Liquity is a decentralized lending and stablecoin protocol that allows Eth holders to obtain maximum liquidity without paying floating interest. During the 519 black swan incident, Liquity withstood the extremely volatile environment and performed quite robustly, proving the strength of its protocol design mechanism. At the same time, after the recent BUSD turmoil, the stablecoin protocol Liquity has also received widespread attention.
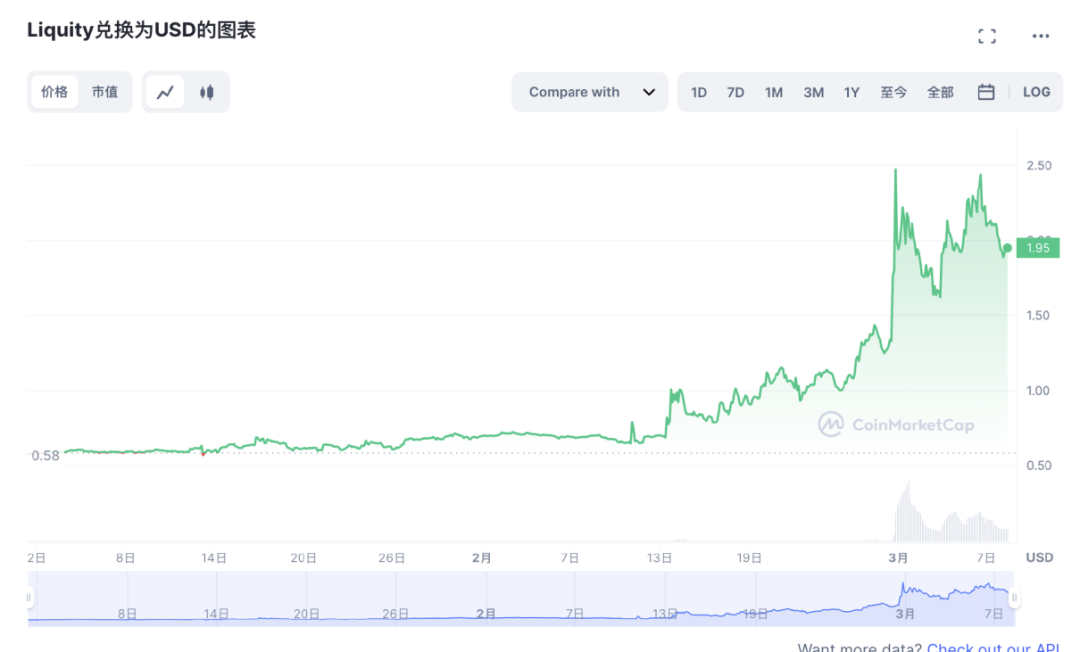
The figure below shows the price trend of Liquity's governance token $LQTY in the past 90 days. It can be seen that $LQTY benefited from the public opinion turmoil in BUSD in February this year. From February 1st to 27th, the price of $LQTY went from $0.711 to $1.278. On February 28th, $LQTY was listed on Binance, and its price further increased times. The current price remains around $2.
 What are Stablecoins and Collateralized Debt Platforms?
What are Stablecoins and Collateralized Debt Platforms?
Assets with stable value are an important part of Ethereum's applications and have grown into an asset class worth tens of billions of dollars. However, the vast majority of these assets are in the form of fiat-collateralized stablecoins, such as USDT and USDC.
Decentralized stablecoins such as DAI, sUSD, and LUSD represent only a small fraction of the total stablecoin supply, which means that the vast majority of stablecoins are centralized.
As collateralized lending platforms Liquity, MakerDao, and Synthetix allow holders to lock up volatile tokens in exchange for newly minted stablecoins. As a result, users can unlock the economic value and liquidity of their investments while maintaining their underlying assets.
What are the disadvantages of existing mortgage lending platforms?
High and unpredictable interest charges: Most platforms charge borrowing fees that accumulate over time. For example, MakerDao charged an annual interest rate as high as 20.5% in the summer of 2019.
