
In the early morning of October 11, 2025, a panic sell-off broke out in the global cryptocurrency market .
The prices of mainstream and Altcoin plummeted simultaneously. This incident, directly linked to the growing urgency of the quantum computing threat, became one of the most significant liquidity crises since the 2021 market crash. Its timing resonated with multiple risk signals, highlighting the profound impact of technological security concerns on cryptoasset valuations.
Before the sell-off, the market was trading at all-time highs, with Bitcoin reaching a peak of $126,080 on October 7th, and Ethereum climbing above $4,500.
However, after the sentiment reversed in the early morning of October 10, the price of Bitcoin quickly retreated from the key support level of $126,000, and the decline of Altcoin was significantly amplified due to insufficient liquidity reserves. Some small and medium-sized market capitalization currencies fell by more than 20% in 24 hours.
The market sell-off on October 11, 2025, set a historic record for margin calls, demonstrating that the panic triggered by the quantum threat has transformed into a substantial liquidity crisis. According to real-time data from Coinglass, cryptocurrency margin calls totaled $19.141 billion over the past 24 hours, a 27-fold increase from the October 10 incident. A total of 1,621,284 leveraged traders worldwide experienced forced liquidations . This figure not only set a new record but also highlights the extreme sensitivity of market structure to concerns about technological security.
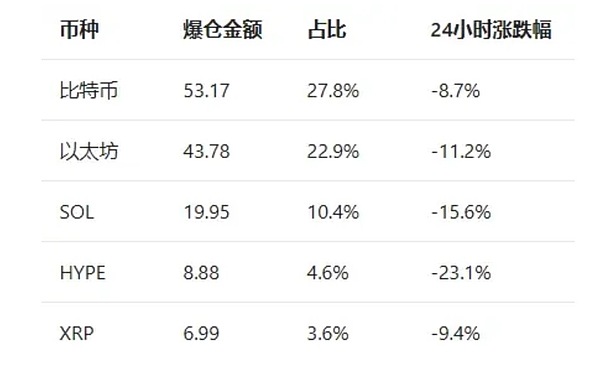
Looking at the distribution of long and short positions, long positions saw liquidations totaling $16.686 billion, accounting for 87.2% of the total liquidation volume, while short positions saw liquidations totaling $2.455 billion, indicating that the sell-off was primarily driven by a stampede of long positions. The largest single liquidation occurred in the ETH-USDT perpetual contract on the Hyperliquid platform, amounting to $203 million, setting a record for single-day liquidations on the platform. Notably, Ethereum, a quantum-sensitive currency, saw significant correlation between its liquidation volume and that of Bitcoin, confirming that concerns about quantum security are spreading beyond Bitcoin to the entire crypto ecosystem.
All traders roared in their hearts, the plunge was so severe that they woke up and returned to BC!
Quantum computing has stolen our home!
Quantum computing is based on the superposition and entanglement principles of quantum mechanics. It uses quantum bits (qubits) to achieve parallel computing and can solve complex problems that are difficult for classical computers to handle.
Its core threat to cryptocurrencies stems from Shor's algorithm, which can crack encryption systems that rely on prime number factorization or discrete logarithm problems in polynomial time. The ECDSA digital signature mechanism widely used in cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin is based on the computational complexity of the discrete logarithm problem.
In contrast, traditional computers would take far longer than the age of the universe to crack a private key. Quantum computers can significantly shorten the cracking cycle through the Shor algorithm, and theoretically it can even be completed in a few minutes.
Judging from the current technological status, there is still a gap between the current level of quantum hardware and the cracking requirements: although Google Willow chip (105 qubits) and IBM Condor processor (1121 qubits) have made breakthroughs in quantum error correction and specific tasks, cracking Bitcoin ECDSA requires about 2,000 logical qubits .
However, Google research shows that through algorithm optimization (such as reducing quantum resource requirements by 20 times), the threshold for realizing quantum threats may be lower than expected.
As the analysis points out, there is no real threat in the short term, but the long-term risk is urgent - current quantum computers do not yet have the ability to carry out actual attacks, but the "harvest now, decrypt later" attack strategy has been warned by experts. More than 60% of the Bitcoin supply (including Satoshi Nakamoto addresses) is stored in quantum-vulnerable addresses. If quantum technology accelerates breakthroughs, the existing encryption system will face severe challenges.
Temporal correlation of quantum threat signals
The event triggering is tightly temporally coupled with multiple quantum security risk signals.
Academic breakthrough catalyst : On October 8, the 2025 Nobel Prize in Physics was awarded to scientists in the field of basic research in quantum computing, directly igniting market concerns about the approaching "Quantum Day (Q-Day)";
Authoritative warnings : Charles Edwards, founder of Capriole Investments, issued a series of statements on October 8-9, stating that 4.5 million bitcoins (worth approximately $550 billion) were stored in early addresses vulnerable to quantum attacks. He emphasized that "quantum resistance upgrades must be completed by 2026," otherwise there could be systemic risks.
Technical proposal controversy : The quantum-resistant Bitcoin upgrade proposal (QRAMP) disclosed at the same time has triggered concerns about hard forks, further exacerbating market uncertainty.
