introduction
Heterogeneous cross-chain has always been a difficulty in the blockchain. How to exchange Ethereum assets with assets on Bitcoin and Solana. In the past, centralized exchanges (CEX) were the best choice. However, with the enrichment of on-chain activities, , asset investment attributes are no longer the only requirement. Driven by Web3 marketing and the wealth creation effect of airdrops, on-chain footprints have become an indispensable way for users to participate in Web3. People need to operate on-chain assets efficiently and quickly. According to Glassnode data, in 2023, the average number of daily active addresses on the Ethereum main network will be 390,000. Ethereum Layer-2 TVL will increase by 60% in 2023, reaching 12 billion US dollars. Public chain interaction data other than Ethereum will also increase. Rapid growth. What is certain is that cross-chain asset cross-chain and cross-chain interoperability on the chain will be a continuing necessity in the future.
1. The evolution process of cross-chain technology
Because each network has its own set of rules, governance mechanisms, native assets, and data formats that are incompatible with other blockchains. Cross-chain bridges often play the role of verifiers, generally using three main methods:
Lock and mint – These bridges lock assets on the source chain and mint assets on the target chain. For example: Polygon's PoS Bridge, Avalanche Bridge (AB), wrapped BTC, wMonero.
Burn and mint – These bridges burn assets on the source chain and mint assets on the target chain. For example: Circle's CCTP, LayerZero's OFT, and Wormhole's xAssets.
Atomic swaps – use liquidity swaps to exchange assets on the source chain with another party for assets on the destination chain. For example: cBridge, Connext, Across.
The current mainstream method introduces relay and light client technology, which transmits information by establishing relays between different chains. Relayers are responsible for validating events on one chain and passing information on to the other chain. The three existing cross-chain technologies all have certain trust and security issues. Most cross-chain solutions rely on a centralized custody mechanism or a specific set of verifiers, which may introduce additional trust and security risks. Another example is cost and scalability issues. The increase in the number of networks means that developers need to continuously update to support more and more complex cross-chain interactions. These problems also make cross-chain bridges the most vulnerable targets. In 2021, Poly Network suffered a hacker attack, resulting in a capital loss of more than $600 million, making it the largest hacker attack in the DeFi field to date. It is not difficult to see that although cross-chain technology continues to develop, there are still key technical challenges. However, it is these challenges that have promoted the development of a new generation of cross-chain technology.
After continuous development and evolution, Omnichain has become the most popular cross-chain technology at present. It connects all chains by building a basic layer. This technical solution is different from cross-chain mechanisms such as Polkadot and Cosmos. Omnichain cross-chain unifies all L1 and L2 into one platform, while Polkadot and Cosmos require users to implement cross-chain based on their own standards. Chains outside the framework still need cross-chain bridges to achieve cross-chain or interoperability. According to usage scenarios, cross-chain solutions are divided into four types: native cross-chain, oracle verification, general cross-chain and liquidity swap. Universal cross-chain is the cross-chain with the largest market space, and Omnichain belongs to the universal cross-chain bridge technology.
Last year, the Bitcoin ecosystem experienced its first major explosion. With the development of Layer 2 and Inscription, Bitcoin is building its own DeFi ecosystem. However, Bitcoin itself does not have smart contract functions, which greatly increases the interconnection between Bitcoin and other ecosystems. needs. In addition, the recent "full-chain" Meme coin omnicat has surged 50 times, allowing the market to once again see the potential of "full-chain narrative".
This article will use the cross-chain solutions ZetaChain and Layerzero to deeply explore the development prospects of Omnichain technology for full-chain empowerment.
