Source: The Token Dispatch
Author: Prathik Desai
Original title: When On-Chain Lending Assembled
Compiled and edited by: BitpushNews
Credit is a "time machine" in the economic system. It allows businesses to incorporate future cash flows into their current decisions.
I believe that credit is one of the most underestimated cornerstones of the financial world. When the credit system is functioning smoothly, people rarely notice it; but its influence permeates every micro-level of business operations. An efficient credit system allows businesses to replenish inventory before shelves become empty, factories to upgrade old equipment before it becomes obsolete, and entrepreneurs to expand hiring in advance before redundant manpower turns into a crisis.
The gap between a good idea and its implementation often stems from limitations in credit access. Bridging this gap is precisely the promise banks make to their customers.
Banks accept customer deposits through accounts and extend them as credit to borrowers. They pay depositors lower interest rates and charge borrowers higher interest rates, earning a profit from the interest rate spread.
However, bank lending is not perfect, and the mismatch between supply and demand is one of its most serious challenges. While private lending fills the gap in areas inaccessible to banks, a gap still exists. This gap reflects investors' hesitation to lend in the current credit environment.
In March 2025, the International Finance Corporation (IFC) and the World Bank released the "Financing Gap Report for SMEs," which estimated that the financing gap in 119 emerging market and developing economies (EMDEs) would reach approximately US$5.7 trillion. This represents about 19% of the collective GDP of these economies.
It is against this backdrop that the development of on-chain lending is extremely promising. On-chain lending is not a new concept; the industry experienced a frenzied cycle in 2022, and it is still being discussed repeatedly for various reasons. However, the current cycle feels completely different.
This article will delve into all the changes that have occurred in the on-chain lending market and why it has the potential to radically transform the future of the lending industry.
Let's begin.
From a single agreement to ecosystem integration
The money market on Ethereum has been around for years. Overcollateralized lending, liquidation bots, yield curves, and the occasional cascading liquidations are nothing new. So when a series of credit-related announcements came out last week, what really caught my attention wasn't the underlying lending primitives, but the players involved and how they repackaged credit.
What excites me is that these isolated partner announcements collectively send a grand signal of convergence. What sprouted in the DeFi silos in the summer of 2022 is now converging. Vault infrastructure, non-custodial wrappers, professional risk management firms, and automated yield optimizations are being integrated and widely distributed.
Kraken has launched DeFi Earn , a retail-friendly wrapper that routes lenders' deposits to vaults (Veda in this case). These vaults then direct funds to lending protocols like Aave . Chaos Labs will act as the risk manager, monitoring the entire engine in real time. Kraken promises lenders up to an annualized yield (APY).
What changes do vaults bring? They provide lenders with self-custody capabilities and transparency. In traditional credit markets, you need to hand over your funds to a fund manager and then wait for monthly disclosures; while vaults integrate smart contracts that can mint ownership certificates for funds and display the deployment of funds in real time on the blockchain.
At almost the same time, Bitwise , the world's largest crypto fund manager, launched a non-custodial vault strategy on its on-chain lending platform Morpho.
This isn't the first time on-chain lending has gained institutional recognition. In 2025, Coinbase launched USDC lending, allowing smart contract wallets to connect and route deposits to Morpho via an on-chain vault. Steakhouse Financial orchestrated this, optimizing returns by allocating funds across different markets.
These developments come at a time when the on-chain lending market is on the verge of explosive growth. Data proves this:
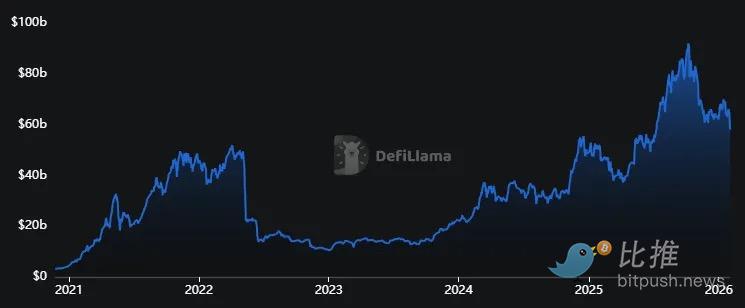
(Data source: DeFiLlama)
The total value locked (TVL) in lending agreements has reached $58 billion, a 150% increase in two years . However, this figure is only 10% higher than the peak in 2022.
