Author | Zack Pokorny
Translated | GaryMa Wu Blockchain
Original link:
https://www.galaxy.com/insights/research/ethereum-blob-market-post-pectra/
On May 7, 2025, the Pectra upgrade went live on the mainnet. Among the series of Ethereum Improvement Proposals (EIPs) implemented, it includes an increase in the target and maximum number of blobs per block proposed by EIP-7691. Blobs were introduced through EIP-4844 (proto-danksharding) in last year's Dencun upgrade to provide a dedicated data publication space for rollups. Since Dencun's launch, the network has maintained a target of 3 blobs per block and a maximum of 6; each blob is 128kb, which equates to approximately 5.5GB of data capacity per day through blobs. After Pectra, the target and maximum number of blobs per block increased to 6 and 9, bringing blob data capacity to about 8.15GB per day. This change impacts the blob market, rollups, and ETH validators, as the reduced blob space scarcity lowers competition between rollups while increasing the network's data availability (DA) capacity. The following will explore the effects of Pectra's blob parameter changes on the blob market, rollups and their users, ETH validators, and ETH supply.
Key Takeaways
● In the five full trading days after Pectra's launch, the number of blobs purchased daily by rollups increased from about 21,200 to 25,600, though the average number of blobs per block remains 33% below the new target of 6.
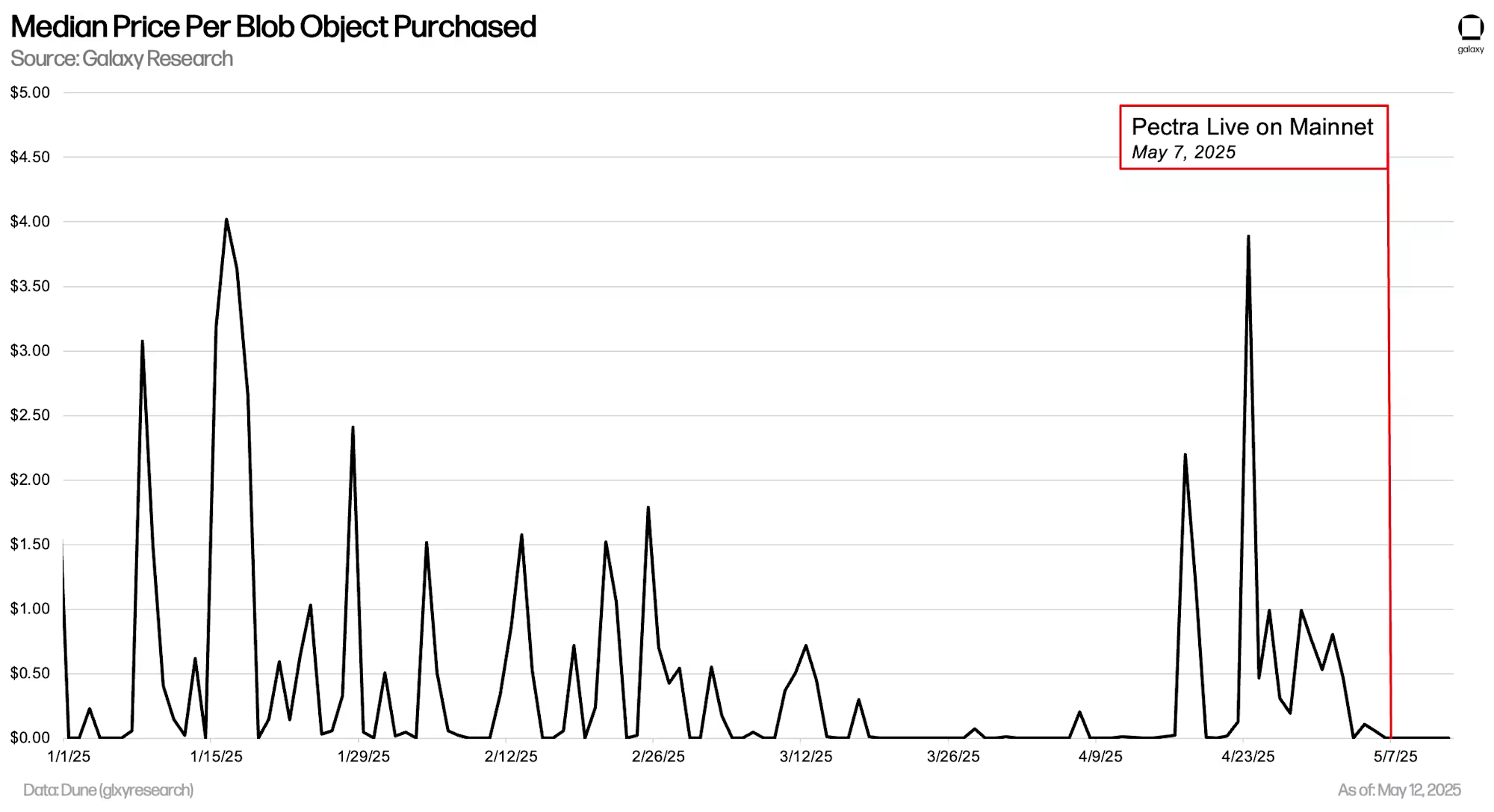
● As the actual number of blobs per block is far below the updated target value, blobs have become almost free again, the first time since mid-April 2025. Rollups are paying less than one-thousandth of a cent per day for blobs, with a cumulative payment of only four-thousandths of a cent since Pectra's launch. This significantly reduces the amount of ETH burned by rollups for data space usage and publication on ETH.
