The 10 stablecoins in this report include: crvUSD, GHO, LUSD, USDT, USDC, UST, DAI, FRAX, MIM, FEI.
Author: DODO Research
Cover: Photo by vackground.com on Unsplash
Foreword:
In 2022, DODO Research released the research report "Liquidity is Not Everything: 10 Stablecoin Projects from an Overall Perspective", and proposed a comprehensive analysis framework for stablecoins, comprehensively analyzing from four aspects: assets, liabilities, liquidity, and usage scenarios stablecoin projects, and analyzed 10 stablecoin projects using this analytical framework.
In mid-2022, after the collapse of Luna (UST), the stablecoin track experienced a period of silence, and the entire stablecoin track also fell with the market. On March 11, 2023, the USDC de-anchor triggered by the SVB crash once again impacted the entire encryption market. As the basic unit of account and basic collateral of the entire DeFi, USDC's de-anchor caused market panic and a large number of pricing distortions, and the market experienced a serious liquidity crisis.
As the Federal Reserve launched the BTFP tool to inject a large amount of funds into the banking system, the US Treasury provided 50 billion US dollars in credit, SVB depositors were protected, and the USDC anchor was restored. Although the crisis has come to an end, the risk of the US banking system is a sharp sword hanging over the heads of every financial participant. The haze has not really dissipated. Taking this opportunity, we have updated the dynamics of the top projects according to the comprehensive analysis framework of stablecoins, including asset and liquidity analysis, etc., and added Curve stablecoins and AAVE stablecoins to our list. Analysis of CoinGHO.
The 10 stablecoins in this report include: crvUSD, GHO, LUSD, USDT, USDC, UST, DAI, FRAX, MIM, FEI.
content update
Note: The yellow part in the background of this article is the content updated in March 2023, and the rest is the content in May 2022.
Analysis of Curve stablecoin, AAVE stablecoin GHO and LUSD.
In the centralized stable currency, update the relevant analysis and data on USDT and USDC.
In the decentralized stable currency, update the relevant analysis and data of DAI and Frax.
Removed stablecoin projects Float, AMPL, ESD.
introduction
In May, Luna crashed and UST broke its anchor sharply, impacting the already sluggish market. Numerous agreements have been liquidated, and the stablecoin market has suffered short-term shocks. According to data from Coingecko and Defillama, the total market value of stablecoins fell by 5.34% after the Luna crash, and DeFi TVL dropped by 43%. The market fluctuated violently. It was not until the smoke cleared that people realized that the asset side of the stablecoin project was so important.
Looking back, people found that the previous steady-state projects were almost all lame giants built on unsustainable credit expansion. The integrity of the stablecoin project was selectively ignored by people. After all, people at that time believed that assets could be created out of thin air based on expectations, and extreme liquidity crises only existed in assumptions, and people were immersed in the high leverage brought about by credit expansion. However, the bloody reality woke people up, and the run began to happen, and the assets were not paid enough.
TL;DR
- It is necessary to examine the stablecoin project from an overall perspective, and analyze it from four aspects: assets, liabilities, liquidity, and usage scenarios. The asset structure determines the solvency of the stablecoin project, the liability structure determines the repayment structure of the stablecoin project, the liquidity mechanism reflects how to achieve short-term stability, and the usage scenario is the root of people's demand for stablecoins.
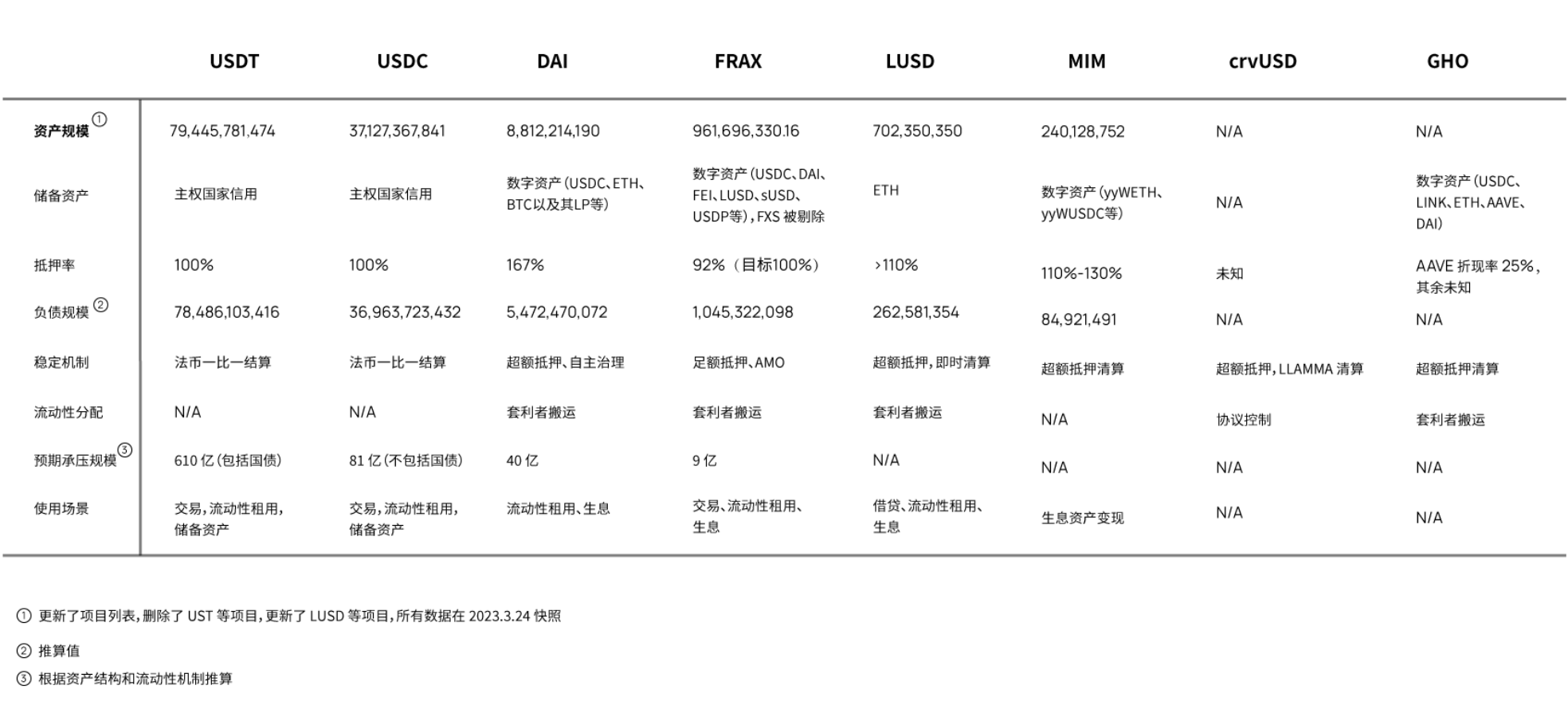
- Both USDT and USDC have the ability to withstand the exchange of tens of billions of dollars in a short period of time, but in comparison, USDC has a more stable asset structure and a stronger ability to deal with extreme liquidity crises.
- The deep reason for UST's collapse is that the market value of expected assets (Luna) cannot reflect the real cash value, and the asset structure is seriously unbalanced. At the same time, the liability structure is deformed, 75% of the liabilities are absorbed by Anchor, and the usage scenarios are limited to the interior of the ecosystem.
- DAI's reserve assets are very stable and diversified, and it still claims to be the safest decentralized stable currency. However, as a trading pair settlement asset, there is still a big gap from USDC. The deposit rate provided by MakerDAO to users is also often criticized, and the subjective initiative of users to hold DAI is also insufficient.
- FRAX's asset structure is very stable compared to UST, and will shift to full mortgage in the future.
- The selection of assets is crucial to stablecoin projects, and assets with higher volatility should correspond to higher mortgage rates. Between capital efficiency and stability, stability should be given priority.
- For projects that rely on market arbitrage to maintain stability, the arbitrage mechanism may fail under extreme market conditions, and relying on the protocol itself to manage liquidity is inefficient.
- Unsecured stablecoins have proven unable to support their debt issuance for a long time, and will eventually turn to fully collateralized stablecoins.
Four Dimensions of Analysis for Stablecoin Projects
Stablecoins can never only look at innovations in liquidity, but must be viewed from a holistic perspective. Assets guarantee redemption, liabilities determine the repayment structure, liquidity management ensures that stablecoins can withstand short-term shocks, and usage scenarios are the source of expansion. Extreme prominence in one aspect may lead to rapid expansion in the short term, but as long as there is a shortcoming in one aspect, it will declare long-term demise.
Stablecoin projects should take into account assets, liabilities, liquidity and usage scenarios. Only a far-sighted design can make the stable currency project go further. The seemingly simple asset and liability side is exactly what people ignore, and the design complexity and design options of the asset and liability side are very deep and wide, and the design of liquidity management cannot be limited to disguised leverage. The payback period should be considered, and the use scenario is the starting point of the project. The team's own resource endowment and historical conditions should be considered comprehensively, and efforts should be made to seize historical opportunities.
This article will analyze 10 representative stablecoin projects from the four dimensions of assets, liabilities, liquidity and usage scenarios. Before the specific analysis, the assets, liabilities, liquidity and usage scenarios are respectively summarized, and some concepts and frameworks are clarified.
assets
The asset side is a key point of the stablecoin project. On the asset side, it is necessary to pay attention to the selection of reserve assets, the proportion of each asset, and the mortgage rate.
These elements constitute the asset structure of a stablecoin project.
Reserve assets refer to valuable assets used by the project to support stable currency redemption. Multicoin Capital mentioned in the 2018 stablecoin overview that the reserve assets of stablecoins include fiat currency, seigniorage stocks and digital assets. Dimitrios Koutsoupakis argued in his 2020 paper that reserve assets include sovereign state credit, token assets within the ecosystem, and token assets outside the ecosystem. Combining various literatures, we believe that there are four categories of reserve assets:
Sovereign country credit: The credit currency issued by sovereign countries is legal currency, as well as traditional financial assets denominated in legal currency, such as money market funds, commercial paper, corporate loans, treasury bonds, and large-denomination certificates of deposit. Digital assets mortgaged by fiat currencies such as USDT and USDC are regarded as sovereign national credit.
Physical assets: precious metals and physical commodities that can be delivered, such as gold, silver, oil, natural gas, etc.
Digital assets: Decentralized digital currencies with a certain market value and liquidity running on the blockchain, as well as derivative tokens and interest-earning assets that can be exchanged for digital currencies, such as BTC, ETH, WETH, etc.
Anticipatory digital assets: the project’s native token or seigniorage share (Seigniorage Share), the transaction price is formed by the market, and is greatly affected by expectations, such as Luna, FXS
Due to the different volatility and liquidity of various assets, different asset ratios have different solvency. The mortgage rate needs to adapt to the selection and proportion of assets. On the whole, the mortgage rate of high-volatility assets is high, and the mortgage rate of low-volatility assets is low. Since most stablecoin projects are not a single asset, it is very important to adjust the asset ratio and choose an appropriate mortgage rate. The capital structure is very important, it can reflect the solvency of the project, its ability to withstand pressure under extreme market conditions, and support for expectations.
debt
The liability side is all the outstanding purchasing power issued by the stablecoin project, which is the sum of the value of all stablecoins in circulation.
Liability structure includes liability scale and circulation distribution.
Liabilities are stablecoins in circulation. For a stablecoin project, how to expand liabilities, which protocols can be accessed, risk geometry, how to balance the debt repayment structure, how to stabilize the speed of liability expansion and the structure of the liability side are all important issues. is something to consider.
The scale of liabilities is easy to check. The data on the chain can be traced and traced, and the distribution of stable coins can be accurately seen. However, since the development of DeFi is still in its early stages, a large number of chip exchanges are still concentrated on centralized exchanges, and some centralized agreements will also absorb stablecoins. Therefore, it is impossible to accurately describe the liability structure at this stage, and we can only judge Approximate distribution.
At this stage, the analytical significance of the liability structure lies in identifying outliers and extreme imbalances . Although the circulation distribution cannot be accurately obtained, the abnormal changes of a certain agreement and the extremely unbalanced ratio structure can be captured. Through early warning, the source of risk can be predicted, and timely adjustment can avoid risks.
fluidity
Liquidity refers to the ease of cashing out stablecoins . Liquidity management includes stabilization mechanism and liquidity allocation.
The extreme stress test can predict the scale of a run that a stablecoin project can withstand under extreme circumstances.
Innovation in liquidity was the focus of the stablecoin project in the last period. Various stablecoin mechanisms were developed and put into experiments. These projects provide valuable experience and data for latecomers, especially the debacle of Luna. We believe that in terms of stabilization mechanisms, they can be divided into two categories:
- One-to-one fiat currency settlement: In theory, users will automatically mint and destroy Tokens when depositing and withdrawing funds. In practice, they will mint and destroy Tokens in batches in a buffered manner. Fiat currency collateral projects such as USDT and USDC use this method.
- Calculation stability mechanism: Calculation stability mechanism emerges in an endless stream. In practice, the mainstream ones are as follows:
Seigniorage stock mechanism: The value of stablecoins in the protocol is fixed and can be exchanged for native tokens of equivalent projects. Stabilize market prices through arbitrageurs.