2. Layerzero: a full-chain interoperability protocol based on Ominichain
LayerZero is a full-chain interoperability protocol that deploys a series of smart contracts (Endpoints) on the chain. Ultra-light nodes are run on the Endpoints, and Oracle (currently Chainlink) and Relayer are used to communicate information between LayerZero Endpoints on the target chain. , to achieve decentralized information cross-chain services. Currently, LayerZero supports information transfer between EVM chains such as Ethereum, BNB Chain, Polygon, Avalanche, Fantom, Arbitrum and Optimism, Metis, and non-EVM chains such as Aptos. Layerzero has a strong investor lineup. Well-known crypto capitals such as a16z, Sequoia Capital, Coinbase Ventures, Binance Labs and Multicoin Capital have basically participated in LayerZero’s financing.
Recently, LayerZero released the latest V2 version. In V2, the message verification and execution processes are clearly separated, and the new DVN and Executor roles are introduced, so that the security and execution of the protocol are no longer related to each other. The DVN is responsible for validating message packets, while the executor is responsible for executing arbitrary logic on the target chain. The current cross-chain operation process is:
When the User Application transmits cross-chain information, it first calls the smart contract of LayerZero Endpoint;
When the message reaches the Endpoint of the source chain, the message is packaged together with the target chain information and sent to the oracle and relay under the chain respectively. In the V2 version, oracle work such as verifying block headers is now undertaken by DVN. DVN is composed of multiple nodes and is jointly responsible for verifying data, which improves the decentralization and security of the entire verification process. After DVN verifies the information, the corresponding transaction proof is submitted to the Endpoint of the target chain.
After verification, the Endpoint of the target chain will forward the message to the target chain to complete cross-chain communication. In the V2 version, the repeater is replaced by Executor, which separates execution and verification. The message execution process is no longer automatically and directly handled by the smart contract, but is handled through the Executor role. As an independent execution entity, Executor helps ensure the accurate and safe execution of cross-chain messages on the target chain, and provides customizable Gas settings to simplify Gas payments.
As a lightweight cross-chain information protocol, LayerZero is the first project to introduce the Omnichain full-chain concept into the encryption industry. After two years of rapid development, LayerZero has processed more than 96,700,000 cross-chain information. With its impressive technical strength and community support, LayerZero currently supports more than 50 chains, and DeFi, NFT, wallets, DEX, bridges, etc. under its ecosystem are also in full bloom.
3. ZetaChain: Layer0 cross-chain network based on Ominichain
ZetaChain is a Layer 1 blockchain based on Ominichain technology that connects smart contract blockchains (such as Ethereum, Solana, etc.) and non-smart contract blockchains (such as Bitcoin, Dogecoin, etc.). ZetaChain consists of a proof-of-stake blockchain and a number of observers and signers that can monitor and update events, transactions and status on external chains respectively. Smart contracts on ZetaChain can conditionally execute arbitrary logic based on events on the external chain, and can directly send transactions to the external chain through a distributed threshold signature scheme. Therefore, ZetaChain can realize a full range of cross-chain decentralized applications without encapsulating or bridging any assets.
ZetaChain was established in San Francisco in 2021 and was founded by early employees of Coinbase. The core team brings together senior industry leaders from leading companies in the industry such as Brave, Coinbase, ConsenSys, THORChain, Cosmos, and 0x Labs.
ZetaChain's core contributors come from 12 countries around the world, including the United States, Canada, France, Brazil, Arminia, the Netherlands, China, South Korea, Singapore, Vietnam, India, and Russia, making its governance philosophy multicultural. The ZetaChain website supports multiple languages, ensuring an accessible and friendly interface for people from different regions.
So far, more than 3,500 smart contracts have been deployed to ZetaChain, and more than 150 dApps have integrated ZetaChain to obtain full-chain liquidity and information through these contracts and dApps.
ZetaChain conducted a seed round of financing on March 9, 2022, and completed 27 million in financing on August 16, 2023. ZetaChain is currently in the final test network stage, and the mainnet is expected to be launched in the first quarter of 2024.
ZetaChain is expected to usher in rapid development under the huge demand of the full-chain narrative and the Bitcoin ecosystem.
