Comparing the virtual asset market with a scale of 1 trillion yuan and the traditional financial market with a scale of 487 trillion yuan, whether Hong Kong, as a financial "hexagonal warrior", can take advantage of this wave to become the financial center of the digital world will largely depend on traditional Financial support and guidance.
Written by: Will Awang, Web3 Attorney;
Gu Jiening, Senior Legal Counsel of Shanghai Mankiw Law Firm
introduction
With the introduction of the "Policy Declaration on the Development of Virtual Assets in Hong Kong" in October last year, Hong Kong's virtual asset VASP system "Encryption New Deal" has been officially implemented on June 1, 2023. This is a major benefit for my country's virtual asset industry in history. The forces of all parties are already ready to move, actively preparing for the Hong Kong Web3 virtual asset market.

Comparing the virtual asset market with a scale of 1 trillion yuan and the traditional financial market with a scale of 487 trillion yuan , whether Hong Kong, as a financial "hexagonal warrior", can take advantage of this wave to become the financial center of the digital world will largely depend on traditional Financial support and guidance . This article will try to sort out a way for traditional finance to enter Hong Kong from the perspective of the ecological positioning of the regulated object of the Hong Kong VASP system (virtual asset centralized exchange), the virtual asset market access of Hong Kong’s financial license, and combined with the current situation of various forces preparing for war. The compliance path of the Web3 virtual asset market.
1. The ecological positioning of CEX in the market
Centralized virtual asset exchange (Centralized Exchange, CEX) is the "top predator" in the market . Due to the lag of policy regulation and other reasons, CEX integrates traditional finance such as exchanges, banks, brokers, futures, trusts, capital Management, payment and settlement and other important roles, basically covering all virtual asset ecology. At first glance, CEX is indeed "too big to fail", but as big as FTX, which was once the second largest in the world, it only took 10 days for its collapse caused by self-theft. Therefore, there is a follow-up new virtual asset custody regulation (proposal) of the US Securities Regulatory Commission (SEC), which intends to split CEX (such as splitting CEX's market-making transaction business from the custody business) to avoid conflicts of interest and self-stealing situations .
Although the U.S. has not yet formed a unified regulatory framework for virtual assets, and although U.S. regulatory agencies have reached the level of political games, there are "corresponding" laws and regulations for the regulation of CEX's various business segments. , and enough practice to land, it can be used as a reference and reference. We look at the ecological positioning of CEX from the perspective of Coinbase, a compliant centralized virtual asset exchange listed in the United States.
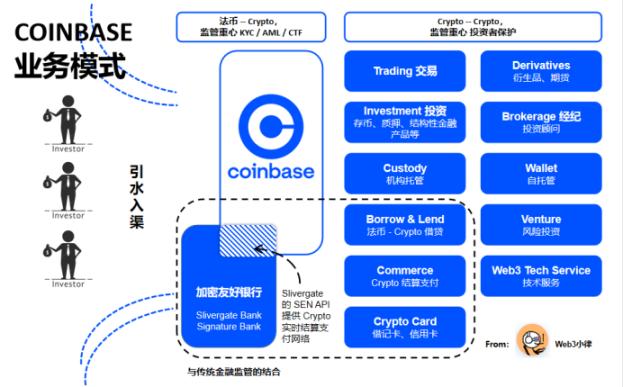
As shown above, Coinbase combined with crypto-friendly banks (although many crypto-friendly banks such as Silvergate Bank and Signature Bank were stifled due to political pressure) such as Silvergate Bank's SEN virtual currency real-time settlement payment network, providing investors with deposits and withdrawals from legal currency to Crypto Exchange, this is the first step of "draining water into the channel". This step of regulation focuses on KYC, anti-money laundering (AML) and anti-terrorist financing (CTF).
After "leading water into the channel", Coinbase provides investors with one-stop full-lifecycle Crypto services, such as Crypto trading (traditional exchange business), Crypto Derivatives trading (Derivatives futures business), financial product investment (broker business), Brokeage brokerage business (brokerage business), Crypto institutional custody business (bank trust business), Crypto payment settlement business (financial payment business), Venture venture capital business (asset management business). Investors can also enter DEX, DeFi, NFT, GameFi and other scenarios through Coinbase's self-hosted Wallet wallet.
At this point, the regulatory focus has shifted to investor protection. We have seen that CEX does gather a lot of businesses that need to be strictly regulated in the traditional financial field. In the United States, these Crypto businesses are basically included in the "corresponding" regulatory framework of traditional finance. by Enforcement” regulatory model, constantly urging the market to comply.
