The Fusaka upgrade is scheduled to be deployed on the Ethereum mainnet on December 3rd to expand the network's processing capacity, maintain decentralization and security.
 Ethereum sets Fusaka hardfork date, preparing for biggest upgrade in 2025
Ethereum sets Fusaka hardfork date, preparing for biggest upgrade in 2025
Ethereum developers are rushing to prepare for the next major upgrade, called Fusaka , which is scheduled to be deployed on mainnet on December 3, 2025 .
The #Ethereum Fusaka upgrade is tentatively scheduled for December 3rd at Epoch 411392 - 21:49:11 UTC 👀 https://t.co/g45BbObfHk pic.twitter.com/bHC2Jm0ocq
— Crypto-Gucci. ETH ᵍᵐ🦇🔊 (@CryptoGucci) September 18, 2025
This will be the next major update for Ethereum - following The Merge , Dencun , and most recently Pectra - focused on expanding data processing capabilities, reducing costs, and improving user experience, while laying the foundation for the future Danksharding roadmap.
Fusaka testnet and mainnet deployment schedule
- Ethereum's Fusaka upgrade is not simply a major Hard Fork , but is designed with a multi-phase roadmap to ensure safety, compatibility, and the best preparation for the entire ecosystem.
- According to information from researcher Christine D. Kim, the Fusaka upgrade schedule is specifically implemented as follows:
- 10/01/2025 : Deployment on Holesky testnet
- 10/14/2025 : Deployment on Sepolia testnet
- 10/28/2025: Deployment on Hoodi testnet
- 12/03/2025 : Officially deployed on Ethereum mainnet
The changes Fusaka brings to Ethereum
Major improvements
The Fusaka upgrade is considered one of Ethereum's most important milestones since Dencun and Pectra. At the time of writing, 12 EIPs have been finalized for implementation, focusing on three main pillars: network scaling, cost optimization, and user experience enhancement.
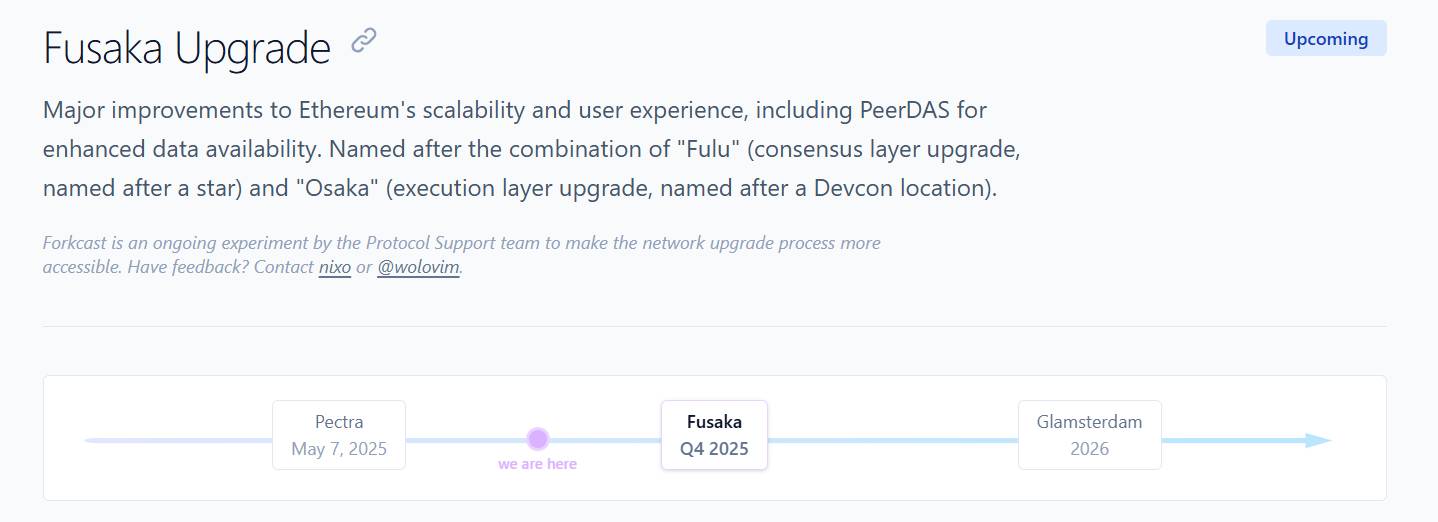
EIP-7594 – Peer Data Availability Sampling (PeerDAS)
- PeerDAS (Peer Data Availability Sampling) is considered a core improvement in the Fusaka upgrade. This mechanism changes the way nodes process data. Previously, each Ethereum node had to download and store the entire blob data, but now PeerDAS allows nodes to only store a small part of the data and coordinate with other nodes to verify authenticity.