At this point, the Active Loans Outstanding dashboard provides a more accurate and comprehensive picture:
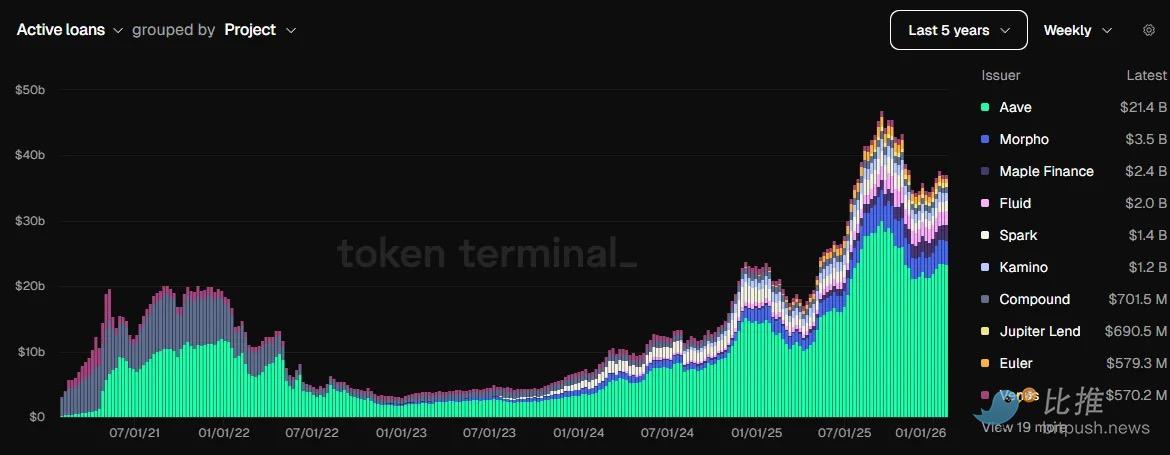
(Data source: Token Terminal)
The dashboard shows that established agreements, including Aave and Morpho, have laid a solid foundation, with active lending exceeding $40 billion in the past few months, more than double the peak in 2022. Currently, Aave and Morpho's fee revenue is six times what it was two years ago.
Why is this time different?
While these visual charts demonstrate investor confidence in lending agreements, I believe the growth of vault deposits over time is more compelling.
In October 2025, total insurance treasury deposits surpassed $6 billion for the first time in history. Currently, these deposits stand at $5.7 billion, more than double last year's $2.34 billion.
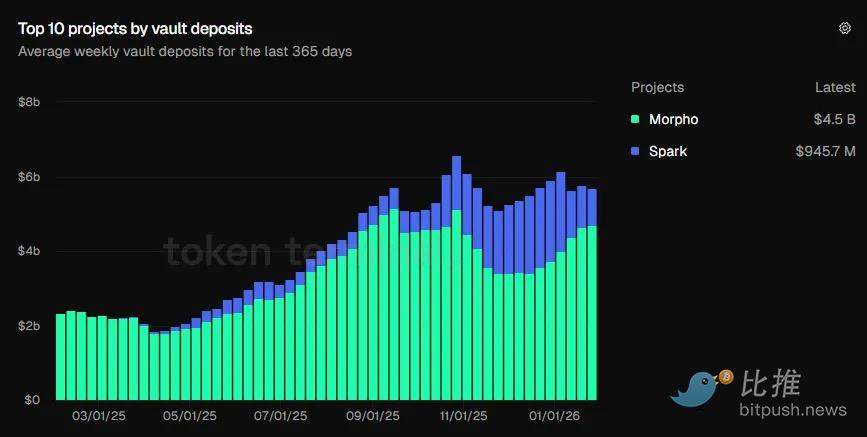
(Data source: Token Terminal)
Statistical charts show that users are increasingly choosing products that offer a complete ecosystem, including vaults, return optimization strategies, risk profiles, and support from professional managers.