Protocol Controlled Assets: Smart contracts control assets and directly regulate the trading pool in the market.
Over-mortgage liquidation: Deposit collateral into the agreement according to the over-collateralization rate, and liquidate when a certain ratio is reached.
There are two main types of liquidity allocation. Allocation to arbitrageurs or the agreement directly interacts with the trading pool. Relying on the market behavior of arbitrageurs can improve efficiency, but facing the risk of losing control under extreme market conditions, direct additional issuance by the agreement will face security risks and efficiency issues.
scenes to be used
The usage scenario is the crux of all current stablecoins and the source of expansion of stablecoin projects.
The demand for stablecoins fundamentally comes from usage scenarios. The current penetration rate of traditional payment scenarios is low, but we can focus on the future.
The currency issued by a sovereign state has its own usage scenarios, and commodity transactions, settlements, and credit expansion within a country are all guaranteed by legal coercion and government coercion. In the world of web3, no one stipulates what protocol you use, and there is no entity large enough to monopolize the vast majority of users, and no protocol can open up a sovereign state-level offline usage scenario. Therefore, it is very difficult to choose what usage scenario to use. To a large extent, it determines the growth space of a stable currency project.
We believe that the stablecoin project can be connected to a certain subdivision scene first, and then expand, and the biggest historical opportunity in the future lies in the value exchange of the virtual world. With the development of DID, Gamefi, and metaverse, the usage scenarios of stablecoins will be outbreaks, and these scenarios are unfamiliar battlefields for fiat currencies.
Next, we will analyze 10 stablecoin projects from an overall perspective, starting with USDT and USDC collateralized by fiat currency.
overall comparison
crvUSD
assets
crvUSD has not disclosed the choice and structure of its reserve assets. Considering the design mechanism of the white paper, BTC, ETH, and CRV are all potential choices.
debt
According to the white paper design of crvUSD, the issuance of crvUSD, that is, the total amount of liabilities, will mainly depend on the amount of collateral, while the structure of liabilities will depend on the distribution of usage scenarios after release.
fluidity
liquidity management
The core innovation of crvUSD is to propose a new liquidity management method, the LLAMMA mechanism. Different from the normal mechanism of setting a fixed point to liquidate the collateral, LAMMA can gradually liquidate the collateral and replace it with USD assets when the price of the collateral drops, instead of liquidating the collateral after falling to a certain liquidation price.
This design allows the collateral to liquidate more value when the price drops, making the entire system more stable.

crvUSD is still an over-collateralized stablecoin project, and there are still problems with the decline in the value of collateral and the unanchoring of stablecoins.
crvUSD burns stablecoins when there is insufficient value to maintain the peg.
scenes to be used
The potential largest usage scenario of crvUSD comes from Curve itself. On the chain, Curve locks a large amount of stablecoin liquidity and collateral.
Users pledge their collateral to mint crvUSD, and crvUSD itself can easily access the liquidity of other stablecoins.
GHO
assets
GHO is an overcollateralized decentralized stablecoin. According to the disclosed information, the reserve assets supported by GHO include ETH, AAVE, LINK, DAI and USDC.
According to the latest proposal, the mortgage rate of the native token AAVE is 400%, and the proportion of the total reserve assets cannot exceed 25%.
The discount rate and key parameters are determined by AAVE DAO.
debt
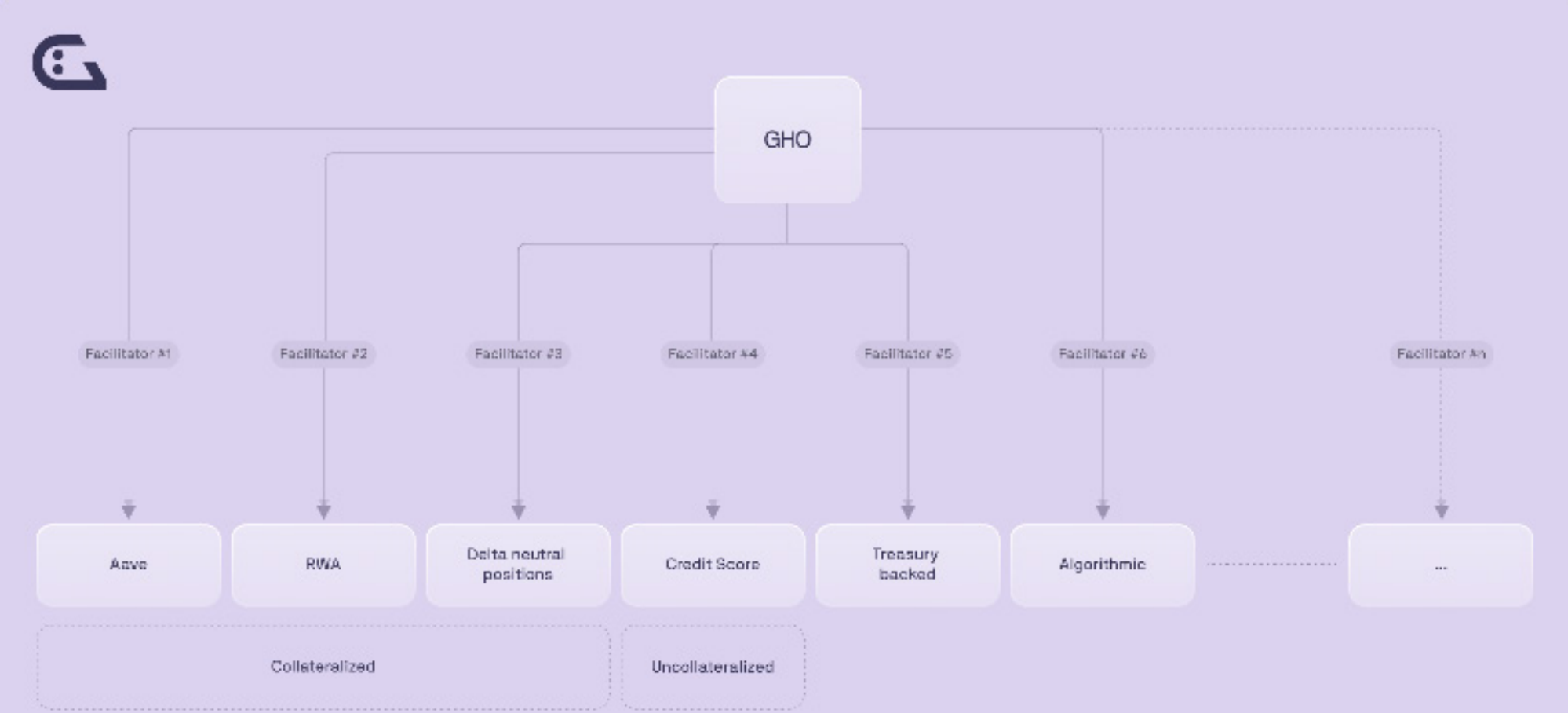
Both the minting and burning of GHO are performed by the issuer (Facilitator). Although there is an issuer, the rules for minting and destroying GHO by the issuer are open and transparent on the chain, and the access of the issuer and the upper limit of the total issuance Determined by AAVE DAO.
GHO itself cannot be used as a mortgage asset in AAVE, which prevents GHO from being loaned out in AAVE. The minting of GHO will be mainly based on user needs.
Currently AAVE DAO has approved two issuers, AAVE V3 Ethereum Pool and Flash Minter.
GHO's issuer plan is as follows, covering mortgage issuance to unsecured issuance. The advantage of this design is that AAVE provides a framework for the issuance of stablecoins, and other entities can apply to become issuers, which can give full play to the advantages of each issuer in their asset field to support the issuance of stablecoins.
fluidity
stabilization mechanism
GHO is hard anchored to the US dollar at 1:1. If the market value of GHO is unanchored, arbitrageurs can quickly smooth out the price difference. If the market price of GHO is higher than $1, arbitrageurs can mortgage assets to lend GHO, then sell GHO in the market, return the loan, and complete the arbitrage, making the market price of GHO drop, and vice versa.
scenes to be used
The biggest potential usage scenario of GHO is still AAVE itself. Although AAVE prohibits GHO as a collateral asset, the same effect can still be achieved by exchanging other stablecoins in the market. AAVE will become a usage scenario of GHO in disguise in this way.
LUSD
assets
asset structure
Since LUSD only allows users to use ETH as collateral, the asset structure of LUSD is very single, all composed of ETH.
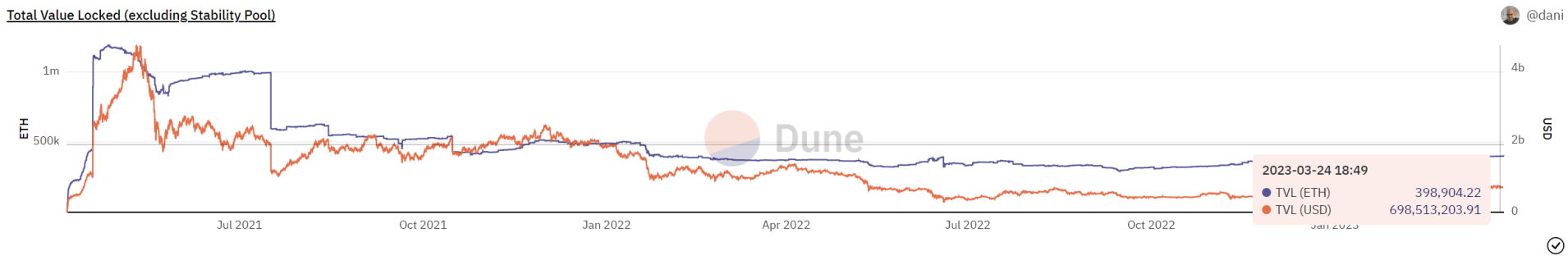
asset analysis
At present, the average mortgage rate of LUSD is relatively high. There are nearly 700 million US dollars of ETH as reserve assets, supporting the issuance of 260 million US dollars of LUSD, with an average mortgage rate of 269.6%. Even considering extreme market conditions, with the asset quality of ETH and the mortgage rate at this level,
It can also be considered that LUSD's reserve assets are sufficient. Combined with its innovative approach to liquidity management, there is less risk of LUSD de-anchoring.
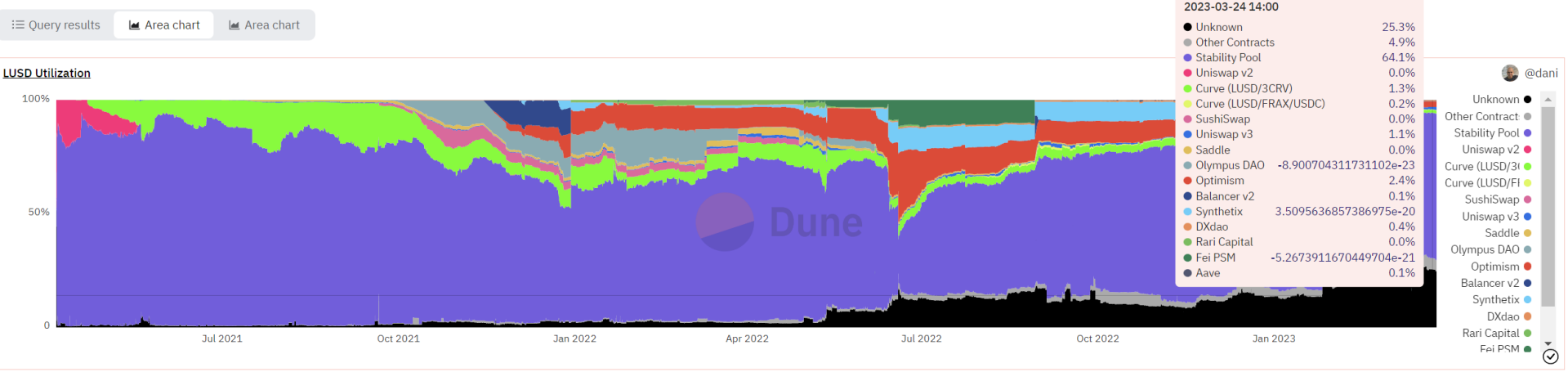
debt
liability structure
64.1% of the issued LUSD is deposited in the Stability Pool. This part can obtain the income from the liquidation of mortgage assets, and it is also an important part of maintaining the anchor of LUSD.
The role of the Stability Pool is detailed in the Liquidity section. The remaining LUSD is basically stored in the liquidity pools of major DEXs, and there are fewer CEXs.
There are still 25% unknown, part of which is passively held by users, and the proportion of the unknown part is increasing, especially after USDC is unanchored, the holding of LUSD has increased.
After USDC is unanchored, the market wants to find a stable currency with a high degree of decentralization and sufficient reserve assets, and LUSD is currently a project that is more in line with market demand.