The compliance path of the above Coinbase virtual asset business in the United States is briefly sorted out for reference:
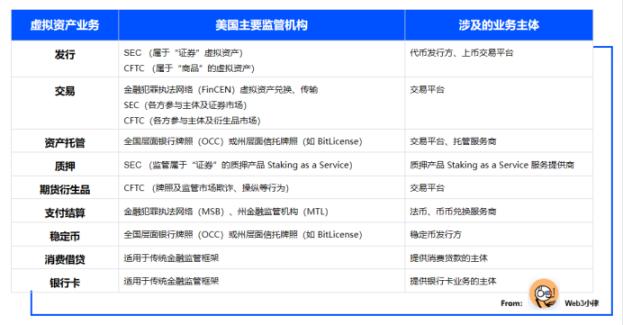
2. Access to virtual asset financial licenses in Hong Kong
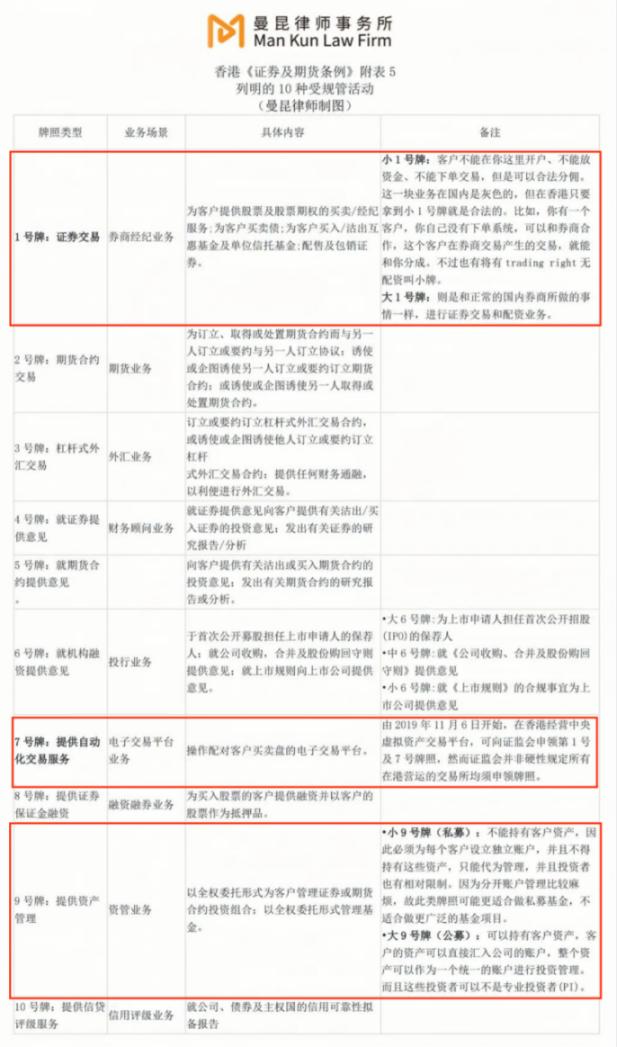
Compared with the large and comprehensive ecological positioning of Coinbase in the United States, as well as many "corresponding" regulatory frameworks, the current new VASP system in Hong Kong is only for the CEX platform for the time being. If a market only has platforms and customers, it will not be possible to form a prosperous and diverse ecology, so we also need to bring in services such as asset management and investment consulting. The prosperity and development of the Hong Kong Web3 virtual asset market must be inseparable from the support and guidance of traditional finance. The following will further clarify the compliance path for traditional finance to enter the Hong Kong Web3 virtual asset market by sorting out the 10 types of financial regulatory licenses of the Hong Kong Securities Regulatory Commission (SFC) (compiled by Shanghai Mankiw Law Firm).
2.1 Deposit and withdrawal of virtual assets (banking license)
According to news reports, Chinese banks in Hong Kong, such as Bank of Communications (Hong Kong), Bank of China (Hong Kong), Shanghai Pudong Development Bank Hong Kong Branch, and virtual banks such as Hong Kong ZA Bank (Virtual Bank) have begun to introduce local virtual banks. Asset companies provide banking services, or have investigated the field. An official of the Hong Kong Monetary Authority also stated: " There is no legal or regulatory requirement that prohibits banks operating in Hong Kong from providing banking services to virtual asset-related institutions ."