Detailed explanation of ZetaChain cross-chain process
ZetaChain supports Omnichain cross-chain fund transfer and cross-chain communication, and is built using the Cosmos SDK. ZetaChain can connect smart contract and non-smart contract platforms by running full nodes on the origin chain and target chain.
There is no need to package assets when transferring value on ZetaChain. The process of cross-chain assets is as follows:
Create an Omnichain account : ZetaChain will generate a TSS public key based on the connected network, which acts as ZetaChain's address on the connected network. ZetaChain will then create an Omnichain account to manage and verify transactions.
The original chain sends a transaction request : the user sends the assets on the external chain to ZetaChain's TSS address (a multi-signature jointly held by ZetaChain's verifiers). ZetaChain's observer node monitors the transaction and submits it to ZetaChain. The cross-chain module is responsible for verifying the validity and legality of transactions.
Verify transaction information : ZetaChain’s cross-chain module generates signatures through the TSS mechanism and broadcasts transactions to the ZetaChain network to lock assets in the TSS address.
Generate ZRC-20 mapping tokens : ZetaChain’s smart contract will mint the corresponding number of ZRC-20 tokens for users. These tokens are mappings of assets on the external chain and can be freely used and transferred on ZetaChain. Users can use ZRC-20 tokens on ZetaChain for transactions, payments, deployment of smart contracts and other operations, or transfer them to other blockchains that support ZetaChain.
Transfer assets to the target chain : Users can specify the target chain and address and withdraw ZRC-20 tokens to the target chain at any time.
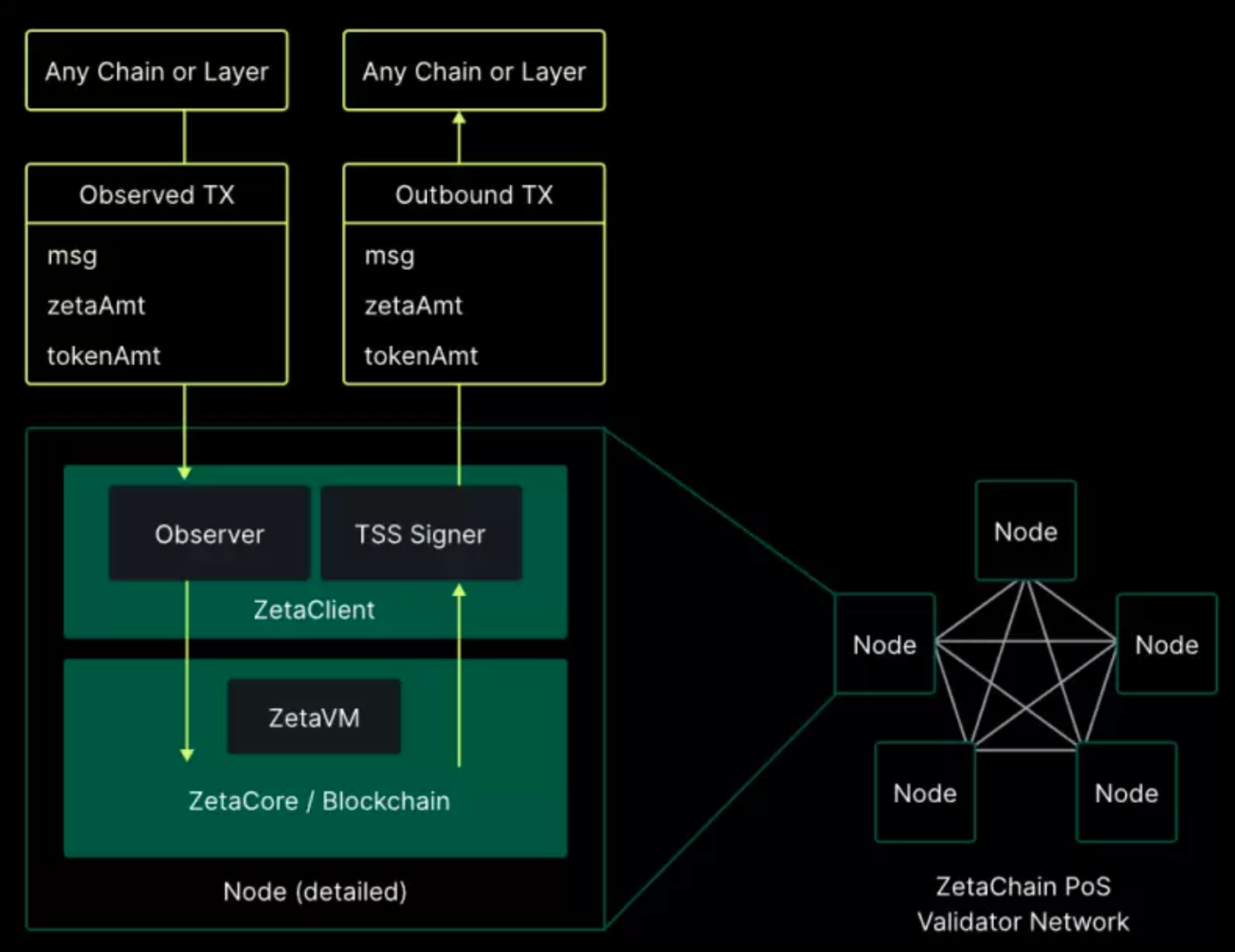
ZetaChain Omnichain Smart Contract
ZetaChain has developed a hybrid transaction model that combines UTXO and Account accounting models, which can help Omnichain smart contracts directly interact with external chains to achieve cross-chain fund/information transfer.
Omnichain smart contracts have the following functions:
ZetaChain's ZetaCore module has built-in ZetaVM, which is similar to Ethereum's EVM. Developers can use it to deploy smart contracts on ZetaChain and conduct dApp development.
ZetaChain's Omnichain smart contract can meet EVM compatibility and full-chain interoperability functions. Developers only need to deploy a single smart contract on the ZetaChain network through ZEVM to connect all target chains, including ZetaChain itself.
