By Patrick Bush & Matthew Sigel
Compiled by Wu Blockchain Blockchain Aki
Original link:
Note that VanEck holds positions in Bitcoin, MSTR, STRK, and STRF.
VanEck views Strategy (MSTR) as a structurally leveraged Bitcoin vehicle and analyzes it from the following dimensions: its net asset value (NAV) premium, compliance status, and how the optionality brought by its capital structure jointly drives its investment opportunities and potential risks.
MicroStrategy (MSTR) accounts for nearly one-third of the market capitalization of pure crypto stocks and constitutes 10% of the weight of the Market Vector Global Digital Asset Stock Index (MVDAPP). Therefore, whether to include it in the portfolio has become a key decision that investment managers who hope to obtain excess returns through the digital asset transformation must weigh. The market debate continues on the pros and cons of holding MSTR, Bitcoin (BTC) or leveraged BTC exposure, and the core reason lies in the complexity of MicroStrategy's capital structure. This judgment is further affected by its issuance of multiple capital instruments, including high-yielding convertible preferred stock (STRK) and higher-yielding but non-convertible preferred stock (STRF), which makes the overall valuation and allocation decision more complicated. In this report, we evaluate the capital structure of MicroStrategy (Strategy) and analyze the pros and cons of building a position in its equity or debt layer. We believe that MSTR common stock is a better investment option compared to other investment tools provided by Strategy. This judgment is based on the following three reasons: maximum Bitcoin exposure, simplest investment strategy structure, and most superior risk/return configuration.
MSTR is a highly leveraged Bitcoin long structure
MSTR shares are leveraged proxy instruments for Bitcoin (BTC): MicroStrategy (MSTR) shares behave like call options on Bitcoin due to its recursive strategy of accumulating Bitcoin through the continuous issuance of equity and debt. This structure provides asymmetric upside potential and is highly sensitive to Bitcoin price fluctuations, making MSTR a popular alternative to holding Bitcoin directly.
MSTR is trading at a substantial premium to its net asset value (NAV): We estimate that MSTR is currently trading at a premium of approximately +112% to the fair value of its Bitcoin holdings and core software business combined. This premium is mainly due to market expectations of continued Bitcoin accumulation in the future, potential compliance advantages, and market momentum from speculative allocations.
MSTR’s premium is essentially a “metastable” crypto reactor that drives its own operation: this premium continuously enhances MSTR’s equity value through a recursive cycle mechanism — its high volatility exposure to Bitcoin attracts capital inflows, enabling the company to further increase its Bitcoin holdings, thereby exacerbating its market premium and forming a positive feedback loop.
Convertible securities increase optionality, but also increase risk: The convertible bonds and preferred stocks included in this strategy (especially STRK and STRF) provide different degrees of yield and Bitcoin exposure, but are accompanied by high structural complexity, downside asymmetry, and sensitivity to market fluctuations. Among them, the convertible bonds due on March 15, 2030 have the largest exposure to MSTR, but even these instruments are still highly dependent on the performance of Bitcoin and the persistence of the MSTR premium.
What is Strategy?
Strategy (formerly MicroStrategy) is an enterprise analytics software provider and pioneered the concept of a “corporate bitcoin vault.” In August 2020, Strategy determined that the large cash reserves on its balance sheet were at risk of inflation in the low interest rate environment at the time. As a starting point for its “Bitcoin Vault Strategy,” the company used $250 million in cash to purchase 21,454 bitcoins (BTC). In December 2020, Strategy issued $650 million in convertible bonds and made it clear that it would continue to purchase bitcoin (BTC) through “financial alchemy.” Since then, Strategy has ceased to be a traditional enterprise software company and has transformed into a leveraged bitcoin financial carrier. Through leverage and the issuance of various forms of equity instruments, Strategy has accumulated 2.7% of the world’s total bitcoin supply, which is approximately $61 billion at the time of writing.
Strategy's explicit goal is to maximize MSTR's share price by increasing the amount of Bitcoin (BTC) that is "benchmarked" per common share. Strategy continuously increases the amount of BTC per share by issuing debt or equity, and calls this dynamic process "Bitcoin Yield". In periods when Bitcoin prices rise and investors' risk appetite increases, the company will choose to leverage or issue additional shares. Therefore, Strategy's exposure to BTC and its leverage structure have a recursive nature, that is, the mechanism is expected to continue to expand over time. When the price of Bitcoin rises, the total value of BTC held by Strategy increases accordingly, so that it can refinance by issuing debt again to further purchase BTC. At the equity level, when BTC is in a bull market, MSTR common stock can usually obtain good capital market pricing, and the company can exchange more BTC for additional shares.
Ultimately, MSTR stock exhibits accelerated exposure to BTC, moving in tandem with the price of Bitcoin, so its price dynamics are somewhat similar to BTC call options.
The logic behind MSTR’s share price premium
MSTR common stock currently trades at a premium to the sum of its Bitcoin Net Asset Value (BTC NAV) and the value of its core software business (hereinafter referred to as the "Premium"). At the time of writing, MSTR common stock trades at a premium of +112% to the fair value of its underlying assets (i.e., BTC holdings plus core business).
Mathematically, we define this premium as follows:

There are many different opinions on the causes of MSTR premium, but we believe that it is mainly driven by four factors:
1. Market expectations for Strategy’s future Bitcoin holdings
2. Investors have limited access to Bitcoin
3. Strategy The amplification effect brought by leverage operation and its institutional advantages
4. Speculative Behavior
The primary reason for the MSTR premium is the market's expectation of Strategy's future Bitcoin holdings. This expected value can be estimated using three core variables: the final number of Bitcoins held (terminal value), the predicted price of Bitcoin in the future, and the discount rate applied to the holding. The large premium currently existing in MSTR stock reflects the market's general expectation that the company will continue to increase its Bitcoin holdings. A positive premium means that the market believes that the value of Bitcoin itself will also rise, so the premium essentially reflects the discounted expectation of the future price of BTC.
The second factor can be called the "compliance premium", which comes from the structural constraints in the current investment environment. Many institutional and individual investors are unable to purchase Bitcoin directly due to regulatory constraints, investment authorization restrictions, distribution channel bottlenecks, or lack of secure custody solutions. Since most investors cannot obtain capital-efficient, leveraged Bitcoin exposure, they choose to invest in MSTR instead. In many jurisdictions, Bitcoin does not have advantages in terms of tax treatment and capital holding requirements, which further drives investors' preference for publicly traded stocks such as MSTR as an alternative.
As a common stock, MSTR also has the financial advantages of being a collateral asset. Because of these investment barriers, MSTR has become a preferred alternative tool for investors who cannot directly access this asset class to gain exposure to Bitcoin.
The third component of the MSTR premium is the market’s recognition of Michael Saylor’s ability to use financial leverage, which is something that most investors do not have. Saylor has demonstrated the ability to raise large amounts of capital at low interest rates, and his corporate structure is also highly resilient during the Bitcoin market downturn. Unlike ordinary margin traders who are often forced to close their positions during down cycles, Saylor can withstand paper losses and hold positions for a long time. During parts of 2022 and 2023, MSTR’s market value remained above the billions of dollars even though Strategy’s shareholder equity deficit was as high as hundreds of millions of dollars, reflecting investors’ confidence in the long-term leverage structure that Strategy has built.
Due to its special structure, MSTR's 30-day historical volatility has been "accelerated" to about 113%, much higher than Bitcoin's own 55%. In short, MSTR stock provides investors with a leveraged Bitcoin investment tool that can be traded on the public stock market. Among them, "premium" is the main factor driving the volatility and performance of MSTR's stock price. By disassembling the weights, correlations and volatility in MSTR's asset portfolio structure (i.e., BTC + main business + premium), we come to the following conclusion: In this "portfolio", the premium contributes about 96.5% of the total return performance and about 87.5% of the overall volatility.
