Author: Patrick Bush, Matthew Sigel, Vaneck Digital Assets Department; Translated by: AIMan@ Jinse Finance
Four key points
MSTR shares are a leveraged alternative to Bitcoin (BTC): MSTR shares behave like call options on Bitcoin in that it uses a recursive strategy of issuing shares and bonds for more BTC as the price of BTC rises. This structure provides asymmetric upside and is highly sensitive to BTC volatility, making MSTR a popular alternative to holding Bitcoin directly.
MSTR trades at a significant premium to its net asset value (NAV): We calculate a combined fair value premium of +112% for MSTR's BTC and core software businesses, driven by expectations of future BTC accumulation, regulatory advantages, and speculative positioning.
MSTR’s Premium is a metastable “crypto reactor” that powers MSTR: Premium powers the equity value of MSTR through a recursive cycle where volatility and Bitcoin exposure attract investor capital, enabling further BTC accumulation, which amplifies Premium.
Convertibles add optionality, but also risk: Strategy’s convertible bonds and preferred stocks (particularly STRK and STRF) offer varying degrees of yield and BTC exposure, but also come with complexity, downside asymmetry, and sensitivity to volatility. Convertibles due March 15, 2030 have the highest MSTR exposure, but even these instruments are closely tied to BTC and the persistence of its premium.
This article is organized as follows
1. What is Strategy
2. The source of MSTR equity “premium”
3. Funding the Bitcoin Treasury Strategy
4. Evaluate the financing sustainability of Strategy
5. MSTR’s capital strategy and Bitcoin yield
6. Evaluate Strategy’s convertible bonds
7. STRK Overview and Analysis
8. STRF Overview and Analysis
9. Conclusion on Strategy’s capital structure
10. Recommendations for Bitcoin Treasury Strategy
11. The main risks faced by Strategy’s Bitcoin financing model
Strategy (MSTR) accounts for nearly one-third of the total market capitalization of the pure equity/cryptocurrency market and 10% of the Market Vector Global Digital Asset Equity Index (MVDAPP). Therefore, its inclusion in the portfolio is a key consideration for investment managers aiming to turn the transformation of digital assets into excess returns.
Due to the complexity of Strategy’s capital structure, there has been controversy surrounding the merits of investing in MSTR, BTC, or even leveraged BTC. This consideration is further complicated by the convertible bonds and equity instruments issued by Strategy, including high-yield convertible preferred stock (STRK) and even higher-yielding non-convertible preferred stock (STRF).
In this report, we evaluate the construction of a Strategy stock or bond portfolio and analyze the pros and cons of holding that portfolio. We believe that MSTR common stock is a better investment option than other options offered by Strategy. We base this view on the following reasons:
1. Maximum BTC exposure
2. Simple investment strategy
3. Strongest risk/reward profile
1. What is Strategy?
Strategy (formerly MicroStrategy), a provider of enterprise analytics software, pioneered the concept of a corporate "Bitcoin treasury". In August 2020, Strategy calculated that the large cash reserves on its balance sheet were vulnerable to inflation in the then-low interest rate environment. The opening move of Strategy's Bitcoin treasury strategy was to use $250 million in cash on its balance sheet to purchase 21,454 BTC .
In December 2020, Strategy issued $650 million in convertible bonds and committed to buying Bitcoin through financial alchemy. Since then, Strategy has transformed itself into a leveraged Bitcoin financial instrument rather than a simple enterprise software company. By using leverage and issuing various forms of equity, Strategy has grown to hold 2.7% of the total Bitcoin supply, equivalent to $61 billion at the time of writing.
Strategy’s stated goal is to maximize the price of MSTR by increasing the BTC “reserves” per common share. By issuing bonds or shares, Strategy can increase the number of BTC per share and calls this dynamic “Bitcoin yield.” During periods of Bitcoin price increases, when investor interest is high, Strategy will increase leverage and issue additional shares in a timely manner. Therefore, Strategy’s BTC exposure and leverage are recursive in nature, as it is expected to grow over time. As BTC appreciates, so will Strategy’s BTC holdings, so it can re-leverage by issuing bonds to buy more BTC. On the stock side, a BTC bull run brings favorable capital markets to MSTR common stock, which enables Strategy to sell shares for more Bitcoin. The result is that MSTR stock provides accelerated exposure to BTC, and its price rises in tandem with BTC price increases. Therefore, MSTR’s price dynamics are a bit like a call option on BTC.
2. Source of MSTR Equity “Premium”
MSTR's common stock currently trades at a premium to the net value of its BTC assets and the combined value of Strategy's underlying software business (a "premium"). As of this writing, MSTR's common stock trades at + 112% of the fair value of its underlying assets (BTC holdings + core business). Mathematically, we define this as:

Source: VanEck Research , as of March 25 , 2025
Many debate the reasons for the MSTR premium, but we believe it is driven by four factors:
Strategy's expectations for future BTC holdings
Investors have limited options for BTC
Advantages of BTC leverage and strategy leverage
Speculation
The first component of the MSTR premium is the market's expectation of Strategy's future Bitcoin holdings . The expected future value of Strategy's Bitcoin holdings can be estimated using three key factors: the number of Bitcoins that will eventually be held, the expected future price of Bitcoin, and the discount rate applied to these holdings. A large part of the MSTR stock premium comes from the market's recognition that the company may continue to purchase more Bitcoin in the future. A positive premium suggests that the value of each Bitcoin will also grow, and therefore reflects a discounted future price of Bitcoin.
The second factor, which can be called the “regulatory premium,” stems from structural limitations in the investment landscape. Many institutional and individual investors are unable to purchase Bitcoin directly due to regulatory restrictions, investment authorizations, distribution bottlenecks, or a lack of secure custody solutions. Since many investors cannot obtain capital-efficient and highly leveraged Bitcoin exposure, they choose to invest in MSTR. The tax treatment and capital holding requirements for Bitcoin in many jurisdictions are less favorable, which leads investors to favor publicly traded equity investment vehicles like MSTR. Since MSTR is a common stock, it also has financial advantages as a collateral asset. These investor restrictions make MSTR an attractive alternative to investing in Bitcoin, especially for investors who would otherwise be excluded from this asset class.
