on-chain transparency and high throughput.
It is currently the decentralized perpetual exchange with the largest trading volume.
Applicable scenarios : Suitable for professional traders who pursue low cost and high efficiency.
4.2 Jupiter
Introduction : Jupiter is a DEX aggregator based on Solana, which also supports decentralized perpetual contract trading and provides up to 100x leverage. The Jupiter Liquidity Provider (JLP) pool acts as the counterparty of the trader. When a trader opens a leveraged position, he borrows tokens from the pool, and 75% of the fees generated by the transaction are allocated to the liquidity provider. Currently, there are only 5 assets supported: SOL, ETH, WBTC, USDC, and USDT.
Features :
Leverage Solana’s high speed and low fees to provide an experience close to that of centralized exchanges.
Supports a variety of trading pairs and leveraged trading.
Deep integration with the Solana ecosystem has attracted a large number of ecosystem users.
Applicable scenarios : Suitable for Solana ecosystem users and novice traders.
4.3 GMX
Introduction : GMX is a multi-chain decentralized perpetual exchange deployed on Arbitrum and Avalanche. It uses the AMM model and provides up to 100x leverage. Currently, it supports 67 perpetual contracts. Liquidity is provided through a multi-asset liquidity pool (GLP pool) owned by the community. Liquidity providers can obtain GLP tokens by staking a single asset, representing their equity in the pool. Platform fees come from user exchanges and leveraged transactions, 30% of which are rewarded to GMX pledgers and 70% are allocated to GLP holders. GMX V2 replaces the GLP pool with an isolated GM pool, and incentivizes through funding fees, loan fees, transaction fees, price impact, etc.
Features :
Liquidity pool design allows users to earn income by providing liquidity.
The transaction fees are low (0.05%-0.07%), and part of the fees are distributed to liquidity providers.
TVL has performed strongly, showing users’ trust in its liquidity.
Applicable scenarios : Suitable for traders who hope to profit through liquidity mining.
4.4 dYdX
Introduction : dYdX was founded in 2018 and initially ran on Ethereum Layer 2 (powered by StarkWare), but has since migrated to its own blockchain dYdX Chain, based on the Cosmos SDK and Tendermint Proof-of-Stake consensus protocol. V4's on-chain/off-chain hybrid model increases speed through off-chain order matching and ensures security through on-chain settlement. Order matching is done off-chain by validators, stored in the in-memory order book, and settlement is performed on-chain. There is no gas fee for placing and canceling orders, and fees are only charged when orders are executed, reducing transaction costs.
Features :
The V4 version introduces decentralized off-chain order books and on-chain settlement.
Supports up to 20x leverage and 199 assets.
The transaction fees are low (0.02% maker, 0.05% taker), which attracts high-frequency traders.
Applicable scenarios : Suitable for users who seek high leverage and professional trading experience.
4.5 Vertex
Introduction : Vertex is a multi-chain decentralized exchange that combines a centralized limit order book (CLOB) and an AMM hybrid model, combining an order book and an automated market maker (AMM) mechanism. Its order book uses a price/time priority algorithm to ensure that orders are executed at the best price, regardless of whether the quote is provided by an AMM or a market maker.
Features :
Layer 2 technology reduces fees and MEV (miner extractable value) risks.
Supports up to 20x leverage and 54 assets.
Emphasize institutional-level trading experience.
Applicable scenarios : Suitable for professional traders who need efficient order matching.
5. Opportunities and Challenges of Decentralized Derivatives Protocols
As an important branch of DeFi, decentralized derivatives protocols are in a stage of rapid development. Market growth, technological progress and global accessibility provide it with broad development space, but challenges such as regulatory uncertainty, technical risks and insufficient liquidity cannot be ignored.
opportunity
Market growth potential: With the maturity of the cryptocurrency market and the participation of institutional investors, the demand for derivatives trading continues to grow. Decentralized protocols are expected to further attract users and seize the market share of centralized exchanges with their transparency and security.