High collateralization ratios due to inefficient liquidation processes: Existing platforms often require large overcollateralization of individual borrower positions.
Specifically, MakerDao’s ETH-B mortgage rate is 130%, ETH-A’s is 150%, and even Synthetix’s mortgage rate is 750%.
No direct redemption mechanism to ensure price stability: Stablecoins pegged to crypto assets are generally not redeemable at face value, and hard-pegged mechanisms cannot be guaranteed due to the lack of direct arbitrage opportunities.
Instead, the existing system relies on less efficient soft-pegging mechanisms that stabilize prices through indirect means. This suggests that crypto-backed stablecoins are generally more volatile than fiat-backed stablecoins.
Fortunately, the author here introduces a better lending protocol, Liquity, to readers. Combined with a deep understanding of the existing mechanism, Liquity proposes the following main advantages to improve the above problems: one-time settlement of interest, a mortgage ratio as low as 110%, and the stable currency mechanism of LUSD.
What exactly is Liquidity?
Liquity is a decentralized protocol that allows ETH holders to obtain maximum liquidity without paying interest.
After locking up ETH as collateral in a smart contract and creating a personal position called a “Trove,” users can gain instant liquidity by minting the U.S. dollar-pegged stablecoin LUSD.
Each Trove must be staked at least 110%. Any owner of LUSD can exchange LUSD for ETH at any time. The protocol maintains the stablecoin at $1 through a redemption mechanism and algorithmically adjusted fees.
Compared with other over-collateralized stablecoins, Liquity has several notable features:
1.Liquity only supports $ETH as collateral, and currently only supports the Ethereum network.
2. Although Liquity's borrowing rate is floating, its borrowing costs (interest) will be settled in one lump sum when users borrow money.
3. Liquity is fully supported by algorithms and contracts and operates independently. After the protocol is deployed, it cannot be modified, and the development team does not have relevant permissions.
How does Liquity realize the loan mechanism of one-time settlement of interest?
Liquity provides liquidity without charging borrowers interest, but the protocol charges borrowing fees as a one-time fee. This is a big relief for DeFi users who are often worried about skyrocketing interest fees. The change of interest rate during the loan period does not affect the loan interest, and the length of the loan cycle does not affect the loan interest. It is more conducive to the control of borrowing costs by long-term borrowers. And since then, DeFi users can use the stable currency LUSD for free to invest in other higher-yielding financial products in the DeFi market.
Liquity is fully supported by algorithms and contracts, and is deployed as a decentralized front-end
A great feature of Liquity is that its protocol is almost entirely managed by smart contracts, and the development team has no management authority over the relevant contracts.
Liquity also does not have its own interface, and is completely supported by third-party platforms. The purpose of this is to enhance the degree of decentralization of the protocol and reduce human intervention.
However, although Liquity's original intention is to allow third-party platforms to compete with each other and provide users with better services. But for now, the functions and product designs of each platform are different, and the overall user experience is not very good.
At the same time, for a platform controlled by a contract, the security of the code is particularly important. Liquity's contract code has been audited multiple times by 2 agencies (Trail of Bits and Coinspect) in 2021.
The content covered by the audit is relatively comprehensive, and the report shows that some risks have not been fixed. As of now, Liquity's contracts have not caused a security incident.
How to ensure security under the extremely low mortgage loan rate of 110%?
When the collateralization ratio of a single position falls below a certain threshold, the lending system must employ certain liquidation mechanisms to ensure a stable token supply is always supported.