The third factor behind MSTR's premium is the market's recognition of Michael Saylor's ability to apply financial leverage, which is unavailable to most investors. Saylor has demonstrated its ability to raise large amounts of capital at low interest rates, and its corporate structure has been resilient during the Bitcoin market decline. Unlike typical margin traders who are often forced to close their positions during market downturns, Saylor is able to absorb losses and maintain long-term positions. During 2022 and part of 2023, MSTR's market capitalization remained in the billions of dollars even as Strategy's equity losses reached hundreds of millions of dollars, reflecting investors' confidence in the long-term leverage structure provided by Strategy.
MSTR's unique dynamics have resulted in a 30-day historical volatility of about 113% , while BTC's volatility is about 55% . In summary, MSTR shares provide investors with a convenient way to invest in leveraged BTC instruments traded on the open market. The premium contributes most of the volatility and performance of MSTR shares. We arrived at these numbers by analyzing the weights, correlations, and volatility in the MSTR (BTC + Business + Premium) portfolio. The total return contribution is 96.5% , and the volatility contribution is about 87.5% .
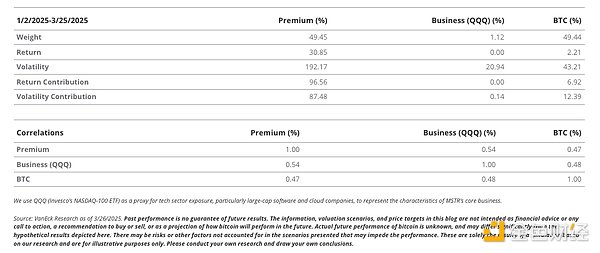
The fourth component of the MSTR premium stems from speculative trading dynamics related to MSTR's volatility and capital structure. Because the premium contributes so much to MSTR's returns and volatility, any disruption to the core drivers of the premium will have a highly negative impact on MSTR's stock price. This is because Saylor uses MSTR's volatility to finance its purchases of BTC. As described below, Saylor's preferred methods of financing BTC purchases are preferred stock, convertible preferred stock, convertible bonds, and common stock, in that order. This order is based on the "BTC proceeds" received by common shareholders, and the proceeds are driven by BTC attributable to each common share. For example, the sale of preferred stock will increase equity dilution, and the proceeds will be directly recycled into BTC proceeds for common shareholders.
The securities sold by Strategy are popular with investors because the high volatility of MSTR translates into numerous trading opportunities in Strategy's capital structure and MSTR options. In fact, Strategy is able to maintain low interest costs on its convertible bonds precisely because the volatility of MSTR makes its options portion very valuable. It can be said that Strategy prices the option value so cheaply in order to attract relative value trading entities. These experienced arbitrageurs trade relative value volatility between various Strategy securities.
As a result, there is a circular relationship between Strategy's premium and its ability to finance more BTC purchases. The premium accounts for most of MSTR's volatility. However, the premium is largely dependent on Strategy's ability to finance BTC purchases. The market is willing to buy Strategy's securities because its capital structure has volatility, and Strategy arguably sells this volatility cheaply. In the Q1 2025 earnings call, Saylor referred to this reinforcing dynamic as a "crypto reactor that can run for the long term."
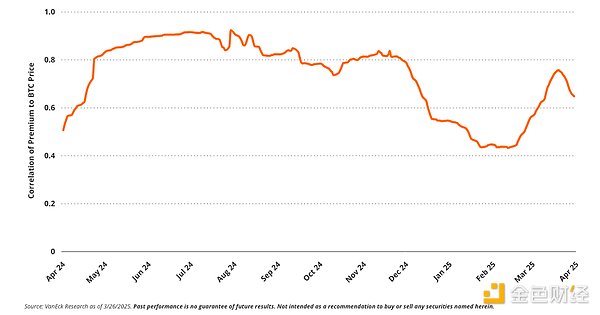
The premium shows a clear positive correlation with the Bitcoin price. Over the past year, its correlation with BTC has remained at 0.52 (T-Stat = 9 ), and its beta coefficient with BTC is about 1.77 . This shows that as the price of Bitcoin rises, the premium tends to widen, further boosting MSTR's stock performance. The connection between BTC prices, speculation, financing capabilities, and MSTR's valuation forms a self-reinforcing cycle that is critical to the company's strategy.
Correlation between MSTR premium and BTC price
Funding a Bitcoin Treasury Strategy
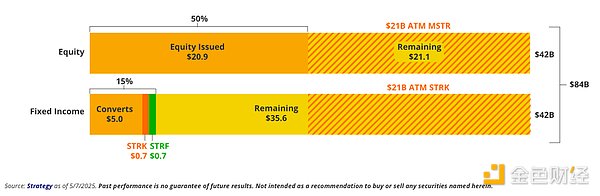
In October 2024, Strategy announced its ambitious 21/21 capital plan, which plans to raise $42 billion by 2027 to purchase BTC by selling $21 billion in MSTR equity and $21 billion in fixed-income securities . In the original plan, Strategy will sell $5 billion in equity in 2025, $7 billion in equity in 2026, and $9 billion in fixed-income securities in 2027. At the same time, Strategy will also sell $5 billion , $7 billion , and $9 billion in fixed-income securities in 2025, 2026, and 2027, respectively, at a similar pace. The target leverage ratio for these bond issuances is between 20% and 30%. Michael Saylor, head of Strategy, calls this "smart leverage," not for speculation, but for strategic acquisitions of "dominant digital assets."
Thanks to the unprecedented cryptocurrency bull run following the launch of the 21/21 program, the company has sold all $21 billion worth of MSTR shares in its At-the-Market (ATM) program by May 2025. In its fixed income portfolio, Saylor sold $5 billion of convertible notes, $875 million of STRK convertible preferred stock, and $850 million of non-convertible preferred stock. During Strategy’s earnings call on May 1, 2025, the company announced an expansion of its funding program to $84 billion , including a new $21 billion MSTR ATM program, an existing $21 billion STRK ATM program, and an additional $14 billion in new convertible debt issuance.
42/42 Financing Plan - 32% Completed
With BTC trading around $95,000 at the time of writing and the Strategy holding 555,450 BTC , we calculate Saylor’s leverage ratio as (debt + preference) / (market cap) to be 9% . This figure represents the lowest leverage ratio for the Strategy since 2020. Given Saylor’s below-average leverage ratio and his stated preference for “convertible, unsecured and non-recourse” debt, it is reasonable to expect additional convertible debt raises in the near future.