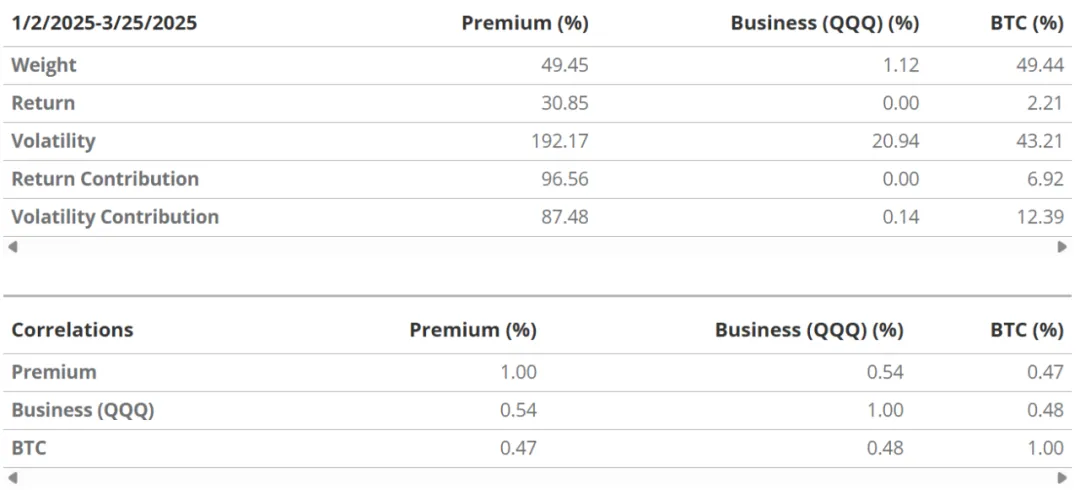
The fourth reason for MSTR's premium stems from its speculative trading dynamics related to volatility and capital structure. Since "premium" dominates MSTR's returns and volatility, once its core drivers are disturbed, MSTR's stock price will be severely impacted. The reason is that Saylor is using MSTR's volatility to "harvest" and raise funds to purchase Bitcoin. As described below, Saylor's preferred financing sequence is: preferred stock, convertible preferred stock, convertible bonds, and common stock. This sequence is based on the equity-enhancing effect of "BTC gains" on common shareholders, which depends on the number of Bitcoins per share. For example, although financing through the sale of preferred stock will cause share dilution, the proceeds of the financing will directly convert into BTC gains for common shareholders.
These securities from Strategy are popular among investors because MSTR's high volatility creates a lot of trading opportunities for all levels of its capital structure and related options products. In fact, Strategy is able to issue convertible bonds at a lower interest rate because MSTR's high volatility greatly increases the value of the options portion of the convertible bonds. It can be said that Strategy deliberately prices this part of "option value" low to attract market participants engaged in relative value trading. These professional arbitrageurs often trade relative value between volatility-related "slices" of different Strategy securities. Ultimately, a circular relationship is formed between Strategy's "premium" and its ability to finance the purchase of more Bitcoin. The "premium" constitutes the main source of MSTR's volatility, but the "premium" itself depends largely on whether Strategy can continue to finance the purchase of Bitcoin. The reason why the market is willing to buy various types of Strategy securities is because its capital structure is highly volatile, and Strategy can also be said to sell this volatility "at a low price." During the Q1 2025 earnings call, Saylor referred to this self-reinforcing dynamic as a “crypto reactor that can run for a long time.”
MSTR's "premium" shows a clear positive correlation with the price of Bitcoin. Over the past year, the premium has a correlation coefficient of 0.52 with BTC (T statistic = 9), and an approximate beta value relative to BTC of about 1.77. This shows that when the price of Bitcoin rises, MSTR's premium tends to expand accordingly, further enhancing its stock performance. The connection between Bitcoin price, speculative sentiment, financing ability and MSTR valuation forms a self-reinforcing cycle structure, which is the key to the company's core strategy.

Correlation between MSTR premium and Bitcoin price movement
Strategy's Bitcoin Asset Allocation
In October 2024, Strategy announced an ambitious "21/21 Capital Plan" with the goal of raising $42 billion to buy Bitcoin by 2027. The plan is to raise funds by selling $21 billion in MSTR equity and $21 billion in fixed-income securities. In the original plan, Strategy plans to sell $5 billion in equity in 2025, $7 billion in 2026, and $9 billion in 2027; at the same time, on the debt side, it will issue $5 billion, $7 billion, and $9 billion in fixed-income securities in three years at the same pace. The target leverage ratio for these bond issuances is set between 20% and 30%. Strategy leader Michael Saylor calls this "intelligent leverage," and its purpose is not to speculate, but to strategically acquire "dominant digital assets."
Benefiting from the unprecedented crypto bull market after the launch of the 21/21 plan, as of May 2025, Strategy has successfully sold all $21 billion worth of MSTR shares through its "market-to-market" plan. In the fixed income segment, Saylor has completed financing including: $5 billion in convertible bonds, $875 million in STRK convertible preferred shares, and $850 million in non-convertible preferred shares. In the earnings call on May 1, 2025, Strategy announced that it would expand its financing to $84 billion, including a new $21 billion MSTR ATM program, the existing $21 billion STRK ATM program, and an additional $14 billion in convertible bond issuance.

42/42 Fundraising Plan Progress: 32% Achieved
With the current Bitcoin price at around $95,000 and Strategy holding a total of 555,450 BTC, we estimate Saylor's leverage ratio ((debt + preferred stock) / market value) to be 9%. This ratio is the lowest leverage ratio Strategy has adopted since 2020. Considering that the current leverage ratio is significantly lower than its historical average and Saylor has publicly stated his preference for "convertible, unsecured, non-recourse" debt, it is reasonable to expect that Strategy will further raise capital by issuing convertible debt in the near future.
Financing through volatility arbitrage

Because MSTR stock has leveraged exposure to Bitcoin, and this leverage is likely to increase as Strategy continues to raise funds to purchase BTC, its stock price is extremely volatile. Most investors are generally reluctant to leverage highly volatile assets (such as Bitcoin), and therefore require higher interest rates as risk compensation. To address this problem, Strategy chose to issue convertible bonds and convertible preferred stocks, and most of the value of these securities comes from the option features embedded in them. Savvy investors prefer this form of issuance because it can be used to implement strategies such as "convertible bond arbitrage." This strategy is inherently risky and complex, and is usually operated by experienced investors. Its basic approach is to buy convertible bonds while short MSTR stock or MSTR options to obtain the difference between realized volatility, implied volatility and other option pricing factors.
This transaction mechanism helps Strategy relieve cash flow pressure because it ensures that the company's interest expenses on debt remain low. Due to the strong market demand for highly volatile convertible securities, Strategy can promise investors extremely low future interest payments. There is a complex and delicate game relationship between Strategy's capital market strategy and the market preferences of potential investors.
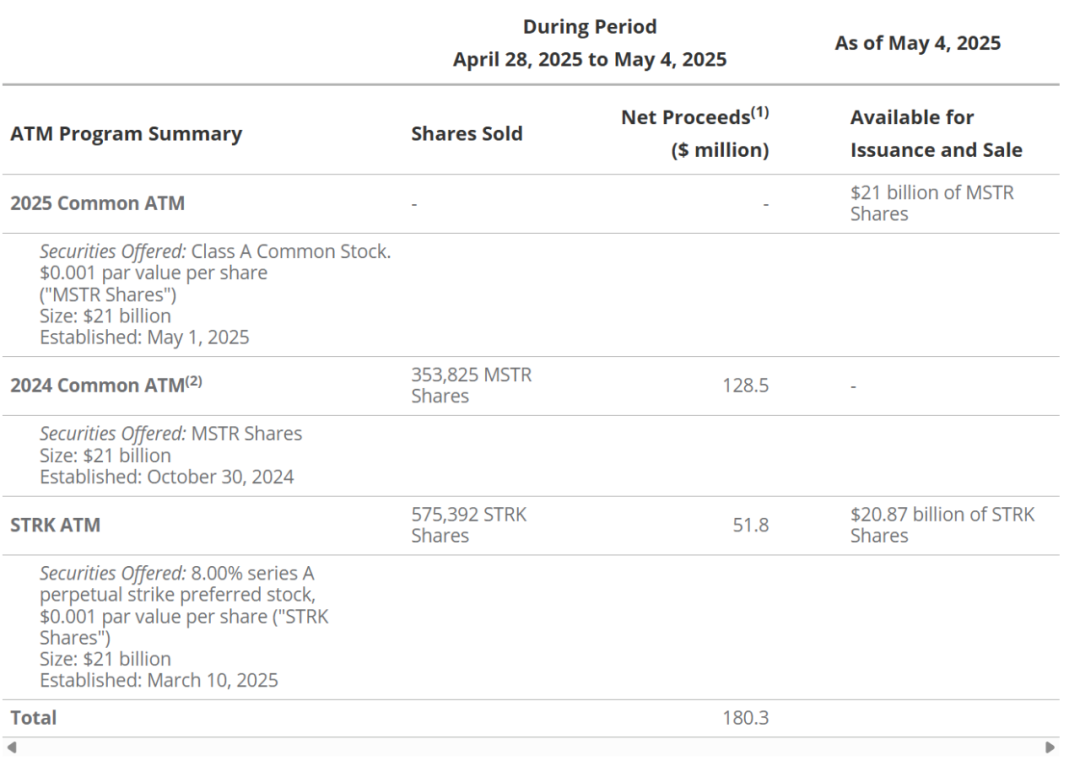
1. Net income is the net amount after deducting sales commissions.
2. The 2024 At-the-Market (ATM) common stock issuance program has been substantially sold out and the sales agreement corresponding to the program has been terminated in accordance with the terms.
