Written by: Jack Inabinet
Compilation: Deep Tide TechFlow
We've been hearing the concept of Shapella upgrades over and over again these days.
In fact, it can be divided into the Shanghai (Shanghai) upgrade of the execution layer and the Capella upgrade of the consensus layer.
Ethereum has ushered in a historic moment. By enabling withdrawals, ETH holders can now preserve collateral liquidity and avoid complex tax disputes and potential regulatory headaches. At the same time, the upgrade also means that Ethereum has taken a huge step towards the establishment of an encrypted native currency system. This article will explore how Shapella can bring more opportunities to the cryptocurrency market and promote decentralized web security.
In September last year, Ethereum developers implemented the Merge scheme, replacing the original proof-of-work (PoW) consensus layer with a liquid pledged beacon chain, reducing ETH issuance by 88% and energy consumption by 99.95%. %.
After the merger, Ethereum is secured by stakers (Stakers) instead of original miners.
Each staker issues a deposit of 32 ETH on the beacon chain to store network data, process transactions and add blocks, and receive Ether rewards to maintain the security of the network. However, these stakers have been unable to withdraw their accumulated consensus layer rewards or stake their original 32 ETH from the Beacon Chain. And that pattern will be changed today.
With Shapella unleashing such a large amount of ETH, the crypto thread on Twitter has been flooded with short-term market price predictions. However, money flows and their impact on prices are only part of the story.
Today, we take a look at why you should care about the Shapella upgrade:
de-risking at scale
Staking is being de-risked on a massive scale, the age of internet bonds has arrived, and cryptocurrencies will never be the same again.
Solo staking and staking-as-a-service (SaaS) enable cryptocurrency participants to generate yield on ETH , but users' collateral remains locked and cannot be sold or transferred.
Liquid Staking Derivatives(LSDs), including Lido's stETH and Coinbase's cbETH, aim to address this lack of liquidity. At present, the total value of LSDs has exceeded 14.5 billion US dollars, and allows ETH holders to obtain income while retaining the liquidity of mortgaged ETH .
For many Ethereum users, liquidity staking Derivatives have become the de facto method of liquidity staking, with LSDs accounting for 42% of all ETH liquidity staking.
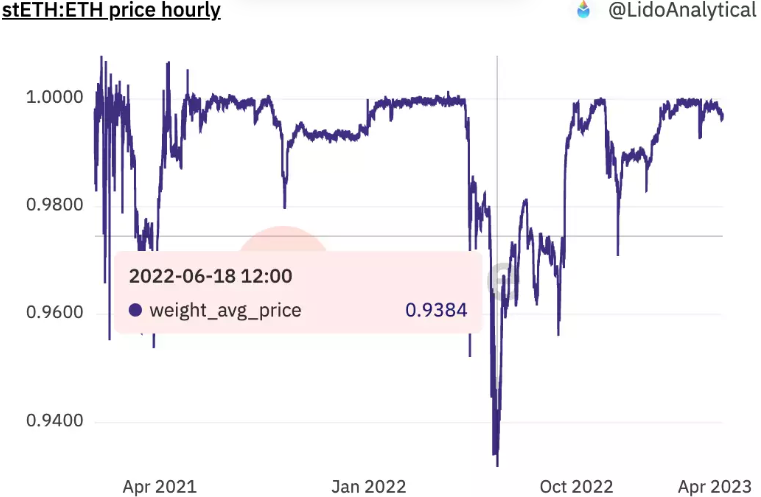
While LSDs improve liquidity, these instruments have been popularly misunderstood as having a 1:1 peg to ETH like stablecoins. However, LSDs can be inherently more illiquid than the underlying ETH collateral.
This flaw was on full display during the credit crunch. During the liquidation of StETH positions of Three Arrows Capital and Celsius starting in May 2022, the price of stETH deviated by 6% in the following month and a half, creating a crisis of confidence for LSD holders. Unable to withdraw, these holders can only rely on the promise of eventual future redeemability to maintain the peg.
tax conundrum
Liquid collateralized Derivatives also present a number of tax and regulatory headaches for many professional institutional investors. Take Lido's stETH as an example, which is the most commonly used liquid collateralized Derivatives, accounting for 74% of the ETH LSD market, it is a token that rebases (Rebase mechanism), and every time it rebases, it will Creates a taxable event for its holder. That's not a viable option for tax-conscious investors.
While investors may view ETH as a commodity, this conclusion is not easily agreed upon for many forms of liquid staking.