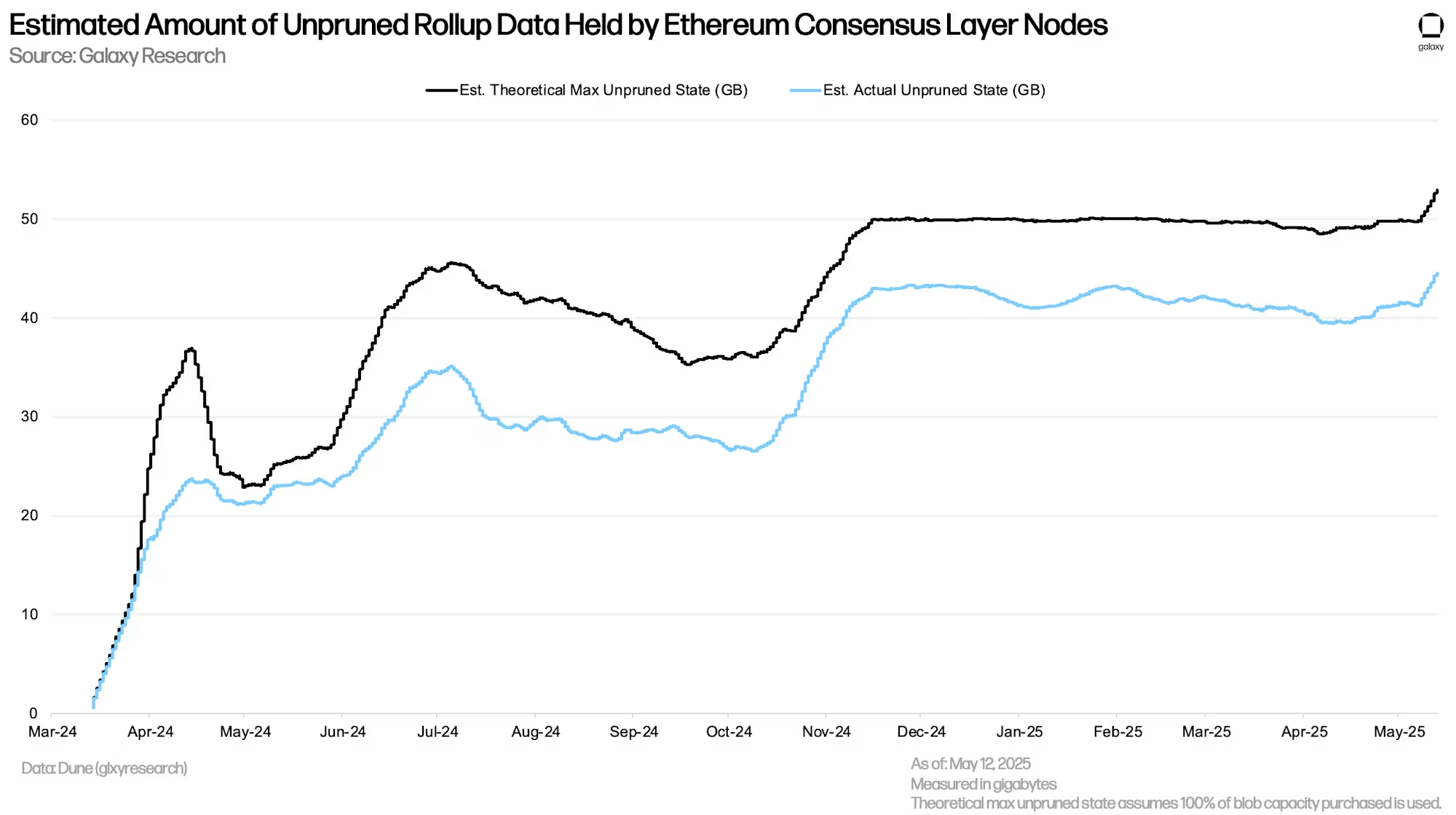
● Nodes must retain rollup blob data for at least 18 days before removing it from their devices. The increase in daily blob purchases means consensus layer nodes now need to retain a new high of approximately 44.6GB of data before pruning.
