Author: Ggg, Redline DAO
In 2010, Vitalik Buterin, the founder of Ethereum, had a warlock account in World of Warcraft. One day, Blizzard decided to cut the role of the warlock and removed the damage part of the life siphon spell. He cried himself to sleep, and realized the horrors of centralized servers that day, so he decided to quit and create the decentralized network Ethereum. In November 2022, FTX, the world's largest Derivatives exchange, was exposed to misappropriating user funds. The founder SBF was arrested by the Bahamas police and was about to be handed over to the United States for trial.
From the warlock player who was inexplicably backstabbed by Blizzard 13 years ago, to the FTX victimized user defending rights today, we are increasingly aware of the importance of the phrase "Not your key, not your coin": even with third-party audits/ Regulatory agencies and centralized servers can still arbitrarily tamper and whitewash data, while on a decentralized network, the on-chain ledger is transparent and cannot be tampered with. As long as we have the private key of our account, we have absolute control over our personal assets.
Decentralization is wonderful, but at what cost?
We who live in the blockchain network are the first person in charge of personal assets. When most users choose an on-chain wallet, the most critical trade-off is how much risk and responsibility am I willing to take for my assets? Take traditional financial institutions as an example:
In the eyes of users who pursue security, they hope to put their money in banks with cumbersome account opening steps but large scale: capital security of large banks (risk) > standard and strict account opening steps (responsibility)
In the eyes of users who pursue applicability, they only need to put their money in WeChat and Alipay. WeChat and Alipay can conveniently complete P2P transactions, and only need an ID card and mobile phone number to complete the registration, even if WeChat and Alipay are only Two listed companies instead of state-backed banking institutions: WeChat's convenience (liability) > WeChat's operational status (risk)
Back to web3, we have two ways to store assets in web3, managed wallet and non-custodial wallet, and before that we need a brief introduction to the principle of the wallet:
wallet and private key
Account generation is the process of creating a private key. On Ethereum, there are two types of accounts: EOA account (External Owned Account, external account) and contract account (a smart contract deployed on the chain through the EOA account):
Taking the EOA account as an example,
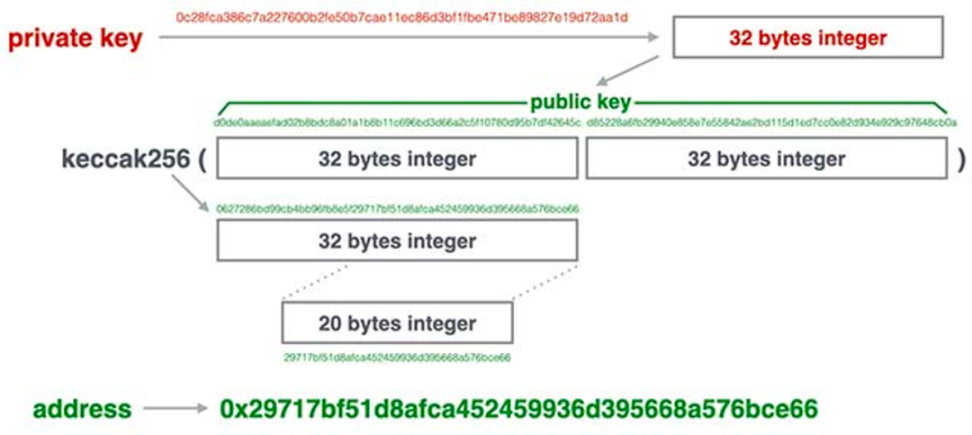
EOA address
By generating a 256bit random number as the private key, and then deriving the corresponding public key by the SHA3 algorithm through the private key, and then calculating the address (the last 20 bytes of the original hash) through keccak-256, a unique The personal account corresponding to the private key. During this process, the private key will be calculated to generate 12 mnemonic words, and we can use the mnemonic words to re-deduce the private key.
At present, the most mainstream Dapp wallets on the main chains are EOA wallets, such as Metamask, Phantom (Solana), BSC Wallet (BSC), and Keplr (Cosmos).
The smart account is a piece of EVM code deployed on the chain through the EOA account, which can realize different functions. However, unlike the EOA account, the contract account does not have a private key and cannot be executed actively. It can only be called by the EOA account. Therefore, the final control of the smart contract wallet = the private key of the EOA account used to deploy the contract. From this level of understanding, smart contract accounts are also controlled by private keys. As long as the wallet address is a contract, it is a smart contract wallet.
Smart contract wallets are divided into multi-signature wallets (Multisig account) and account abstract wallets (Abstract account):
Multi-signature wallets: As early as 2013, multi-signature wallets have become the first choice of the IMF. This technology was originally developed in the Bitcoin ecosystem, and now there are excellent multi-signature wallets (such as Gnosis Safe) in Ethereum: the Ethereum Foundation uses a 4-of-7 multi-signature wallet ( That is, create a smart contract for depositing funds, and control the contract through 7 EOA accounts, and the signature can only be completed if more than 4/7 of the EOA accounts are signed)
Account abstraction is to use a single EOA wallet to control the contract address to achieve the effect of simulating EOA with smart contracts. Popular projects such as Argent/Loopring belong to the account abstraction wallet
Apecoin Contract Address
According to teacher Liao Xuefeng's introduction:
In a decentralized network, there is no trust institution like a bank. In order to conclude a transaction between two nodes, it is necessary to implement a mechanism for secure transactions under zero trust.
