On the morning of August 29th, Beijing time, OpenAI released GPT-Realtime, its most advanced end-to-end speech model to date, in a livestream, and announced the full launch of the Realtime API in production. Compared to previous voice AI products, GPT-Realtime offers superior performance and a lower price point, designed to help developers more easily build efficient and reliable voice agents.
Along with the performance improvements, GPT-Realtime's pricing has been significantly optimized, down 20% from its predecessor, GPT-4o-Realtime-Preview. Previously, GPT-4o-Realtime-Preview cost $40 per million audio input tokens and $80 per million audio output tokens. The adjusted price for GPT-Realtime is now $32 per million audio input tokens ($0.40 for cached input tokens) and $64 per million audio output tokens. This optimized pricing allows developers to build efficient voice agents at a lower cost while enjoying superior performance.
OpenAI has also optimized conversation context management, allowing developers to flexibly set token limits and cut off multiple rounds of conversations at once, significantly reducing the cost of long conversations.
01. In-depth analysis: smarter and more expressive speech models
The new GPT-Realtime model represents a significant leap in performance. OpenAI claims it is its most advanced production-grade speech model to date, achieving significant improvements in following complex instructions, accurately invoking tools, and generating more natural and expressive speech.
OpenAI claims that GPT-Realtime can execute complex commands more accurately, generate more natural and expressive speech, and support seamless switching between multiple languages within a sentence. In internal benchmark tests, the model demonstrated a higher level of intelligence. Compared to previous voice AI models, GPT-Realtime significantly improves in the following aspects:
Sound quality and expressiveness: It can simulate human intonation, emotion, and speaking speed, and supports developers to customize the tone of voice, such as "fast and professional" or "gentle and considerate", to enhance the user experience.
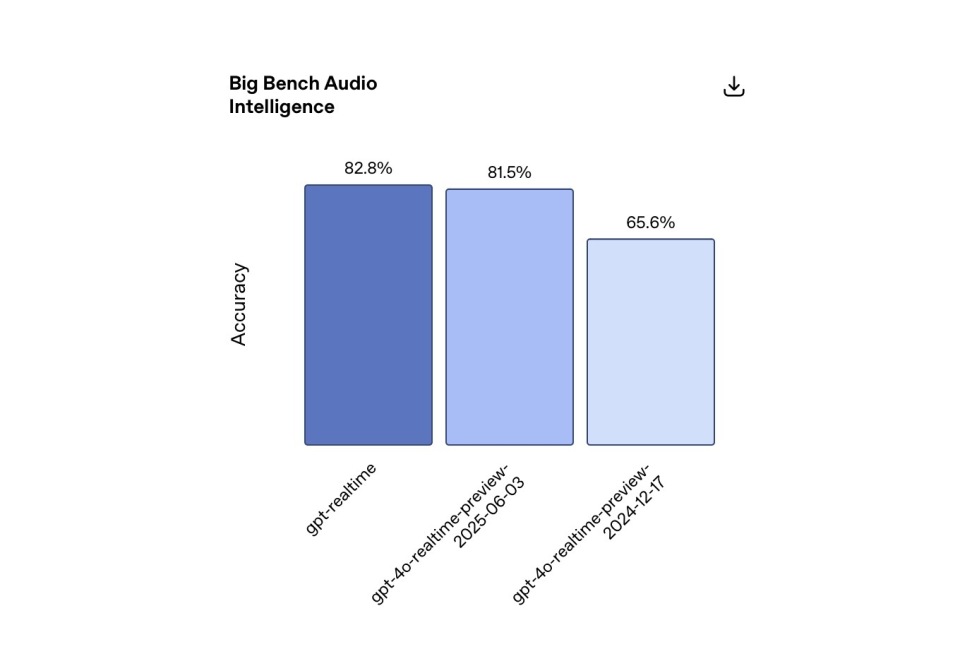
Intelligence and Comprehension: It not only processes text and speech but also recognizes nonverbal signals (such as laughter), flexibly switches between languages within a sentence, and accurately processes alphanumeric sequences. Internal testing shows that GPT-Realtime achieved an accuracy of 82.8% in the Big Bench Audio inference test, far exceeding the 65.6% achieved by its predecessor, GPT-4o-Realtime-Preview, in December 2024 and 81.5% as of June 3rd of this year.