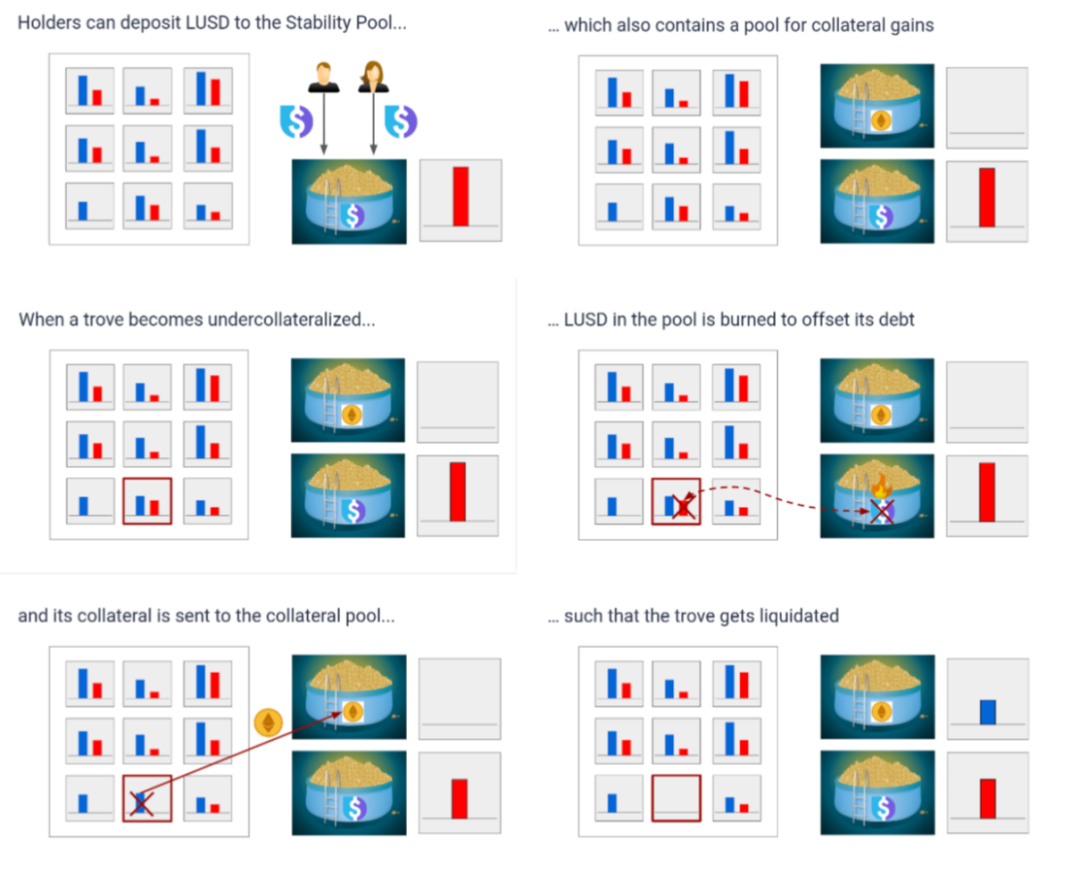
Liquity invented an unprecedented two-step liquidation mechanism based on the stability pool mechanism and the redistribution mechanism, which can immediately liquidate undercollateralized positions, called the stability pool mechanism.
The Stability Pool is the first line of defense in maintaining the solvency of the system. By providing liquidity, the Stability Pool is used to repay the liquidated Trove's debt, ensuring that the total supply of LUSD is always backed. When a Trove is liquidated, the LUSD corresponding to the Trove's remaining debt is burned from the balance of the stable pool to pay off the Trove's debt. In exchange, all collateral from Trove is transferred to the stability pool. The stable pool is funded by users depositing LUSD into it (called stable providers). Over time, stability providers lose a proportional share of their LUSD deposits while gaining a proportional share of liquidated collateral. Since Trove will likely be liquidated with a collateral ratio of just under 110%, stability providers will expect to receive a higher dollar value of collateral relative to the debt they repay. For example, if a Trove with $109 worth of ETH and 100 LUSD in debt is liquidated, 100 LUSD will be destroyed and the stable pool provider will receive $109 worth of ETH. Therefore, this expected return also motivates users to provide liquidity to the stable pool.