This involves Strategy pricing implied volatility, setting strike prices, and adding redemption prices to maximize the tradability of each issuance. For example, setting a redemption price slightly closer to the current price allows Strategy to set a cap on the upside of the option portion of its bond, making the derivative more like a "capped call" with a delta that is typically lower than a regular call option. In addition, setting a strike price in the convertible security that is far from the current price can also reduce the value of the option portion and its delta. Lowering delta means that fewer MSTR shares (or options) are required for the option hedge embedded in the convertible security. Many convertible bond arbitrage investors prefer low-delta issuance structures because such transactions require less capital and are more suitable for trading-based fund management needs.
Strategy Financing Sustainability Assessment
Although Strategy's core software business generates some operating income, the purchase of Bitcoin through financing will generate significant cash needs. Based on Strategy's published documents and public statements, we expect its total debt to increase to $13 billion by the end of 2025 (a significant increase from approximately $8 billion in April 2025) and to $19 billion by the end of 2026. At the same time, we expect its preferred stock size to increase to $7.5 billion in 2025 and further to $15.5 billion in 2026. We expect Strategy's annual interest expense to reach $48 million by the end of 2025 and grow to $87 million in 2026. At the same time, the preferred stock (STRK) is expected to bring in $217 million in dividend payments in 2025 and $904 million in 2026. These figures are based on our estimates of the market's expectations for MSTR's bond coupons and preferred stock dividends. Although Strategy retains the option to pay dividends on STRK preferred stock in the form of common stock, such an approach would dilute the interests of existing MSTR shareholders as it would reduce the amount of BTC held per share.
With revenues of $475 million expected in 2025, Strategy still needs to rely on financing to cover its fixed-income expense obligations. Of course, its continued ability to raise funds is premised on the performance of Bitcoin prices. If Bitcoin prices continue to rise, it will be relatively easy to obtain new capital. Between August 2024 and May 2025, Strategy raised $28.7 billion in financing to increase its BTC holdings from 226,000 to 555,450. However, during the crypto market downturn from June to December 2022, Strategy only raised $49 million and $11 million through equity and debt issuance, respectively. With a new round of fixed-income securities issuance bringing higher cash expenditures, Strategy's financing environment will become particularly difficult if the market enters a bear market.
The return of the "random buying" scheme is better than the concentrated buying of Strategy
Investing in MSTR is similar to investing in Bitcoin call options to some extent, because MSTR has a leverage amplification effect (i.e., "torque") on BTC price fluctuations. However, in fact, this is more like a strategy of dynamically replicating BTC call options, that is, continuously increasing leverage exposure during the rise in BTC prices. The game logic of Strategy is: once the financing conditions are met, expand its BTC position, which usually occurs during the rise in BTC prices.
The risk of this strategy is not only the price drop, but also the fact that when the financing chain breaks, MSTR's premium will shrink sharply.
In addition, the timing of capital injection for this strategy is often during a controversial period, that is, increasing positions when the BTC price is high, which poses a risk of “buying high”.
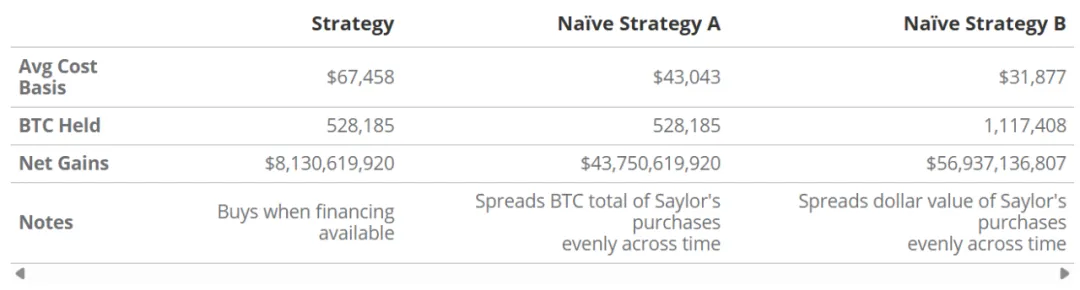
Strategy's purchase of Bitcoin at local highs will result in a "paper loss" compared to other options, because this practice raises the average purchase cost of the company's overall BTC holdings above the average price that would be formed if a random purchase scheme was adopted. Whether Strategy's purchases themselves caused these "local highs or lows" is another question. In any case, this strategy of buying at high prices will be disadvantageous to MSTR shareholders compared to a simple, randomly executed BTC allocation method. On the other hand, MSTR's structure has the so-called "positive convexity": as the price of BTC rises, the dollar value of BTC represented by each share increases and amplifies; at the same time, the increase in BTC holdings brought about by the new financing will also increase the proportion of BTC per share. Therefore, MSTR investors will gain increasing BTC exposure as the price of BTC rises.
Without the help of this "shell structure" of the enterprise, it is almost impossible for ordinary investors to replicate Saylor's Bitcoin strategy. Although individual investors can increase their margin balances during the price increase by purchasing BTC futures contracts, and then buy more BTC, they cannot "patiently" hold leveraged positions during the price decline. Because futures contracts are resettled daily at market value, profits and losses must be settled in real time. Once a retracement occurs, insufficient margin must be immediately replenished (margin call). If the BTC price falls below its margin level, traders will be forced to close their positions. Therefore, even if a savvy trader tries to imitate Saylor's strategy, as BTC rises and gradually increases positions, a mild pullback may trigger a forced liquidation, thereby clearing all positions. This daily margin requirement makes it almost impossible for ordinary investors to replicate Strategy's long-term BTC accumulation strategy through the futures market. In contrast, Strategy has a significant financial structure advantage and can execute leveraged BTC allocation strategies with higher efficiency.
MSTR’s capital layout and “Bitcoin yield rate” indicator analysis
Strategy has financially engineered its balance sheet to include a significant amount of debt and shares outstanding to increase its exposure to Bitcoin per common share. This is because its core goal is to continually increase the sensitivity of common shares to BTC prices and the corresponding holdings. Saylor calls this continued increase in the number of BTC per share “BTC Yield.” This key performance indicator is measured by tracking the change in BTC holdings per share over time. As of May 2025, the year-to-date BTC yield is approximately 14% on an outstanding common share basis, and approximately 13% on a fully diluted basis. Strategy’s minimum BTC Yield target for 2025 is 25%, which means that the BTC holdings for every 1,000 shares of MSTR will increase from approximately 1.79 BTC on May 8, 2025 to approximately 1.99 BTC by the end of the year.
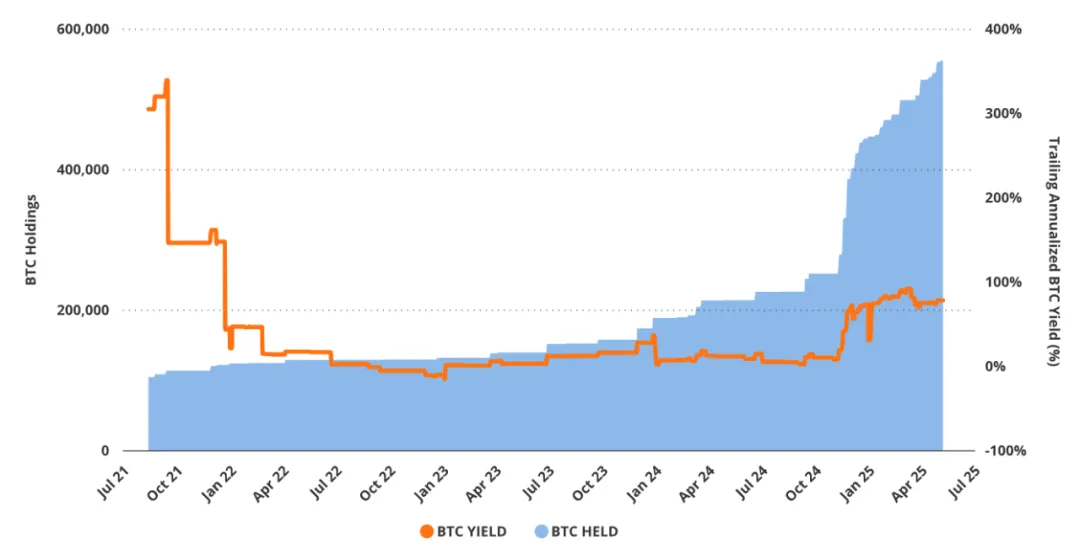
Strategy’s Bitcoin yield slowed month-on-month
Strategy management has multiple options for increasing "BTC yield". On the one hand, they can increase the "numerator" by acquiring BTC through the sale of various financial instruments; on the other hand, they can also repurchase common stock to reduce the "denominator". Since MSTR stock is currently trading at a premium, a relatively more logical approach is to sell "overvalued stocks" or issue debt in exchange for BTC. Selling common stock through the ATM mechanism to purchase BTC may be the most direct way, but it is also the most dilutive and requires the purchase of the largest number of BTC. Saylor mentioned this structural dynamic in the first quarter 2025 earnings call, noting that they prefer to acquire BTC by selling perpetual, non-convertible equity securities.