Liabilities Analysis
Most of the issuance of LUSD is used to obtain asset liquidation income, and has not entered circulation. This actually leads to a problem, that is, LUSD has a small depth and poor liquidity in DEX, which is not good for expanding usage scenarios. The proportion of passive holdings has increased, and the proportion is second only to the Stability Pool, which shows that LUSD has considerable hedging properties and meets part of the market's demand for hedging decentralized stablecoins.
fluidity
liquidity management
LUSD's liquidity management is based on its unique clearing and redemption mechanism, thereby achieving anchoring.
liquidation mechanism
Each user mortgages ETH to form a treasury (Trove). When the mortgage rate of the treasury drops to 110%, the treasury will be liquidated, the mortgage assets will be attributed to the Stability Pool, and the corresponding amount of LUSD in the Stability Pool will be destroyed. This will cause the Stability Pool to obtain the mortgage assets, the user will suffer a 10% asset loss, the corresponding amount of LUSD will be liquidated immediately, and the LUSD will remain anchored.
When the LUSD in the stable pool is liquidated, a debt redistribution mechanism will be triggered. The protocol will sort the positions from high to low risk, and then allocate the loans and collaterals of high-risk positions to low-risk positions one by one.
This unique liquidation mechanism encourages users to deposit LUSD into the Stability Pool, because users can get benefits from asset liquidation, and it also encourages users to choose a higher mortgage rate when mortgage assets, because a lower mortgage rate will make the vault's Collateralized assets are more easily liquidated. And encourage users to increase the mortgage rate to reduce the risk of their own positions, because when the Stability Pool fails, the collateral of high-risk positions will be liquidated first.
redemption mechanism
LUSD can be redeemed for $1 worth of ETH at any time, which forms an arbitrage mechanism. When the market value of LUSD is lower than $1, arbitrageurs buy LUSD in the market, redeem $1 of ETH in the agreement, complete the arbitrage, and the price of LUSD rises to $1. Liquity will charge a redemption fee when redeeming, and its calculation formula is base rate * redeemed ETH. It increases with each redemption, but decrements over time if no new redemptions occur. The purpose of this is to limit large redemptions with higher fees, and limit borrowing directly after large redemptions.
Risk Management Mechanism
Liquity also employs a risk-tiered management mechanism. First, Liquity uses the mortgage rate of the entire agreement to measure the overall risk level. When the total mortgage rate of the entire agreement is greater than 150%, it is low risk, and less than 150% is high risk. When the risk is low, the user will not be liquidated as long as the mortgage rate of the position is greater than 110%. When the risk is high, those with a mortgage rate less than 150% are at risk of being liquidated, and users also need to ensure a mortgage rate greater than 150% when opening a new position until the agreement returns to low risk.
Liquidity extreme stress test
The liquidity pressure of LUSD can be measured by two key indicators, ETH price and the overall mortgage rate of the agreement. Based on the current asset status and total mortgage rate, that is, when the price of ETH is around 1800 and the total mortgage rate is 269%, when ETH falls to around US$1,000, the overall mortgage rate of the agreement will drop to about 150%, and it will continue to decline. This makes the agreement enter a high-risk state. In a high-risk state, liquidation will become more frequent, which can be regarded as a tight liquidity.
scenes to be used
At present, the usage scenarios of LUSD are relatively scarce, and there are only two main usage scenarios, one is to deposit LUSD into the Stability Pool to earn the proceeds from asset liquidation, and the other is to passively hold to reduce risks.
USDT
USDT Compared with our observation on May 10 last year, the biggest change is the change in asset structure.
The circulation of USDT once fell to 65 billion US dollars in December last year, and the current circulation is 76.1 billion US dollars, which is not much different from last year when the article was published. When USDC was unanchored, the amount of USDT minted increased significantly.
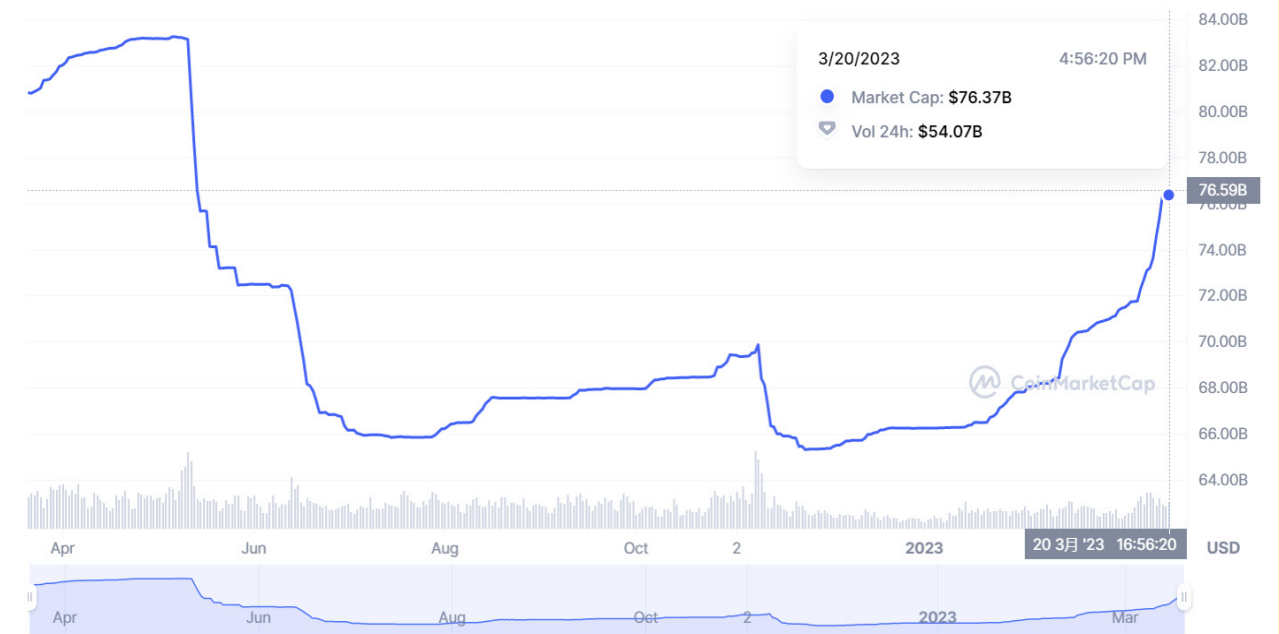
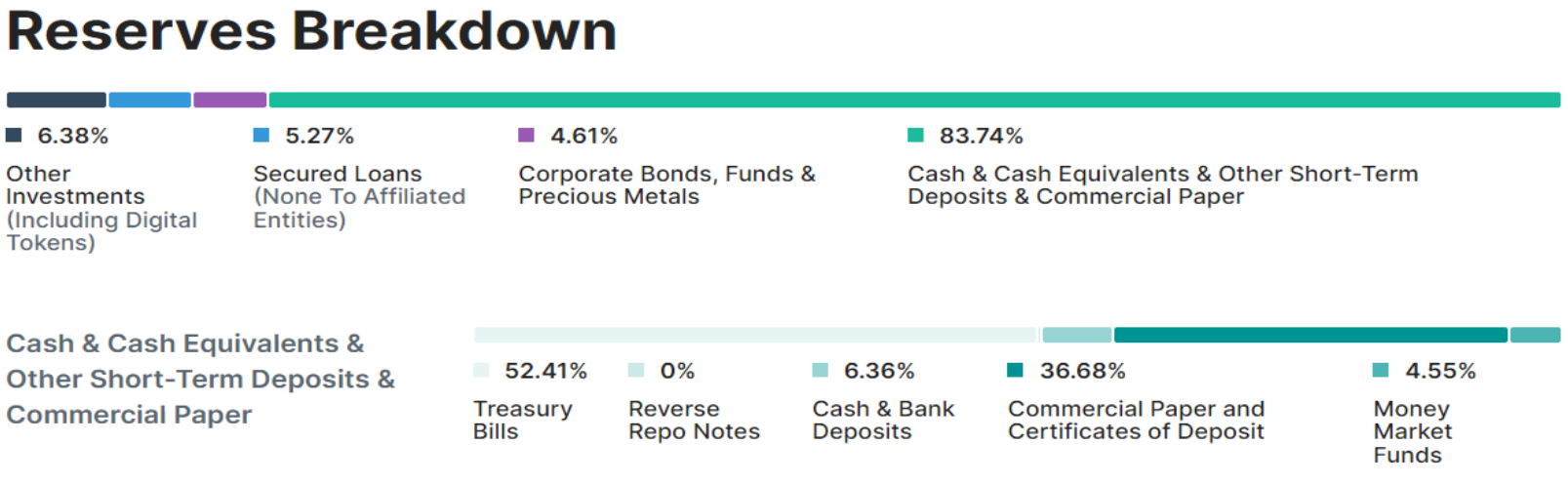
It can be seen that in the USDT reserve assets, the proportion of cash and its equivalents has not changed much, but the structure of cash and its equivalents has changed significantly, commercial paper has been emptied, and the proportion of money market funds has increased significantly, from 4.55% to 13.39% %, the proportion of US national debt has also increased significantly, from 52.41% to 71.25%.
Due to the improvement of asset structure, USDT's ability to deal with runs has been enhanced, and in extreme cases, it can handle a run of about 55 billion US dollars.
But at the same time, because the USDC incident exposed the risks of centralized stablecoins on the traditional financial side, USDT actually faces the same problem.
That is, the asset impairment risk and liquidity risk caused by the banking crisis.
The liability side has not changed significantly, and the main usage scenarios of USDT are still transactions and as a fiat currency deposit and withdrawal channel.
assets
asset structure
Since LUSD only allows users to use ETH as collateral, the asset structure of LUSD is very single, all composed of ETH.
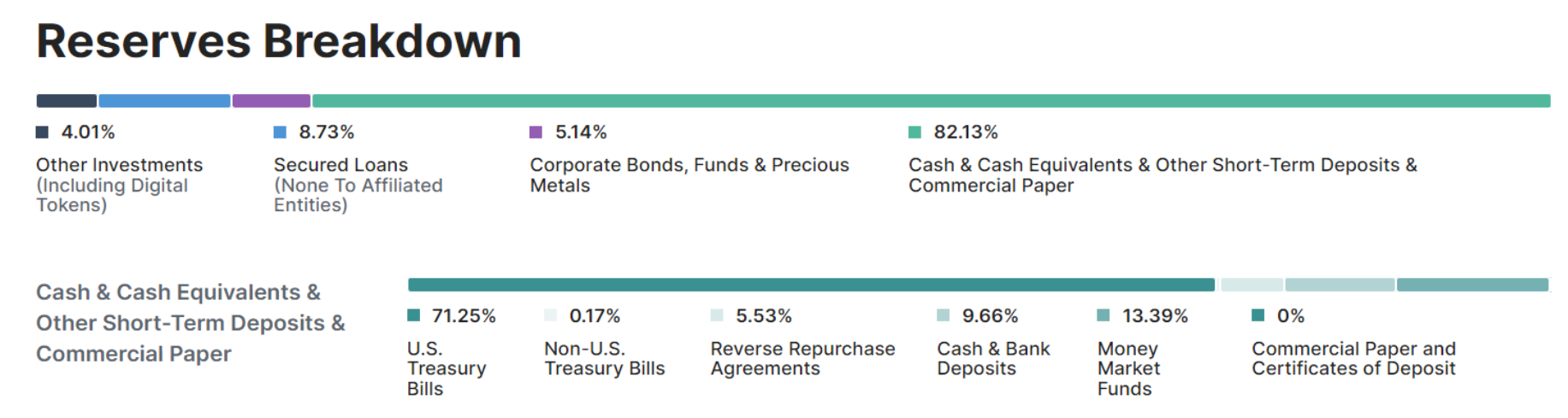
The asset structure of USDT is shown in the figure above. There are more than 80% of cash and its equivalents. This part includes about 50% of U.S. Treasury bonds, about 10% of monetary funds and cash, and about 35% of commercial paper and certificates of deposit. About 5% of assets are corporate bonds, funds and precious metals, about 5% of assets are loans, and about 5% of funds are used for investment. As of May 16, the total asset scale was around 76 billion.
features
On the whole, USDT assets are almost all denominated in legal currency, and legal currency represents the credit of a sovereign state. But from a structural point of view, there are differences in subdivided assets, liquidity, quality, etc. U.S. treasury bonds, cash, and money market funds are among the most liquid parts, which account for about 50% of the total assets. The yield is relatively low, but the quality is the highest. The other parts are used by Tether to make profits, and the liquidity and security are slightly lower. Among the overall assets, the most risky one is commercial paper. The structure is very similar to the asset structure of a commercial bank. A large part of Tether's profit comes from holding US treasury bonds, commercial paper, issuing loans and investing income.
Tether's asset structure has changed a lot compared to 21 years. The biggest change is that the proportion of commercial paper has dropped significantly, from 60% to about 30% now, and more of it has been replaced by government bonds and money market funds.