Let’s analyze the following figure as a specific example, where you can see the debt in red and the collateral in blue, we assume that this Trove is lower than 110%. Next, the system can burn LUSD equivalent to this Trove debt from the stable pool. In return for being burned, all collateral Ether in liquidated Troves will be sent to the Stability Pool and distributed proportionally to all depositors. Additionally, since liquidations occur when Trove collateralization is less than 110%, stable pool providers are likely to receive a net gain whenever Trove is liquidated. For example, if a Trove with $109 worth of ETH and 100 LUSD in debt is liquidated, 100 LUSD will be destroyed and the stable pool provider will receive $109 worth of ETH. )
 What happens if the stable pool is empty when liquidation occurs?
What happens if the stable pool is empty when liquidation occurs?
If the stable pool is empty, the system will use the reallocation mechanism. In this case, the system reallocates the debt and collateral in the liquidated vault to all other existing vaults.
The redistribution of debt and collateral is proportional to the value of the collateral in the receiver's vault. This means that Troves with high collateralization ratios will receive more debt and collateral from liquidated positions than those with lower collateralization ratios, ensuring that the system does not create cascading liquidations.
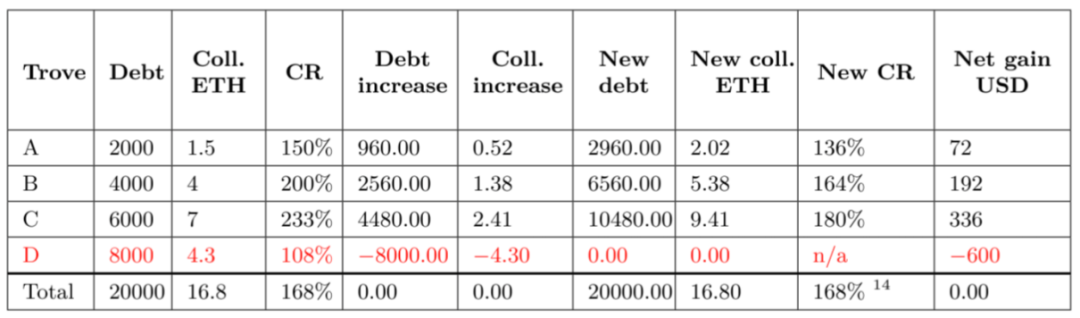
For example, this table shows that Trove D needs to be liquidated due to insufficient collateralization ratio and redistributed to A, B and C proportionally according to its share of collateralization ratio, where A gets new debt 8000*1.5/(16.8-4.3) = 960, and got a new collateral 4.3*1.5/(16.8-4.3) = 0.52
 What is the redemption mechanism?
What is the redemption mechanism?
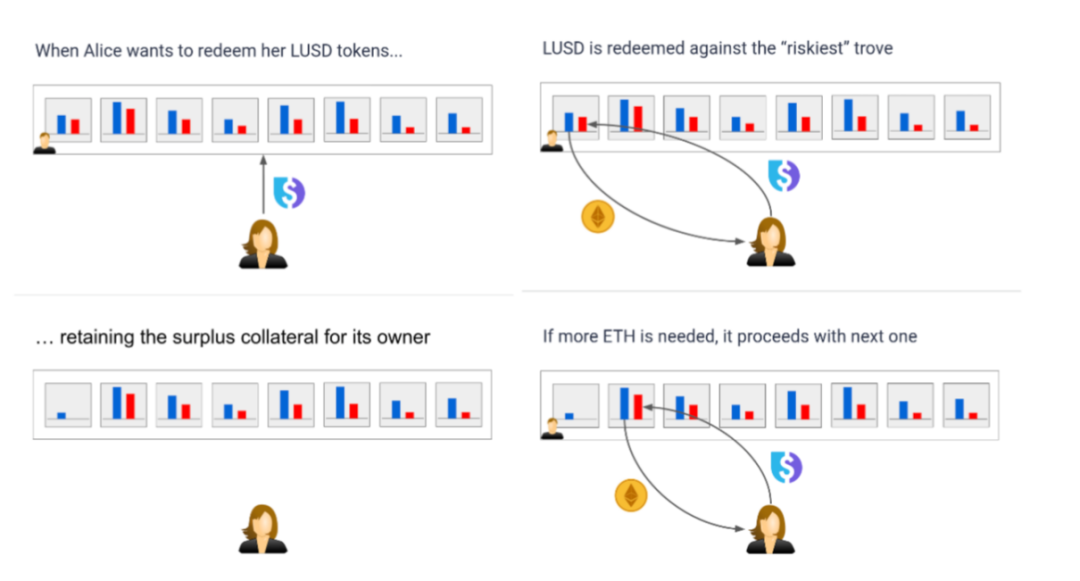
LUSD also has a stabilization mechanism called redemption. Redemption means that any holder of LUSD (whether obtained through collateralized borrowing or not) can exchange $1 LUSD for $1 ETH at any time.