● The reduction in blob costs has improved the profit margins of rollups, both relatively and absolutely, with Base benefiting the most in terms of net income after on-chain costs. Nevertheless, transaction costs for some mainstream rollups have remained unchanged or slightly increased since Pectra's launch.
● All data comes from the Ethereum blob market and its impact on rollups section of the Galaxy Research public dashboard.
Blob Market
Since Pectra's launch on May 7, 2025, the daily number of blobs purchased by rollups has increased by 20.8%. In the 60 days before Pectra, rollups averaged 21,200 blob purchases daily. In the five full trading days after the upgrade, they averaged 25,600 daily blob purchases. The corresponding daily data capacity increased from 2.7GB before the upgrade to 3.3GB currently.
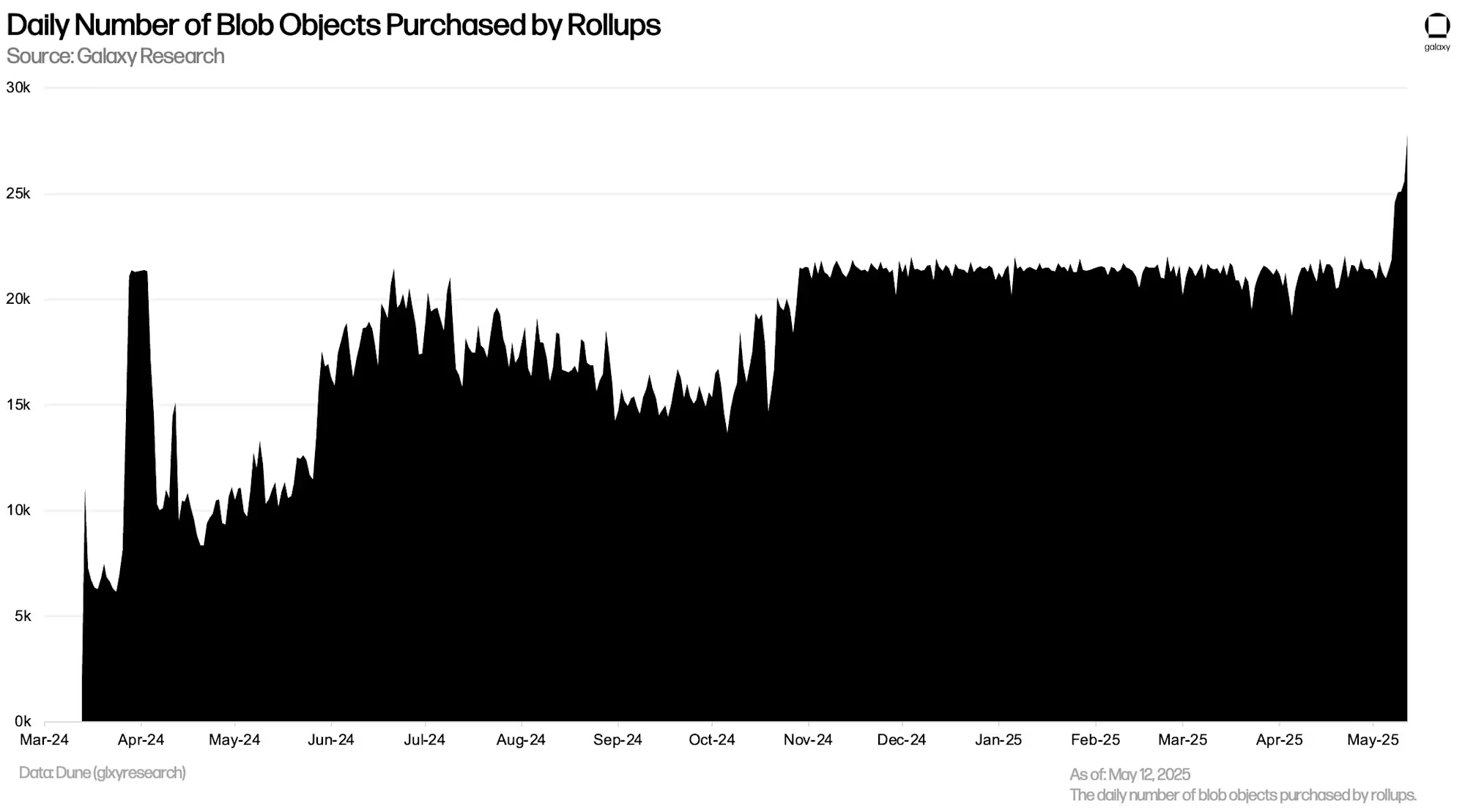
Despite the increase in blob purchases, only two-thirds of the new target blob quantity has been used daily since Pectra's launch. Therefore, while blob usage was consistent with the target before Pectra, rollups have not yet reached the new demand level to consistently achieve the new target rate.