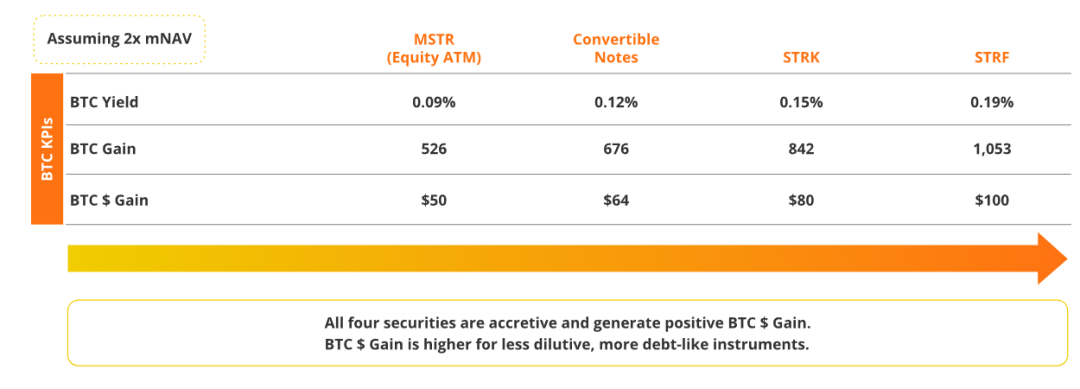
Comparison of BTC indicators for various securities under $100 million insurance
If Saylor does not issue any additional common shares in the process of achieving Strategy's BTC yield target, it will need to purchase approximately 58,312 BTC, which is approximately $5.9 billion at current prices. On the other hand, if this exposure is achieved entirely through the issuance of additional common shares, it will need to issue approximately 25.8 million shares to purchase approximately 106,305 BTC, which is currently worth approximately $10.8 billion. Considering the high recognition and strong demand for Strategy's capital structure in the capital market, Strategy is likely to successfully achieve its 2025 BTC yield target of 25%.
High BTC yields face sustainability challenges
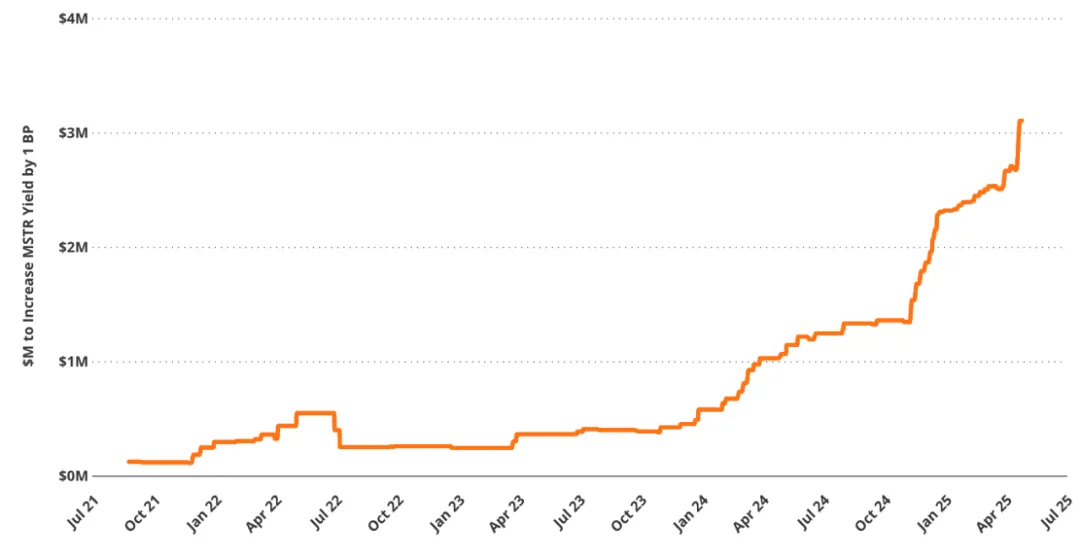
Dollar amount required to increase MSTR yield by 1 basis point (in millions of dollars, 90-day moving average)
There is a fact about Saylor's Bitcoin strategy: high levels of BTC yields are unsustainable because of diminishing marginal returns. As the total amount of BTC held by Strategy continues to increase, it will become increasingly difficult to further achieve significant increases in BTC yields. This is because, as the total BTC holdings continue to expand, the amount of additional BTC required to increase the yield by each basis point (bps) will increase disproportionately, that is, the marginal BTC efficiency will gradually decrease.
For example, in August 2021, MicroStrategy only needed to add approximately 2.6 BTC to achieve a 1 basis point increase in BTC yield; by May 2025, that number had surged to 58 BTC.
If measured in US dollars, the capital required to achieve the same unit rate of return has jumped from approximately $126,000 to $5.5 million. This reflects a basic mathematical law: as Strategy's BTC holdings continue to expand, the marginal rate of return brought by each additional BTC continues to decline, while the capital expenditure required to achieve the same rate of return is increasing exponentially. This increasing nonlinear efficiency loss constitutes a decreasing upper limit to Strategy's sustainable profitability.
Strategy Convertible Bond Analysis
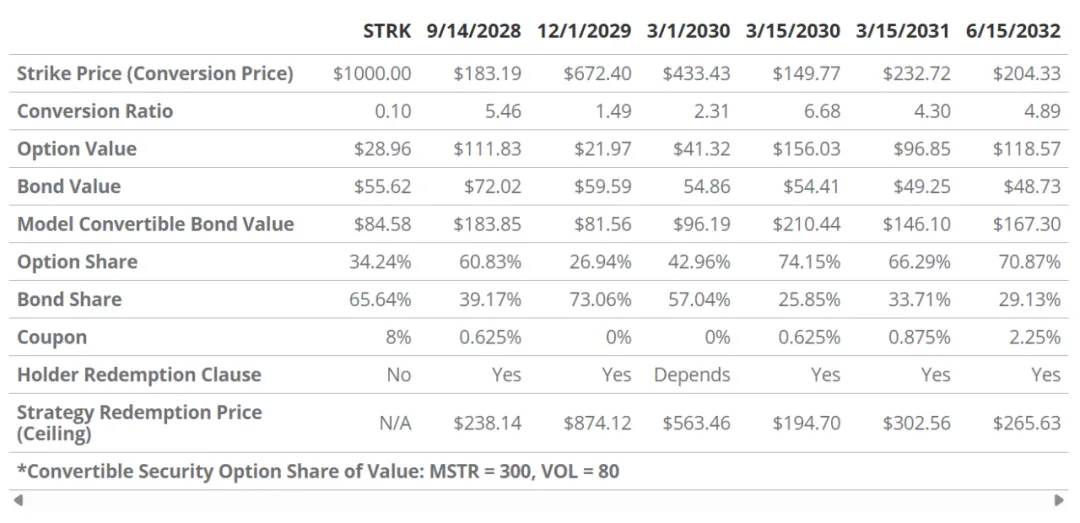
Convertible bonds are hybrid securities that combine the stability of a fixed-income instrument with the upside potential of equities. They are typically structured as a traditional bond with an embedded call option that allows the holder to convert the bond into MSTR common stock under certain conditions.
Therefore, the total value of a convertible bond consists of two parts: the value of the bond + the value of the conversion option.
When investors buy convertible bonds, their principal is actually divided into two parts: one part is allocated to corporate bonds, and the other part is allocated to call options. Because of this, the pricing of convertible bonds is sensitive to two types of variables: one is variables related to option pricing, such as the underlying price, Delta, Gamma, etc.; the other is factors related to bond pricing, such as interest rate levels and credit spreads.