It can be seen that such licensed banks in Hong Kong (banking licenses issued by the Hong Kong Monetary Authority) will serve as a channel for Crypto deposits and withdrawals, and will play the role of "leading water into the channel" in a direct or indirect way, and achieve the role of investors Onborading . Direct ways such as: Hong Kong Zhongan Bank (ZA Bank) plans to launch virtual asset trading services to retail investors by cooperating with local licensed virtual asset exchanges, and ZA Bank will seek regulatory approval. This is obviously a strong cooperation method for Zhongan Bank as a traffic portal. Indirect methods such as: HashKey PRO has established a partnership with Hong Kong Zhongan Bank (ZA Bank) and Bank of Communications (Hong Kong) as a settlement bank to provide legal currency deposit and withdrawal services.

2.2 Virtual asset centralized exchange (VASP license)
According to the latest amendments to the Anti-Money Laundering and Counter-Terrorist Financing Regulations 2022 (the Anti-Money Laundering Regulations) and the Guidelines Applicable to Operators of Virtual Asset Trading Platforms (VASP Guidelines), from 1 June 2023, all Centralized virtual asset exchanges operating in Hong Kong or actively promoting their services to Hong Kong investors must be licensed and regulated by the SFC, regardless of whether they provide security token trading services.

According to different regulatory authorizations, SFC will supervise the security token transactions conducted by virtual asset exchanges in accordance with the Securities and Futures Ordinance (No. 1 license + No. 7 license); Regulation of non-security token transactions on virtual asset exchanges (VASP license). In practice, OSL and Hashkey Group, which have obtained No. 1 license (securities trading) and No. 7 license (providing automated trading services), still need to apply for a VASP license if they want to provide non-securities token virtual asset services.

According to news reports, we have seen that many traditional CEXs are actively preparing to apply for VASP licenses, and traditional financial institutions such as Tiger Securities and Shanghai Greenland Finance are interested in applying for VASP licenses. Interactive Brokers, a global automated electronic brokerage, has launched virtual currency trading in Hong Kong through a partnership with OSL, enabling its professional investor clients to trade Bitcoin (BTC) and Ethereum (ETH).
Since the "Anti-Money Laundering Regulations" and the VASP guidelines only define "virtual asset services" as: operating virtual asset exchanges, currently only the relevant business entities of virtual asset exchanges are included in the regulatory framework of the VASP system, and other virtual asset businesses are still applicable to old system. However, it does not rule out that the Hong Kong Financial Services and the Treasury Bureau will include other virtual assets and virtual asset services in the form of gazetted announcements.
2.3 Virtual asset custody (TCSP trust license)
The VASP guidelines put forward the requirement of "safe custody of customer assets" for the operation of CEX, that is, the platform operator should hold customers in trust (TCSP trust license) through a wholly-owned subsidiary company (ie "associated entity") Money and customer virtual assets. This means that CEX under the VASP system is a combination of VASP license + TCSP trust license, and the TCSP license is used for independent custody of investors' assets to avoid the situation of guarding and stealing.
Since traditional banks can only hold legal currency assets, the custody of virtual assets can only be placed under trust accounts, which also gives TCSP trust licenses new business scenarios . The full name of TCSP license is Trust or Company Service Providers. Companies that provide virtual asset custody services, whether they are wallet service providers or institutional custody service providers, generally also need to hold TCSP trust licenses, such as exchanges OSL, Hashkey Group, Gate.io Group Each has its own TCSP trust company. In addition, wallet infrastructure and digital asset custody service provider Liminal has also recently obtained a TCSP license.
2.4 Virtual asset asset management (No. 9 license + Uplift)
License No. 9 itself only supports the provision of traditional asset management services, and does not include virtual asset asset management . Therefore, if a licensed asset manager wants to hold more than a certain percentage of virtual assets in its investment portfolio, it needs to perform an Uplift on the basis of the No. 9 license and submit an additional report to the SFC to obtain a license . Although there are more than 2,000 No. 9 licensed institutions in Hong Kong, as of the end of 2022, only six institutions, including Xinhuo Asset Management, Lion Global Asset Management, MaiCapital, and Fore Elite Capital, have obtained SFC approval to manage investment in virtual assets in compliance. portfolio of assets.