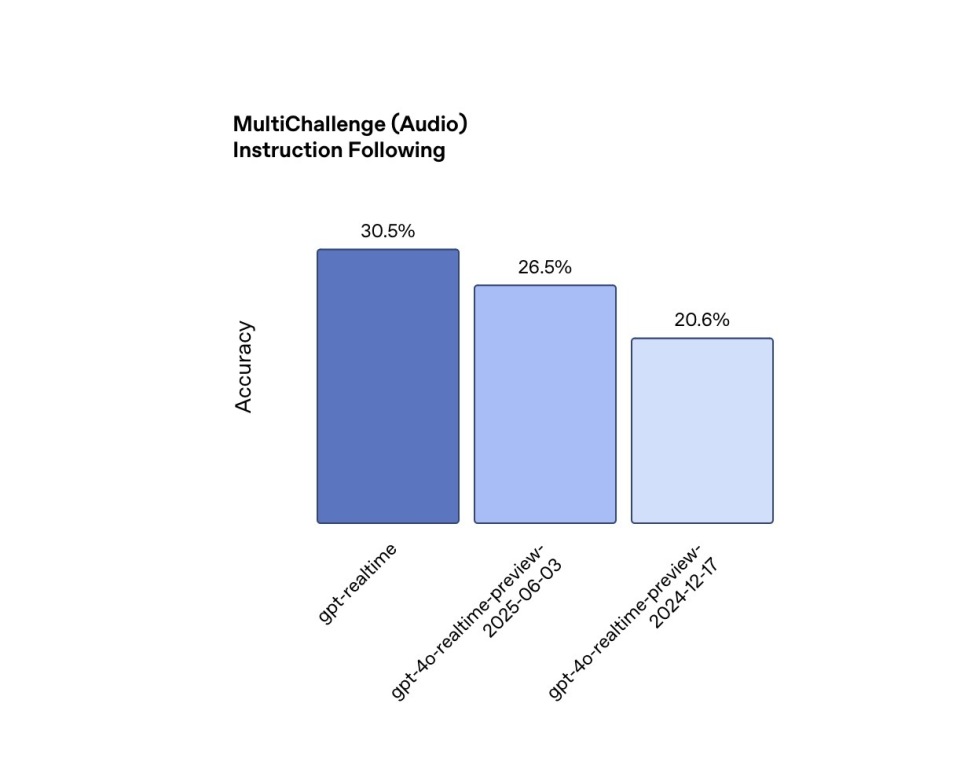
Command Following: Command following is a key capability for reliable agents, and GPT-Realtime has also improved in this area. In MultiChallenge Audio testing, GPT-Realtime achieved 30.5% command execution accuracy, enabling it to more reliably follow developer-specified prompts, such as reading legal disclaimers verbatim during support calls. This performance surpasses the 20.6% achieved by the previous generation, GPT-4o-Realtime-Preview, in December 2024 and 26.5% in June 3rd of this year.
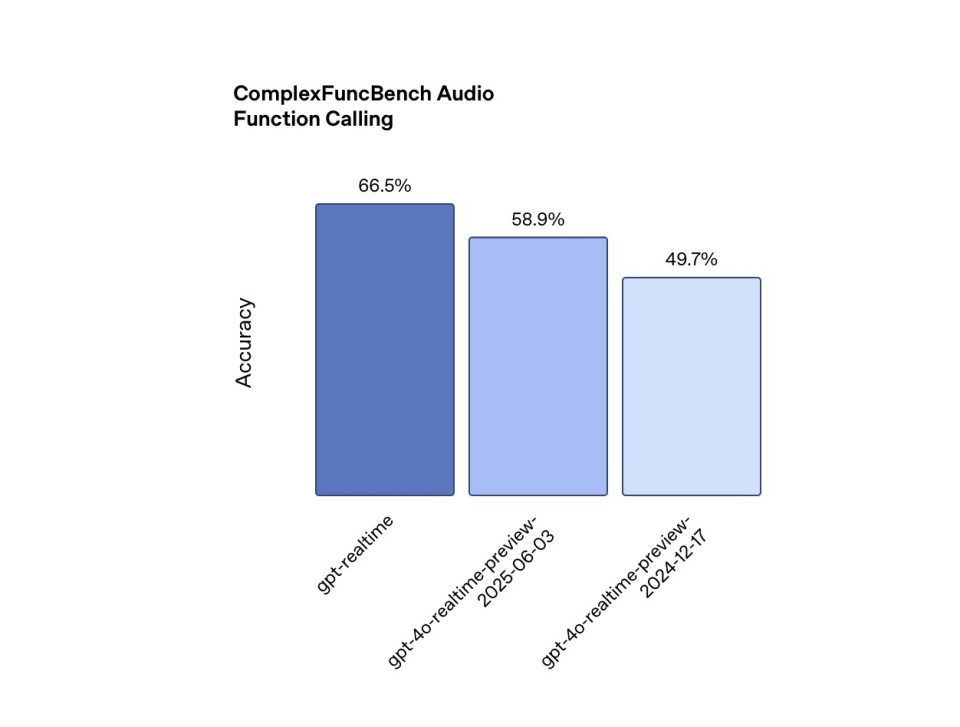
Function Calls: To be effective in the real world, voice agents must effectively use external tools. In the ComplexFuncBench Audio test, GPT-Realtime achieved a 66.5% accuracy rate for function calls and supports asynchronous calls, ensuring smooth conversations without interruptions while waiting for results. In comparison, GPT-4o-Realtime-Preview achieved a 49.7% accuracy rate in December 2024 and a 58.9% accuracy rate in June 3rd of this year.