Special terms were included in the convertible bonds issued by Strategy, which limited the upside of the attached options and provided investors with a mechanism for principal protection. Strategy embedded a "call right" in the bonds, allowing the company to repurchase the bonds at par plus unpaid accrued interest after the call date. The most common term is that the company has the right to choose to redeem the bonds when MSTR's stock price reaches 130% of the convertible bond's exercise price. This term takes effect after the call date and essentially sets a cap on the value of the options attached to the bonds. In addition, with the exception of the convertible bonds that mature on March 1, 2030, Strategy gives all other convertible bond holders the right to sell the bonds back to the company at par after the "holder redemption date." If Strategy encounters financial difficulties, this put-back term can be regarded as an implicit floor (protection floor) on the bond price.
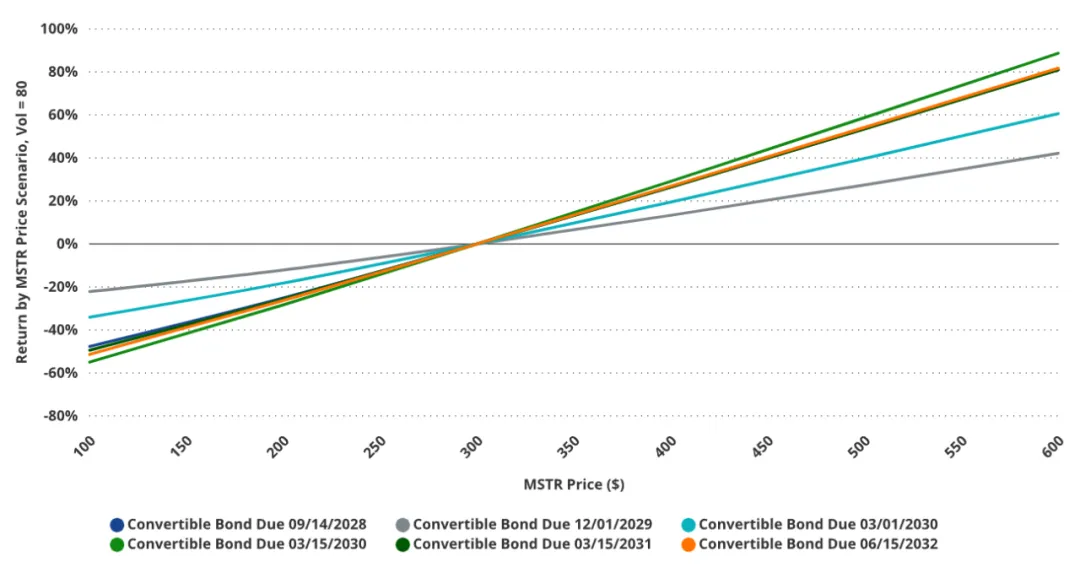
March 15, 2030 Convertible bonds have the most leverage on MSTR stock price due to their large option component
MicroStrategy's convertible bonds have a lot of option value embedded in them, due to the high volatility of the underlying stock (MSTR). Depending on the terms of the offering, the options component can account for up to 74% of the total convertible value. The higher the percentage, the greater the investor's exposure to MSTR's stock price fluctuations. This exposure can change significantly with changes in MSTR volatility and whether options are in the money or out of the money. Of all the outstanding convertibles, the Class B bonds due in March 2030 have the risk characteristics that are closest to the performance of MSTR stock. In high volatility scenarios (e.g., MSTR volatility > 80), the bonds are most sensitive to MSTR's stock price, whether the stock price rises or falls. In contrast, the convertible bonds due in December 2029 are the least sensitive because the embedded options are far out of the money, which makes the options a smaller proportion of the overall bond valuation, thereby weakening their impact on bond price changes.

Strategy Convertible Bond Implied Credit Spread vs. BTC Adjusted Credit Valuation
The bond portion of Strategy's convertible bonds has been controversial because the market has embedded a high credit spread when pricing these bonds. The larger credit spread reflects the market's higher risk assessment of Saylor's bonds, which makes these bonds "undervalued" (i.e., relatively cheap and high yielding). As Saylor pointed out in the first quarter 2025 earnings call, Strategy's fixed income securities credit spreads fluctuate between 500 basis points and 1,250 basis points, which means that the credit risk of its bonds is already in the credit spread range of "subprime or highly speculative bonds." Saylor believes that the current credit spread is so high because the market has failed to properly assess the actual value of the Bitcoin collateral assets backing its bonds. Saylor pointed out that rating agencies did not fully evaluate Strategy's bonds, which led many long-term institutional investors to choose not to buy these bonds because of the perceived high risk. This lack of investment demand further depressed the market price of the bonds and widened the credit spread.
Saylor used the option pricing model to analyze Strategy's convertible bonds on his own to prove that the market has underpriced these bonds when the collateral value is insufficiently assessed. He therefore proposed two self-created concepts: "BTC Rating" and "BTC Risk" to measure the potential risk of Strategy's debt. BTC Rating refers to: based on the current Bitcoin market price, the value of Strategy's BTC holdings is equivalent to how many times the face value of a certain bond. This indicator applies to all convertible bonds and is adjusted during the evaluation process based on the priority repayment order of the bonds when BTC is liquidated. For example, as of the current BTC market price, the convertible bonds due on September 14, 2028 have a BTC rating of 52.1 times, which means that based on the repayment priority of the bond, the value of Strategy's Bitcoin is approximately 52.1 times the face value of its bonds.
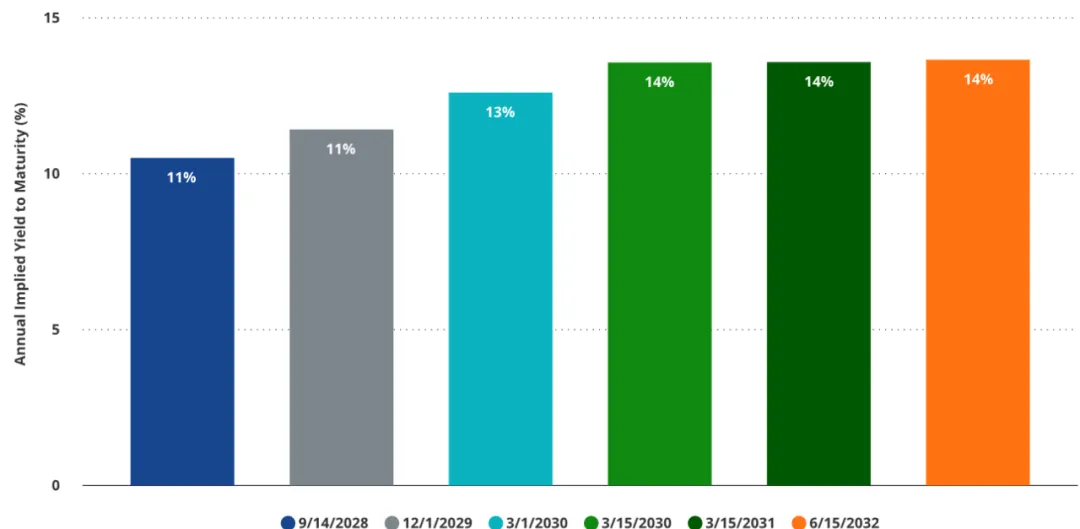
MSTR Implied yield on the bond portion of a convertible bond
A core concern about convertible bonds issued by Strategy is that their pricing is highly dependent on the value of embedded options. As a result, many convertible bonds currently trade well above their par value, which is often considered a price floor. This also means that once the option premium disappears, the total value of the bonds may fall sharply. For example, as of May 7, 2025, the market price of convertible bonds maturing in 2028 was $227.15; if MSTR's stock price is below the bond's conversion price of $183.19 at maturity, the bond will only be worth $100 (par value) at maturity, assuming all other conditions remain unchanged, which reflects the large proportion of option premiums in this type of instrument.
Another important risk associated with embedded options is their high sensitivity to changes in volatility, which is also one of the key factors in option pricing. We estimate that if volatility drops from 85 to 50, the average price of the convertible bond will fall by about 13%; if volatility further drops to 30, the average price drop will expand to about 20%. The market performance of MSTR stock is largely driven by the "premium", which contributes 87% of its volatility and 96% of its total return. In our view, this means that when investors buy MSTR convertible bonds, they are not only buying an option on MSTR stock, but also buying an option on the "continuation of the premium". This "premium" is essentially closely related to the price of Bitcoin. As the price of BTC rises, the company obtains more financing capabilities to continue to increase its holdings of BTC, thereby raising the expected value of its holdings and further driving speculative buying of MSTR shares in the market. But if the price of Bitcoin falls, MSTR's premium is likely to fall simultaneously. We estimate that the beta value between the two is about 1.77, which means that the value of the premium portion may fall more significantly than the decline in BTC. Such a decline will directly erode the value of the embedded option component in the MSTR convertible bond.