Let's assume that Xiaoming and Xiaohong want to make a deal. One way to create a transaction is that Xiaohong claims that Xiaoming gave him 10,000 yuan, which is obviously not credible;
There is another way to create a transaction: Xiao Ming claims that he gave Xiao Hong 10,000 yuan, as long as it can be verified that this statement is indeed made by Xiao Ming, and Xiao Ming really has 10,000 yuan, then this transaction is considered to be Effective.
How to verify the statement made by Xiaoming?
The signature created by the private key allows the verifier to confirm the originator of the statement: anyone can verify the result of the digital signature and the transfer through the public key. Since only Xiao Ming who has the private key can initiate this statement, it can I am sure that this statement was indeed made by Xiao Ming.
In the Ethereum network, such transactions include not only P2P transfer transactions, but also calls to smart contracts.
So when we use the wallet on a daily basis, it is equivalent to calling the local private key through the wallet platform to complete the signature on the chain.
Wallet security, threshold and censorship resistance
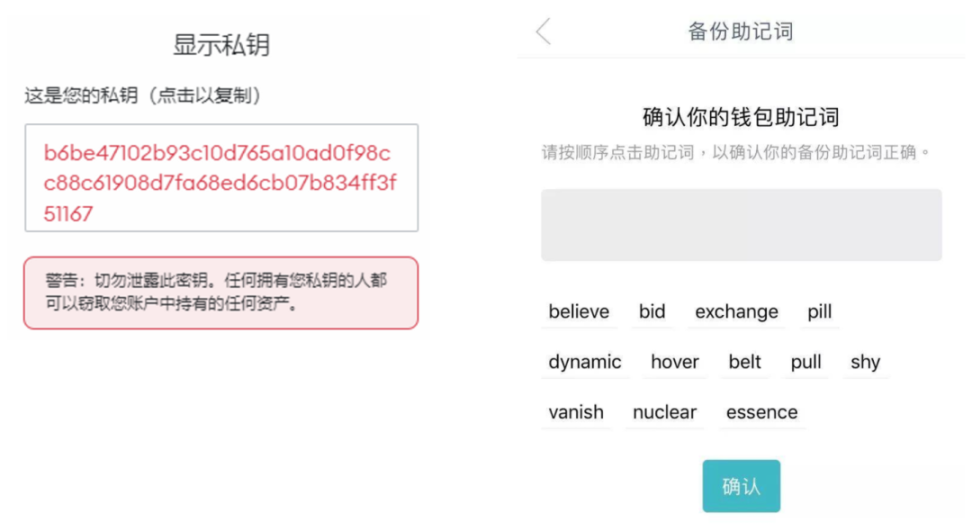
Everything in the wallet is built around the private key. A wallet is essentially a tool for 1. creating a private key, 2. keeping the private key, 3. using the private key, 4. backing up the private key, and 5. restoring the private key. The current mainstream private key backup/recovery scheme is mnemonic words, which are 12/24 word combinations that appear when registering a wallet:
The mnemonic can deduce the plaintext of the private key. When the user migrates the wallet to a new device, he only needs to enter the mnemonic on the wallet app to derive the private key, thereby regaining control of the wallet
For users, private key = mnemonic, but these two concepts are still different in the daily use of wallets: mnemonic is the backup and recovery scheme for the user's private key
A metaphor: the mnemonic is equivalent to copying your key. When your key is lost, you can regenerate the same key through the mnemonic
Since the private key is the only certificate for us to interact with the blockchain network, our responsibility is to keep our wallet private key and seed phrase safe. The safest way to create an account is, of course, in an offline environment, by running random numbers (private keys) and the SHA256 algorithm through the code to generate your own address, but undoubtedly this threshold is too high and it is not suitable for most users. Therefore, when choosing a wallet, users need to consider three points: security, threshold and anti-censorship:
Security: How expensive is it for hackers to crack wallet private keys/mnemonic words
Taking the hardware wallet as an example, hackers can only obtain the user's private key by phishing or stealing the private key offline
Barrier: How easy is the wallet to use?
During the registration process of Metamask, users need to record 12 mnemonic words, and they need to re-enter 12 mnemonic words when changing devices, while Binance’s exchange registration and device change login can be completed with one-click email login
Censorship resistance: Whether the ultimate control of the wallet is in the hands of the user
If the wallet app saves the mnemonic words imported by the user and uploads them to the server in plain text, hackers can steal the user's wallet by cracking the server. And even if there is no hacker attack, there is still the possibility that the Slope project party will guard against itself, and it has not achieved anti-censorship.
There are two main categories of wallets: non-custodial wallets and centralized custodial wallets.