As a result, blobs have become almost free again, as only two-thirds of the target blob quantity is used per block. This is the first time blobs have been this cheap since mid-April 2025. Since Pectra's launch, the median price per blob is only $0.00000000035 (9 zeros). This means rollups are paying at most $0.0000092 per day, with a total blob cost of only $0.0000395. In other words, rollups are paying less than one-thousandth of a cent per day, totaling no more than four-thousandths of a cent. Note that this fee does not include the type-3 transaction fees required for on-chain blob execution, only the cost of the blobs themselves.
In the 60 days before Pectra, rollups averaged $16,250 in daily blob fees, totaling approximately $1,095,000. This fee has decreased by nearly 100%.
Data Capacity and Impact on ETH Nodes
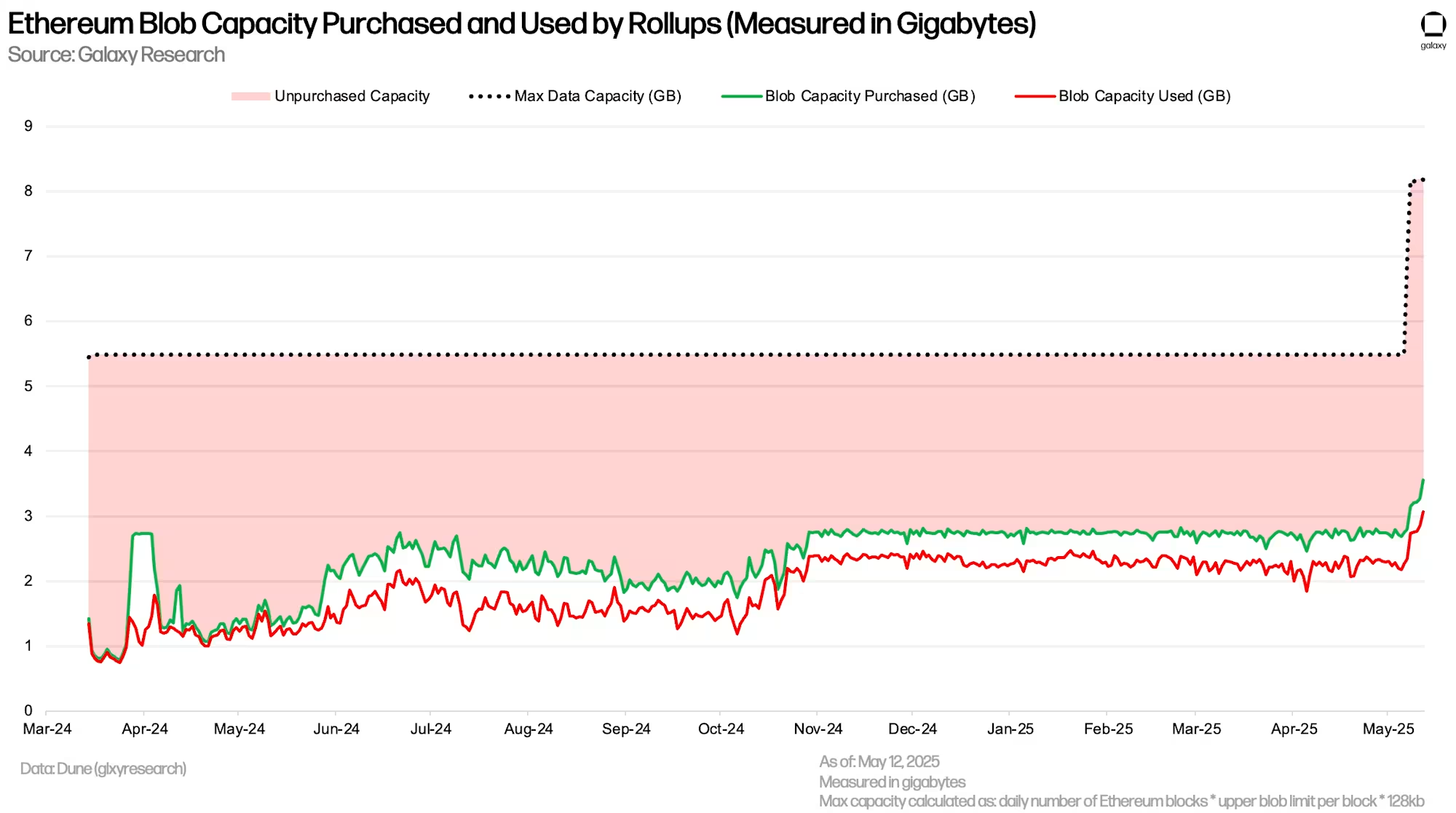
After Pectra's implementation, a larger proportion of the total daily data capacity through blobs remains unpurchased. Thus, although rollups are buying more blobs and more data space, the relative usage proportion of total daily capacity is lower. Once rollup demand reaches the new target level, the blob market will operate more efficiently from a capacity perspective, as the new target rate is only 33% lower than the maximum, compared to 50% under the old parameters.