The fixed income portion of the convertible bond (straight bond) also faces risks related to the "premium". The valuation of this portion of the bond depends to a certain extent on the company's future financing ability. Strategy's current operating income is not enough to cover the interest payments on its fixed income obligations, let alone the repayment of principal at maturity. Once the premium shrinks, the company's financing ability will be limited, and the credit spread may widen, thereby depressing the market value of the corporate bond portion of the convertible bond. The direct cause of the deterioration of the premium is likely to be the decline in the price of Bitcoin. The downward trend in the price of Bitcoin will further increase the valuation pressure of Strategy's convertible bonds, because the possibility of achieving "full recovery" value in the BTC liquidation scenario will also decrease.
We do not view the above adverse scenarios as inevitable, but rather emphasize that the value of both components of the MSTR convertible - the options portion and the bond itself - are driven by the same fundamental factors, namely the premium of the Bitcoin price to MSTR shares. While some investors may be able to hedge these risks, many investors will find it difficult to fully understand them, let alone effectively manage them. MSTR convertibles may be attractive to investors who want to obtain income with upside potential, but they also contain a lot of structural and market risks. Such instruments are more suitable for sophisticated investors with dynamic hedging capabilities and the ability to deeply analyze equity-linked debt structures.
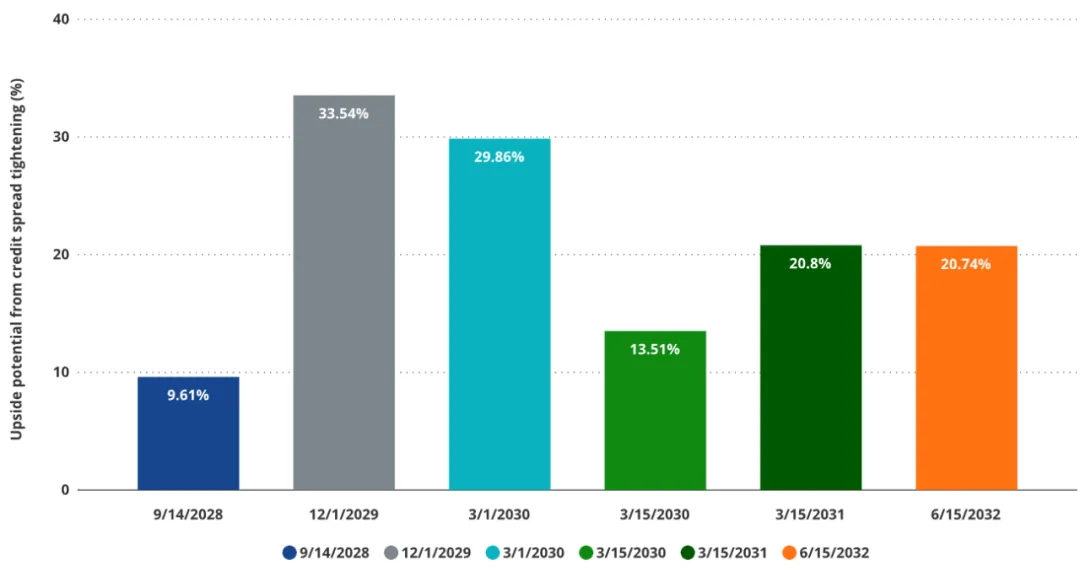
The upside potential of convertible bonds brought by the narrowing credit spread
Despite the structural risks, the convertible bonds issued by Strategy also provide investors with a "speculative tool" to bet on the progress of the accounting system for crypto assets. If credit rating agencies take a more positive view of Bitcoin as a debt-collateralized asset in the future, credit spreads may narrow significantly, thereby significantly increasing the valuation of the bond portion of convertible bonds, thereby driving up overall prices. Even if only the most conservative "real" credit spread level envisioned by Saylor is reached, we estimate that the median valuation of convertible bonds will increase by about 16%. In particular, convertible bonds with a high proportion of bond components will see the most significant price increases.
The two most attractive convertible targets are currently: the Dec 1, 2029 bond (+31% expected upside) and the Mar 1, 2030 bond (+26% expected upside). Given that the March 2030 bond option portion is close to in-the-money, its "credit spread" if repriced to Saylor's "BTC credit rating" combined with its higher embedded option value may be attractive to adventurous speculative investors. However, for traditional "long" investors, the multiple risk exposures contained in this type of convertible may be too complex to effectively manage. From a relative value perspective, we believe it is less attractive than other parts of MSTR's capital structure.
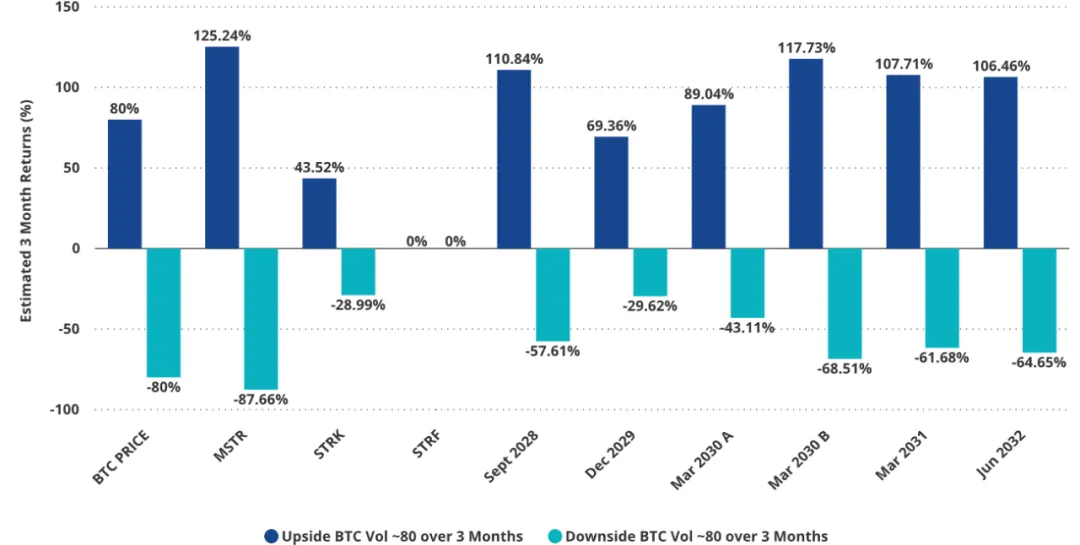
MSTR stock price simulation (Bitcoin ±80% volatility, MSTR volatility = 80)
STRK Overview and Analysis
STRK is described as "a preferred, perpetual, convertible equity security" that combines multiple concepts into one instrument. The security provides a perpetual dividend of 8% of par value per year, which can be paid in cash or common stock. However, if the company chooses to pay dividends in the form of common stock, it must comply with certain restrictions, such as: when the MSTR stock price is less than 35% of the price on January 27, 2025 (US$347.92), the total number of common shares that the company can use to pay dividends will be capped. STRK also has MSTR stock options with no expiration date (there is no time value decay in its option portion, that is, no Theta loss), and enjoys the liquidation priority of typical preferred stocks. Its structure is similar to a convertible bond, but it is subordinated to the company's other debt instruments. It is essentially a fixed-income security with a deeply out-of-the-money call option: its option exercise price is US$1,000 - about 2.5 times the MSTR stock price on May 7, 2025.
As of writing, we estimate that about 36% of STRK's current price is derived from its embedded call option, which allows holders to gain upside exposure to MSTR shares. Due to MSTR's extremely high volatility and the perpetual maturity of the option, the Delta of the option is close to 1, which means that the sensitivity to the underlying price changes is close to perfect, despite being deeply out-of-the-money. This means that STRK's price fluctuations (especially its option part) have been highly synchronized with MSTR's price fluctuations. Before MSTR's stock price approaches STRK's conversion strike price, STRK's sensitivity to volatility changes presents a significant asymmetric structure and is mainly biased to the downside. For example, if the implied volatility rises from about 80% to 120%, we expect STRK's price to rise only slightly, not more than +0.01%; but if the volatility falls from 80% to 40%, STRK's price is expected to fall by about -3%, and if it falls further to 20%, the price decline will widen to about -19%.