These signals form a clear timeline with the sell-off in the early hours of October 11th, reflecting a significant decrease in investors' tolerance for quantum security flaws in cryptocurrencies. This incident not only exposes the vulnerability of digital assets to the pressures of technological iteration but also provides a key case study for the subsequent evaluation of quantum-resistant technology solutions and research on mechanisms to restore market sentiment.
Bitcoin's scale and risk assessment exposed to quantum threats
Currently, about 25% of the circulating bitcoins (or 4.5 million) are stored in early blockchain addresses that are vulnerable to quantum attacks. The encryption mechanisms used by these addresses do not take into account the threat of quantum computing, and their public keys have been exposed in past transactions, making them potential targets for quantum cracking.
A typical case is the 1.1 million BTC held by Bitcoin founder Satoshi Nakamoto. These assets have long been dormant in addresses from the early "payment to public key" (P2PK) era. Their public keys have been completely exposed and will face direct theft risks after quantum computers break through the ECDSA algorithm .
Based on the current Bitcoin price of $120,000, the potential loss of 4.5 million exposed assets could reach $5.4 trillion, accounting for 222% of the current total market value of Bitcoin (US$2.43 trillion), highlighting the severity of the risk exposure.
Risks are significantly concentrated: over 10 million Bitcoin addresses have exposed public keys. Older wallets, which haven't been moved in the past, are vulnerable due to technical flaws and are therefore prime targets. Systemic threats have triggered chain reactions in the market. For example, following the release of Google's Willow quantum chip in December 2024, Bitcoin prices plummeted 6.25% in a single day, with 572,000 accounts liquidated within 24 hours, totaling $1.75 billion.
Institutional holdings further amplify the risk. For example, BlackRock's iBit fund holds 3% of Bitcoin (worth $62 billion). Concentrated holdings may trigger a liquidity crisis under quantum attacks.
Analysis of market selling behavior
The sell-off in cryptocurrencies triggered by the quantum threat is essentially the result of a combination of psychological panic and structural market fragility. This dual mechanism not only amplifies short-term price fluctuations but also, through the overlay of historical memories, creates a systemic risk transmission path.
Psychological dimension: the triggering and amplification of FUD emotions
Breakthroughs in quantum computing technology trigger market fear, uncertainty, and doubt (FUD) through three paths.
The overlay of historical memories: The suddenness of technological breakthroughs directly impacts investors' core perceptions of cryptocurrency security. Following the release of Google's Willow chip benchmark results in December 2024, despite Satoshi Nakamoto's early design of quantum-resistant solutions like single-use addresses, investors' lack of awareness of Bitcoin's quantum resistance worsened sentiment. Bitcoin's price plummeted from $100,000 to $94,000 within 24 hours, a drop of approximately 6%. Altcoin, owing to even weaker confidence in their security, saw a 20% drop across the board.
Risk warnings from authoritative institutions exacerbated the spread of panic. Noah's Arc downgraded the Bitcoin ETF rating to "sell", emphasizing the market's neglect of quantum risks. After BlackRock added a quantum computing warning to its ETF risk factors, Bitcoin's volatility increased significantly during the consolidation phase above $100,000.
The expectation of "presentization of future risks" has shortened the market panic brewing cycle. Investors are worried that under the "harvest now, decrypt later" attack mode, the currently held crypto assets may be cracked after quantum technology matures. This long-term risk is compressed into short-term selling motivation.
The fragility of the market structure further amplified the decline during the panic, particularly due to differences in asset attributes and the risks of leverage mechanisms. From an asset attribute perspective, Altcoin were particularly hard hit during the sell-off due to their poor liquidity and high risk appetite among holders.
How to mitigate short-term risks
The short-term response focuses on reducing the quantum attack surface of the current encryption system, and the core measures revolve around address security optimization.
The general consensus in the industry is that reusing addresses will prolong the exposure time of public keys and increase the risk of quantum computers inferring private keys through public keys.
Therefore, users are strongly recommended to adopt a one-time address mechanism to reduce the public key exposure window by generating a new address for each transaction.
In addition, some projects are exploring hybrid encryption solutions as a transition. For example, Blockstream is testing a combination of traditional hash algorithms and SPHINCS+ quantum-resistant signatures, which provides an additional layer of protection against quantum attacks while maintaining transaction verification efficiency.
For historical risk addresses, AvaLabs co-founder Emin Gün Sirer proposed a targeted solution, suggesting that Bitcoins minted by Satoshi Nakamoto in the early days using the P2PK format be protected or frozen for a limited period of time to reduce the quantum vulnerability of old addresses.
Final Thoughts
The leveraged market shrank by hundreds of billions overnight. To those warriors whose funds were wiped out but whose faith remained undimmed, please note: numbers are just dust; your value far exceeds this. It's not that we haven't experienced liquidation before; we've even been decimated and still managed to add to our positions with a smile.
A day in the crypto world is like a year in reality—every scar is a medal, every restart is an evolution.
The market never shirks opportunity; what's lacking is the courage to start over. Pack your bags, and we'll see you at the next peak!