ETH generates approximately 7,100 blocks daily, with each block capable of containing up to 9 blobs, indicating a maximum daily blob capacity of about 8.17GB, with a target of 5.45GB; this value fluctuates with actual block count. Currently, only 3.3GB of data space is purchased, equivalent to 40% of the daily maximum capacity and 61% of the target capacity. In comparison, during the month before Pectra, an average of 50% of total capacity and 99% of the target capacity was purchased daily.
Each blob can hold up to 128KB of data. Rollups do not need to use the full 128KB (e.g., using 100KB is fine), but a single blob cannot exceed this limit. The difference between blob capacity purchases (green line in the chart) and actual usage (red line) shows the gap between the actual data filled by rollups daily and the upper limit. The average blob fill rate after Pectra is 86%, compared to 82% in the 60 days before the upgrade.
The increase in daily purchased blob data volume means consensus layer nodes must store more rollup data. Nodes must retain this data for at least 18 days before deletion. Before Pectra, this meant nodes needed to retain 40GB to 44GB of data. In the days following Pectra, this value continued to rise, reaching a historical high of 44.6GB as of May 12, 2025. If current blob demand persists, nodes are expected to store around 60GB of rollup data; if the target rate is reached, this could increase to approximately 95GB to 100GB.
Rollup Costs and ETH Burning
Since Pectra's launch, rollups have averaged $11,015 daily in blob-related costs (including blob objects and type-3 execution layer transaction fees), compared to $20,660 in the 60 days before the upgrade, a 51% decrease.
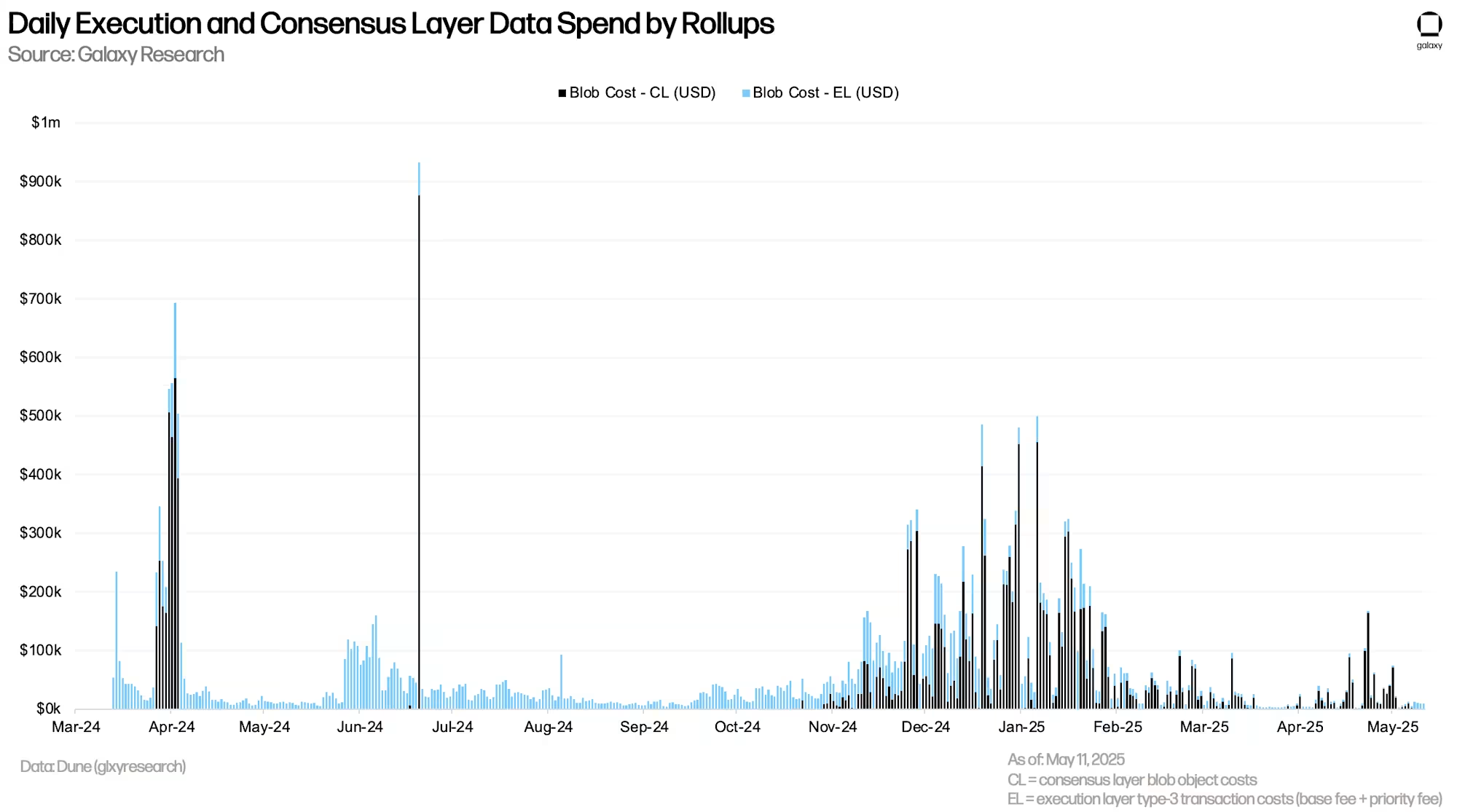
The sharp rise in ETH L1 fees has kept rollup costs at a certain level in blob activities. Within a week of Pectra's launch, ETH L1 base fee increased by over 650%. Without this surge, the cost of rollups executing blobs would be lower, and fewer ETH would be burned through blob activities.