In addition to enhanced intelligence, the model has been trained to generate higher-quality speech with more human-like intonation, emotion, and speed. It can follow fine-grained instructions, such as "speak quickly and professionally" or "speak softly with a French accent," providing a more personalized experience for users. Furthermore, GPT-Realtime supports image input and can recognize the content of photos or screenshots. For example, users can upload a screenshot and ask the model to "read the text within it," further expanding its application scenarios.
To showcase these advances, OpenAI has released two new voices, Cedar and Marin, available only in the API, which demonstrate the most significant improvements in natural speech. This attention to detail is designed to address key industry challenges: OpenAI's upgrades are directly aimed at creating a more engaging and less robotic user experience.
02. Empowering developers: API upgrades for production-grade intelligent agents
In addition to the new models, the Realtime API itself is now production-grade. Since its public beta in October 2024, OpenAI has collected feedback from thousands of developers and made corresponding improvements. The API's architecture processes audio directly through a single model, designed to reduce latency and preserve speech details. This offers significant advantages over traditional multi-model pipelines for speech-to-text and text-to-speech.
A key new feature is support for remote Model Context Protocol (MCP) servers. This open standard simplifies how AI models connect to external data. Developers can now pass the URL of a remote MCP server through session configuration, allowing the Realtime API to automatically handle tool calls, eliminating the need for manual integration. This simplifies connecting AI models to proprietary data sources, a critical step in building powerful business intelligence while prioritizing user data and privacy.
The Realtime API now also supports image input, enabling multimodal conversations where agents can analyze and discuss what the user is seeing. Images are treated as snapshots in the conversation rather than live video streams, ensuring developers maintain control over what the model sees. This unlocks use cases such as having agents describe photos or read text from screenshots.
Additionally, new Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) support allows direct integration with public telephone networks, PBX systems, and other enterprise telephony endpoints, facilitating the deployment of voice agents in business environments such as call centers.
Early adopters are already seeing results. Real estate platform Zillow received early access to the Realtime API, which it will use to power its next-generation home search. "It demonstrates enhanced reasoning capabilities and more natural speech, enabling it to handle complex, multi-step requests like filtering listings based on lifestyle needs," said Josh Weisberg, the company's head of AI.
03. The fiercely competitive voice AI arena
OpenAI's release of the GPT-Realtime model comes amidst fierce competition in the voice AI market, with major competitors actively advancing their own voice technology development and deployment. In May of this year, Anthropic launched a voice model for its Claude AI, making a strong entry into the field. In July, Meta acquired voice startup PlayAI for $45 million, aiming to strengthen its AI assistant and smart glasses technology. This move further intensified the competition for talent within the industry.
The open source community is also a powerful competitive force that cannot be ignored. In July, French startup Mistral released the Voxtral model, licensed under the Apache 2.0 license. Officials promise that its service price will be less than half the price of similar APIs while delivering cutting-edge performance. This month, Xiaomi released its self-developed large-scale sound understanding model, MiDashengLM-7B. This model innovatively uses subtitle-based training methods to achieve a comprehensive understanding of speech, music, and ambient sound, and also uses a business-friendly license.
Traditional tech giants are also continuing to invest in voice AI. In April of this year, Amazon launched Nova Sonic, a real-time expressiveness model, and integrated it into its Alexa+ assistant. Innovation in voice AI has also extended to specialized startups. For example, Stability AI focuses on developing on-device voice processing technology, while companies like Sesame AI are creating AI assistants that are described as "stunningly lifelike" by incorporating human-like features such as natural pauses and slight stuttering into speech.
OpenAI is optimizing its state-of-the-art speech models to make them easier to use, more powerful, and more cost-effective. This move represents a strategic move in the face of increasingly fierce platform competition. OpenAI hopes to leverage its superior developer experience to gain an advantage in the voice AI war, becoming a key factor in determining the outcome.
This article comes from " Tencent Technology ", author: Wu Ji, published by 36Kr with authorization.