Funding BTC purchases by capturing volatility
Issue Name | Circulation | Potential Dilution | interest rate (%) | state | maturity | Strike Price ($) |
2030 Convertible Notes A | 800 | 5.34 | 0.000 | ITM | March 2030 | 149.80 |
2031 Convertible Notes | 604 | 2.60 | 0.875 | ITM | March 2031 | 232.70 |
2032 Convertible Notes | 800 | 3.92 | 2.250 | ITM | June 2032 | 204.30 |
2028 Convertible Notes | 1010 | 5.51 | 0.625 | ITM | September 2028 | 183.20 |
2029 Convertible Notes | 3000 | 4.46 | 0.000 | ITM | December 2029 | 672.40 |
2030 Convertible Notes B | 2000 | 4.61 | 0.625 | ITM | March 2030 | 433.40 |
STRK Convertible Preferred Stock | 744 | 0.00 | 8.000 | ITM | permanent | 1,000 |
STRF Perpetual Preferred Stock | 711 | N/A | 10.000 | N/A | permanent | N/A |
Source: 2025 Strategy as of March 25 , 2025. Past performance is no guarantee of future results. This report does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any security mentioned herein.
MSTR stock is extremely volatile because it is tied to BTC leverage, and as Strategy funds more BTC investments, leverage is likely to increase. Most investors view the use of additional leverage to purchase volatile assets such as BTC as a disadvantage and therefore demand high interest rates. Strategy addresses this issue by issuing convertible bonds and convertible preferred stocks, which derive much of their value from the option features embedded in them.
Sophisticated investors prefer these offerings because they allow them to engage in activities such as convertible stock arbitrage. In this risky and complex trading strategy, sophisticated investors buy convertible bonds and sell MSTR stock and/or MSTR options to profit from differences in realized volatility, implied volatility, and other components of the option pricing model.
This transaction mechanism helps Strategy solve cash flow problems by reducing debt interest expenses. Due to the huge market demand for high-volatility convertible securities, Strategy can promise investors extremely low future interest expenses. There is a complex interaction between Strategy's capital market strategy and the market demand of potential investors.
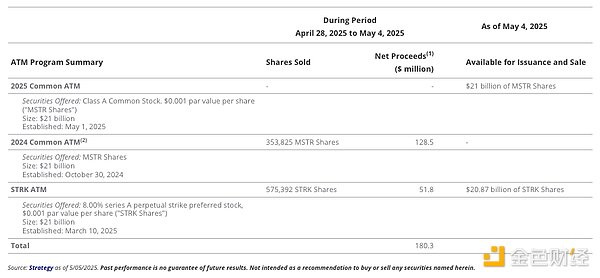
Net proceeds are the amount after sales commissions are deducted.
The 2024 Universal ATMs have been substantially exhausted and the sales agreement for the program has been terminated in accordance with its terms.
This involves the Strategy pricing implied volatility, setting a strike price, and adding a call price to maximize the tradability of each issue. For example, a call price slightly closer to the market allows the Strategy to cap the upside on its bond option tranche. The result is that the derivative behaves more like a "capped call" with potentially lower delta than a vanilla call. Selecting a convertible bond strike price that is well below out-of-the-money can also reduce the value of the option tranche, thereby reducing delta. Lowering delta means reducing the amount of MSTR stock (or options) needed to hedge the convertible bond options. Many convertible arbitrage participants favor issues with lower deltas because they are less capital intensive to trade on their balance sheet.
IV. Evaluating Strategy’s Financing Sustainability
While Strategy's core business is able to generate some operating income, its financing to purchase BTC will bring huge cash needs. Based on Strategy's documents and statements, we expect its total debt to reach $13 billion by the end of 2025 (up from about $8 billion in April 2025 ) and $19 billion by the end of 2026. We also expect preferred equity to increase to $7.5 billion in 2025 and $15.5 billion by 2026 .
We forecast that annual interest expense will reach $48 million by the end of 2025, increasing to $87 million by 2026. Meanwhile, preferred stock (STRK) dividend expense is expected to increase from $217 million in 2025 to $904 million in 2026. We estimate these numbers based on the market's expected demand for MSTR bond coupons and preferred stock dividends. While Strategy retains the option to pay STRK preferred stock dividends in common stock, doing so would dilute the interests of existing MSTR shareholders as each share would receive less BTC.
With projected revenues of $475 million in 2025, Strategy relies on financing to pay down its fixed-income debt. Of course, the ability to raise new capital depends on the price of Bitcoin. If the price of Bitcoin continues to rise, obtaining new capital will become a breeze. Between August 2024 and May 2025, Strategy increased its BTC holdings from 226,000 to 555,450 by raising $28.7 billion in financing. On the other hand, during the cryptocurrency downturn from June 2022 to December 2022, Strategy only raised $49 million and $11 million through equity and bond offerings, respectively. Bear markets can be challenging for Strategy due to increased cash outlays from new fixed-income securities issuance.
MSTR is a convex bet on BTC price
Investing in MSTR is somewhat similar to investing in BTC call options due to its leverage sensitivity (or "torque") to BTC price movements. However, it is actually more similar to trying to dynamically replicate BTC call options by increasing leverage exposure as prices rise. The strategy is to increase BTC positions when funding is available, which usually happens when BTC prices rise. The risk of this strategy is not only the decline in price, but also the shrinking premium due to the collapse of BTC funding purchases. In addition, the timing of the strategy's capital deployment may not be appropriate, such as when BTC prices reach highs.
The net profit from “native” buying exceeds that from strategy buying
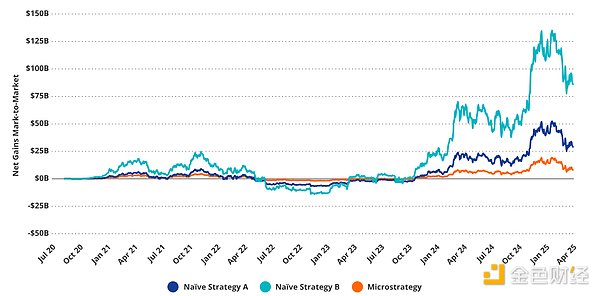
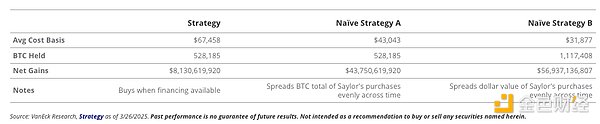
Compared to other strategies, Strategy's local high buying generates "losses" because Strategy's BTC buying is at a higher average price than random BTC buying. Whether Strategy buying is the cause of local "highs and lows" is another question. In any case, compared to the native, randomly implemented BTC buying strategy, this local high buying strategy is at the expense of shareholders. However, on the other hand, due to the "positive convexity" of MSTR, BTC price changes lead to a continuous increase in the US dollar value of each BTC share, and new financing leads to an increase in BTC holdings per share, so MSTR provides recursive upside for BTC prices. Therefore, as the price of BTC rises, investors' BTC position exposure will also increase.