Non-custodial wallet: users keep their own mnemonic words
a. Taking the mainstream wallet Metamask as an example, MetaMask is a non-custodial (or self-custodial) cryptocurrency wallet. Non-custodial means that MetaMask does not store any data about the wallet, and the private key data is in the browser or mobile application at the local level. When the user needs to perform on-chain signature activities, Metamask will call the private key from the local file for signature . And if the user's private key and mnemonic are lost/stolen, Metamask will not be able to help the user find it, and the user's assets will be permanently lost
b. Recognized as the most secure hardware wallet (such as Ledger), it uses a hardware device to generate the private key and wallet address offline, and then imports the public key of the address to the web wallet such as Metamask, and then passes Ledger when signing is required. The offline confirmation of hardware, because the private key does not have access to the Internet at all, it is difficult for hackers to steal the private key in the hardware wallet. However, if the user loses the mnemonic phrase or is phished, the protective effect of the hardware wallet will also be reset, and the user's assets will still be stolen. - Escrow wallet
Exchange wallets such as Coinbase/Binance have adopted the method of hosting wallets. The difference is that the account displayed in Coinbase is not the user's own private key, but the account number displayed in the Coinbase program instead of Etherscan. It can be understood that users trust Coinbase and entrust assets to Coinbase instead of owning them, so Coinbase accounts cannot interact with Dapp such as Uniswap
Source: Binance
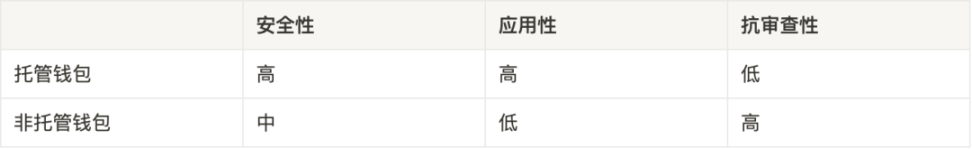
Generally speaking, in the custody wallet, the project party keeps the mnemonic phrase on its behalf, and the threshold for registering and restoring the wallet is low, but the security of the wallet depends on the project party rather than the user itself, and the project party has the actual control of the wallet; the non-custodial wallet The mnemonic phrase is in the hands of the user, and the threshold for registering and restoring the wallet is high, but the security and censorship resistance are very high.
The pitfalls of the mnemonic scheme
With the continuous development of WEB3, more and more demands and application scenarios have emerged, and the ecology on the chain is booming, especially the Defi Summer in 2021 has attracted a large number of users who originally only traded on exchanges to migrate their assets to On the chain, as of March 2022, MetaMask monthly active users have reached 30 million, but at the same time, as the most mainstream mnemonic account recovery solution, mnemonic words have become the main target of hackers: for ordinary users, The most common wallet theft event is that the mnemonic is copied on the clipboard, or the private key file stored locally is stolen when encountering a phishing website.
When a hacker conducts an attack, he needs to measure the cost of the attack and the return obtained. All private keys (12 mnemonic words) are a subset of the dictionary. As long as the permutations of the dictionary are exhausted, the hacker can obtain all assets on the chain . However, this input-output ratio is bad. If the dictionary arranges all the combinations through a violent algorithm;
The current mainstream mnemonic is 12 English words, and the thesaurus has a total of 2048 words. That is 2048^12=5.44e39 species (5444517870735000000000000000000000000000);
If such a huge computing power is to be used, hackers can already control the BTC network through a 51% attack;
Therefore, the method with a higher return rate for hackers is to obtain the user's mnemonic phrase through phishing, or steal the private key saved on the user's local device.
Continuing with Metamask as an example, hackers can obtain stored mnemonic phrases and private keys in two places:
mnemonic
a. After the wallet is created, the user needs to keep the generated mnemonic well. It is generally recommended to copy it on a white paper with a pen and paper and keep it properly. However, some lazy people will use the clipboard to copy and paste and save it in doc Documents, even WeChat chat records; b. If the hacker has installed malicious software on the user's mobile phone/computer, and monitors the user's clipboard at all times, he can steal the private key just created. For example, QuickQ VPN has been exposed to copy the user's clipboard to steal the mnemonic. private key
a. At the same time, Metamask generally encrypts the private key and saves it on the local device where the wallet is created so that it can be called at any time. If it is a Metamask plug-in installed on Chrome:
i. Storage location on Windows, Metamask private key storage address:
C:\Users\USER_NAME\AppData\Local\Google\Chrome\User Data\Default\Local Extension Settings\nkbihfbeogaeaaoehlefnkodbefgpgknn.
ii. Storage location on Mac: Library>Application Support>Google>Chrome>Default>Local Extension Settings>nkbihfbeogaeaaoehlefnkodbefgpgknn
b. That is, the security of Metamask depends on the security of Chrome. Once Chrome's firewall is breached by hackers, hackers can obtain the user's address private key and transfer all assets. This is why hardware wallets are safer than plug-in wallets such as Metamask.