Before 2018, the premise for SFC to regulate virtual asset management services was that the managed virtual assets belonged to "securities" or "futures contracts" as defined in Schedule 1 of Hong Kong's Securities and Futures Ordinance. The "Statement on Initial Coin Offerings" states that if the digital tokens involved in the token offering meet the definition of "securities", provide trading services or provide advice on such digital tokens, or manage or promote investment in digital tokens Funds, may constitute "regulated activities". However, this has left many virtual assets that do not belong to the category of "securities" or "futures contracts" in a regulatory gap, which is not conducive to investor protection.
On November 1, 2018, SFC issued the "Statement on the Regulatory Framework for Virtual Asset Portfolio Management Companies, Fund Distributors and Trading Platform Operators", which will manage virtual assets that are not "securities" or "futures contracts" The behavior of the SFC has been included in the regulatory framework, which has broadened the scope of SFC's supervision of the cryptocurrency field. On 4 October 2019, the SFC further promulgated the "Standard Terms and Conditions for Licensed Corporations Applicable to Management of Portfolios Investing in Virtual Assets" (the "Terms and Conditions"), which is Hong Kong's The historical turning point of the asset attitude, the key point is that the fund management companies that require more than 10% of the cryptocurrency target in the managed investment portfolio need to obtain an additional license from the SFC in addition to the traditional No. 9 license.
Specifically, if the fund managed by a licensed company falls under the following two circumstances, it needs to be subject to the supervision of the SFC: (a) a portfolio that has indicated that the investment target is virtual assets; (b) an investment of 10% or more of the total asset value Investment portfolio in virtual assets. Among them, "virtual assets" refer to assets that express value in digital form, which can be in the form of digital tokens (such as digital currency, utility tokens, or tokens collateralized by securities or assets), any other virtual goods , encrypted assets or other assets of a substantially similar nature, whether or not such assets constitute "securities" or "futures contracts" as defined in the SFO.
The "Terms and Conditions" not only require the virtual asset fund management company to maintain no less than 3 million Hong Kong dollars in liquidity or its variable prescribed liquidity at all times, but also based on the principle of best interests, the principle of fair trade and the rules of information disclosure, the Fund's daily There are extremely detailed regulations on the allocation of buying and selling orders, related transactions, and cross-order transactions in management. In addition, the document also put forward strict terms and conditions for fund management companies in terms of anti-money laundering and combating terrorist financing, fund auditing, fund asset custody, fund risk control management, fund daily operations, fund marketing and risk disclosure.
It should be noted that for a company engaging in fund distribution business for qualified investors in Hong Kong, it generally needs to apply for a No. 1 license (securities trading).
2.5 Other businesses of virtual assets
Since the "Anti-Money Laundering Regulations" and VASP guidelines only define "virtual asset services" as: operating virtual asset exchanges, currently only the relevant business entities of virtual asset exchanges are included in the regulatory framework of the VASP system, Derivatives transactions, proprietary transactions , market maker, pledge and other businesses are not involved for the time being. However, it does not rule out that the Hong Kong Financial Services and the Treasury Bureau will include other virtual assets and virtual asset services in the form of gazetted announcements.
Regarding Stablecoin, the SFC also made it clear in the "Consultation Summary" that the Hong Kong Monetary Authority has released the "Consultation Summary of Encrypted Assets and Stablecoin Discussion Documents" in January 2023, stating that it will implement Stablecoin regulations in 2023/24. Regulatory arrangements will establish a licensing and licensing system for Stablecoin related activities. Until Stablecoin are regulated, the SFC believes that Stablecoin should not be included for retail trading .
The attributes of NFT are linked to the attributes of the assets behind it, and there is no clear definition under the VASP system yet. When SFC issued a reminder to investors on NFT risks on June 6, 2022, it stated that if NFT is a true digital representation of collectibles (art, music or movies), activities related to it are not within the scope of SFC's supervision. However, some NFTs cross the boundary between collectibles and financial assets, and may have the attributes of "securities" regulated by the Securities and Futures Ordinance, so they will be regulated.
2.6 A New Path to Real World Asset Tokenization (RWA)
Real World Assets (RWA) tokenization refers to converting the monetary value of real assets into digital tokens so that their value can be reflected and traded on the blockchain. RWAs can represent many different types of traditional assets (both tangible and intangible), such as commercial real estate, bonds, precious metals, art, wine, and just about any asset that has a store of value that could be tokenized, making it easier to Circulation, trading and financing can also increase its transparency, Liquidity and value.