As an individual investor, it is nearly impossible to replicate Saylor's strategy without a company "wrapper". While investors who buy BTC futures can see their margin balance grow as the BTC price rises, allowing them to buy more BTC, they cannot "patiently" hold this leverage when the price falls. Futures contracts are marked to market daily, which means that gains and losses are settled regularly, and margin calls must be met immediately when there is a retracement. Margin traders will be liquidated if the BTC price retraces below their margin balance.
Therefore, while a savvy trader might copy Saylor’s strategy and add to his position as BTC appreciates, even a slight pullback could trigger a forced liquidation that would completely wipe out that trader’s position. This daily margin requirement makes it difficult for individual investors to replicate Strategy’s long-term accumulation strategy using futures. As a result, Strategy has a huge financial advantage that allows it to run leveraged BTC strategies more efficiently.
5. MSTR’s Capital Strategy and Bitcoin Return
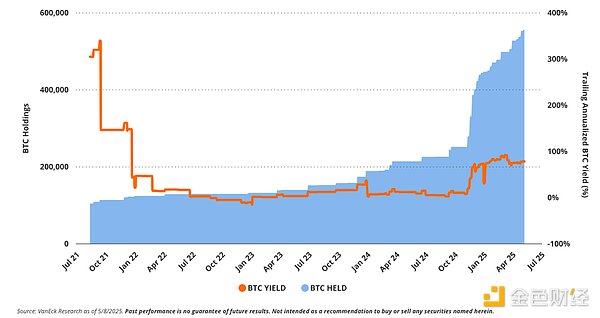
Strategy’s financial engineering has added significant amounts of debt and equity to its balance sheet to gain more BTC exposure per common share. This is because Strategy’s core objective is to increase the exposure of its common shares to BTC. Saylor refers to the increase in the number of BTC per share as the “BTC yield. ” This key performance indicator (KPI) for Strategy is calculated by comparing BTC holdings per common share over time. As of May 2025, the year-to-date BTC yield is approximately 14% based on outstanding common shares and approximately 13% on a fully diluted basis. Strategy’s minimum target for BTC yield in 2025 is 25% . This is equivalent to increasing the number of BTC per 1,000 shares of MSTR stock from approximately 1.79 BTC as of May 8, 2025 to approximately 1.99 BTC by the end of the year.
Strategy ’s Bitcoin (BTC) Yield Faces Tough Forward Comparison
Strategy's management team has many options for generating BTC revenue. They can sell various financial products to acquire BTC, thereby increasing the numerator, or they can purchase common stock to reduce the denominator. Since MSTR is trading at a premium, it makes more sense to sell "high-priced stocks" or issue bonds to acquire BTC. Selling common stock through a market offering to purchase BTC may be the simplest way, but it is also the most dilutive way to acquire equity and requires the purchase of the most BTC. Saylor mentioned this dynamic in the first quarter of 2025 earnings call, noting that they prefer to acquire BTC by selling permanent, non-convertible common stock.
BTC KPIs for issuing $100 million of different securities
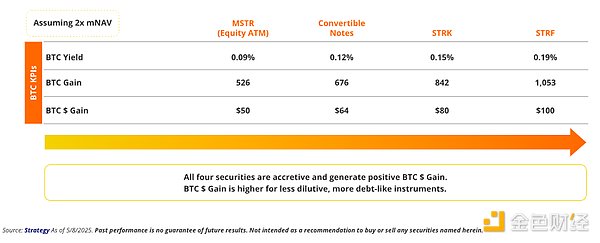
If Saylor does not issue additional common shares to achieve Strategy's yield target, he will need to purchase 58,312 BTC, which is worth about $5.9 billion at current prices . On the other hand, if Saylor only increases exposure through common shares, he will need to issue about 25.8 million common shares to purchase 106,305 Bitcoins ( about $10.8 billion at current BTC prices). Given the huge demand for Strategy's capital reserves in the capital market, it does not seem difficult for Strategy to easily achieve a 25% yield in 2025 .
High BTC yields are unsustainable
Amount required to increase MSTR yield by 1 basis point (90-day moving average) (US$ million)
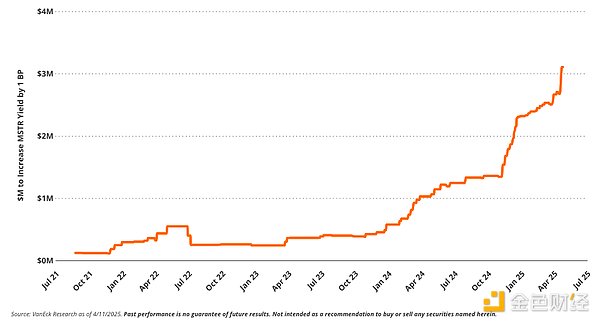 The reality of Saylor's Bitcoin strategy is that high Bitcoin yields are difficult to sustain due to diminishing returns to scale. As the Strategy team accumulates more BTC, it becomes increasingly difficult to generate more meaningful additional Bitcoin yields. This is because, as total BTC holdings grow, the amount of BTC required to generate each incremental basis point of yield also increases disproportionately.
The reality of Saylor's Bitcoin strategy is that high Bitcoin yields are difficult to sustain due to diminishing returns to scale. As the Strategy team accumulates more BTC, it becomes increasingly difficult to generate more meaningful additional Bitcoin yields. This is because, as total BTC holdings grow, the amount of BTC required to generate each incremental basis point of yield also increases disproportionately.
For example, in August 2021, MicroStrategy needed only 2.6 BTC to generate one basis point of Bitcoin yield. By May 2025, that number had soared to 58 BTC . In U.S. dollar terms, the capital required to generate the same unit of yield increased from approximately $126,000 to $5.5 million . This reflects a basic mathematical reality: as the Bitcoin base of the Strategy platform continues to grow, the marginal yield contributed by each additional BTC decreases, while the capital required to generate yield increases exponentially. This compounding inefficiency leads to a decreasing upper limit on sustainable yields.