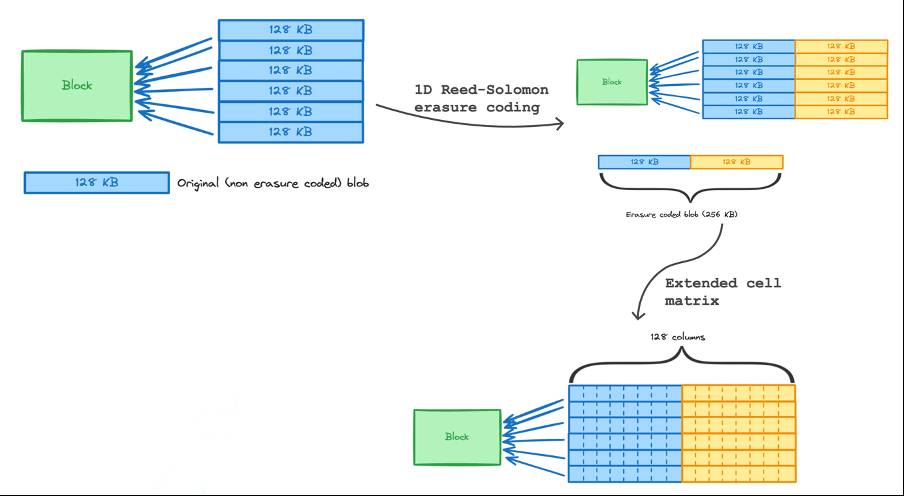
- For example, when a node needs to be sure that the entire blob exists, it can randomly ask many other nodes to provide data samples. If the samples all match, it can be sure that the blob is complete and has not been tampered with.
- Thanks to that, the system still ensures the integrity and availability of all data without increasing the resource burden, thereby greatly reducing transaction costs on layer-2 such as Arbitrum, Optimism or zkSync, which depend on blobs to store data off-chain.
- PeerDAS also paves the way for Ethereum to be able to process up to 128 blobs/ Block in the future, raising throughput to a level competitive with other blockchains while still maintaining decentralization.
EIP-7825 - Transaction Gas Limit Cap
- In the Fusaka upgrade, EIP-7825 decided to set the gas cap for each transaction at 16,777,216 gas (2^24). The goal is to avoid a situation where a single “heavy” transaction takes up almost the entire Block capacity, thereby ensuring fairness in the use of blockspace and keeping the network running more stably.
- For the average user, the change will be almost invisible, as most current transactions consume far less gas than the 16.8M threshold. However, for application developers deploying complex smart contracts, it is likely that they will need to Chia operations into multiple transactions to accommodate the new limit.
- On the Layer 2 side, EIP-7825 may impact the batching mechanism, but in return, it brings more stability and sustainability to the entire system.
- For validators and node operators, this upgrade brings clear advantages, Block will become easier to handle, reducing the risk of local congestion when encountering transactions with too large capacity.
EIP-7918 - Blob base fee bounded by execution cost
- One of the problems with Ethereum after the Dencun upgrade is that the blob fee market sometimes doesn't work well. Specifically, when the execution cost on layer-2 is much higher than the blob cost, the blob fee can drop to a minimum of only 1 Wei. This makes the blob fee price no longer reflect the true value of the network resources.
- To solve this problem, EIP-7918 introduces a reserve price mechanism for blobs, directly linked to the execution cost. Thanks to that, blob fees are always maintained at a reasonable level, no matter how the market fluctuates, blob fees cannot drop too low, reflecting the actual supply and demand.