This evolution is precisely why I remain optimistic; it stands in stark contrast to the chaos of the "DeFi Summer." Back then, the lending market seemed more like a closed loop: users leveraged their investments by depositing collateral, lending out funds, buying more collateral, and then depositing again to obtain higher returns. Even if collateral prices fell, users could at least receive token incentives from the platform. But when these incentives disappeared, the loop collapsed.
Even though the current cycle is still built on the same primitive—"over-collateralized lending"—it has a different and more solid foundation. Today's vault has evolved into a wrapper, transforming agreements into automated asset management tools, while risk managers step into the spotlight to set the red lines and safeguards.
This shift has changed the attractiveness of on-chain lending to both investors and lenders.
During the "DeFi Summer," lending protocols were simply another way to make quick money. Once the incentives dried up, the game was over. We saw this happen with Aave's Avalanche deployment: incentives attracted a large number of deposits and funded a leveraged cycle, but when subsidies waned, the cycle collapsed. As a result, outstanding debt on Avalanche plummeted by 73% quarter-over-quarter in Q3 2022.
Today, lending has evolved into a well-supported ecosystem with professional roles responsible for risk, return optimization, and liquidity.
Structure of the on-chain credit stack
This is how I understand the entire stack:
Settlement layer (bottom layer): Settlement funds in the form of stablecoins . They can be moved instantly, reside at any time, and be deployed immediately, and are extremely easy to audit.
Money market layer: In mature markets like Aave, lending is enforced by code and collateral.
Wrappers and Routers: This layer is responsible for pooling lenders' funds and routing them to borrowers. Vaults act as wrappers, packaging credit products in a way that is easy for retail investors to understand. For example, the Veda wallet is presented on Kraken's Earn platform as: "Deposit X, earn up to Y% in returns."

Curators: They sit atop the agreement, deciding which collateral is allowed, setting liquidation thresholds, managing risk exposure concentration, and deciding when to exit positions as collateral value declines. This is exemplified by Steakhouse Financial's role on Morpho, or asset management firms like Bitwise injecting their expertise directly into the vault rules.
AI-Optimized Engine (Nervous System): The AI system operates 24/7 to manage on-chain credit risk. Manual risk management is difficult to scale and increases risk during periods of high volatility, leading to poor returns or even liquidation. The AI engine tracks borrowing demand, oracle bias, and liquidity depth to trigger timely withdrawals or alerts and provides decision support to the team when risk exceeds limits.
It is this 24/7 optimization, risk mitigation, audited insurance vaults, planned strategies, institutional endorsements, and professional risk management that makes the current market feel safer and the risks more controllable.
Challenges that still exist
Of course, none of these measures can completely eliminate risk. The most easily overlooked risk is liquidity risk. While vaults offer better liquidity than orphanages, they still operate within the same market environment. When market liquidity is scarce, vaults may face difficulties withdrawing funds due to excessively high exit costs.
Furthermore, there is the risk of discretion on the part of the planner. When users deposit funds into an insurance account, they are essentially trusting someone's judgment in allocating the market, selecting collateral, and setting thresholds. While this is common knowledge in credit operations, lenders must understand that non-custodial does not equate to zero risk.
Summarize
Despite the challenges that remain, on-chain lending is changing the crypto landscape and extending into the real economy.
The operation of the credit market relies on time and operating costs. Traditional lending is costly due to the enormous expenses involved in verification, monitoring, reporting, settlement, and enforcement. A large portion of the interest charged by banks to borrowers is actually to cover these unavoidable costs, rather than purely the "time value of money."
On-chain lending significantly reduces time and operating costs:
Stablecoins minimize settlement time;
Smart contracts shorten the enforcement time;
Transparent ledgers reduce audit and reporting time;
Vaults eliminate operational complexity for users.
These cost savings will be particularly significant when applied to the credit gap for SMEs. On-chain lending won't fill a trillion-dollar gap overnight, but lower credit costs will make identity verification easier and access more inclusive. Ultimately, this will reshape the global economy.
Twitter: https://twitter.com/BitpushNewsCN
BitPush Telegram Community Group: https://t.me/BitPushCommunity
Subscribe to Bitpush Telegram: https://t.me/bitpush