The mortgage rate of USDT is 100% mortgaged by legal currency, which is a fully mortgaged stable currency.
asset analysis
USDT is a centralized stable currency project. The biggest advantage in terms of assets is that it holds relatively high-quality assets in traditional finance. While maintaining asset liquidity, it can continue to bring benefits through the mature market of traditional finance. This part can fully support the entire team. But Tether’s biggest risk also lies in its centralized management and asset thunderstorms. We can see that commercial paper, investment, loans, and corporate bonds, these risky assets, account for a total of 47.14% of the total assets. In times of liquidity crisis and local credit crisis, the risk of insolvency becomes higher. Moreover, Tether has not disclosed the bad debt rate of its high-risk assets, etc., which is somewhat opaque.
debt
liability structure
Tether's liabilities are mainly USDT in circulation, among which USDT issued on TRON and ETH is the largest, accounting for about 90% of the total.
These liabilities exist in various forms in exchanges, smart contracts and personal wallets.
Liabilities Analysis
Tether's liabilities are not many in DeFi. Tether's usage rate in DeFi scenarios is lower than that of USDC, so a large part of the liabilities are concentrated in transaction scenarios. Therefore, such a liability structure requires Tether to do a good job in liquidity management. Provide sufficient liquidity.
fluidity
liquidity management
The stable mechanism of USDT is one-to-one settlement with legal currency, as shown in the figure below. But in terms of specific operations, Tether does not issue USDT continuously, that is, there is a time lag between when Tether receives the payment and when it issues new USDT. Mining USDT usually involves casting a large amount of USDT at one time, and the issuance also needs to go through an authorization process.
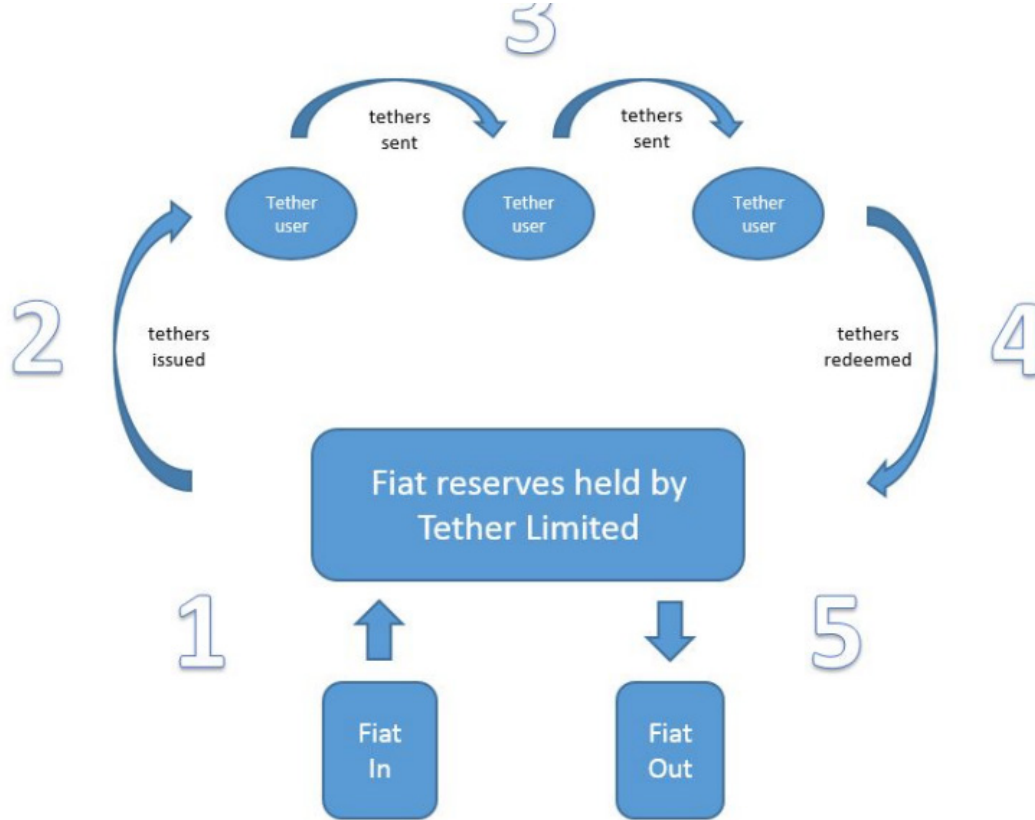
The process of USDT redeeming fiat currency, for Tether, is the process of responding to user withdrawals. Tether responds to withdrawals, first of all through its most liquid assets, bank deposits and monetary funds, this part is about 10%, which can meet a large number of short-term withdrawal needs, and secondly, the liquidity of US treasury bonds is slightly less liquid, this part accounts for about 40% , Under extreme market conditions, there is a risk of asset depreciation in the face of a market liquidity crisis. Other assets have poor liquidity and are difficult to realize in the short term. Secondly, Tether has also set up a shareholder capital buffer to deal with a large number of short-term withdrawal needs, which is about 160 million.
In terms of liquidity distribution, Tether directly distributes liquidity to users who make deposits through its contracts. New tokens are issued to the market in this form. Tether has a USDT buffer. When USDT is insufficient, new USDT will be minted and put into the market superior.
Liquidity extreme stress test
Let's consider, USDT can bear the run limit under extreme market conditions, USDT's assets can be redeemed immediately, 10%, about 8 billion. The spot trading volume of the U.S. treasury bond market is more than 500 billion U.S. dollars. If there is no major problem in market liquidity (the U.S. treasury bond has only flashed three times in the past), we can assume that Tether’s U.S. treasury bond can be liquidated quickly. It is about 38 billion, plus the previous 8 billion in cash, basically can cope with the cash-out scale of 44 billion US dollars in the short term.
Superimposed panic factors, there has never been a run of more than 50% in history, so it can be considered that USDT can maintain sufficient liquidity under extreme market conditions.
scenes to be used
The biggest usage scenario of USDT is digital currency transactions. According to data from the data analysis platform Nansen, seven of the top ten addresses on ETH are exchange addresses, including six centralized exchanges and one DEX (Curve), while USDT is used in other scenarios other than digital currency transactions. The performance is weak, especially in the proportion of DeFi applications, which is significantly lower than that of USDC. USDT is also an access object for the liquidity of other stablecoins, that is, an anchor for other stablecoins, and has also become a reserve asset for some stablecoin projects.
USDC
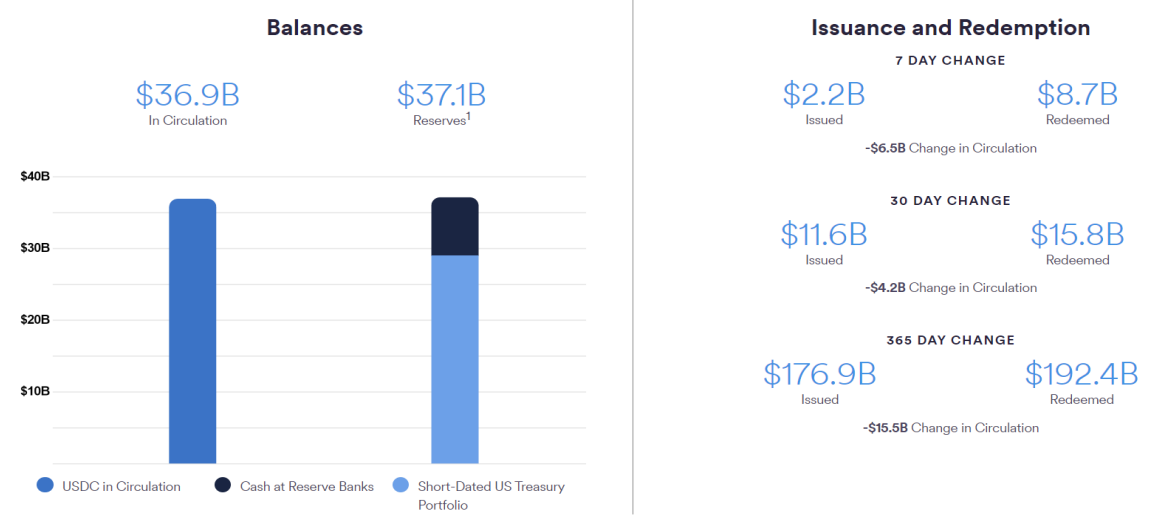
Compared with last year, USDC's circulation has dropped significantly, and it has experienced the SVB incident, the most serious unanchor in history.
The circulation of USDC on May 10 last year was about 50 billion US dollars, and now the circulation of USDC has dropped to 36.9 billion US dollars, and a large amount of USDC has been redeemed into legal tender.
After the unanchor event, the circulation of USDC has been decreasing, and currently there is no tendency to stabilize.
The asset structure of USDC has also changed to a certain extent. Its asset reserves are all composed of bank deposits and short-term US treasury bonds. There are currently 8.1 billion bank deposits, accounting for 21.95% of the total assets.
USDC has suffered a large number of redemption and withdrawals recently, and there is no problem in itself. However, the risk comes from whether Circle’s deposit bank supports a large amount of cash withdrawals and whether there is any liquidity problem. This belongs to the category of traditional finance. Therefore, we can only assume that USDC can handle almost all demand for redemption.
assets
asset structure

The last time USDC disclosed its asset structure was in May 2021. As shown in the figure above, it can be seen that Circle's asset structure is significantly different from Tether's.
Circle’s calculation of cash and its equivalents does not include U.S. Treasury bills, certificates of deposit and commercial paper, only bank deposits and money market funds, all of which are instantly redeemable.
The proportion of Circle's cash assets is as high as 61%, while Tether's bank deposits plus money market funds are less than 10%. Large-denomination certificates of deposit accounted for 13%, U.S. Treasury bonds accounted for 12%, commercial paper and corporate bonds accounted for 14%, and other assets accounted for only 0.2%.
features
The asset characteristic of USDC is that highly liquid cash assets account for a high proportion, while high-risk corporate bonds and commercial paper account for only 14%. Part of Circle's investment business is implemented by its holding SeedInvest, which uses USDC to invest in projects.
The mortgage rate of USDC is 100% mortgaged by legal currency, which is a fully mortgaged stable currency.
asset analysis
USDC's high proportion of cash assets enables it to cope with a large number of short-term withdrawal needs, which helps to stabilize expectations and prevent runs, and the asset structure is relatively reasonable. There may be very little liquidity crisis in USDC, because its cash ratio is much higher than that of commercial banks, and it can cope with a large number of cash withdrawal needs in a short period of time. But at the same time, Circle's asset structure is not regularly disclosed, and it still faces problems in transparency, which is unavoidable for centralized stablecoin projects.
debt
liability structure
The current circulation of USDC is about 50 billion U.S. dollars, which exists in exchanges, smart contracts and personal wallets in various forms. However, USDC and USDT are structurally different. USDC’s locked positions in major DEXs It is about 2 billion, which is 1.5 times that of USDT. In mainstream lending agreements such as AAVE and Compound, the circulation of USDC is more than 4 billion, which is more than twice that of USDT.
Liabilities Analysis
More of USDC's liabilities flow within DeFi, which will put less pressure on USDC to honor its liabilities. Liquidity management is also less stressful.
fluidity
liquidity management
The stability mechanism of USDC is a one-to-one settlement with fiat currency. Similar to USDT, USDC also has a buffer mechanism, and new USDC will be issued at intervals.
In response to cash withdrawals, USDC will first use the most liquid cash asset, which accounts for about 60%, or about 30 billion US dollars. The liquidity of U.S. Treasury bonds and large-denomination certificates of deposit is slightly less, and this part accounts for 25%.
liquidity management
USDC has a strong ability to deal with extreme market conditions, and can withstand a selling pressure of more than 30 billion U.S. dollars in a short period of time, which has never happened in history. It can be considered that USDC's ability to withstand liquidity pressure is very strong. The main risks of USDC come from undisclosed changes in asset structure, the possibility of a reduction in the proportion of cash assets, audit fraud, and the extreme global financial crisis.
scenes to be used
USDC has seized the historical opportunity and has been widely used in transactional scenarios. It is also widely used in DeFi protocols, and the adoption rate is more than double that of USDT.
At the same time, USDC provides the strongest fiat currency liquidity, has become the anchor of other stablecoins, and has also become the reserve asset of some stablecoin projects.
USDT, USDC asset structure comparison table

UST
The short-term impact caused Luna to return to zero in just two days. Of course, the short-term impact may have been prepared, and there are countless speculations on the market.
But its irrational asset-liability structure is the root cause of its complete inability to stop the shock.
The collapse of UST proved that reserve assets cannot be completely composed of prospective assets, and the speed of credit expansion needs to be controlled.
assets
asset structure
UST's reserve asset is Luna. At the beginning of 2022, Terra began to purchase $BTC and $AVAX as its own reserve assets. But compared with the market value of Luna and UST, the market value of BTC and AVAX is not high. UST's reserve assets are mainly Luna.
Because UST has suffered a de-anchor in the near future, and Luna has also returned to zero, we take Terra's asset status on May 6 as an example to analyze UST's reserve assets.