Driven by technological progress: Layer 2 solutions (such as Arbitrum, Optimism) and high-performance public chains (such as Solana, Sui) have significantly increased transaction speeds and reduced costs. For example, Hyperliquid achieves 20,000 transactions per second through its Layer 1 blockchain, which is close to the performance of centralized exchanges. In the future, the maturity of cross-chain technology and interoperability protocols will further promote asset mobility and market expansion.
Innovative products and services: Decentralized protocols can quickly launch a variety of financial products, such as perpetual contracts, synthetic assets, and options, to meet user needs. In the future, the protocol may expand to the field of traditional financial derivatives, further broadening market coverage.
Community governance and participation: The decentralized governance model DAO enhances user participation and loyalty. For example, dYdX implements community decision-making through dYdX DAO, and users can vote to influence the development of the protocol. This model not only improves user stickiness, but also promotes the healthy growth of the ecosystem.
Global accessibility: Decentralized protocols do not require identity verification (KYC), and global users only need a crypto wallet to participate, greatly expanding the market size. This feature provides users with financial freedom and opportunities, especially in areas where traditional financial services are insufficient.
challenge
Regulatory uncertainty: Regulatory policies in different countries and regions vary significantly, which may restrict the development of the protocol and bring legal risks to the operation of the protocol and the issuance of tokens. The protocol needs to find a balance between the concept of decentralization and compliance requirements, which increases the difficulty of operation.
Technical risks and security risks: Smart contract vulnerabilities and blockchain network congestion are the main risks. For example, the recent Hyperliquid margin call incident resulted in a loss of approximately $4 million, highlighting the threat of technical risks. In addition, network congestion may lead to transaction delays and high fees, affecting user experience.
Insufficient liquidity: Compared with centralized exchanges, decentralized protocols support fewer assets and generally have lower liquidity, especially in the long-tail asset market. Liquidity fragmentation may lead to large slippage and low price discovery efficiency.
Intensified competition: As more protocols enter the market, competition is becoming increasingly fierce. For example, Hyperliquid leads with high performance, but Jupiter and Vertex are also working on technological innovation. Protocols need to continue to innovate to maintain their competitive advantage, otherwise they may face user diversion.
6. Conclusion
As an important innovation in the DeFi field, decentralized derivatives protocols are reshaping the traditional financial derivatives market through blockchain technology and smart contracts, bringing users a transparent, secure and globally accessible trading experience. Hyperliquid stands out among many protocols and becomes a market leader with its high-performance Layer 1 blockchain, gas-free order book model, and transaction speed and experience close to centralized exchanges. As mature players, dYdX and GMX remain competitive with their strong user base and TVL, while Jupiter and Vertex show their potential through ecological integration and technological innovation. However, compared with centralized trading platforms, decentralized derivatives protocols are still limited by fewer asset types, blockchain network performance bottlenecks, and insufficient liquidity. Looking ahead, with the advancement of Layer 2 technology, high-performance public chains, and the growth of user demand, this track is expected to further challenge the status of centralized exchanges and promote the continuous evolution of the crypto financial ecosystem by launching more innovative products, optimizing user experience, and gradually adapting to regulatory requirements.
about Us
As the core investment and research center of the Hotcoin ecosystem, Hotcoin Research focuses on providing professional in-depth analysis and forward-looking insights for global crypto asset investors. We have built a three-in-one service system of "trend analysis + value mining + real-time tracking". Through in-depth analysis of cryptocurrency industry trends, multi-dimensional evaluation of potential projects, and all-weather market volatility monitoring, combined with the weekly "Hotcoin Selection" strategy live broadcast and "Blockchain Today's Headlines" daily news delivery, we provide investors at different levels with accurate market interpretation and practical strategies. Relying on cutting-edge data analysis models and industry resource networks, we continue to empower novice investors to establish a cognitive framework, help professional institutions capture alpha returns, and jointly seize value growth opportunities in the Web3 era.
Risk Warning
The cryptocurrency market is highly volatile and investment carries risks. We strongly recommend that investors fully understand these risks and invest within a strict risk management framework to ensure the safety of their funds.