ZetaChain's UTXO-Account hybrid transaction model combines the UTXO model for input/output and an EVM-compatible programmable layer to help developers build more complex Omnichain DApps.
ZetaChain’s smart contracts have the following features:
Cross-chain interoperability : ZetaChain’s smart contracts can interact natively with different blockchains without encapsulating or bridging any assets. This allows dApp developers to take advantage of multiple chains, avoid setting up too many liquidity pools on different chains and causing liquidity dispersion, and centralize liquidity to achieve a wider range of application scenarios and functions. Each node of ZetaChain runs a complete node of the external chain to achieve active observation. Through observers and consensus mechanisms, it realizes off-chain communication without trusting third parties. ZetaChain not only provides message delivery, but also realizes asset custody and direct off-chain status through smart contracts. Modification, based on the communication mechanism, further builds the framework of cross-chain asset management and smart contracts.
Manage external assets : ZetaChain’s smart contracts can directly manage and use a variety of native assets on external chains, including Bitcoin, ETH, ERC20, Algorand ASA, etc. This makes asset transfers more convenient and efficient, without the need for additional intermediaries or fees.
Simple development interface : ZetaChain provides a unified interface for dApp developers so that logic and status can be centralized on ZetaChain, simplifying the development process and improving flexibility. Developers can use common programming languages and frameworks to trigger events on connected blockchains, achieve programmability, and build cross-chain applications.
Security of ZetaChain
In terms of verification mechanism, ZetaChain combines [Relay] and [Multi-party verification scheme], using the distributed verification node architecture within the network and the threshold signature scheme TSS to verify transactions, thereby reducing the risk of centralization:
Distributed verification node network : ZetaChain uses verification nodes within its own network to replace relays and oracles to help verify cross-chain transaction information and implement price feeding functions. In this way, ZetaChain improves the security and trustworthiness of transactions.