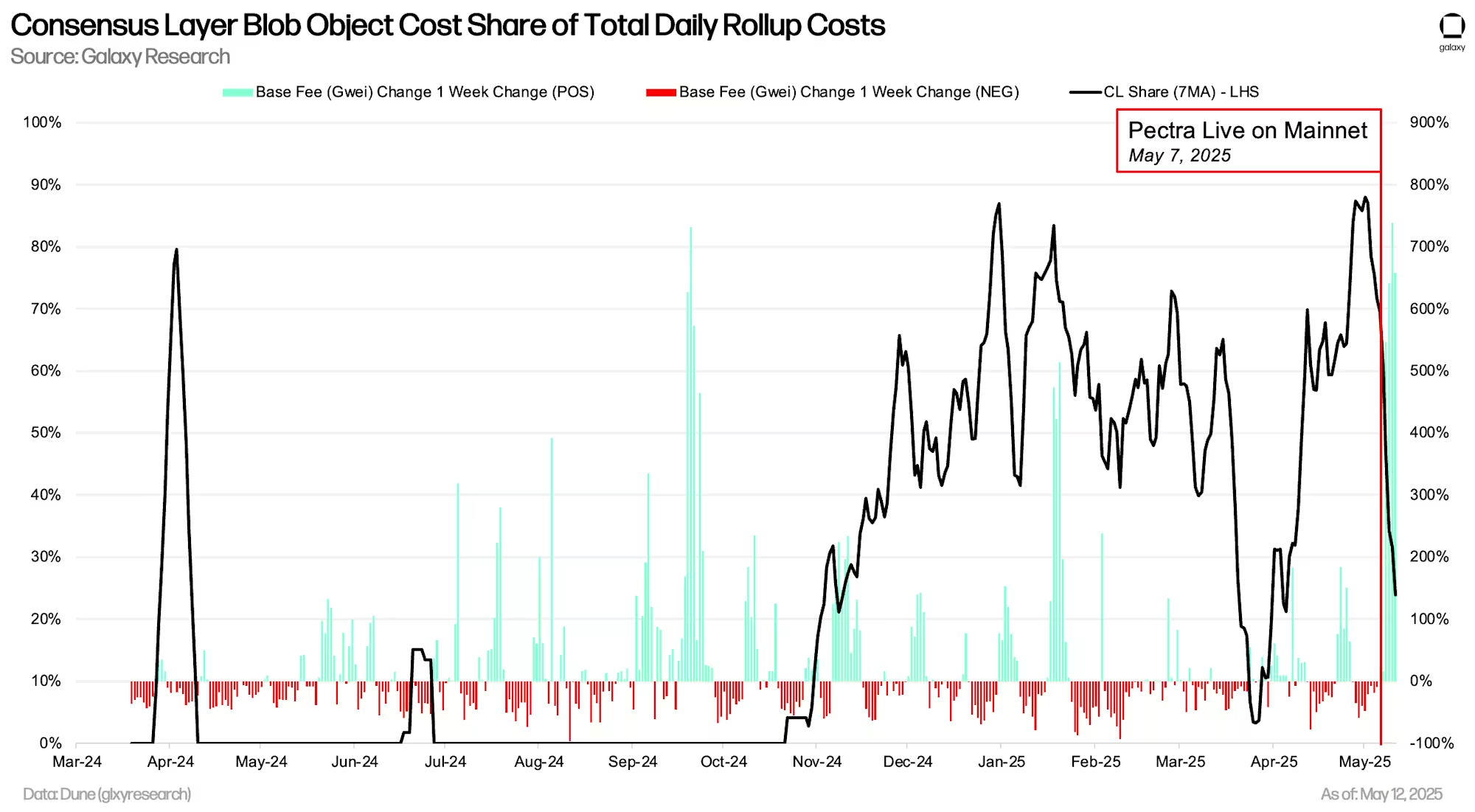
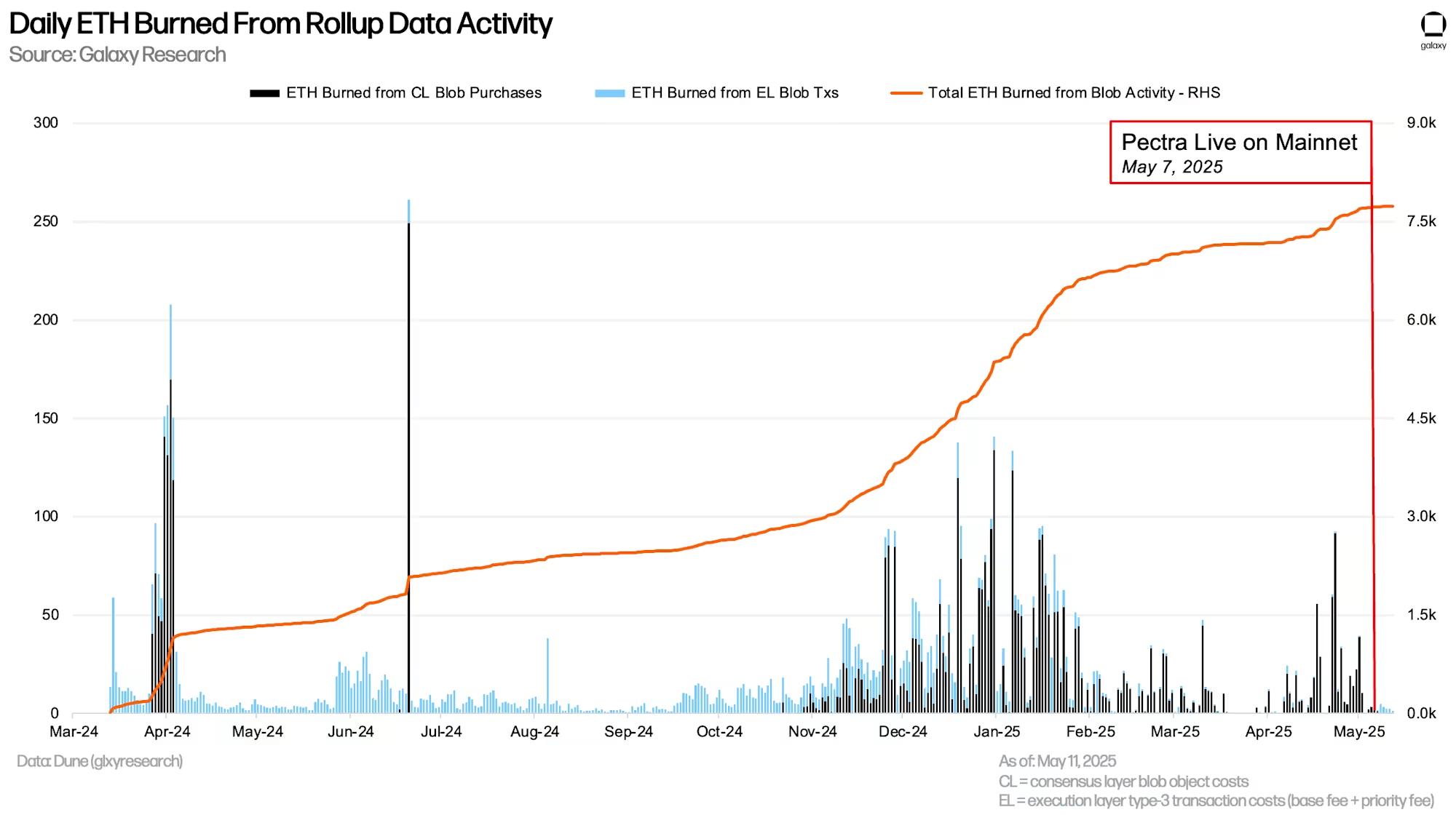
ETH burned through data publication activities via blobs (including blob purchases and type-3 execution transaction costs) has significantly decreased after Pectra's launch. In the 60 days before the upgrade, an average of 11.22 ETH was burned daily, with only 37.1% coming from execution layer fees. After the upgrade, an average of 3.26 ETH is burned daily (a 71% decrease), with 99.99% coming from execution layer base fees.