At that time, the price of Luna was around $80, the market value was around 27 billion, the market value of UST was around 18 billion, LFG held around 3 billion worth of BTC, around 100 million worth of AVAX, and some other scattered assets. The total reserve assets are about 30 billion, of which Luna accounts for 90%.
features
Terra's assets are very characteristic. Its UST market value is basically supported by Luna, an expected asset. Luna's transaction price is formed by the market and fluctuates greatly. In the last round of bull market, Luna's market value has always exceeded UST , reflecting the expected premium for Luna.
asset analysis
The market value of Luna is supported by expectations . It is undeniable that during the previous expansion process, Luna also experienced short-term UST unanchoring and falling, but in the end it returned to anchoring through the arbitrage mechanism, which established a certain market confidence and more It is a market that has come out of a substantial premium UST. But the risk is that reserve assets are too affected by expectations and are highly volatile. Although the team realized this and began to introduce reserves such as BTC, extreme market conditions have already occurred before the ratio of Luna has dropped. In extreme market conditions, Luna will experience a liquidity crisis and face the risk of a sharp decline in market value, leading to a death spiral.
Therefore, when the real risk of a run occurs, Terra's reserve assets are not the 30 billion US dollars on paper , but the real realized value, but this value is unknown. Judging from this crash, Luna has fully realized in the short term (Two days) the value that can really be realized is less than 2 billion US dollars.
debt
liability structure
Most of the UST in circulation is in its own ecology. Among them, the Anchor protocol has absorbed a large amount of UST, as high as 14 billion US dollars on the 5.6th. In January, the figure was only more than 5 billion. Anchor promises a fixed rate of return of close to 20%, generating a large amount of interest every day, with a rolling increase. About 1 billion of the remaining UST is on the cross-chain bridge, about 10 is in the non-Terra chain DeFi protocol, and the remaining 2 billion is in exchanges, other protocols of the Terra ecosystem, and personal wallets.
Liabilities Analysis
Terra's debt structure is unreasonable. Except for Anchor, other agreements in Terra's ecology have not absorbed much UST . This structure has caused Terra's debt growth pressure to be much greater. Nearly 75% of debts are covered by this fixed-rate agreement. Absorbed, so liquidation and selling pressure in extreme cases is a huge risk. However, Terra's liabilities are all denominated in UST. As long as extreme market conditions do not occur, it can be continued on a rolling basis. However, in extreme market conditions, the scale and liquidation point of this part of liabilities are worth noting.
fluidity
liquidity management
Terra's stabilization mechanism is shown in the figure below. Terra provides quotations through its internal oracle system. Inside the oracle, the price of UST is constant at $1. When there are too many USTs in the market, the market price of UST is less than $1, and arbitrageurs will buy UST in the market. It is sold at a price of $1 in the agreement, and at the same time, the agreement mints Luna of equivalent value according to the market price of Luna, and the arbitrageur sells Luna in the market to complete the arbitrage. During this process, the circulation of UST will gradually decrease through the arbitrage mechanism, and the price of Luna will temporarily drop. And vice versa.
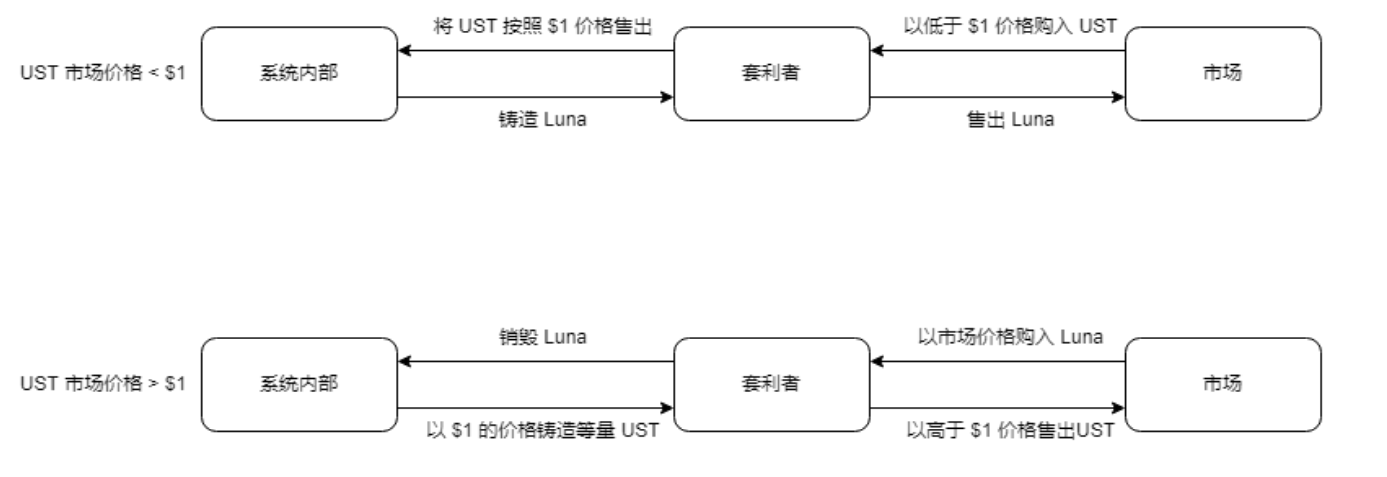
According to the Terra white paper
It can be seen that in the whole process, Terra actually allocated liquidity to arbitrageurs, relying on arbitrageurs to absorb and release UST, and Terra's daily arbitrage limit is 300 million US dollars, that is to say, Terra's daily arbitrage Absorb or release liquidity of up to US$300 million. Terra's mechanism can make the native token Luna absorb the issuance value of UST, that is, the seigniorage income. Theoretically speaking, as the demand for currency in the market becomes higher, the circulation of UST will increase through the release of arbitrageurs, and the value of Luna will increase accordingly. When the demand for currency in the market decreases, the circulation of UST will decrease through the recovery of arbitrageurs. The value of Luna decreases accordingly.
However, Luna is an anticipatory asset, and the price is formed by market transactions, which is greatly affected by expectations. In extreme market conditions, both UST and Luna are sold out, and the market value drops. Luna is affected by expectations and arbitrage selling pressure, and its market value may be low UST, which further stimulates market panic and throws out UST, forming a death spiral.
Liquidity extreme stress test
In extreme market conditions, from the perspective of assets, the assets that Terra can use include Luna (Luna held by LFG), BTC, etc., as well as arbitrageurs in the market. Under extreme market conditions, arbitrageurs will sell Luna crazily. Judging from the market starting on 5.9, too much short-term selling of Luna will cause a liquidity crisis and the market value will drop rapidly. That is to say, the market value of UST is 50% higher Luna, in the short term, does not have much real redemption value. In fact, it only supports less than 2 billion UST exchanges.
scenes to be used
The usage scenarios of UST are concentrated within the Terra ecosystem, and the largest usage scenario is the Anchor protocol.
DAI
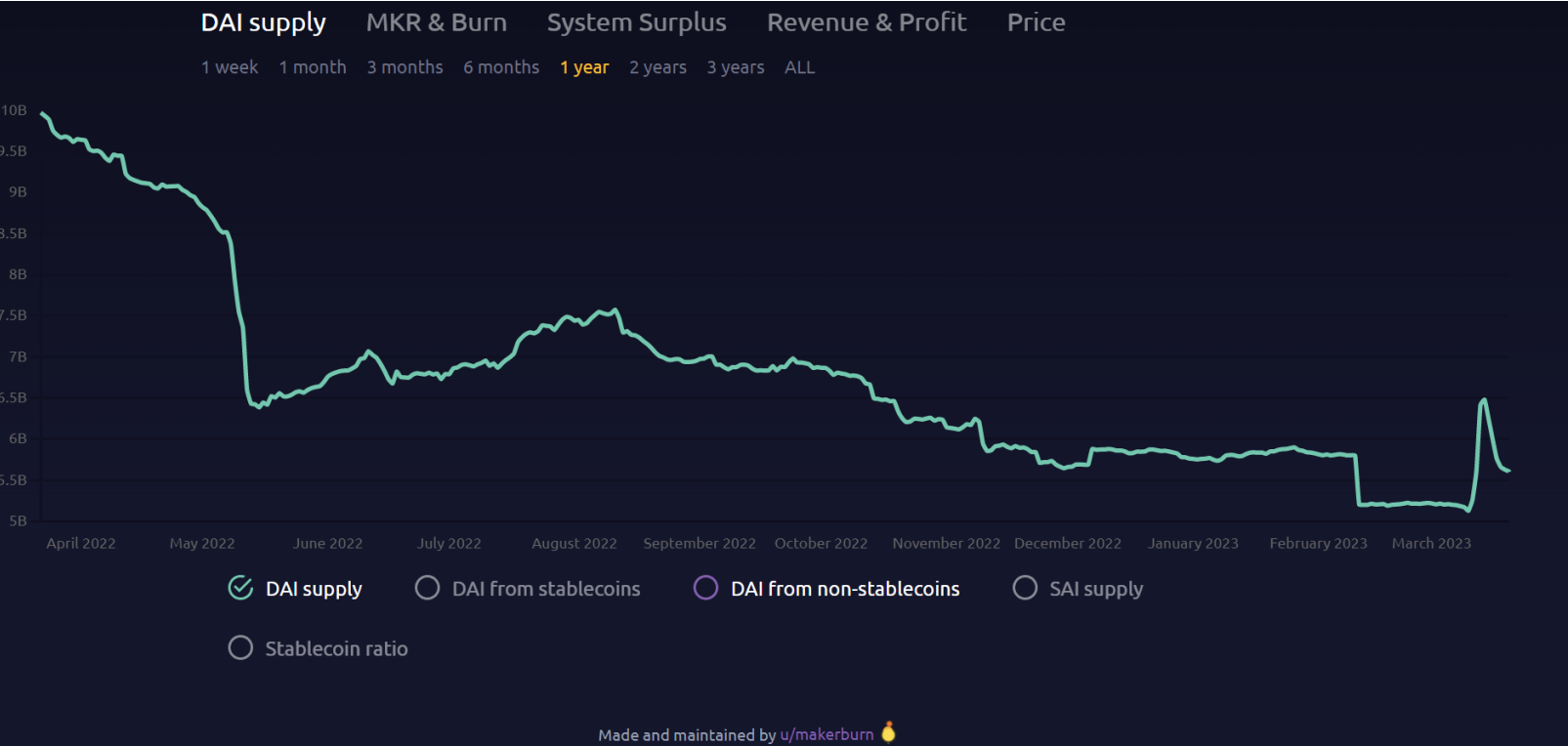
The current circulation of DAI is around $5.6 billion, which is not much different from the observed data on May 16 last year. In the past year, the circulation of DAI first rose slowly and then declined.
During the period when USDC was unanchored, the circulation of DAI jumped sharply, which is closely related to arbitrage activities.
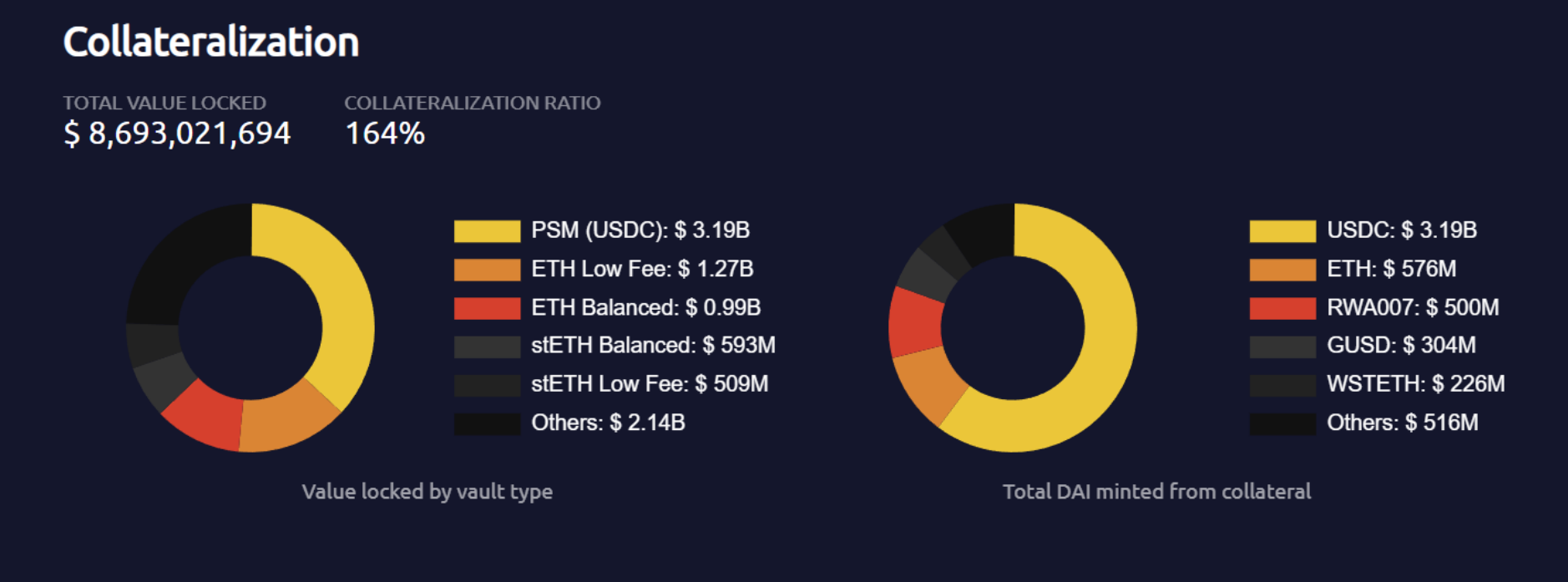
The asset structure of DAI reserve assets has changed a lot. The proportion of ETH as a reserve asset has dropped significantly, from about 25% to 14.3%, and the proportion of USDC as a reserve asset has risen sharply to 65.3%. The proportion of RWA as a reserve asset has also risen sharply to 12.4%, and the remaining reserve assets account for a relatively small proportion. As the ratio of USDC and RWA to reserve assets increases, the degree of decentralization of DAI decreases, introducing external market risks.