Omnichain Account/TSS : ZetaChain uses TSS (Threshold Signature Scheme) to verify and sign cross-chain transactions without packaging assets or relying on third parties, and performs cross-chain fund transfers with non-smart contract networks through TSS. TSS is independent of the blockchain and is functionally similar to a multi-signature protocol. Transaction verification is completed through multi-party signatures, which can help ZetaChain reduce single-point failure risks and centralization-related risks in verification.
ZetaChain's network includes two roles: observer and signer. Observers are responsible for monitoring and verifying events and status on external blockchains to ensure that the data of cross-chain interactions is accurate. Signers use Threshold Signature Scheme (TSS) to perform cross-chain transactions. TSS provides a secure and flexible way to manage keys for cross-chain transactions, because it requires the cooperation of multiple signers to generate valid signatures, which means that when all signers do evil at the same time, there is a chance that security issues will arise. . This greatly reduces the risk of single points of failure and fraud.
When handling cross-chain interactions, ZetaChain takes multiple verification and security measures to ensure the authenticity and integrity of transactions. For example, data collected through observers requires consensus on ZetaChain, which ensures that information coming in from external chains is verified. At the same time, the TSS mechanism ensures that transactions sent to external chains are verified by multiple parties, increasing transaction security.
4. The difference between ZetaChain and Layerzero
Both ZetaChain and Layerzero use Omnichain technology, and there are certain differences between them.
LayerZero: Full-chain interoperability protocol
Light client verification mechanism: LayerZero adopts a light client verification mechanism, which only verifies the block header without storing the complete blockchain data, which reduces the cost of use.
Cross-chain communication: LayerZero focuses more on providing a universal cross-chain message passing mechanism to communicate and exchange data through message passing.
ZetaChain: full-chain application platform
Active observation of complete nodes: ZetaChain requires each node to run a complete node of the external chain to achieve active observation.