VI. Evaluating Strategy’s Convertible Bonds
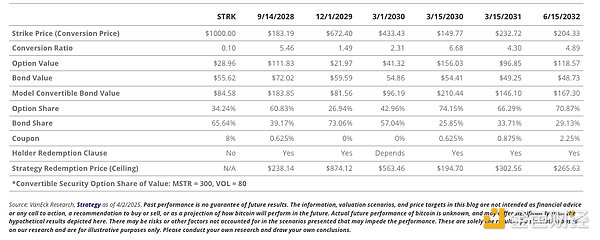
Convertible bonds are hybrid securities that combine the characteristics of fixed income with the upside potential of stocks. Specifically, they consist of a traditional bond and an embedded call option that allows the holder to convert the bond into MSTR common stock under certain conditions. The total value of a convertible bond is equal to the value of the bond plus the value of the conversion option. Therefore, an investor who purchases a convertible bond will allocate part of the principal to the company's bonds and part of the principal to the call option. Therefore, the price of a convertible bond is very sensitive to option pricing variables (such as the underlying price, Delta, Gamma, etc.) as well as bond pricing factors (such as interest rates and credit spreads).
Strategy's convertible bonds have special terms that limit the upside of the attached options while also providing some principal protection to investors. Strategy has embedded a "call option" that allows the company to repurchase the bonds at par plus unpaid accrued interest after the call date. The most common term in Strategy's convertible bonds is that the company can redeem the bonds if MSTR's trading price reaches 130% of the convertible bond's strike price. This term limits the upside of the bond option value after the call date. Except for the bonds due on March 1, 2030, Strategy also allows its convertible bondholders to sell their bonds back to Strategy for cash at par after the call date. This can be considered a floor on the bond price if Strategy gets into financial trouble.
The convertible bond due on March 15, 2030 has the greatest leverage on the MSTR price due to its large option component.
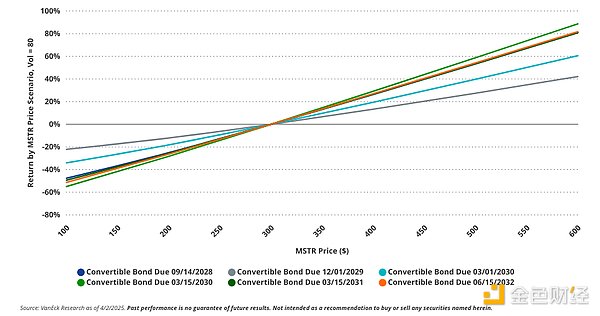
MicroStrategy's convertible bonds contain significant option value due to the high volatility of the underlying stock. Depending on the offering, options can account for up to 74% of the total value of the bonds. The higher this percentage, the greater the investor's exposure to MSTR's stock price movements. This exposure can change significantly depending on MSTR's volatility and whether options move in- or out-of-the-money.
Among the outstanding convertible bonds, the risk profile of the Class B bonds due March 2030 is closest to that of MSTR shares. In a high volatility scenario (e.g., MSTR Volatility > 80 ), this class of bonds has the highest sensitivity to MSTR stock prices, whether the stock is rising or falling. Conversely, the December 2029 bonds have the lowest sensitivity because their embedded options are the farthest out-of-the-money. This results in the options contributing less to the total value of the security, reducing their impact on bond price movements.
Strategy Convertible Bond Implied Credit Spread vs. BTC Adjusted Credit Estimates
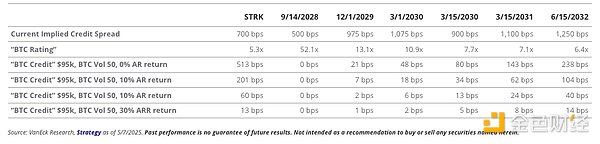
The bond portion of Strategy’s convertible bonds has been the subject of controversy due to the high credit spreads on each bond. The higher credit spreads reflect the market’s assessment of the risk of Saylor’s bonds, and therefore the bonds are priced “lower.” As Saylor noted in its Q1 2025 earnings call, credit spreads on Strategy’s fixed income securities range from 500 basis points to 1,250 basis points . This puts Strategy’s bonds in the same category as “two or three times junk bond credit spreads.”
Saylor believes that these credit spreads are so wide because the market fails to properly assess the value of the Bitcoin collateral backing these bonds. Saylor claims that because credit agencies failed to adequately assess Strategy’s bonds, many long-term investors were reluctant to purchase them due to perceived risk. This depressed the market price of the bonds and exacerbated the widening of credit spreads.
Saylor conducted an independent analysis of Strategy's bonds using an option pricing model to demonstrate that the bonds were undervalued due to incomplete collateral consideration. Saylor proposed the concepts of "BTC rating" and "BTC risk" to describe the potential risk of Strategy's debt. The BTC rating refers to the face value of the bond calculated at the current BTC market price multiplied by the Bitcoin held. This metric applies to all bonds and is adjusted based on priority when Strategy's BTC holdings are liquidated. For example, the BTC rating of the bonds due on September 14, 2028 is 52.1 times because the value of BTC held by Strategy, calculated at the current BTC price and based on the priority of the bonds, is 52.1 times the face value of the bonds.
Saylor combines the "BTC rating" with an options pricing model, using the current BTC price and volatility to determine the probability that BTC will trade below the BTC liquidation price, resulting in each bondholder being fully compensated. He calls the calculated probability "BTC risk," which he then feeds into the bond pricing model to generate a new "credit spread," which he calls "BTC credit." As shown in the table above, Saylor believes that the market overprices the probability of default for each of Strategy's bonds, causing these bonds to trade at prices lower than the "correctly" assessed bond prices.