Impact on L2
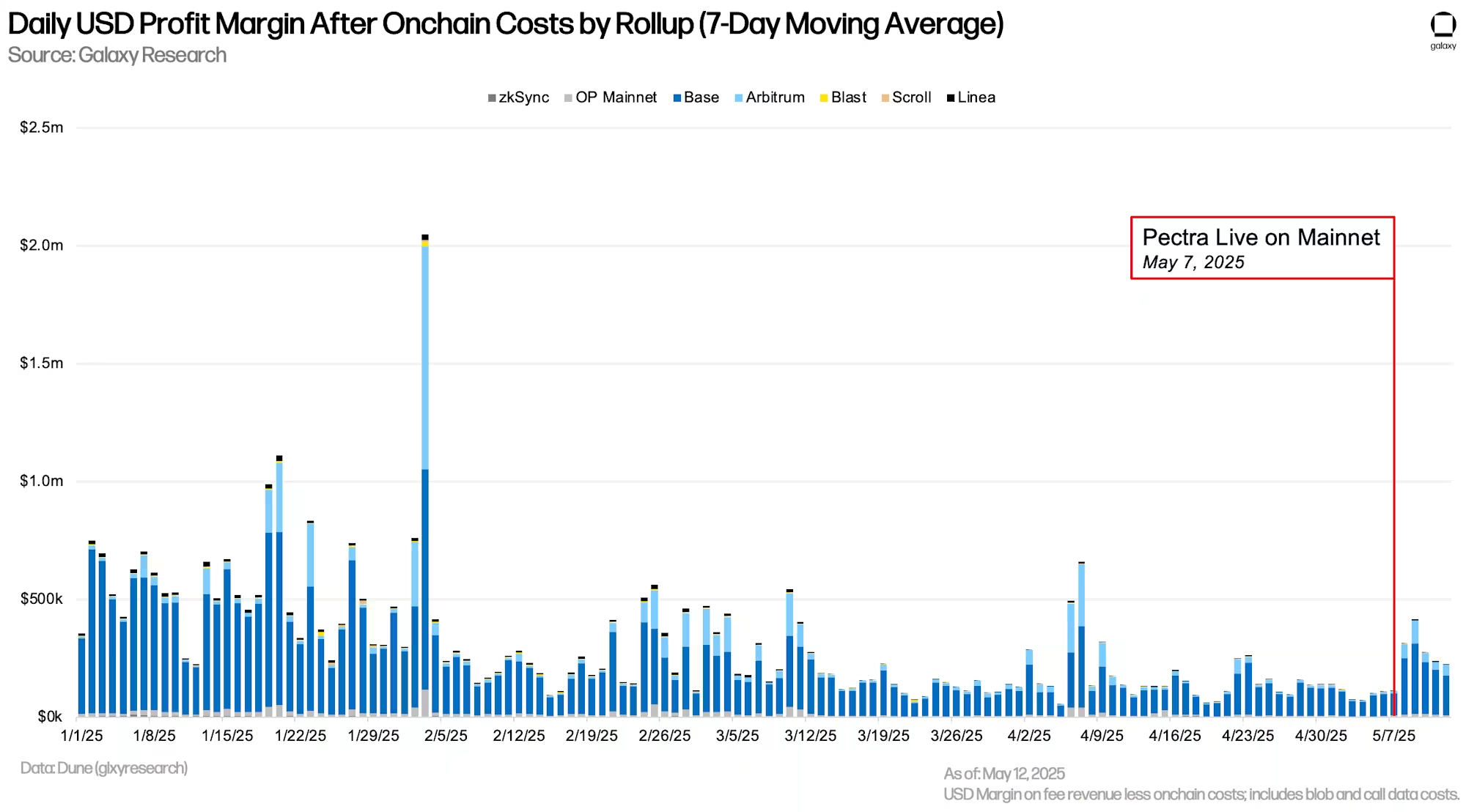
After deducting on-chain costs, most rollups have seen improvements in both relative and absolute profit margins. Linea and Base show the strongest profit rates among observed rollups, with seven-day moving averages of 98.86% and 98.54% respectively. Blast has demonstrated the most significant profit rate improvement after on-chain costs, rising from over 50% before Pectra to more than 80% currently.

After on-chain costs, rollups' net income has increased following Pectra, due to factors including reduced data costs and increased activity and transaction fees. The revenue and net earnings of each rollup have at least doubled, with Base generating the highest absolute revenue of $1.22 million under current market conditions, with a net income of $1.12 million after on-chain costs.
Conclusion
Rollups have not yet fully utilized the Ethereum data availability expansion provided by Pectra. Consequently, this has reduced the daily fees paid by rollups for blob DA activities. The upgrade currently offers a more favorable financial environment for rollups while also increasing the number of daily blobs used. The Pectra adjustments to Ethereum blob parameters also raise a critical question: nodes must bear more pressure for storing blob data. As Ethereum expands its blob DA, node operators will need to take on more data storage responsibilities.