Off-chain communication without trusting third parties: ZetaChain implements off-chain communication without trusting third parties through observers and consensus mechanisms. It not only provides message delivery, but also allows assets to be directly hosted in smart contracts and managed by smart contracts.
Cross-chain asset management and smart contract framework: ZetaChain further builds a cross-chain asset management and smart contract framework based on the communication mechanism, and can become an application layer cross-chain platform.
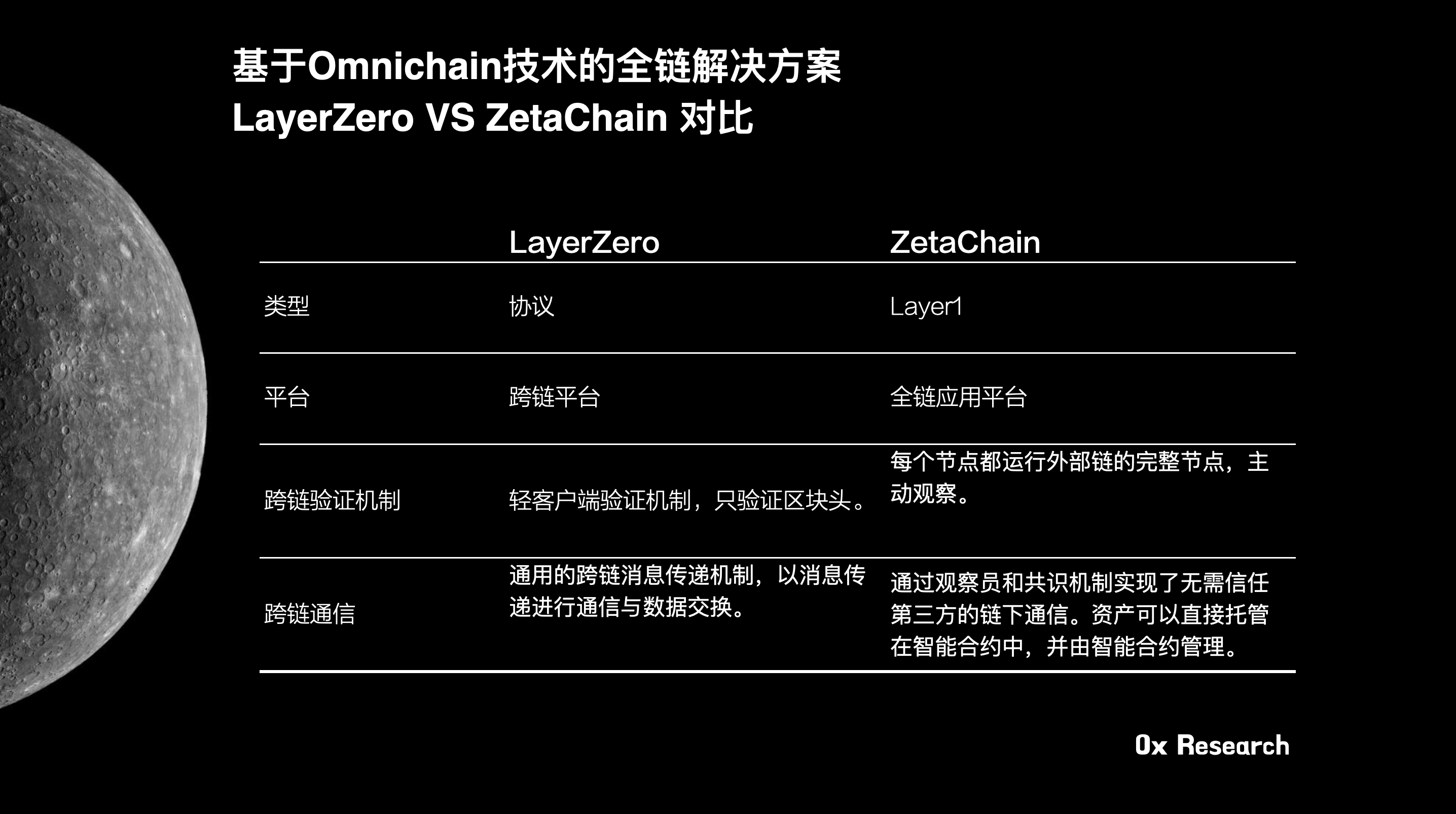
Generally speaking, the full-chain solutions LayerZero and ZetaChain each have their own unique features, but the most special thing about ZetaChain is its support for full-chain smart contracts. Full-chain smart contracts not only allow applications to run on any chain, but also allow developers to build more complex and efficient applications. A full-chain application developed based on ZetaChain can perform operations on multiple different blockchains such as Ethereum, Bitcoin, and Dogecoin, and developers only need to manage a single smart contract. From a user perspective, it also greatly reduces the complexity of managing multiple wallets. For example, in future scenarios, you can directly use $Matic to purchase Stepn NFT on BSC). In addition, as a public chain, ZetaChain's token will also become a universal GAS asset that can be used for payment on multiple chains.
5. Market space for full-chain solutions under Omnichain technology
ZetaChain Ecology
ZetaChain test network has connected BTC, BNB, ETH and Polygon 4 chains. In 2023, the number of monthly active users (MAUs) on the ZetaChain testnet dApp ecosystem exceeded 780,000+. ZetaScan data shows that testnet dApps on ZetaChain generated 14,000,000+ cross-chain transactions.
ZetaChain Ecosystem has more than 150 dApp partners that have completed testnet integration ( ZetaChain Ecosystem ), and more than 46,000 dApp contracts have been deployed.
The first native BTC smart contract support has been completed, allowing users to use DeFi through Bitcoin wallets.
The ecological components of ZetaChain include the following aspects:
ZetaChain : Provides native full-chain smart contract support, enabling full-chain dApps to directly interact natively without any asset packaging or bridging.