This redemption will start with the riskiest position. When a redemption is initiated, the process occurs in several steps. All Troves are sorted from lowest to highest collateral ratio, i.e. from most risky to least risky.
The redeemed LUSD is used to repay the debt of the riskiest Trove(s) in exchange for their collateral. The remaining collateral of Trove owners is left with them.
If more ETH needs to be redeemed, the system will look for the next highest risk Trove. It can be seen that the redemption mechanism has a positive impact on the total collateralization of the system, and it increases the robustness of the entire system.
 And the base interest rate of the agreement will rise every time the user redeems, that is to say, the borrowing fee and the redemption fee will increase. On the one hand, it can avoid large-scale redemption, on the other hand, it can reduce borrowing, further promote $LUSD circulation reduction, and help currency price stability. However, $LUSD is more volatile in price compared to other stablecoins.
And the base interest rate of the agreement will rise every time the user redeems, that is to say, the borrowing fee and the redemption fee will increase. On the one hand, it can avoid large-scale redemption, on the other hand, it can reduce borrowing, further promote $LUSD circulation reduction, and help currency price stability. However, $LUSD is more volatile in price compared to other stablecoins.
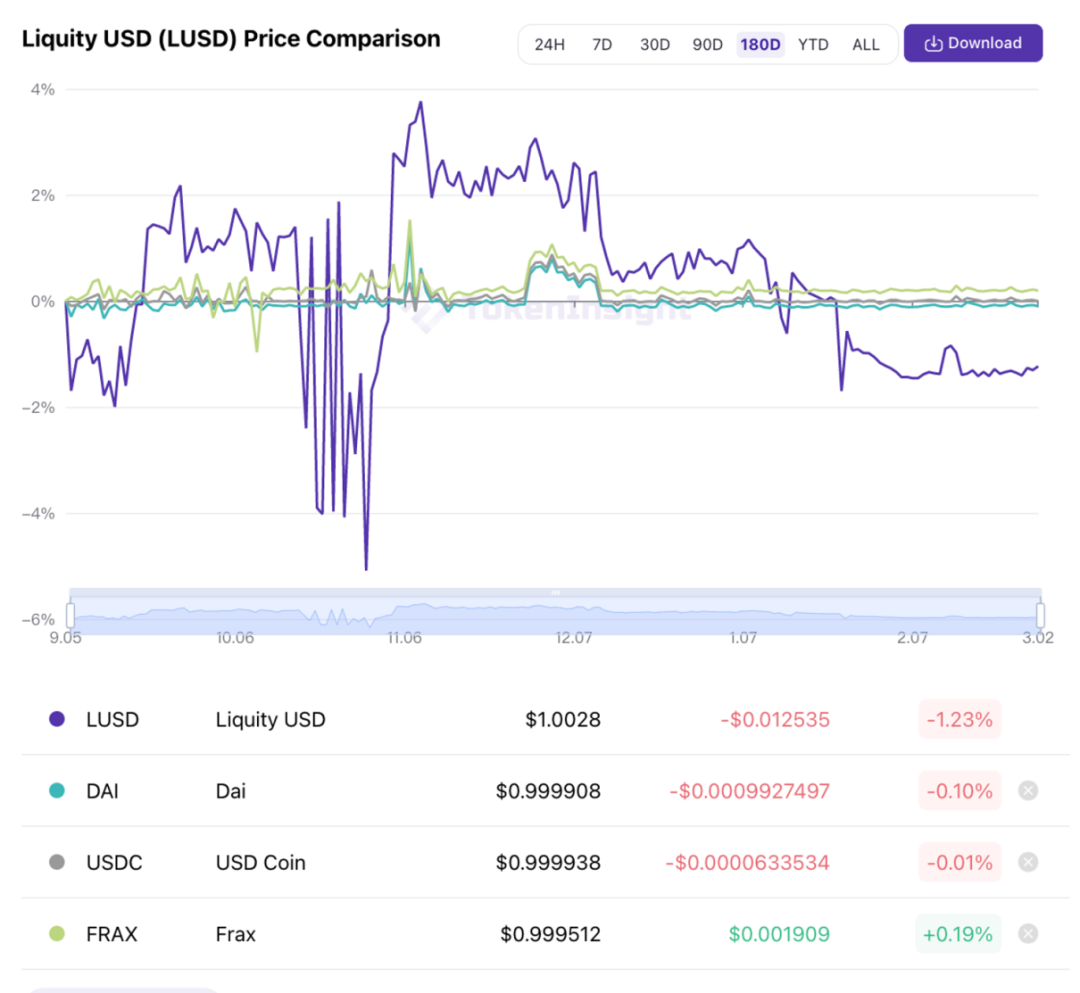 How is LUSD pegged to the US dollar?
How is LUSD pegged to the US dollar?
The upper and lower ranges of the stablecoin LUSD are guaranteed by two mechanisms: 1. The ability of LUSD to convert rigidly into ETH, that is, 1 LUSD can be exchanged for ETH worth 1 USD.
2. 110% minimum mortgage rate guarantee. They are all realized by a user-led arbitrage mechanism, which we call "hard hook mechanism".
Redemption creates a natural price floor. Whenever 1 LUSD trades below 1 USD, holders and speculators are incentivized to exchange 1 LUSD for 1 USD worth of ETH and sell ETH immediately.