assets
asset structure
DAI is a stable currency backed by mainstream assets and overcollateralization. The collateral it supports includes stablecoins USDC, ETH, BTC, LINK, UNI, YFI, MANA, MATIC, Uni-V3 and Curve LP of some high-liquidity assets, and off-chain asset RWA. The current asset size is about 10 billion US dollars , with an ATH of over $20 billion.
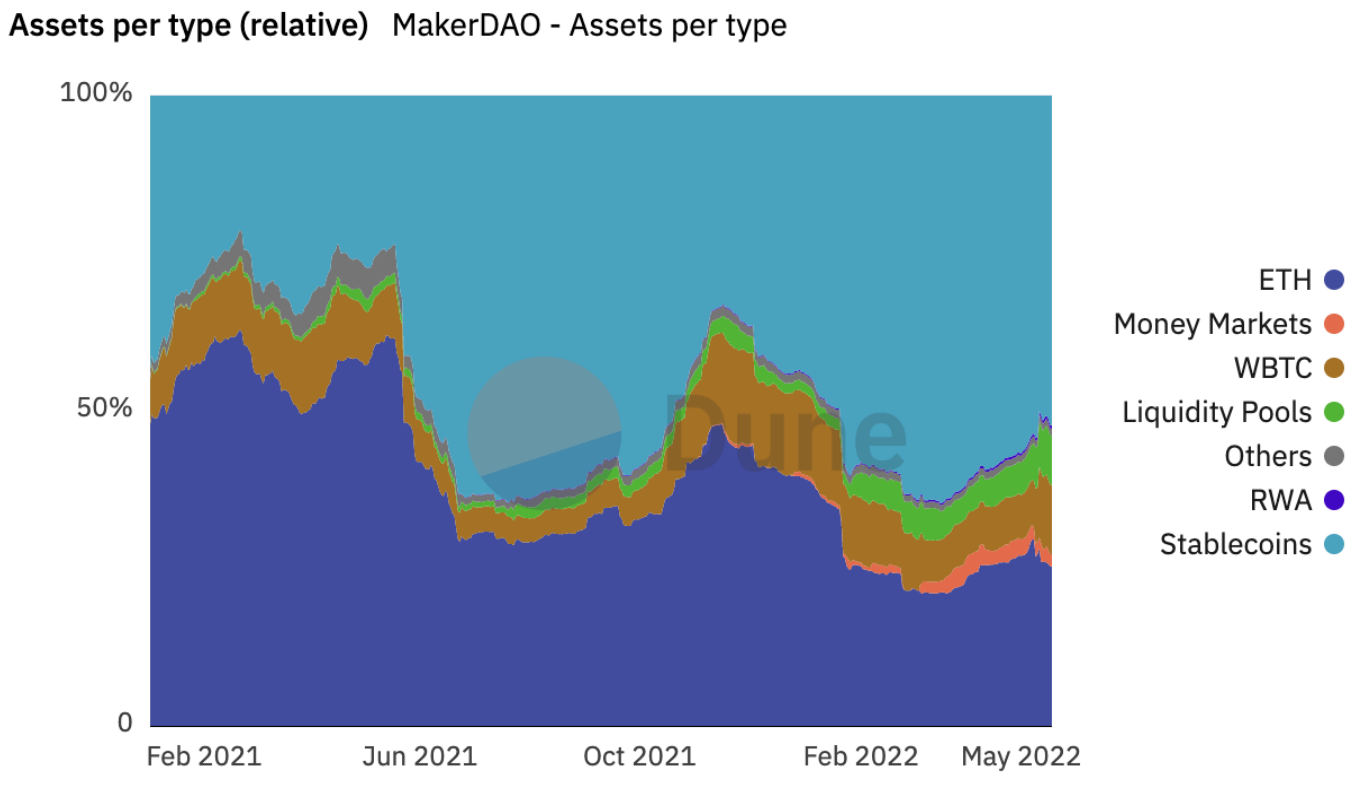
features
DAI maintains stability through external market factors, such as collateralized debt positions (CDP), autonomous response mechanisms, and external economic incentives to achieve decentralization. MakerDAO uses a set of scientific governance systems including Executive Voting and Governance Polling to allow MKR holders to manage the financial risks of the agreement and DAI, such as stability fees, guarantee types, and guarantees. rate, etc. to ensure its stability, transparency and efficiency. At present, DAI's reserve assets are characterized by high liquidity and relatively low volatility, releasing liquidity without sacrificing exposure to mainstream assets.
asset analysis
The collateral behind DAI is selected by the diversity of assets, the average daily transaction volume of millions of dollars, and the relative stability of each token, mainly ETH and BTC, and the mortgage rate is around 150%. It was not until the deployment of Curve 3pool that the volatility of DAI was effectively managed, and holders also had more liquidity options.
debt
liability structure
At present, the total circulation of DAI is about 6 billion, of which about 3.5 billion are in the external address (EOA), 720 million are locked in the cross-chain bridge, 550 million are in DEX, and 590 million are in the lending agreement.
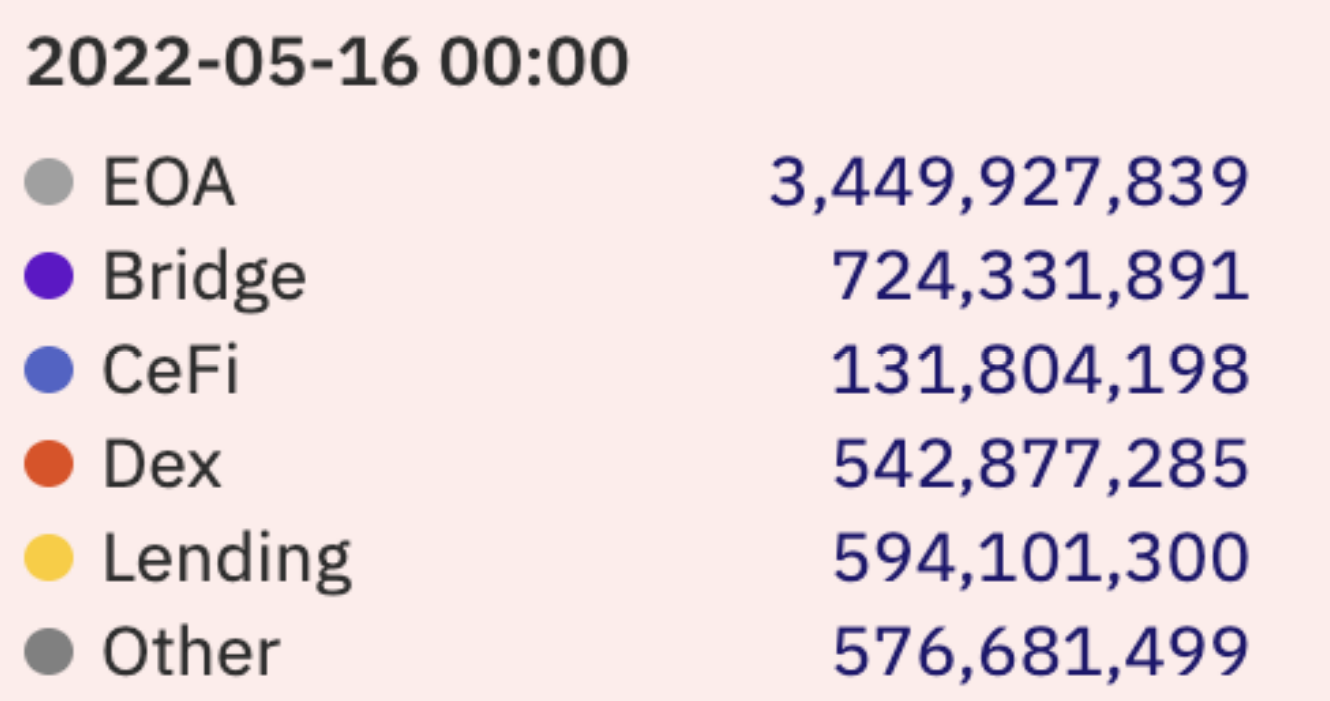
Liabilities Analysis
Coingecko data shows that DAI's 24-hour transaction volume is about 350 million US dollars, combined with more than 50% of its circulation in external wallet addresses, it can be seen that DAI is a more popular stable currency. Its ratio in lending agreements and cross-chain bridge locks also shows that DAI is currently an integral part of the multi-chain DeFi Lego.
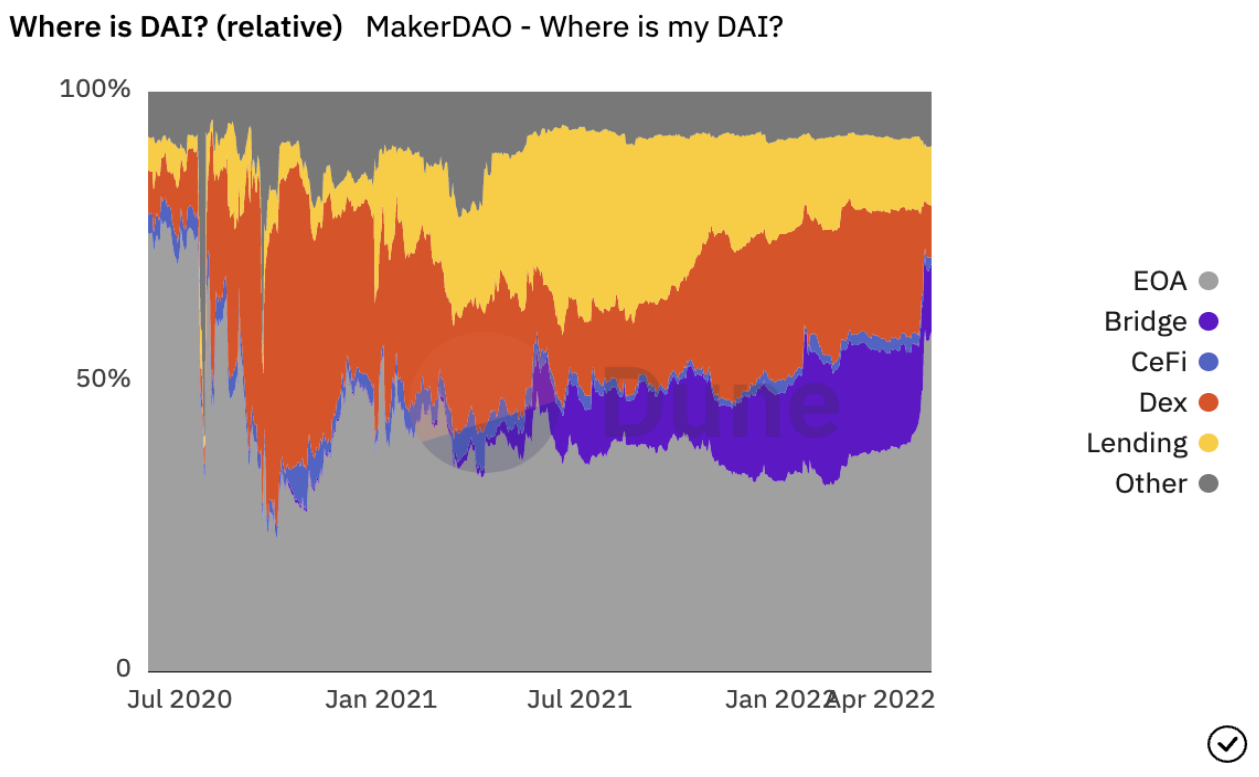
fluidity
liquidity management
As a multi-collateralized and over-collateralized stablecoin, DAI is mostly a mainstream reserve asset with high liquidity, which is sufficient to support users to redeem collateral and avoid runs and liquidations caused by violent market fluctuations.