Other than Metamask, some non-custodial wallets are not even highly censorship-resistant, such as the theft of the Slope wallet on Solana: when Slope’s mobile application created a Phantom wallet, it sent mnemonic words to their Sentry server through TLS. The seed phrase is then stored in clear text, meaning anyone with access to Sentry can access the user's private key.
EOA Account Hacked
Fenbushi Capital Founder Wallet Stolen:
The reason why Shen Bo's wallet was stolen was that the mnemonic word was leaked. The wallet used at the time of the theft was Trust Wallet. The stolen amount included about 38.23 million USDC, 16.07 ETH, 720,000 USDT and 4.13 BTC. The Wintermute wallet was attacked and lost about 160 million US dollars. The reason for the theft was that Wintermute used Profanity to create a Vanity wallet in order to save Gas fees (starting with 0x0000000, which can save Gas when calling smart contracts):
Profanity is designed to help people generate accounts with special visual effects, such as accounts that start or end with special characters. On the other hand, some developers use it to generate accounts that start with many zeros. After Profanity obtains the first 32-bit private key SeedPrivateKey, in order to collide with the required account address, it will continuously iterate the private key through a fixed algorithm, up to 2 million times (the value comes from the article disclosed by 1INCH ). When the PublicKey is known, we can get the SeedPrivateKey by enumerating the SeedPrivateKey and Iterator. The amount of calculation is about 2^32 times 2 million times, and a graphics card with a large computing power can complete it in a few days or even a few hours.
The contract account was stolen
The contract deployment address of Paraswap was stolen:
According to the investigation report of SlowMist: The hacker address (0xf358..7036) has obtained the private key authority of ParaSwap Deployer and QANplatform Deployer. The hacker withdrew $1,000 from ParaSwap Deployer and transferred it to and from the QANplatform deployer address as a test. Using the AML platform to analyze 0xf358..7036, we found that hackers also stole The SolaVerse Deployer and several other high-profile addresses. So far, hackers have stolen more than $170,000 in funds. Ronin Bridge was hacked in March this year, losing 173,600 ETH and 25.5 million USDC:
The hacker made up a non-existent company, hooked up Axie’s senior engineer through Linkedin and WhatsApp, used the new job opportunity to lure him, arranged an interview, and finally offered a generous salary, but the offer file was poisonous, so he successfully invaded Axie’s system and stole The engineer deploys the private key of the EOA address of the contract.
When creating a wallet, 12 words need to be manually transcribed for safety reasons, and it is best not to take pictures of this white paper and save it. Even with trusted open-source password saving software like 1password, we can't use the convenience of copy-paste saving because of the risk of clipboard theft
When restoring the wallet, that is, when changing the login device, you need to turn out this blank paper and re-enter 12 words
Keeping a piece of white paper with 12 words on it sounds unreliable and unweb3: We look forward to living in the future of the metaverse, but our account security depends on a piece of white paper invented in the Song Dynasty. So far, these two steps are enough to dissuade most web2 players. After all, in the web2 world, most of the registration processes can use one-click login with google account/ios account.
New solution for account recovery without mnemonic
In order to lower the threshold of the wallet and attract more users to WEB3, we need to use a social account login scheme such as Web2 without losing the security and censorship resistance of the wallet. Therefore, we need a more convenient and secure account recovery solution, and all current discussions point to an end: no mnemonic. There are currently two implementation schemes for helpless words: the MPC scheme and the social recovery scheme.
MPC scheme: the private key is calculated and generated by multiple parties, so as to avoid single-point accidents caused by the loss/theft of the private key on the client side.
It can be understood as: MPC is a 3FA, each verification method holds a key fragment, and the door lock does not have a separate key. When one of the key fragments is lost, the user can use other verification methods to restore the lost key. key fragment Social recovery scheme: store funds in smart contracts, control the EOA wallet through the multi-signature/single-signature scheme, and designate a trusted third-party guardian. When the private key of the EOA wallet is lost, the third-party guardian replaces the control of the contract , so the user does not need to save the mnemonic.
The current discussion usually discusses social recovery and account abstract wallet side by side. It should be noted that the social recovery solution is a standard and function on smart contracts. It was proposed by EIP-2429 in 2019, which means that users can control the contract through guardians. The private key is replaced; the recently hotly discussed EIP-4337 is a discussion about account abstraction, which we will discuss in the following chapters
MPC scheme
The MPC scheme is that when creating an EOA wallet, multiple parties jointly create private key fragments. In 2019, the paper "Two-Party Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Based on Secure Multi-Party Computation" was published at CRYPTO 2019, officially bringing the realization of MPC into everyone's field of vision. MPC stands for Secure Multi-Party Computation.
Multi-party computation (MPC) is a branch of cryptography that began nearly 40 years ago with the pioneering work of Andrew C. Yao. Using multi-party computing, the generation of private keys no longer needs to be completed at a single point, but can be calculated and held by a group of multi-party (n parties) who do not trust each other (n fragmented private keys). This technology is DKG (Distributed Key Generation).
Distributed key generation can be done in a way that allows different types of access structures: a conventional "t out of n" (provably valid signature as long as t out of n private key fragments participate in the signature) setup will be able to Withstand up to t arbitrary failures in operations related to the private key without compromising security.