Since the redeemed LUSD is destroyed, each redemption reduces the stablecoin's supply and increases its price.
Since the arbitrage robot can automatically trigger the redemption mechanism whenever there is an arbitrage opportunity, if the LUSD:USD exchange rate falls below 1 USD, it will quickly recover, thus forming a floor for the price.
The 110% minimum collateralization ratio creates a natural price ceiling of $1.10. When the LUSD:USD exchange rate exceeds this level, arbitrageurs can make an instant profit by borrowing the maximum amount against their collateral and selling LUSD in the market for more than $1.10.
For example, if 1 LUSD is trading at $1.11, an arbitrageur could lock up $110 worth of Ether, take out a loan of 100 LUSD and sell it for $111. Regardless of whether the arbitrageur's loan is liquidated, the arbitrage gain of $1 is obtained.
 Summarize
Summarize
Liquity itself has a high degree of decentralization, the protocol is fully supported by contracts, and the community and development teams have very little intervention in the protocol itself.
However, it also has some shortcomings in user experience. Since Liquity does not have its own front-end, the front-ends developed by third parties have different shapes and functions, which may cause some inconvenience in use.
Mechanistically, Liquity only supports $ETH collateral, and only charges a one-time loan fee. Compared with Maker's multi-collateral and multiple interest rate models, it has more advantages.
Moreover, LUSD is not as stable as other stablecoins in terms of price stability, and has higher volatility. Although it is managed and operated by the contract, Liquity's contract has not had any security issues and has continued to operate stably. But at present, its ecology is relatively weak, and the usage scenarios of tokens are not rich enough.
In the future, as the industry pays more attention to decentralization, the recognition of this agreement may gradually increase, which will also have a positive effect on ecological development.