ZETA : ZetaChain’s native token, used to pay handling fees for cross-chain transactions, participate in consensus mechanisms, deploy and run smart contracts, transfer assets and connect multiple blockchains.
ZetaEVM : A virtual machine compatible with Ethereum that can deploy and run full-chain smart contracts on ZetaChain to achieve seamless transfer of cross-chain assets and data.
ZRC-20 : A unified token standard for the entire chain, allowing assets on external chains to be deposited and withdrawn from ZetaChain, enabling local use of multi-chain assets.
ZetaChain Connector : A cross-chain messaging mechanism that allows users to send data and value between any connected blockchains, enabling interoperability between multiple chains.
ZetaChain DApps : A series of decentralized applications developed based on the ZetaChain platform, covering multiple fields such as payment, DeFi, art, games, and social networking, providing users with a variety of functions and experiences.
Developers are allowed to participate in a variety of ways in the ZetaChain ecosystem.
- Native cross-chain application
Developers can develop full-chain dApps on ZetaChain. ZetaChain's dApps can directly interact with multiple blockchains without any asset packaging or bridging.
Eddy Finance is a decentralized exchange (DEX) built on the ZetaChain blockchain. ZetaChain enables Eddy to simplify the transfer of native assets across the network without the need to wrap tokens. It also supports cross-chain unified liquidity pools, combining native assets including Ethereum, BTC, BNB and stablecoins to optimize efficiency. ZetaChain brings tremendous value to BTC by seamlessly integrating BTC into the EVM ecosystem.
zkMe is an identity oracle (anti-zombie/anti-counterfeit currency, KYC, player ratings, etc.) that protects user anonymity and privacy through zk technology while maintaining full compliance. ZetaChain enables zkMe to anonymously verify user credentials across the chain ecosystem. Through ZetaChain, zkMe supports the first Omnichain Soul Tokens (Omni SBTs), allowing users to manage their entire on-chain identity across all on-chain ecosystems using only one wallet.
Bounce Finance is a decentralized auction protocol that enables users to create and participate in various types of auctions on multiple blockchain networks. ZetaChain can implement Cross-Chain Auction-as-a-Service on Bounce. This includes creating and participating in various types of DeFi auctions on any chain, including the Bitcoin network, with support for native BTC.
Weave6 is one of the recipients of grants from ZetaChain to support the Omnichain NFT ecosystem. ZetaChain provides technical, marketing, protocol design and network assistance.
- Promote interoperability between blockchains
Developers can build powerful cross-chain applications by passing messages (data and value) between L1 and L2 through simple function calls to trigger existing smart contracts.
- Enable existing dAPPs to quickly gain full-chain functionality
In November 2023, Sushi announced its expansion to ZetaChain, allowing users on Sushi to exchange native BTC across 30 networks. Sushi is a leading multi-chain decentralized exchange (DEX) deployed on more than 30 chains, offering unique cross-chain exchange through SushiXSwap. ZetaChain will allow Sushi users to exchange Bitcoin and any other asset in just one step without the need for wrappers or bridges. Leveraging ZetaChain's ZRC-20 standard, Sushi can also scale to use native BTC on its 30 connected chains.
In December 2023, Dmail Network announced a cooperation with ZetaChain. Users can create 8-11 digit email NFT domain names for free through ZetaChain and enable email services. In the future, Dmail Network also plans to use ZetaChain for native cross-chain payments, including Bitcoin. Interoperability.
Unleashing the DeFi potential of Bitcoin
Introducing DeFi into the Bitcoin ecosystem is of great significance. Bitcoin accounts for about 50% of the total market value of the entire cryptocurrency. Introducing Bitcoin into DeFi will provide a large number of high-quality mortgage assets for DeFi, which is conducive to the stability of DeFi's underlying assets. Previously, some projects introduced BTC into the Ethereum ecosystem by minting Bitcoin-anchored coins on Ethereum. However, these Bitcoin-anchored coins only accounted for a very small part of the entire BTC circulation.