Implied yield on the bond portion of the MSTR convertible bond
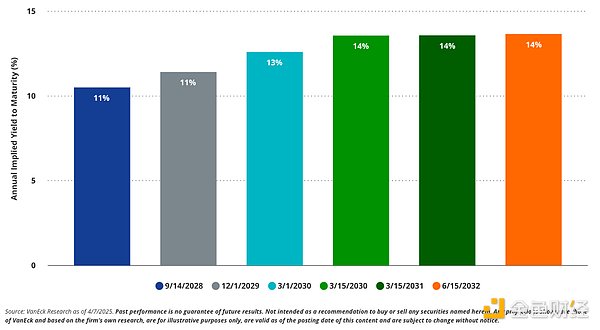
Strategy A key issue with convertible bonds is that their pricing is heavily influenced by the embedded option component. As a result, many bonds are currently trading well above their par value, which provides support for downside risk. This means that if option premiums decline, a large portion of the bonds could decline in value. For example, as of May 7, 2025, the 2028 convertible bond was priced at $227.15 . If MSTR's stock falls below the bond's conversion price of $183.19 at maturity, the bond would be worth only $100, assuming all other factors remain constant. This reflects the large option premium embedded in these instruments.
Another significant risk associated with embedded options is the sensitivity to changes in volatility, as well as other factors that affect option pricing. We estimate that if volatility falls from 85% to 50% , the value of the bond will fall by about ( -13% ) on average. A further drop in volatility from 85% to 30% would result in an average price drop of about ( -20% ).
MSTR's stock performance is largely driven by its premium, which accounts for 87% of its stock's volatility and 96% of its total return . We believe this suggests that investors in MSTR's convertible bonds are not just buying an option on the stock itself, they are actually buying an option on the premium to persist. This premium is primarily driven by the price of Bitcoin. As the price of Bitcoin rises, the company gains greater financing capacity to buy more shares, which in turn drives up the expected value of its holdings and supports speculation in MSTR stock.
If the price of Bitcoin falls, the premium may also fall. We estimate the beta coefficient of the relationship to be approximately 1.77 times , which means that the value of the premium relative to Bitcoin may fall significantly. Such a decline would erode the value of the option portion of the convertible bond.
The fixed income portion of the convertible bond is also at risk due to the premium. The value of a regular bond depends in part on the company's ability to raise funds in the future. Strategy's revenue is insufficient to repay its fixed income debt, let alone repay the principal when it matures. A decline in the premium will weaken Strategy's ability to raise funds and may cause credit spreads to widen. This will reduce the value of the corporate bond portion of the convertible bond. The trigger for the premium to erode could be a decline in the price of Bitcoin. A decline in the price of Bitcoin also exacerbates the value of Strategy's convertible bonds because the likelihood of fully recovering value in the event of Bitcoin liquidation is reduced.
This downside scenario is not inevitable, but serves to highlight that both components of the convertible bond - the options and the bond itself - are tied to the same underlying drivers: Bitcoin price and MSTR premium. While some investors may be able to hedge these risks, many struggle to understand them, let alone manage them effectively. MSTR convertibles may be attractive to investors seeking income and potential upside, but they also involve many risks. These instruments may be suitable for sophisticated investors who can execute dynamic hedging strategies and analyze the behavior of equity-linked debt.
Tighter credit risk leads to higher value
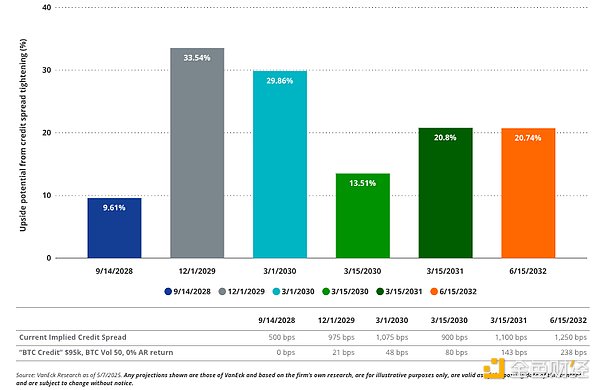
However, Strategy’s convertible bonds provide an exciting vehicle for speculating on advances in cryptocurrency accounting practices. If credit rating agencies were to become more optimistic about Bitcoin as debt collateral, this could result in a significant narrowing of credit spreads. This would significantly boost the value of Strategy’s convertible bonds by increasing the share of the bond. If Strategy’s bonds met Saylor’s lowest estimate of their “true” credit spreads, we calculated a median increase in convertible bond value ( +16% ). In fact, convertible bonds with a larger share of the bond value experienced the largest price increases.
The two most attractive price targets are the Dec 1, 2029 bonds ( up 31% ) and the Mar 1, 2030 bonds ( up 26% ). Given that the Mar 1, 2030 bonds are closer to in-the-money on their options, the upside from their credit spread conversion to Saylor “BTC credit”, combined with their high option value, may be attractive to bold speculators. However, for traditional long-only investors, the range of risk exposures these bonds present may be difficult to manage. On a relative basis, we believe they are less attractive than other parts of MSTR’s capital structure.
MSTR price simulation (BTC +/- 80% @ MSTR Vol = 80)
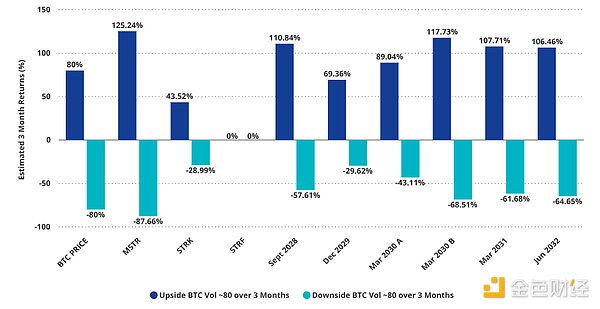
The simulation assumes MSTR Vol = 80 and BTC drops 80% in 3 months.
Source: VanEck Research , as of April 2, 2025. All forecasts in this article are VanEck 's forecasts based on its own research, are for reference only, are valid as of the date of publication, and are subject to change without notice. This report does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any security mentioned herein.
7. STRK Overview and Analysis
Known as a "preferred perpetual convertible stock," STRK combines several concepts into one security. It offers a perpetual dividend of 8% of par value, payable in cash or in common stock. However, there are limitations to using common stock in lieu of dividends, such as limiting the total number of shares required to pay the dividend, for example, if the value of MSTR falls below 35% of its January 27, 2025 stock price of $347.92 . STRK also offers options on MSTR stock, which have no expiration date (no theta decay in the value of the option components) and have liquidation rights typically associated with preferred stock. Similar to a convertible bond, but with a lower priority, STRK is a fixed-income security with an attached call option that is deeply out-of-the-money and has a strike price of $1,000, which is 2.5 times the current trading price of MSTR (as of May 7, 2025).