- EIP-7918 not only solves the short-term problem, but also lays the foundation for the development of layer-2 ecosystems on Ethereum. As blob demand increases, this price floor mechanism will help the market maintain price discovery effectively, ensuring that Ethereum can scale without risking the fee mechanism.
EIP-7935 - Set default Gas Limit to XX0M
- EIP-7935 proposes to raise Ethereum's default gas limit from 36 million to a higher level (still under discussion). In principle, this change does not require a Hard Fork because the Gas Limit is decided by the validator. However, to ensure network stability under larger computational loads, the EIP is included in the Fusaka upgrade to prioritize testing and deployment.
- Raising the gas limit will directly increase Ethereum's throughput, allowing more transactions to be processed per Block. In addition, a higher Gas Limit also paves the way for more complex smart contracts, serving DeFi applications, AI, and dApp models that require a lot of computational resources.
- By increasing the Gas Limit, users will benefit significantly with faster transaction speeds and more stable costs. Application developers have more space to deploy complex smart contracts without worrying about hitting the Gas Limit.
- In particular, Layer 2 will have more blockspace to process data. However, this needs to be closely coordinated with EIP-7825 ( gas limit for each transaction) to avoid the risk of conflict.
- Despite the benefits, EIP-7935 also comes with technical challenges. At the client level, both the Consensus layer and execution layer will have to be constantly tested and refined to ensure that large Block can be transmitted quickly through the gossip network without causing delays or temporary Fork .
- In addition, validators and node operators will be under greater pressure because heavier Block mean the need for more powerful hardware and higher processing capabilities.
Increase blob size
- After successful deployment and stable operation on mainnet, Fukasa upgrade will move to the next phase with small Hard Fork called BPO Fork , focusing on adjusting blob capacity .
- 12/17/2025 – BPO1 : Increase blob target/max from 6/9 → 10/15.
- 07/01/2026 – BPO2 : Continue to increase blob target/max from 10/15 → 14/21.
- In the long term roadmap, there will be a total of 5 BPO Fork to increase blob capacity. The goal is to meet the growing needs of layer-2s while maintaining network stability.
- It is worth noting that BPO (Blob Parameter Only) batches only change the blob target and blob limit parameters, and do not require client updates at all.
- In the initial phase, Fusaka will not impact blob capacity. However, as BPO Fork are deployed one after another, blob capacity will be adjusted incrementally, instead of changing suddenly.
- Ethereum researcher Christine D. Kim said: According to some preliminary analysis on Fusaka Devnet-5, blob capacity is expected to more than double in just two weeks after the Fusaka upgrade is deployed."
They'll be reconfirming the exact dates, times, and epoch numbers over the next few days.
— Christine D. Kim (@christine_dkim) September 18, 2025
They also agreed that based on some preliminary analysis on Fusaka Devnet-5, blob capacity should be more than double over the two weeks following Fusaka activation.
- The ethPandaOps development community said: “The initial conclusion is that we can increase the maximum blob count to 15 in BPO1 and 21 in BPO2. There will be a total of 5 BPO Fork in Fusaka, so the mainnet can scale safely.”
- Blobs play an important Vai in storing large amounts of data off- Off-Chain , making layer-2 networks more efficient and reducing transaction costs. Since the Dencun upgrade was deployed, blob usage has been steadily increasing: the current Medium is 5.1 blobs per Block, up from just 0.9 blobs per Block in March 2023, according to data from Dune.