- Unleash BTC liquidity
Through the ZetaChain cross-chain network, users can interact with the DeFi of other chains in their Bitcoin wallets. On the one hand, it simplifies the user's operation path, and on the other hand, it expands the boundaries of the Bitcoin ecosystem. For holders, they can earn income in DeFi by providing Bitcoin without exchanging wBTC, and have the security attributes of native BTC.
- Unleashing BRC20 Liquidity
Although the market value of BRC20 has risen rapidly due to Fomo and popularity, the current narrative of BRC20 is still dominated by concept scarcity and fair sale. How the BRC20 track releases its liquidity to promote and develop the track’s innovation points and new narratives will be the future growth point of BRC20.
ZetaChain's Ominichain smart contract can interact directly with Bitcoin's native assets. Users only need to attach a small note through the Bitcoin wallet to trigger the contract on ZetaChain, which can further write data to other chains, thereby enabling direct transactions between Bitcoin and other chains.

write at the end
In the last cycle, the "Ethereum killer" was just a fantasy. Now multi-chain coexistence has become a reality, and the future of Web3 will be a multi-chain world. Omnichain's full-chain technology helps realize the circulation of assets and information and breaks down blockchain silos, thereby enhancing the functionality of the entire blockchain ecosystem. In addition, cross-chain will also help promote the development of a wider range of blockchain applications and services.
Most cross-chain bridges involve transaction fees for locking, unlocking, or transferring assets. These fees will cover the computing resources and security measures required for the operation of the cross-chain bridge, and are also the source of cross-chain bridge revenue. Just like bridges in the real world, continuous economic returns are obtained by virtue of the economic exchanges between the destinations connected and the high-quality services they provide.
Through Omnichain technology, users can participate in Dapps on other chains using the original chain wallet, and there is no need for frequent asset cross-chains. For developers, full-chain functionality and full-chain liquidity can be easily obtained.
As an innovative cross-chain technology, ZetaChain brings new possibilities and opportunities to the blockchain ecosystem. By achieving full-chain interoperability, it solves the current problems of blockchain fragmentation and non-interoperability, providing users with a more convenient, direct and secure cross-chain experience. Smart contracts on ZetaChain can directly interact with different blockchains locally without encapsulating or bridging any assets, thus supporting the development of more cross-chain applications and services. ZetaChain’s team has rich blockchain experience and technical strength, has completed multiple rounds of financing, and established cooperative relationships with partners in multiple fields. ZetaChain is currently in the test network stage and is about to launch the main network. It is expected to usher in rapid development under the huge demand of the full chain narrative and the Bitcoin ecosystem. ZetaChain is a blockchain project worthy of attention and anticipation, and is expected to bring revolutionary changes to the entire blockchain industry.
References:
https://zetachain.notion.site/ZetaChain-One-Pager-7ba1136d6109465ab335f926fdc2ca09?pvs=4
https://zetachain.notion.site/ZetaChain-Manifesto-32b7525aae394255a0409e27d82ce741?pvs=4
https://s2.tokeninsight.com/static/research/file/levelPdf/OmniChain_%E7%9A%84%E6%9C%AA%E6%9D%A5%EF%BC%9AZetaChain%EF%BC%8C% E7%AC%AC%E4%B8%80%E4%B8%AA%E5%8F%AF%E5%AE%9E%E7%8E%B0%E5%AE%8C%E5%85%A8%E4% BA%92%E6%93%8D%E4%BD%9C%E6%99%BA%E8%83%BD%E5%90%88%E7%BA%A6%E7%9A%84%E5%85% AC%E5%85%B1_Layer1_%E5%8C%BA%E5%9D%97%E9%93%BE.pdf
https://foresightnews.pro/article/detail/41572
https://foresightnews.pro/article/detail/45423
https://www.blocktempo.com/20000-words-deep-parse-zetachain/
https://learnblockchain.cn/article/6641