This asymmetry stems from the fact that the call options embedded in STRK are currently deeply out-of-the-money and perpetual. In this type of structure, when volatility rises to a certain level, the probability of "the option eventually entering the in-the-money state" is limited, resulting in a flatter response of the option value to the upward volatility, thereby weakening its upward reaction. Conversely, when the current volatility of MSTR decreases, the probability of entering the in-the-money will decrease rapidly, which will trigger a far more disproportionate price drop. This "convex volatility exposure", limited upside and significant downside risk together constitute the core risk characteristics of STRK. Looking further, STRK can be regarded as a "long-term call option that allows you to get dividends but is limited in upside" type of security, but its upside potential is still clearly capped compared to directly buying MSTR shares.
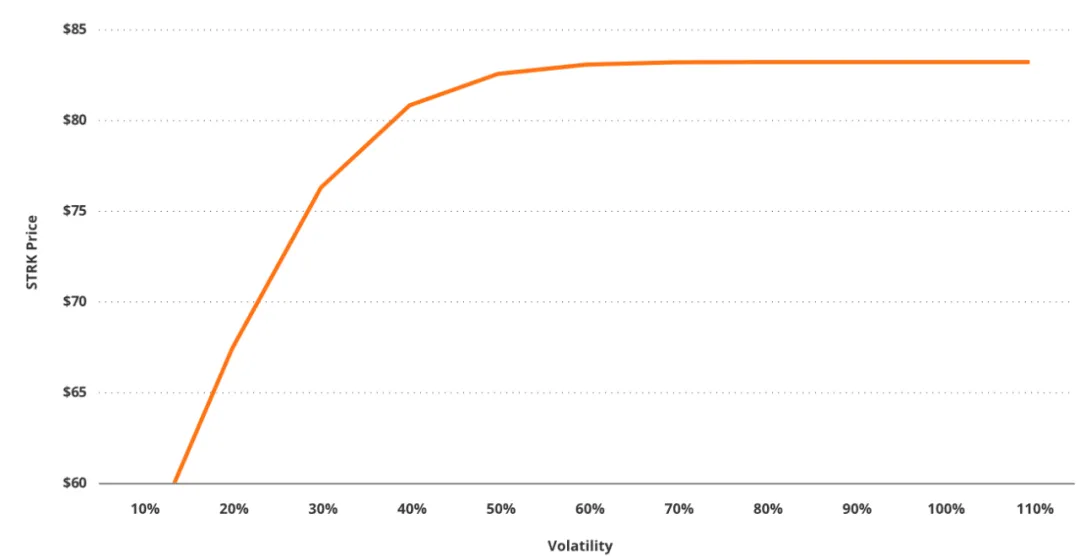
As volatility decreases, STRK value declines asymmetrically
From a pricing perspective, we expect STRK's price volatility to be significantly lower than MSTR's share price, both in the upside and downside. For example, if MSTR's share price rises by 100%, we estimate that STRK's price will only rise by about 37%, while if MSTR's share price falls by 50%, STRK's price is expected to fall by about 17%.
However, in a downside scenario, STRK's credit spread is also likely to widen, which will significantly affect the valuation of its preferred stock tranche. For example, if the credit spread increases from 700 bps to 1,200 bps (a 500 bps widening) and MSTR's stock price falls by 50%, the combined effect is expected to cause STRK's price to fall by about 30%. We believe this scenario is more likely to occur because Strategy's credit spreads generally move in the same direction as MSTR's stock price. Interestingly, STRK's implied credit spread is closer to Saylor's "BTC credit assessment" based on Bitcoin valuation, in contrast, Strategy's convertible bonds are more deviated from their valuations. This means that STRK's credit spread has relatively limited upside to converge to the Saylor model.
Strategy's Debt Profile and Capital Structure
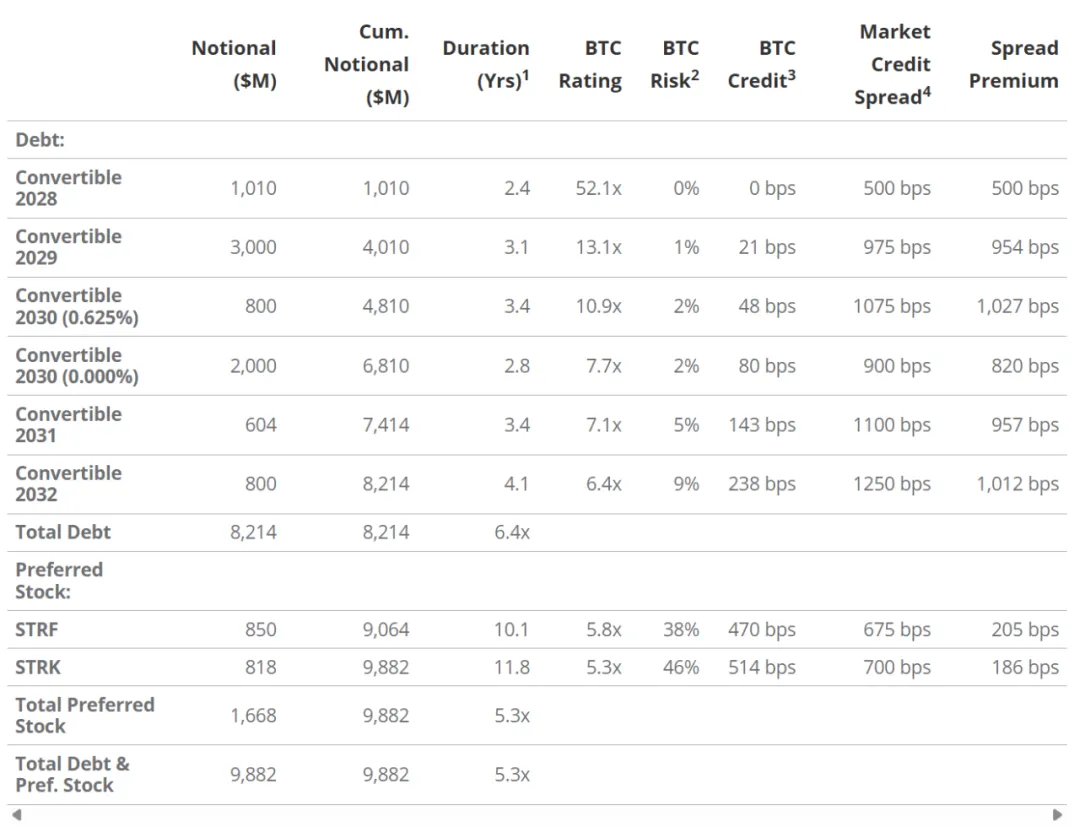
Hypothetical scenario: Bitcoin price $95,000, 50% volatility, 0% ARR (“skeptic” scenario)
As mentioned earlier, Strategy plans to issue approximately $20 billion of STRK in the future. This additional issuance will further increase the number of claims on the company's dividend income, thereby increasing the overall risk exposure level. Even without considering future STRK issuance, Strategy's ability to pay existing STRK dividends in cash is already strained. It should be noted that STRK's repayment priority in the company's capital structure is even lower than a series of convertible bonds issued by Strategy. Therefore, Saylor defines STRK's BTC Risk level (BTC Risk) as much higher than convertible bonds. Without considering the basic scenario of Bitcoin price increases, Strategy's internal assessment shows that there is a 46% probability that the value of BTC holdings will be lower than the nominal support value of STRK in the next year.
In our view, STRK's multiple structural features present significant downside risks without providing commensurate upside potential. These factors include weak Bitcoin asset support, uncertainty about the terms under which the company can suspend dividends, and a small embedded option component that makes it difficult to provide a substantial leveraged return. In addition, STRK's price lacks the opportunity to gain significant upside through a re-rating of credit spreads.
Therefore, we believe that STRK's risk-return structure is not ideal for long-term investors, especially compared to the structure of MSTR common stock. However, for investors with strong hedging capabilities and high trading activity, the volatility characteristics and dividend yield reflected by STRK may be attractive. For active income-oriented investors who want to obtain stable returns while retaining some upside potential in MSTR shares, STRK may become an attractive allocation tool. In addition, if investors are very optimistic about the long-term performance of Strategy, STRK's option component provides a Delta close to 1, while having a high dividend rate, which may also make it attractive in a long strategy.
STRK Overview and Analysis
STRF is a standard preferred stock instrument that pays a 10% cash dividend per year at a fixed rate. Unlike STRK, STRF does not have the flexibility to pay dividends in the form of common stock. As of now, the market price of STRF is $94.30, so its effective annualized yield is about 10.6%. The valuation of STRF is mainly subject to the level of market interest rates and Strategy's credit spread. According to the terms of the agreement between Strategy and STRF holders, the coupon rate will increase by 100 basis points for each missed dividend, up to a maximum of 18%. If four consecutive dividends are missed, or eight dividends are missed cumulatively, STRF holders will be given the right to nominate a director to the Strategy board of directors. This right will be automatically revoked after all overdue dividends are paid. From a capital structure perspective, STRF has a higher repayment priority than the common stock of STRK and MSTR, so it has a relatively stronger claim right when the company is liquidated. But the support strength of this right is still limited, because according to current calculations, STRF's BTC rating is 5.8 times, while STRK is 5.3 times.