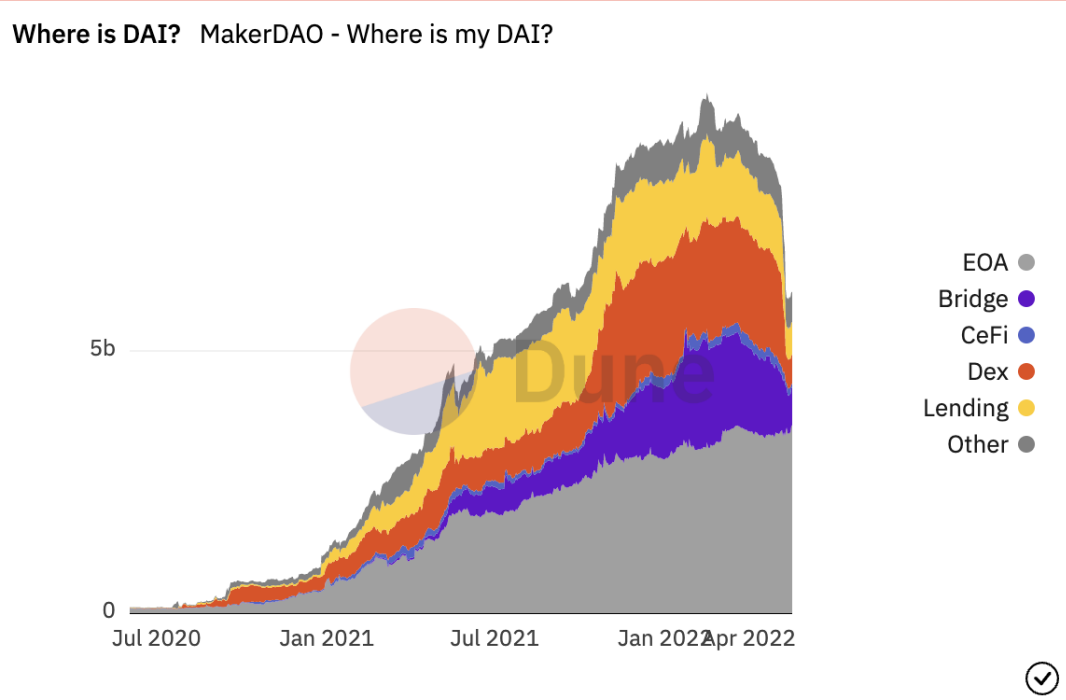
Liquidity extreme stress test
We can speculate that under extreme market conditions, when the value of mortgage assets shrinks sharply, DAI still has Peg Stability Module (PSM) and Curve 3pool as the core of its guaranteed anchor value.
scenes to be used
At present, DAI still regards itself as the safest decentralized stable currency, known as "Wrapped USDC", and there is still a big gap between USDC and USDC as a trading pair settlement asset.
The deposit rate provided by MakerDAO to users is also often criticized, and the subjective initiative of users to hold DAI is also insufficient.
FRAX
Frax's circulation slowly declined to around $1 billion. The price has remained anchored, briefly discounting by 6% during USDC unanchoring.

The capital structure of Frax's reserve assets has undergone significant changes. Frax changed the mortgage rate, set the reserve asset mortgage rate to 100%, and Frax removed FXS as reserve assets, and there will be no new FXS as mortgage assets to support Frax. The collateralization ratio increased from 85.25% to 92%.
This also means that Frax has abandoned the native token as a reserve asset and switched to a fully mortgaged stable currency. There are still some FXS remaining, but no new ones will be added in the future.
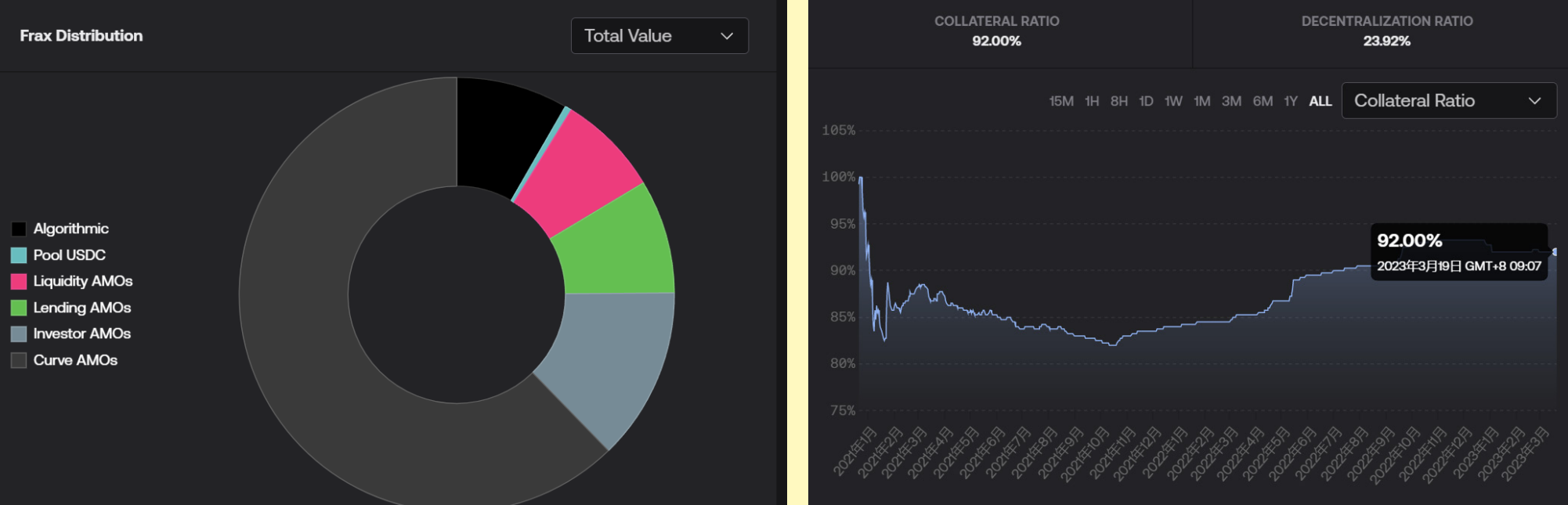
assets
asset structure
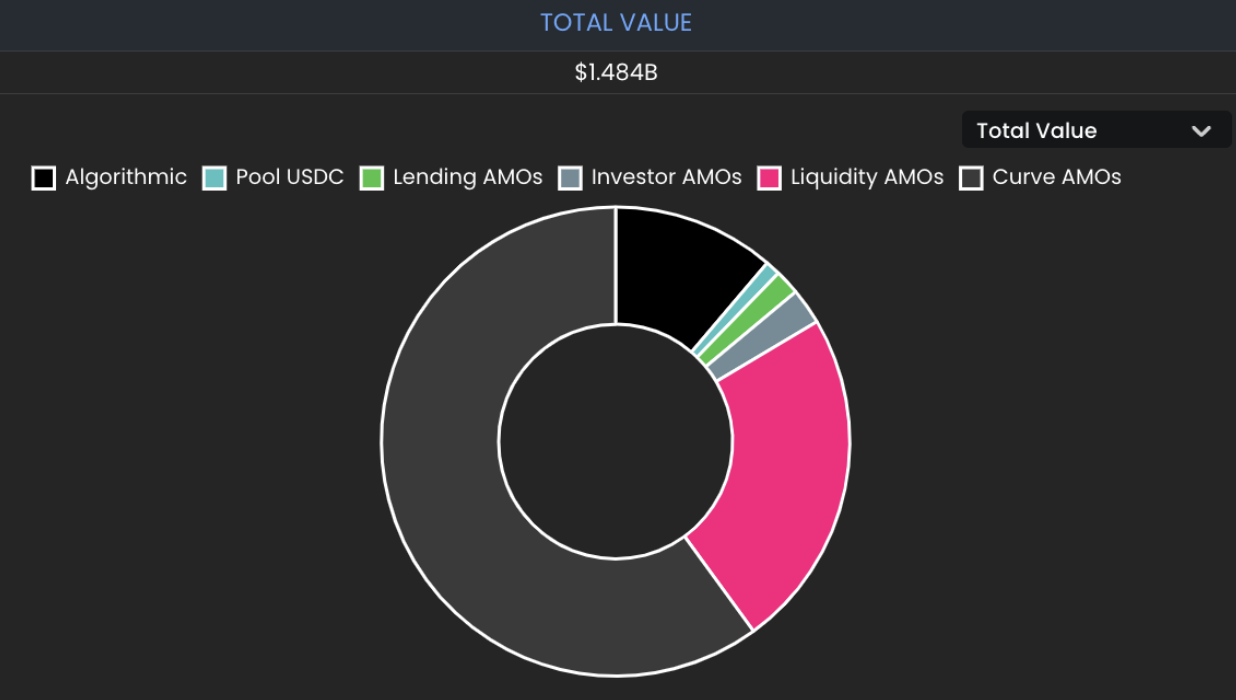
Initially, FRAX is a stablecoin backed by USDC (now accepted including DAI, FEI, LUSD, sUSD, USDP) and FXS as collateral. The collateral ratio (CR) of the two assets is controlled by the protocol AMO algorithm. Therefore, FRAX is also known as a partially collateralized algorithmic stable currency. CR determines the ratio of external and internal collateral required to mint or redeem FRAX. In the future, the non-full mortgage part of FRAX will accept the off-chain asset RWA. At present, FRAX's non-FXS collateral scale is about 1.2 billion US dollars (the current stablecoin collateral ratio is 89%).
features
The asset options accepted by FRAX are basically over-collateralized or fully-collateralized stablecoins, and the native token FXS that absorbs its volatility with the US dollar. Collateral stablecoins are also used by different AMOs to earn protocol income without reducing the collateralization rate.
asset analysis
Frax Finance achieves a flywheel effect by absorbing the volatility pegged to the US dollar through its native token FXS. Both stablecoin collateral and FXS are used by AMO to accumulate protocol income, and its income is also used to support the non-full mortgage part and feed back FXS holders. In addition, FRAX can not only earn income by using Curve AMO, but also greatly increase the liquidity of FRAX and strengthen its anchoring with the US dollar, achieving an effect similar to the central bank intervening in the market to maintain price anchoring.
debt
liability structure
At present, the total circulation of FRAX is about 1.18 billion, of which more than 50% are used for Curve 3CRV pool to earn income, and about 20% have become stablecoin-denominated trading pairs in DEX.
Liabilities Analysis
FRAX has about 1b liquidity on Curve, accounting for more than 70% of the circulation, and the 30-day trading volume is nearly 100 billion U.S. dollars, with high liquidity and demand. Based on the current CR of 89%, the current liability structure is basically healthy.

fluidity
liquidity management
First, FRAX uses a two-way arbitrage mechanism to maintain its anchor, for example, if the CR is 85%, then minting 1 FRAX requires depositing USDC worth 0.85 USD and FXS worth USD 0.15. As the growth rate increases, it means that the liquidity of FXS has increased relative to the supply of FRAX, and more FRAX can be redeemed, with a small percentage impact on the supply of FXS. Thus, the system can absorb more FXS sell pressure from FRAX redemptions without risking a negative feedback loop and CR will decrease.
Secondly, the agreements deposited in Frax AMO are all agreements that can redeem assets immediately to ensure the redemption of stablecoin collateral and FRAX. The revenue accumulated by the treasury will also be used for rainy days.
Liquidity extreme test
Similarly, under extreme conditions, the market value of FXS will plummet, and CR will rapidly soar from a lower percentage to a higher percentage, triggering a run. A certain percentage of FRAX holders may then withdraw all collateral from the system through redemption, and the remaining holders will hold undercollateralized FRAX. But FRAX's CR is not designed to fluctuate quickly, so there will be no situation where the CR greatly exceeds the actual percentage of collateral in the system. Furthermore, this divergence typically occurs during periods of sustained growth in demand for FRAX, and FRAX still has sufficient liquidity to support an outright exit of a FRAX position.
scenes to be used
At present, FRAX has gradually become a pricing method for multi-chain assets, and its use scenarios in the DeFi ecosystem have quietly surpassed DAI.
MIM
Unlike UST, MIM's asset structure is more reasonable. The reserve assets are completely native digital currency assets, which are crypto native stablecoins. However, the mortgage rate is low, limited by the immaturity of the DeFi market, and there are still some risk factors.
assets
asset structure
MIM is a stable currency that is collateralized by interest-bearing assets. Abracadabra will update a white list of mortgage assets, such as yvWETH, yvWUSDC, etc. in Yearn. Behind these assets are assets such as ETH and USDC. The asset scale is around 1.8 billion.
features
An obvious feature of MIM's reserve assets is the high proportion of long-tail assets. MIM is a stable currency that provides liquidity for these assets, and is essentially a lending agreement. Through the pool in Curve, MIM can be exchanged for stable coins with better liquidity to realize its purchasing power.
asset analysis
MIM's asset selection is interest-bearing assets, which provide liquidity for these assets. These assets are Defi native assets, which are different from USDC and USDT, which rely on traditional financial markets to earn interest.
While Abracadabra provides liquidity for these assets, it will extract a part of the interest as agreement income. This is a sustainable business model. As the DeFi market matures, the discount scale of these assets will become larger and larger, but Currently small in scale and exposed to the risk of extreme market volatility. In MIM, different assets have different mortgage rates. Users who mortgage these assets can get 75% to 90% of the asset value of MIM according to different assets. Therefore, the mortgage rate is about 110% to 130%. Low, large fluctuations may cause unanchoring.
debt
liability structure
The total circulation of MIM is about 1.8 billion, of which 230 million is in the Curve MIM+3 pool, 420 million is in the Uni V3 pool, and 1 billion is in the cross-chain contract. These three contracts account for more than 80% of the total circulation, and the liability structure is relatively simple. MIM runs completely on the chain, the data can be checked and traced, and it is open and transparent.