Threshold signature scheme (TSS) is the name given to this combination of distributed key generation (DKG) and distributed signatures.
At the same time, when one of the private key fragments is lost/exposed, the MPC solution supports recovery and replacement of the private key fragments, achieving the effect of ensuring account security without changing the account.
The MPC scheme achieves that there is no complete private key in account creation, use, storage, backup, and recovery. Through the joint generation/holding of private key fragments by multiple parties and the TSS threshold signature scheme of "t out of n", it achieves better than Metamask It is more convenient to generate/hold private key wallets at a single point. Security and anti-censorship: Compared with traditional mnemonic schemes, it greatly improves the security of users, even comparable to hardware wallets
safety
a. No private key/mnemonic: In the process of wallet generation, all parties (wallet project party and user) generate private key fragments through MPC, and the complete private key has never appeared in the whole process. It can be understood that MPC is True private keyless wallet;
b. The cost of hacking attacks is greatly increased: Even if hackers invade the user's local device, they can only obtain private key fragments. Only when the hacker has mastered the wallet server + the user's local device can the user's property be stolen.
threshold:
Social login: Users can create an account on the MPC wallet through authentication methods such as email (assuming that the MPC wallet adopts a 2/2 signature scheme, that is, two private key fragments can be signed at the same time).
Censorship Resistance:
The centralized organization (wallet side/backup device) only holds fragments of the private key of the account and cannot control the user's account.
Social Recovery Program
The social recovery solution is deployed on the smart contract account. The smart contract wallet can be understood as deploying a contract for managing funds on the chain with the EOA account. Like ordinary smart contracts, the deployer's EOA wallet has control over the smart contract. right.
The smart contract wallet is not a solution without a private key, because the controlled EOA wallet has a private key; But the smart contract wallet can change the user's signature private key through the social recovery scheme; The social recovery option is to have a guardian replace your key if your key is lost.
Two years after the EIP-2929 proposal, in 2021, Vitalik first proposed a wallet application case for social recovery in the forum:
When creating a smart contract wallet, users can designate other EOA addresses as "guardians", and the "guardian" address needs to be signed and confirmed on the chain and pay gas fee;
The user's EOA account serves as a "signature private key" that can be used to approve transactions;
There are at least 3 (or more) "guardian" EOA accounts who cannot approve transactions but can change the "signature private key". Changing the "signature private key" also requires the "guardian" to pay gas fee for signature confirmation;
The signing private key has the function of adding or removing guardians, but the whole process takes a while (usually 1-3 days).
In everyday usage scenarios, users can use smart contract wallets with social recovery functions (such as Argent and Loopring) like ordinary wallets, and confirm transactions with their signing keys. In this way, each transaction can be quickly completed with a single confirmation, just like in traditional wallets (such as Metamask):
The account abstraction wallet is no different from Metamask in the creation of private keys.
Since the EOA wallet that controls the contract is only used as a "signature private key" and the control can be transferred through the guardian, the user does not need to keep the mnemonic.
○ But because it is calling the contract, it supports non-native tokens such as USDC/USDT (such as ETH is the native token used to pay gas fee on Ethereum) for payment, which will undoubtedly greatly reduce the difficulty of interaction for new Web3 players: in principle, In the same transaction, the project party will pay the gas fee after swapping the user's USDC into ETH .
①Users use web3 for the first time and want to register a wallet, but need to find three trusted friends who already have EOA wallets in web3, and ask them to pay gas fee to become their guardians;
②If the user wants to compensate a friend's gas fee and use the newly created wallet to transfer money three times, then to create a wallet, a total of 6 gas fees need to be given, and there is no cost for creating an account with an MPC wallet.
e. Restoring the private key
If users lose their signing keys, they can apply for social recovery. Users need to contact their guardians and ask them to sign a special transaction (the user or guardian pays the gas fee) by changing the signature public key registered in the wallet contract to a new signature. This is much simpler: the guardian can visit a web page, such as security.loopring, view the recovery request and sign it.
However, in terms of the security of the private key, it has not reached the height of the MPC wallet:
The cost of being attacked: Hackers can still obtain the complete private key by invading the user's device. In other words, the user's use of the smart contract wallet is only a way to retrieve the private key in the scenario where the private key is lost
Low censorship resistance: Since the social recovery plan needs to appoint a "guardian", there is a possibility that the "guardians" will collude with each other
The main risks of social recovery are: ① Collusion: If some users know that they are part of a recovery, they may be interested in the execution of the recovery attack; ②Targeted attack: The external agent may know the owner of the recovery and target the weakest point needed to perform the recovery attack; ③ General exposure: An attacker who manages to infect a large user base with environmental dependencies and gain access to multiple identities may also have side effects on unaffected users through recovery.