Many cryptocurrency exchanges, decentralized protocols, and SaaS providers pool liquid staking returns to provide investors with steady income. This gives them a securities-like quality that the SEC is trying to avoid in their recent settlement with Kraken.
Adding to the regulatory confusion, protocols like Lido and RocketPool have previously chosen and continue to incentivize liquidity on their LSDs. It can be argued that these incentives further confer security properties on Derivatives, as maintaining the peg is partly dependent on token issuance.
solution
Since the inception of the token chain, SaaS and standalone liquidity staking solutions have been viable options for ETH holders looking to preserve collateral liquidity. This only requires two Ethereum Improvement Proposals (EIPs) and an Ethereum Hard fork to achieve. Enabling withdrawals will be a game-changer for onlookers and hard-line users who feel "if I don't control the keys, I don't control the assets".
As the CTO of a London-based liquidity mortgage firm puts it, institutions are finally able to access collateral liquidity while retaining control and no longer have to wrangle with the taxman.
Avoiding complex tax headaches and potential SEC regulatory action—while earning risk-free yields at the protocol level and preserving liquidity in collateralized ETH—is now easier than ever. Today’s upgrade not only provides liquidity beyond the LSD solution, but also allows the market to begin reallocating stake and weakening Lido’s massive 31% control over the validator set.
Shapella empowers stakers and is a critical step towards further decentralization of network security.
internet bond
People have long drawn an analogy between Ethereum liquidity staking and fixed income instruments in traditional finance.
Stakers provide 32 ETH as collateral (principal) and are rewarded (interest). This relationship is not dependent on either party's ability to repay the loan, but is instead supported by future economic activity on Ethereum, aka fee income. Essentially, liquidity staking on Ethereum is a perpetual instrument with no risk of default.
go to market
Another benefit of Shapella is making Ethereum more marketable
In traditional financial markets, lending rates are typically calculated as a spread over the risk-free rate (often represented by U.S. Treasury yields).
The gap between the risk-free rate and the cost of borrowing is designed to capture the additional risk (especially the risk of default) that comes with lending money to borrowers other than the U.S. government. Treasury bonds are traded every day, and the yield is affected by the forces of supply and demand, converging on the market interest rate. Unfortunately, despite having almost zero default risk (similar to U.S. Treasuries), the yield on ETH liquidity collateral failed to become a risk-free rate for cryptocurrencies because it did not reach the level of market rates.
The rate of return that the network pays to Ethereum depends on 2 important factors: the number of validators and the fees incurred. As the number of validators increases, the fee is distributed to a larger and larger set of validators, reducing the expected income of some given node, but also subsidized by a higher ETH issuance rate.
Currently, the market can only react to the increased attractiveness of ETH liquidity staking opportunities: more market participation as ETH holders see yields on liquidity staking become more attractive relative to other yield sources Investors are willing to stake liquidity. In theory, the market responds to attractive liquidity staking rewards by increasing the number of validators, thereby eliminating temporary arbitrage opportunities.
To date, our inability to respond to the declining relative attractiveness of liquidity staking has resulted in artificially low yields when block demand is limited or compelling investment alternatives emerge. Capital transfers are not an option for liquid staking; after Shapella, this dynamic changes. Stakers can now withdraw their 32 ETH off the beacon chain in search of yield, or choose to withdraw when the risk-free rate is no longer attractive enough.
Due to the constraints of the PoS consensus, the necessary withdrawal and exit queuing mechanisms limit rapid outflows from liquidity staking. Similar mechanisms exist in traditional finance. For example, when a "circuit breaker" occurs, asset transactions will be stopped within a predefined range. While not a perfect "market rate," Ethereum has taken the final step toward becoming an internet bond through Shapella.
"How much is money worth?" is a fundamental question in finance, and the risk-free rate of return is the backbone of that system. Shapella translates Ethereum’s liquidity staking yield into something closer to the market’s risk-free rate.
If ETH were to become a currency, having a native risk-free rate similar to U.S. Treasuries as a cornerstone for loan pricing and financial valuation would go a long way in facilitating adoption, especially in attracting financial professionals and institutional investment By the side.
historic moment
Forget flow, in the long run, enabling withdrawals will provide a major means of de-risking for many cryptocurrency market participants who feel that LSDs are simply not enough.
Whatever happens immediately, today will be a pivotal moment in cryptocurrency history: Since the launch of the blockchain, Ethereum’s Shapella upgrade represents a major step toward establishing a crypto-native currency system.