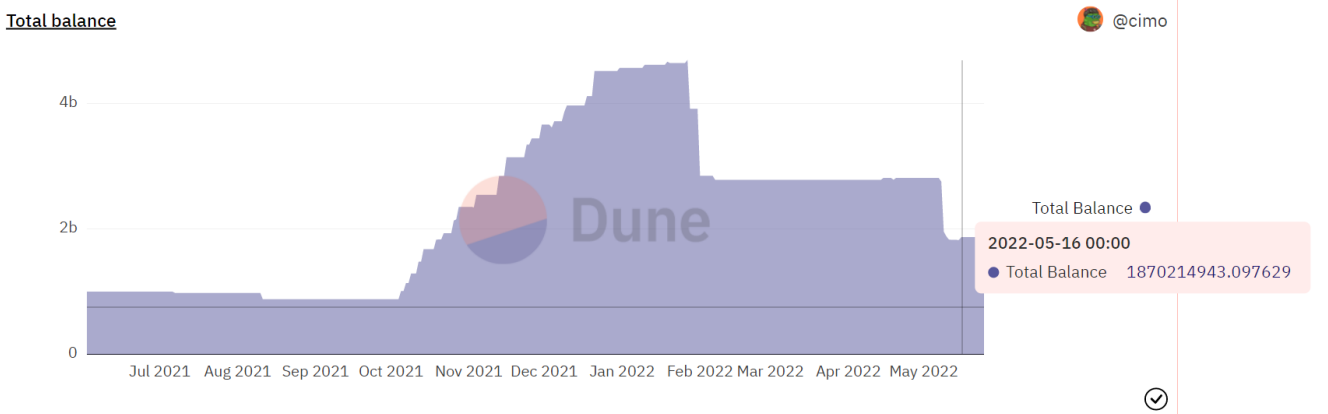
Liabilities Analysis
The pool on Curve has a liquidity of 230 million, accounting for about 10% of the total circulation. The pool's 30-day transaction volume is 11.2 billion US dollars, almost all reflecting the liquidity of MIM.
fluidity
liquidity management
The most basic liquidity management method of MIM is to redeem mortgage assets. However, the mortgage rate of MIM is low. In extreme market conditions, users may give up redeeming mortgage assets and sell MIM directly. MIM has its own treasury and uses a multi-signature mechanism to deal with extreme situations. The address has 3.23 million USDT, 8.32 million CRV and 5.95 million MIM. Considering that the positions of MIM will not be sold under extreme market conditions, the total value of the buffer is about 15 million US dollars after excluding MIM. Smaller scale.
Liquidity extreme stress test
The risk of MIM lies in that under extreme market conditions, the value of mortgage assets will be greatly reduced, while the mortgage rate of MIM is relatively low, and the funds in the treasury are less than 1% relative to the circulation, so under extreme market conditions, they are facing the risk of unanchoring.
scenes to be used
MIM provides liquidity for interest-earning assets, and its usage scenarios are limited. If users have usage needs,
Generally, you will choose to replace MIM with more universal USDC, USDT, DAI, etc.
FEI
The core of FEI is very similar to DAI, but the asset structure is relatively single, and the usage scenarios are more scarce.
assets
asset structure
FEI is a stable currency anchored by an algorithm to manage PCV to maintain the value of the US dollar, but it is actually over-collateralized. Currently about 75% of PCV is ETH, 7.8% is DAI, 7.5% is LUSD, and 2.5% is VOLT. PCV is also used in income strategies to increase treasury revenue.
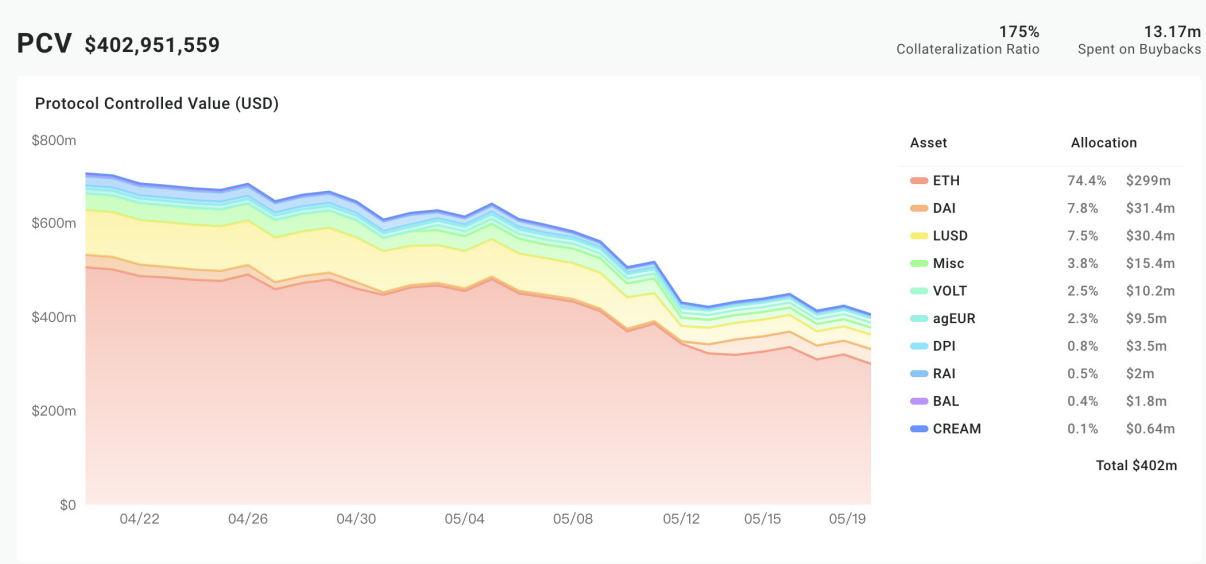
features
FEI is actually a stable currency generated by over-collateralization, supported by its maintenance anchor module Peg Stability Module (PSM), and PSM also earns protocol income.
The current system mortgage rate of FEI is 175%, which is higher than that of MakerDAO.
debt
liability structure
At present, FEI is about 530 million in circulation. Among them, nearly 60% are owned by the agreement, and 40% are externally circulated.
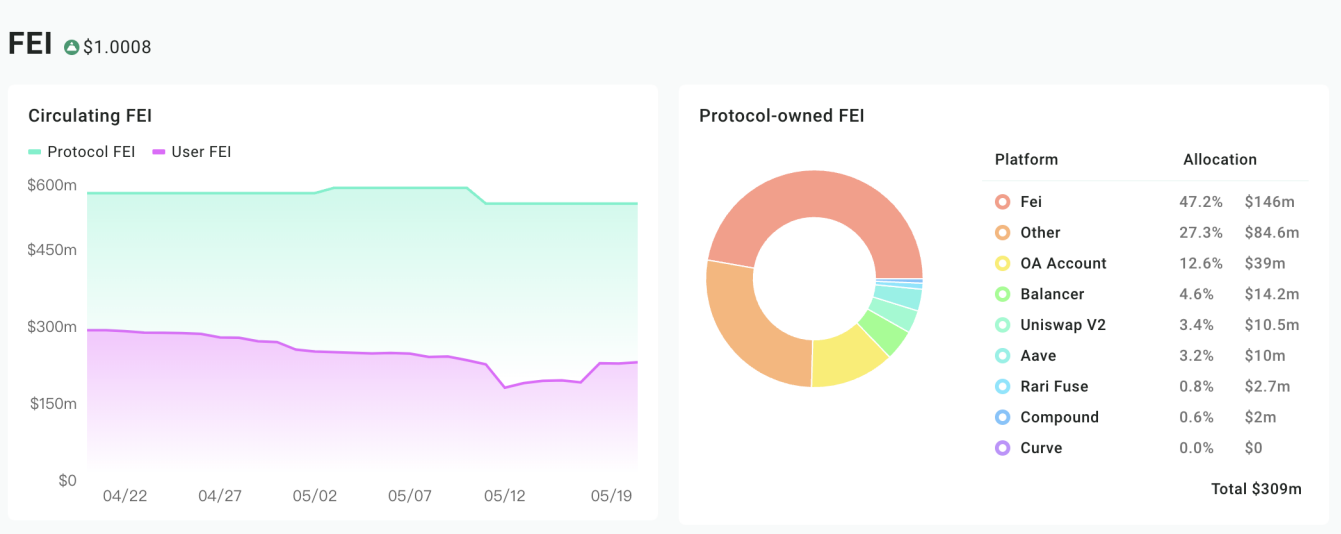
Liabilities Analysis
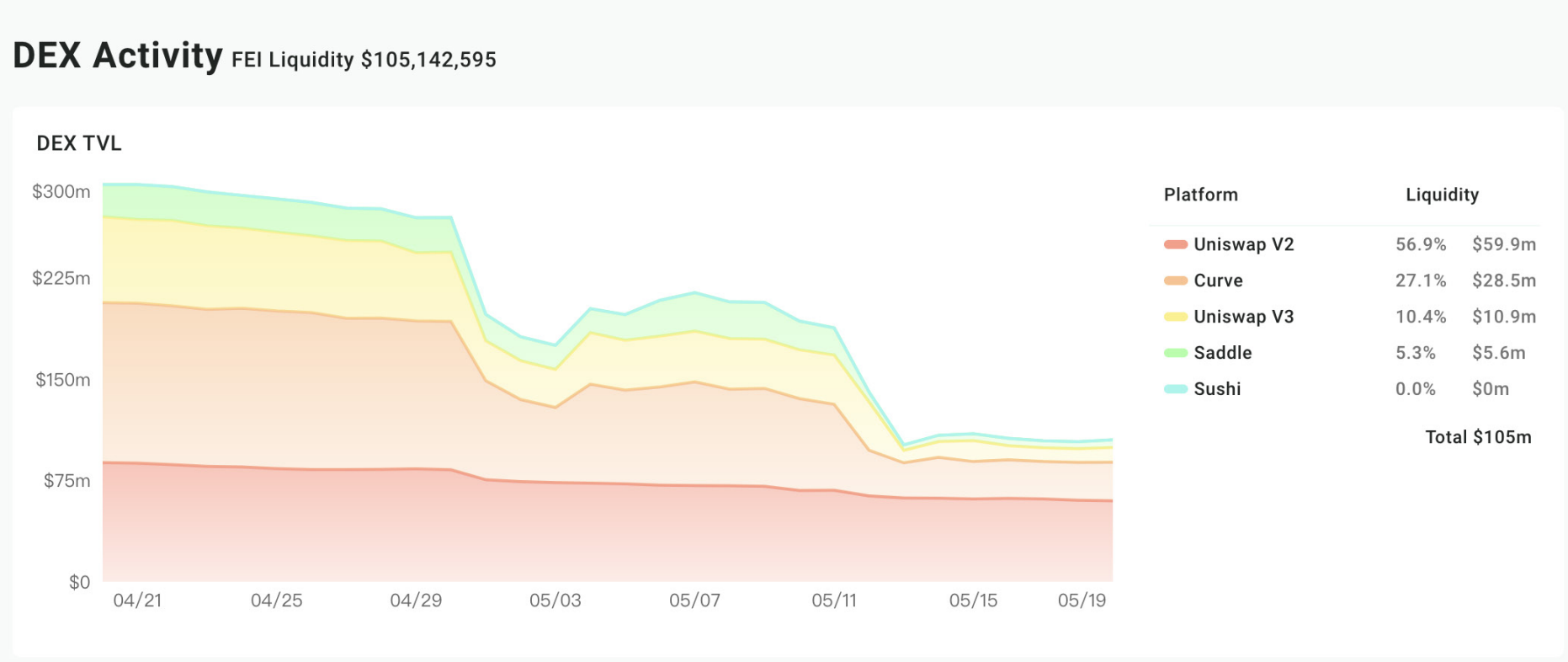
FEI currently has 100m of liquidity on DEX, of which Uni-V2 has 60m of liquidity, Curve has nearly 30m of liquidity, and the overall 30-day trading volume is about 500 million US dollars.
However, FEI's liability structure is unreasonable. Judging from the cut of ATH's PCV, FEI has not been accepted by the external ecology.
fluidity
liquidity management
FEI maintains the anchor through arbitrage: when the price of FEI is below $1 for a long time, anyone can trigger the peg restoration to make the price rise. The agreement will withdraw all the liquidity it owns, use the retrieved ETH to buy FEI to the linked price, the remaining ETH plus FEI will provide liquidity again, and destroy the remaining FEI. In addition to the active operation of the protocol, there are also some mechanisms that encourage users' voluntary behavior to anchor the price. When the price is lower than the pegged price, users who sell will have an additional 4% loss, and users who buy will receive an additional 2% reward.
Liquidity extreme test
If the treasury does not exit the FEI position, FEI has 100m of liquidity in DEX to deal with the run, and the 175% mortgage rate is enough to maintain FEI's collateral payment, and FEI will not break the anchor for a long time.
scenes to be used
The essence of FEI is similar to DAI, so currently only the related derivative agreement Volt of FEI uses it as a treasury reserve asset, and the scenarios are very limited.
in conclusion
How to choose reserve assets is very important: for a stablecoin project, the first thing to consider is how to choose reserve assets. New