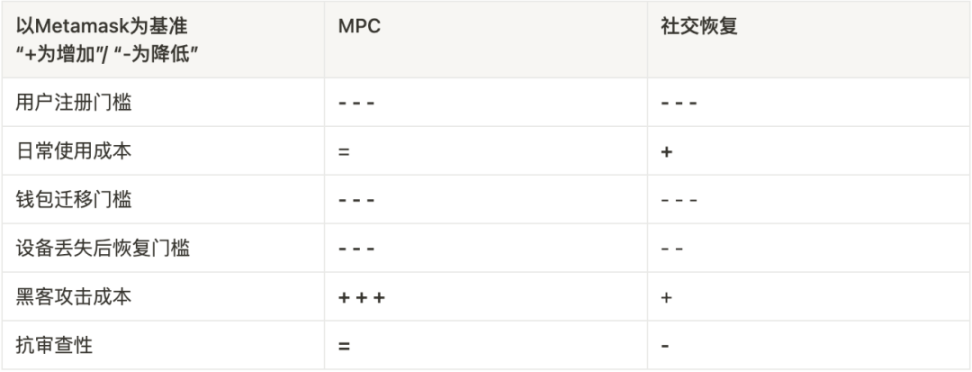
With the account recovery solution without mnemonic words, we can look forward to a new generation of Web3 wallets, that is, wallets that can register and log in using email addresses. We selected the representative projects of MPC wallet and account abstraction wallet to analyze separately: they all reached the low threshold of no mnemonic in terms of user access, and we evaluated them separately from the aspects of security and anti-censorship——
Bitizen
Among the MPC wallets, the Bitizen wallet, which is more thorough in anti-censorship and convenience, adopts 2/3 of the TSS scheme. Let us analyze it from the security and anti-censorship of the wallet:
safety:
a. Create
In order to achieve strong censorship, after the user completes the wallet registration, he can use the second device to back up the private key fragments via Bluetooth, using the 2/3TSS scheme: Bitizen server, the user's local device and the user's second device.
b. Keep
Since the complete private key was not generated during the wallet creation process, there is no mnemonic: the user's Bitizen account will be associated with the user's cloud disk and email address, and the user only needs to log in with the email address to use the Bitizen wallet normally.
c. use
① The user obtains the private key fragments stored in the Bitizen cloud and the private key fragments stored on the local device through face recognition authentication to sign (2/3);
②After the second device backs up the private key fragments via Bluetooth, it can be completely saved offline, and it does not need to be used at all on weekdays (the signature only needs to be completed by Bitizen's server and the user's main device).
d. backup
① Back up the local private key fragments to the user's cloud disk;
②When the user needs to change the device to log in, he only needs to pass the email and face authentication, and Bitizen will request the user to restore the backup of the private key fragment from the cloud disk. e. Recovery ①Similarly, when the user's device is lost/mistakenly deleted Bitizen's local files, the private key fragments can be recovered through the cloud disk;
②When the user cannot even log in to the cloud disk, Bitizen will recalculate the private key fragment through the private key fragment on the server and the user's second backup device, allowing the user to resume normal use.
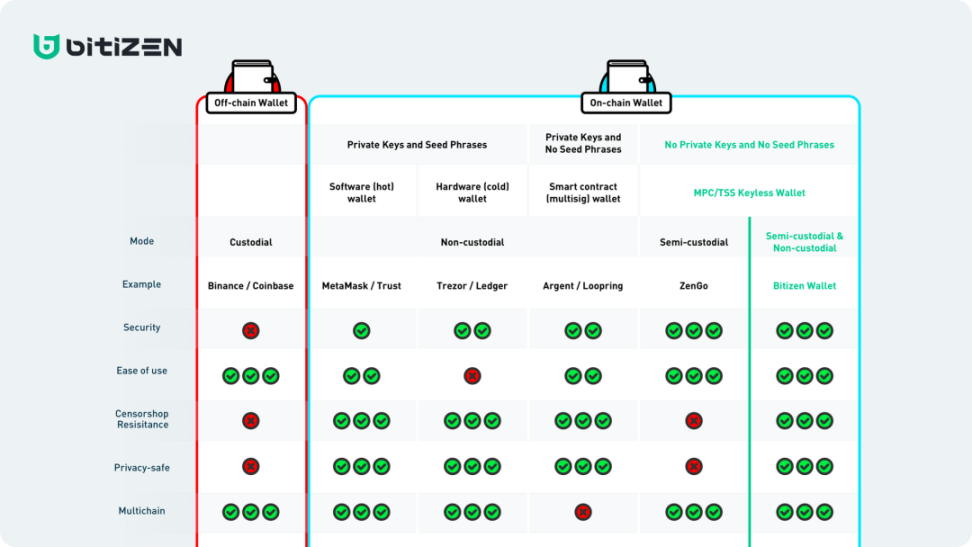
Source: Bitizen
Censorship Resistance:
2/3 of the TSS scheme allows users to have absolute control over their own wallets (2/3 of the private key fragments are in the hands of users), even if Bitizen goes bankrupt or Rug Pull, users can still exercise control over their wallets normally.