These protective clauses make sense to a certain extent, given that MSTR has not generated substantial cash flow since 2021, but they are still fragile given the high volatility of Bitcoin. If MSTR's core business deteriorates further or the company loses access to capital markets, it may be forced to suspend STRF's dividend payments. In this case, STRF will be closer to a long-term subordinated bond with significant credit risk, but no longer have any equity-like upside potential. If this event coincides with a drop in the price of Bitcoin (a very likely scenario), the value of STRF will suffer a substantial impact. The biggest challenge facing STRF is that it cannot enjoy the benefits of Bitcoin's rise, but is exposed to the risk of a sharp drop in Bitcoin's price. Since a drop in Bitcoin prices may weaken Strategy's ability to meet its cash payment obligations, this will lead to an increase in its credit spread. This view is also supported by the data: STRF has a correlation of 50% with MSTR and 55% with BTC. Based on current market prices, we estimate that the implied credit spread of STRF is about 6.1%. If the credit spread approaches the median level of 10.25% for Strategy convertible bonds, STRF's valuation will fall by about 28%. Similar to STRK, STRF is also highly exposed to changes in the price of Bitcoin and the premium of MSTR shares.
In our view, STRF's risk profile is not ideal for long-term investors, as the multiple risk factors it faces are difficult to accurately assess and price, and there is a clear upper limit to its upside. However, for investors with advanced strategy capabilities, STRF's risk-return structure may be more attractive: such investors can use the dividend income obtained from STRF to configure Bitcoin-related options, thereby obtaining a certain upside exposure or downside protection.
Strategy Financing System Summary
The overall capital structure of Strategy is highly dependent on the following three core elements:
1. Bitcoin Price
2. The company’s ability to continue raising funds to purchase more BTC
3. Price volatility of BTC and MSTR
MSTR provides an asymmetric investment structure that combines leveraged Bitcoin exposure, regulatory accessibility, and the liquidity advantages of the secondary market. Although its capital structure is relatively complex and comes with certain substantial risks, MSTR's design provides investors with a difficult-to-replicate leverage path and strategic option structure, making it a unique investment tool to participate in Bitcoin's upside potential. For investors who are unable or unwilling to hold Bitcoin directly and have difficulty managing futures strategies on their own, MSTR is a more operational and effective alternative. To maintain the effectiveness of this investment logic, it still depends on maintaining investor confidence, stable capital market financing capabilities, and the company's high discipline at the execution level.
From a strategic perspective, Strategy provides several key insights for companies considering implementing a Bitcoin asset allocation.
First, when implementing a Bitcoin asset allocation strategy, companies must establish clear strategic goals. Strategy provides a typical example in this regard: it always focuses on increasing the amount of BTC held per share, rather than following traditional financial indicators (such as dilution or corporate value denominated in fiat currency). Under the leadership of Michael Saylor, the company re-anchored its valuation logic to Bitcoin itself. Saylor's understanding of "success" is not based on dollar earnings, but depends on the number of Bitcoins represented by each share of MSTR. This high focus on the goal enables the company to maintain strategic consistency and stability in long-term decisions even in market fluctuations.
Second, companies must develop a well-structured financing strategy to leverage market mechanisms to drive continued accumulation of Bitcoin. Strategy achieves this by leveraging the market’s appetite for volatility and embedded option structures. Led by Michael Saylor, the company has built a financial ecosystem that attracts retail investors and active traders through the issuance of convertible bonds, preferred stocks, and common stocks. Bitcoin’s high volatility is transmitted to MSTR, further supporting the market’s demand for trading its various securities. For example, as of now, the total open interest in MSTR stock options is as high as $95 billion, which has exceeded GOOG ($80 billion) and AMZN ($84 billion), and the market capitalization gap between the three is very large - GOOG’s market capitalization is about 15 times that of MSTR. This “flywheel effect” enables Strategy to complete Bitcoin purchase financing on favorable terms, namely: lower cash payment obligations and without relying entirely on traditional debt or common stock issuance.
Finally, any company that intends to implement a similar strategy must recognize that the market demand for securities linked to Bitcoin will not appear automatically, but needs to be actively promoted and shaped. Investor participation, innovative financial structure design, and highly transparent communication mechanisms will be key elements. Whether through traditional securities issuance, structured products, or digital asset integration solutions, companies must create financial instruments that are both profitable and have high upside potential in order to effectively attract capital. Because the "Bitcoin asset allocation strategy" is fundamentally in conflict with many core assumptions of traditional financial theory, HODLers must establish an unbreakable investment narrative to support the rationality and attractiveness of their Bitcoin strategy. Michael Saylor's high frequency of exposure in the public opinion field is not accidental, which reflects his deep understanding of a core fact: for the Bitcoin asset strategy to really work, the market must first "believe" in this strategy.
Strategy Core risks faced by Bitcoin financing mechanisms
A series of macro-environmental, structural factors and execution-level risks may weaken Strategy's ability to continue to advance its Bitcoin asset accumulation strategy, thereby affecting MSTR's valuation support.
1. Bitcoin price decline: Strategy's business model is based on the premise of long-term Bitcoin price increases. If the price of BTC continues to fall, it will not only weaken the value of the company's existing holdings, but also shake the feasibility of its future financing capabilities, thus posing a fundamental threat to the entire strategy.
2. Declining volatility of Bitcoin or MSTR: Declining volatility will weaken investors’ interest in MSTR convertible bonds and preferred stocks, which essentially rely on the value of embedded options to attract funds. Lack of sufficient volatility will directly affect its financing ability and market appeal.
3. MSTR premium (relative to net asset value) collapses: The market premium of MSTR's stock price relative to its net asset value (NAV) is an important support for its upside potential and the issuance of value-added shares. If this premium shrinks or collapses significantly, it will seriously weaken the company's ability to raise funds through the capital market and directly reduce the potential return space for shareholders.
4. Deterioration of core business operations: Although Strategy's software business is increasingly marginalized in the current strategy, it still provides support for the company's cash flow to a certain extent. If this business shrinks further, it will weaken the company's financial flexibility in the market downturn cycle and limit its ability to cope with external shocks.
5. Regulatory changes promote the implementation of leveraged Bitcoin products: If new ETFs or structured products emerge, they can provide investors with more direct leveraged Bitcoin exposure. MSTR’s market position as an “alternative tool” may be weakened, thereby reducing investors’ demand for it as a Bitcoin Proxy (indirect investment vehicle).
6. The rise of similar strategies brings competitive pressure: More and more new entrants are beginning to imitate Strategy's Bitcoin asset allocation model, which may lead to the dispersion of investor attention and saturation of the capital market for leveraged BTC exposure. Since these emerging competitors are much smaller than Strategy in size, they can often achieve higher BTC returns and BTC holdings per share with less capital, thus posing a substantial threat to Strategy's market dominance.
7. Forced to liquidate BTC holdings due to debt repayment pressure: If there is a severe pullback or tightening of financing channels, Strategy may be forced to sell its Bitcoin holdings to meet debt repayment obligations, which will directly weaken its BTC holdings per share and pose a substantial impact on the sustainability of its Bitcoin asset allocation strategy.
8. Weakening investor demand for Strategy securities: Strategy plans to raise more than $22 billion through the issuance of securities to continue purchasing Bitcoin. If investor demand declines, it will directly weaken the company's ability to execute the strategic financing plan, thereby affecting the continuity of its Bitcoin asset accumulation path and capital structure deployment.
9. Risk of dilution of Bitcoin holdings per share: When Strategy issues additional common shares to fulfill its dividend or financing obligations, it will directly lead to a decrease in Bitcoin holdings per share, thereby weakening its core performance indicator - the performance of Bitcoin yield.
10. Capital market instability: Strategy (MSTR)'s business model relies on continuous and smooth capital market financing channels. If there is a liquidity crunch or functional interruption in the capital market, it will not only threaten its daily operations, but also hinder the implementation of its Bitcoin asset expansion plan.
11. Rising interest rates: Rising interest rates will increase the cost of debt issuance and weaken investors' interest in low-yield convertible bonds, thereby limiting Strategy's ability to raise funds to purchase Bitcoin.