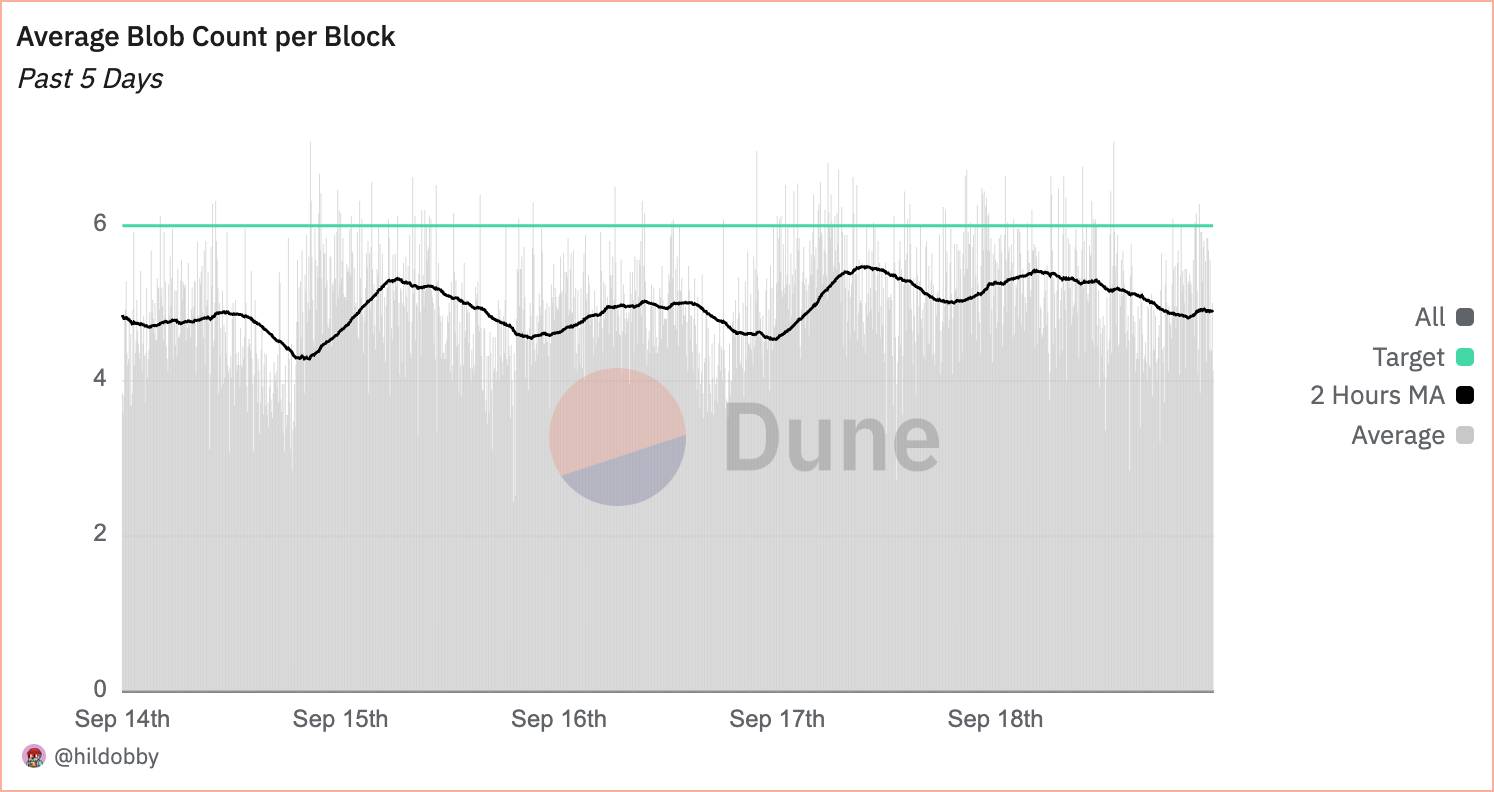 Medium blob usage per Block since Dencun. Source: Dune - @hildobby (September 19, 2025)
Medium blob usage per Block since Dencun. Source: Dune - @hildobby (September 19, 2025)
- Therefore, BPO Fork were deployed right after Fusaka to both meet the expansion needs from future layer-2s and ensure stability for the entire Ethereum network.
Glamsterdam upgrade expected to "dock" in 2026
- After the Fusaka upgrade is complete, Ethereum will move towards the Glamsterdam upgrade in 2026. The most important highlight is EOF (EVM Object Format), a major improvement to the Ethereum Arm Virtual Machine (EVM).
- EOF provides a new, cleaner, and more structured bytecode format. Instead of the old , Capital , and unmanageable bytecode format, EOF separates code and data. This allows smart contracts to be validated as soon as they are deployed, rather than having to be checked repeatedly during execution.
- This mechanism saves gas, increases security, and provides better support for advanced technologies like zero-knowledge proofs .
Coin68 synthesis