Unipass
Account Abstraction Wallet Take Unipass as an example. Unipass adopts the method of smart contract + MPC wallet, combining the advantages of the two solutions:
In terms of transactions, any token supported by the wallet (mainstream, highly liquid tokens) can be used to pay the gas fee;
In the custody of the private key, MPC (2/2) and TSS technology are used to generate the private key in a distributed manner, so that the possibility of the private key being obtained by hackers at a single point will not occur - the private key is divided into two pieces, and one piece is stored in Unipass On the server, one copy is saved in the user's local device;
In recovering the private key, Unipass uses the DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM) scheme, and the user can use the email address as the "guardian" instead of other EOA addresses, which greatly reduces the threshold for users to find a guardian: there is no need for a guardian to use the area The block chain only needs the mailbox of the guardian.
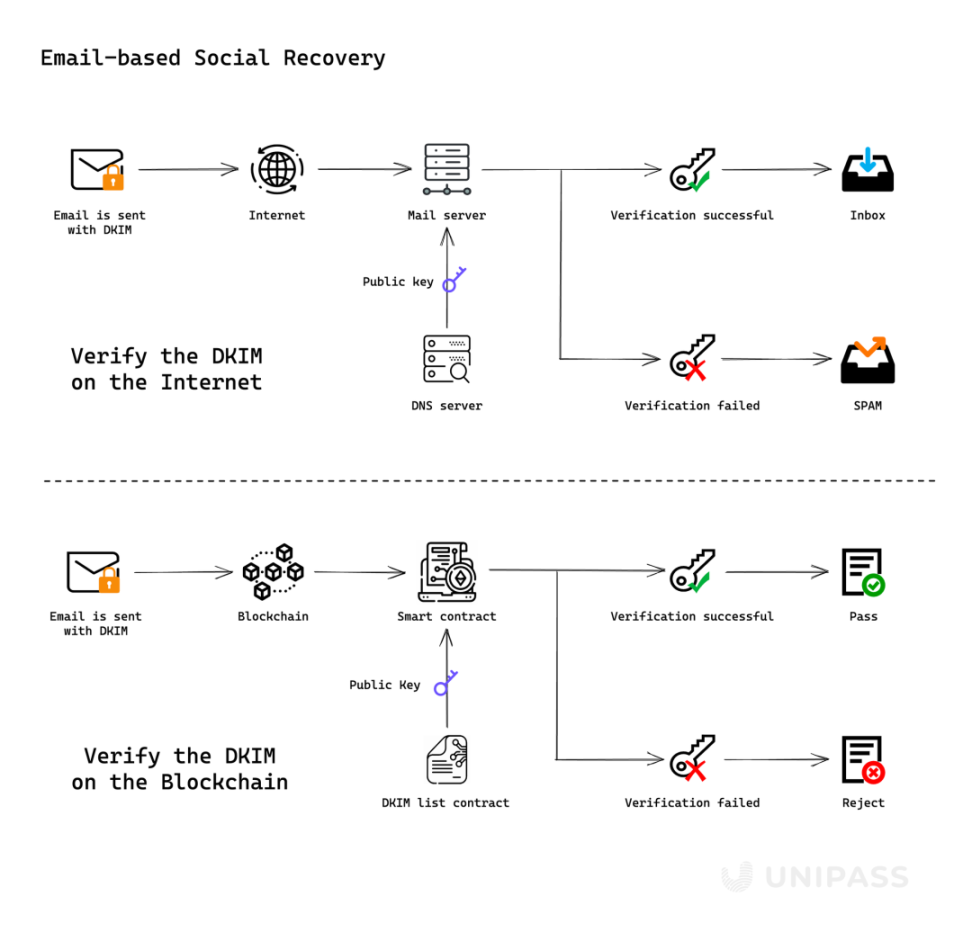
Source: Unipass
Low threshold —> high applicability
Low-threshold wallets are not the end of wallet applications, and the current Web3 infrastructure still has a certain distance compared with Web2's traditional finance. The automatic deduction and regular automatic payment functions provided by Visa have brought great convenience to users, but it is still difficult to implement on Ethereum. Account abstraction accounts may be the next highly applicable blockchain wallet narrative: Visa published the article "Auto Payments for Self-Custodial Wallets (Auto Payments for Self-Custodial Wallets)" to explore the use of account abstraction wallet Argent on the StarNet network Automatic Programmable Payments, allowing users to automatically pay using a self-hosted wallet without signing every transaction. And how is the account abstraction wallet realized? The concept has actually been around for a long time.
Account Abstraction - From EIP-2938 to EIP-4337
With the proposal of EIP-4337, the topic of account abstraction has come back to everyone's attention. The social recovery scheme and account abstraction (using smart contracts as EOA wallets, that is, account abstraction) have been proposed earlier than EIP-1271, and have been implemented by Argent and other wallets in Layer 2 such as StarkNet. Recently, the EIP-4337 scheme that has been hotly discussed in the community (Account abstraction) How is it different?