Since the "Policy Declaration", the Hong Kong government has carried out a series of actions related to RWA. On February 16, 2023, the Hong Kong government successfully issued a tokenized green bond of HK$800 million. bond. The subsequent digital Hong Kong dollar is also a Stablecoin anchored by the legal Hong Kong dollar. At the same time, the Hong Kong government is also working to further regulate the Security Token Offering (Security Token Offering), which will bring non-standard and poor liquidity markets such as the real estate market, private debt and equity markets, and the art market. A new financing channel.
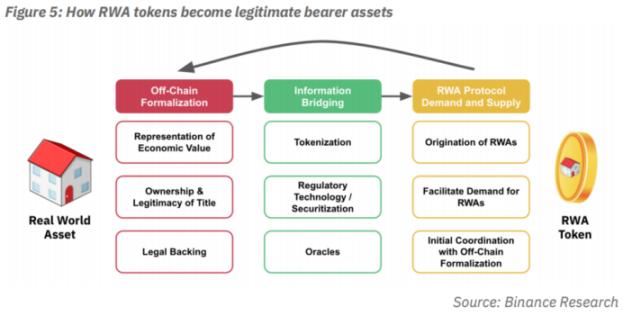
Traditional financial institutions such as Goldman Sachs, Hamilton Lane, Siemens, and KKR have all announced efforts to put their real-world assets on the chain. Additionally, crypto-native DeFi protocols such as MakerDAO and AAVE are being adjusted to be compatible with RWA. Traditional financial institutions can rely on their own rich financial assets and resources to enter the Hong Kong RWA market, further industrialize virtual assets, and let finance help the real economy .
3. The compliance practice of traditional finance entering the Hong Kong Web3 virtual asset market

Through the above analysis, applying the business model of Hashkey Group to the framework of Coinbase, we can see that a relatively complete compliant CEX business model has basically been formed, and each business can correspond to the corresponding regulatory framework, such as Deposit and withdrawal of virtual assets (cooperation with banks), security token transactions (No. 1 license + No. 7 license), non-security token transactions (VASP license), virtual asset custody (TCSP license), venture capital ( 9 plate). It can be seen how fast, accurate and ruthless the Hong Kong government's new VASP regulations directly target CEX.
Fourth, write at the end
Gary Gensler, chairman of the US SEC, talked about the SEC's regulatory thinking on CEX in his work video "What Are Crypto Trading Platforms?" in August 2022: (1) Based on the 90-year-old US Securities Law , to protect the interests of investors. (2) It is necessary to split CEX (such as splitting CEX's market-making transaction business and custody business) to avoid conflicts of interest and self-stealing situations.
This was fully reflected in the FTX incident, so there will be a follow-up SEC's new regulations (proposals) for virtual asset custody. The 1933 Glass Steagall Act against the background of the Great Depression (strictly separate the investment banking business of the bank from the commercial banking business to avoid the risks brought about by the investment banking business), and the 2010 Dodd Frank Act against the background of the subprime mortgage crisis (splitting the big financial Institutional speculative proprietary trading, strengthening the supervision of financial Derivatives to prevent systemic financial risks) are bloody lessons from the financial crisis.

Hong Kong's VASP system has fully learned the above lessons, and first "led water into the channel" through CEX. In this context, KYC anti-money laundering (AML) and anti-terrorist financing (CTF) are the top priorities. After that, we will see a series of detailed regulations issued in the second half of the year regarding the opening of retail investor investment, how to protect investors, and how to gradually liberalize the definition of virtual assets and virtual asset services. If you want to wear the crown, you must bear its weight. Only on the basis of meeting the regulatory requirements, can friends at the poker table participate in the distribution of this huge cake and promote the long-term development of the market.
Positive policies are bound to be accompanied by deeper reasons. From a geopolitical point of view, whether the conflict between the CIPS RMB cross-border settlement system backed by the mainland and the US dollar-based SWIFT settlement system will lead to borderless and license-free regional The development of blockchain payment network? Going a step further, can Hong Kong seize the new narrative of "Web3 virtual assets" that is very suitable for its own temperament and revive it? We don't know for the time being, but what we can see is the current climate and people, and what we can see is Hong Kong where the wind is blowing.
Reference:
[1] Heavy | The countdown to running ahead! In-depth interpretation of Hong Kong's virtual asset VASP licensing system (June 1, 2023)
[2] A brief analysis of the legal compliance of the Web3 project in the US exhibition industry, starting from the global regulatory compliance of CEX listed in the US
[3] This article tells the story 丨 How do virtual currency funds develop their businesses in Hong Kong in compliance?