At the time of writing, we calculated that 36% of STRK's price comes from call options, which gives holders upside exposure to MSTR. Due to the high volatility of MSTR and the perpetual duration of the option, the delta of MSTR options on STRK is close to 1, even though they are deeply out-of-the-money. This means that STRK's price movements are very close to MSTR's price movements (in the options part of STRK).
Until MSTR's stock price approaches the conversion strike price, we expect STRK's sensitivity to changes in volatility to be asymmetric and heavily skewed to the downside. For example, if implied volatility rises from approximately 80% to 120% , we estimate STRK to rise by less than ( +0.01% ). However, if volatility falls from 80% to 40% , we expect STRK's price to fall by ( -3% ), while a further drop in volatility to 20% would result in a loss of approximately (-19% ).
This asymmetry arises because the call option embedded in STRK is currently far out-of-the-money and is essentially a perpetual option. In this case, volatility above a certain level has little effect on the probability of the option ultimately achieving an in-the-money return, but rather weakens its upside reaction. Conversely, a reduction in MSTR's current volatility would significantly reduce the probability of ultimately achieving an in-the-money return, resulting in a disproportionately large price drop. This raised volatility exposure, limited upside, and huge downside are key features of STRK's risk profile. Taking a step back, it is interesting to view STRK as a security that can earn a reward for holding a call option, but the upside is limited compared to just buying MSTR.
STRK value falls asymmetrically as volatility decreases
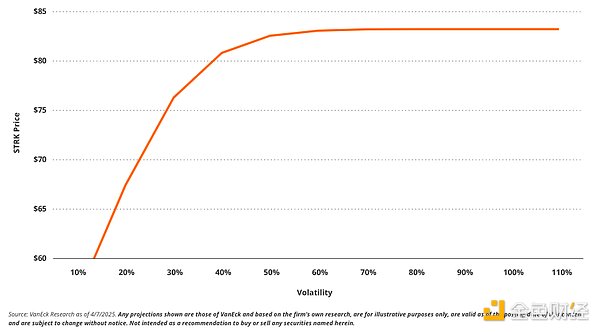
From a pricing perspective, we expect STRK's price movements to be significantly muted relative to MSTR's share price movements (both up and down). For example, we calculated that, all else being equal, an increase in MSTR's share price ( +100% ) would result in an increase in STRK's price by approximately ( +37%). Conversely, a decrease in MSTR's share price (-50% ) would result in a decrease in STRK's value ( -17%).
However, in a downside scenario, STRK’s credit spreads will most likely also widen, which is an important factor affecting the value of its preferred stock component. For example, if the credit spread increases by 500 basis points , from 700 basis points to 1,200 basis points , and MSTR’s stock price falls ( -50%), the combined effect could cause STRK’s price to fall by approximately (-30% ). We believe this scenario is likely to occur because Strategy’s credit spreads tend to follow MSTR’s price. Interestingly, STRK’s implied credit spread is closer to Saylor’s BTC-based estimate than Strategy’s conversion value. This means that STRK’s credit spread has less upside after converging to Saylor’s calculated value.
StrategyDebt and Capital Structure
Assuming BTC price is $95,000, BTC volatility is 50%, and BTC ARR is 0% (“Skeptic”)
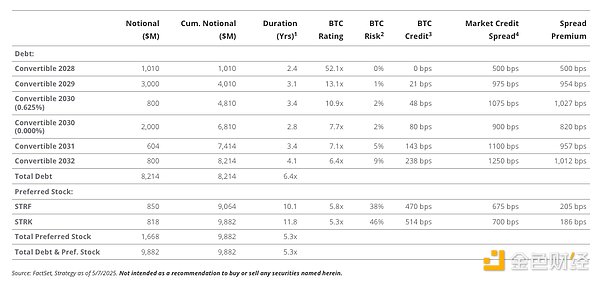
1The duration of convertible bonds is calculated to the date of sale. The duration of preferred stocks is calculated based on the Macaulay duration.
2 Calculate the probability of BTC rating falling below 1x at the end of a given duration using a lognormal model adjusted for BTC ARR and BTC volatility.
3Calculation method: BTC risk annualization, assuming the risk is the same every year and that collateral cannot be recovered when it is insufficient. BTC credit = (-ln(1 - BTC risk ) ÷ duration ) .
4Source : Bloomberg, Kynex . Assuming borrowing costs of 0.50% and volatility of 60% to calculate credit spreads on convertible notes. Assuming the embedded call option in STRK is worth 200 basis points.
As mentioned above, Strategy plans to issue approximately $20 billion of additional STRK. These future issuances will further increase the dividend income generated by Strategy, thereby improving its risk profile. Even without additional STRK issuance, Strategy's ability to pay existing dividends in cash appears to be limited. STRK's position in the capital structure is even lower than Strategy's series of convertible bonds, so Saylor classifies STRK's BTC risk as much higher than convertible bonds. Based on Strategy's benchmark assessment (not BTC price appreciation), there is a 46% probability that the value of BTC held by Strategy will fall below STRK's implied support within one year.
We believe that several structural factors of STRK present considerable downside risk and lack of corresponding upside potential. These factors include: weak BTC support, dividend suspension, and small option component of the bond. In addition, the possibility of price appreciation through credit spread re-rating is low.
Therefore, we believe that STRK's risk-reward profile is not ideal for long-term investors, especially compared to MSTR stock. However, for very active investors who are good at hedging STRK's risk, its volatility and dividend profile may be attractive. STRK may be very attractive to income-oriented, proactive investors who want to get some income from MSTR stock. In addition, long-term investors who are very optimistic about Strategy stocks may find STRK more attractive because its option component has a Delta value close to 1 while also providing an attractive yield.
8. STRF Overview and Analysis
STRF is a common preferred stock instrument that pays a fixed 10% cash coupon annually. Unlike STRK, it does not have the flexibility to pay dividends in common stock. Currently, STRF is trading at $94.30, so its effective annual yield is about 10.6% .
Its valuation is primarily driven by prevailing interest rates and Strategy's credit spread. Under the terms of the agreement between Strategy and STRF holders, each non-payment of a dividend will result in a 100 basis point increase in the coupon rate, up to a maximum of 18% . In the event of four consecutive non-payments or a total of eight non-payments, STRF holders will have the right to elect directors to Strategy's board of directors. This right will be revoked once all unpaid dividends are repaid. STRF ranks higher in the capital structure than STRK and MSTR common stock, giving it a stronger claim in the event of liquidation. However, this claim is weaker as its BTC rating is 5.8x , while STRK is 5.3x.