From EIP-86 in 2015 to the recent hot EIP-4337, the core ideas of developers revolve around "the contract is the wallet", and account abstraction enables users to interact with the main network in an intuitive way. In this way, the user can precisely control the key permissions of the account. Since the code of the EOA account has been stipulated, it is impossible to carry out modular and functional design on the EOA wallet, such as adding functions such as batch transfer/social recovery, so everyone puts the breakthrough on the smart contract. The closest proposal to EIP-4337 is EIP-2938. EIP-2938 also defines a new smart contract operation protocol, but it needs to be modified at the consensus layer, and it is difficult for developers to maintain it. EIP-4337's The main innovation is that the main network does not require consensus-level protocol changes.
- In EIP-1237, the signature initiation of the contract address needs to rely on the centralized Relayer for signing, and the Relayer is centralized, and the standards of each Relayer are different, and it is not compatible with multi-chain/multi- Dapp;
- In EIP-4337, Bundler is proposed to replace Relayer. Bundler is a decentralized multi-party, which improves the anti-censorship of smart contract wallets and unifies signature standards, which can greatly reduce the difficulty of integration for developers;
- EIP-4337 will have an impact in the future, but for now it does not improve the user experience. Therefore, the enthusiasm for discussing this solution is limited to VC and developers. It is more like Move to Aptos, which makes VC and other capital and developer communities fanatical. For web3 users, is this Layer 1 written in solidity or Move? The user experience hasn't changed much at the moment.
①After all, from the account abstraction wallet Argent, since 2018, it has completed financing of 56.2 million US dollars. After 4 years of development, there are only 7.4w addresses: Just like the rise of defi, users in the currency circle have switched from exchanges to Metamask The rise of Metamask is due to the digging of high APY mines. At present, the upsurge of smart contract wallets still needs a new catalyst;
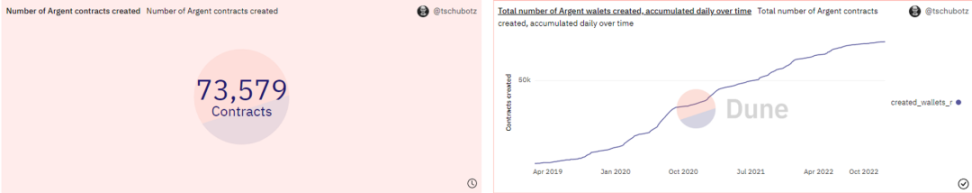
Source: Dune
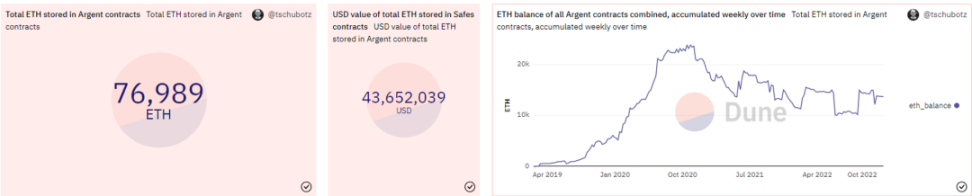
Source: Dune
③However, with the implementation of the account abstraction proposal of the Ethereum main network, it means that Argent users can seamlessly connect from StarkNet to the Ethereum main network, and the sparks ignited in this process are also worth looking forward to.
Use Cases
① Refined authority control: refine the single signature authority of EOA: ▽Give X TokenB transfer quota in User A’s contract ▽Give the authorized tokenC of the B user contract the transaction authority instead of the transfer authority ▽When the contract is not used for a long time, the right to use the contract will be automatically transferred ②Diversified payment methods of Gas: payment by others or any token payment
③Automatic deduction/automatic refund
Embrace the future of Web3
As a common saying goes, there are 4.8 billion web2 users, and web3 users have just exceeded 100 million in 22 years. We are still in the early wild stage of blockchain development.
Going back to the question at the beginning of the article: "How much risk and responsibility am I willing to take for my assets?", can I not only need to remember my private key, but also ensure that my wallet is not lost?
I have always heard traditional VCs asking: Is there any scenario that only web3 can do but web2 can't? We believe that the Web3 wallet is one of the examples of facing the traditional Web2: only in the decentralized network of Web3, we can expect a good wallet that meets censorship resistance, security and user experience. Don't take responsibility. The emergence of such a wallet is also an important basis for 4.7 billion Web2 users to embrace the future of Web3: the wallet is not only the first entrance to Web3, but also a domain name on the chain (such as ENS), a soul-bound token (Soul-Bounded Token), If there is no secure wallet environment, the construction of Web3 Lego will not have a solid foundation.
We need to think more seriously. There are not many opportunities to shoot in the bear market. MPC has shown us a future where EOA wallets are easier to use and more secure, and can adapt to all current EVM chains. There is still a long way to go for smart contract access to Dapp There is a way to go, the social recovery plan is currently looking weak, but the future possibility of smart contracts is exciting. Who do we want to bet on? We will hand in this answer with real money.
2022 is a dark year for cryptocurrencies, but we still believe the future is bright. We are Awakened Warlocks in World of Warcraft, and we want to create a world where no one can take Siphon Life from us (unless the proposal is voted through).