These protections are significant given that MSTR has not generated significant cash flow since 2021, but they are still quite thin given BTC's volatility. If MSTR's core business deteriorates further, or the company loses access to capital markets, it could suspend its dividend. In this case, STRF would begin to resemble a long-term subordinated bond, with higher credit risk but no equity upside. If this happens simultaneously with a decline in BTC, which is likely, the value of STRF will be significantly affected.
The biggest challenge facing STRF is that it will not be able to benefit from Bitcoin's rise in the face of a significant drop in BTC prices. Since a drop in Bitcoin prices will weaken Strategy's ability to meet its cash obligations, it will increase credit spreads. This view is empirically supported as STRF has a 50% correlation with MSTR and a 55% correlation with BTC. We calculate STRF's credit spread to be approximately 6.1% based on current market prices . If this credit spread is close to the median convertible bond credit spread of 10.25% , this will cause STRF's value to fall ( -28% ). Like STRK, STRF is also heavily affected by BTC prices and the MSTR premium.
We believe that STRF 's risk profile is not ideal for long-only investors, as the risk factors it faces are difficult to cover given STRF's capped upside. However, STRF's risk profile may be ideal for very sophisticated investors, who can use STRF's dividends to purchase options to gain some upside exposure or downside protection on BTC.
IX. Conclusion on Strategy’s capital structure
Strategy's entire capital structure is highly correlated with the following:
The price of BTC
Strategy ’s ability to raise more funds to buy BTC
BTC and MSTR price fluctuations
MSTR offers an asymmetric portfolio that combines leveraged BTC exposure, regulatory convenience, and open market liquidity. While MSTR's capital structure is complex and carries significant risks, its design provides investors with a unique tool to participate in Bitcoin's upside through leverage and strategic selectivity that is difficult to replicate. MSTR is a more practical and efficient option for those who are unable or unwilling to hold Bitcoin directly or in managed futures strategies. Continued investor confidence, stable access to capital markets, and strict execution remain critical to maintaining this investment philosophy.
10. Recommendations for Companies Considering a Bitcoin Treasury Strategy
From a strategic perspective, Strategy offers several important lessons for companies considering implementing a Bitcoin treasury strategy.
First, there must be a clear purpose behind adopting a Bitcoin treasury. MSTR’s strategy reflects this, focusing on increasing BTC holdings per share rather than following traditional financial metrics such as dilution or enterprise value in fiat currency. Under the leadership of Michael Saylor, the company has recalibrated its valuation framework around Bitcoin itself. Saylor believes that success is not based on returns in US dollars, but rather the number of Bitcoins represented by each MSTR share. This clear purpose allows for consistent, long-term decisions even in volatile markets.
Second, the company must develop a well-structured financing strategy that leverages market dynamics to support Bitcoin accumulation. Strategy does this by leveraging investor appetite for volatility and embedded options. Saylor has built a financial ecosystem that attracts retail investors and active traders through convertible bonds, preferred stock, and common stock offerings. BTC volatility exacerbates MSTR’s volatility, which in turn sustains demand for its securities. For example, open interest in MSTR stock options (used to trade against MSTR’s capital structure) is higher than Google and Amazon ( $95 billion and $80 billion , respectively). This dynamic exists despite Google’s market cap being 15 times that of MSTR. This flywheel effect enables Strategy to fund its Bitcoin purchases with favorable terms, lower cash obligations, and non-sole reliance on traditional debt or equity offerings.
Finally, companies adopting a similar strategy must recognize that market demand for Bitcoin-linked securities will not automatically materialize. Investor participation, innovative structures, and transparent communication are essential. Whether through traditional issuance, structured products, or digital asset integration, companies must design financial instruments that provide both returns and huge upside to attract capital. Since implementing a Bitcoin treasury strategy will contradict most financial theories, holders must construct a firm investment narrative to support the Bitcoin strategy. Michael Saylor's high profile is not accidental, indicating that the market defaults that the market needs to believe in the Bitcoin treasury strategy to succeed.
11. The main risks faced by Strategy’s Bitcoin financing model
A range of macro, structural, and execution risks could impair Strategy's ability to maintain its Bitcoin accumulation strategy and support MSTR's valuation.
Bitcoin price falls
Strategy's business model is premised on the appreciation of BTC. A continued decline in BTC prices could undermine the value of existing holdings and the feasibility of future financing.
BTC or MSTR volatility decreases
Lower volatility has dampened investor appetite for MSTR’s convertible bonds and preferred shares, which rely on options to attract capital.
The collapse of MSTR’s premium to NAV
The market premium over NAV has largely driven MSTR's upside and its ability to issue accretive equity. A sharp contraction would hurt financing capabilities and shareholder returns.
Core business operations deteriorated
While Strategy's software business is becoming less valued, it still contributes to cash flow, but if that business shrinks further, it could limit its financial flexibility during a market downturn.
Regulatory changes make leveraged BTC products possible
New ETFs or structured products that provide leveraged BTC exposure could reduce the need for MSTR as a proxy tool.
Emerging competition from copycat strategy
New companies adopting a BTC treasury-like model could divert investor interest and saturate capital markets seeking to gain BTC exposure through leverage.
Emerging competitors can achieve higher BTC yields and BTC per share than Strategy with less capital because they are smaller in size relative to Strategy
Compulsory liquidation to discharge debt obligations
In the event of severe losses or a funding shortfall, Strategy may be forced to sell its BTC holdings to repay debts, negatively impacting BTC per share.
Strategy Securities Demand Weakens
Strategy plans to raise more than $22 billion to continue its BTC purchase plan. The decline in investor demand will affect its ability to execute this plan.
BTC shareholding dilution per share
Actions such as issuing new shares to meet dividend or financing obligations could reduce BTC per share, thereby harming Strategy’s core KPI: Bitcoin yield.
Capital market instability
MSTR's business model depends on continued access to well-functioning, liquid capital markets. Market disruptions could threaten its operations and funding for expansion.
Rising interest rates
Rising interest rates would increase debt issuance costs and reduce investor appetite for low-yielding convertible bonds, limiting Strategy’s ability to fund BTC acquisitions.







