With the approval of the US Bitcoin spot ETF and the development of the RWA protocol in the DeFi field, cryptocurrencies are accelerating to the forefront, and more and more users are participating in on-chain DeFi, trying to find new profit opportunities. However, the cumbersome on-chain operation steps are discouraging some Web3 newcomers.
The Web3 world already has thousands of cryptocurrencies, countless Layer1, Layer2, and now Layer-3, as well as cross-chain bridges connecting different blockchains. In this vast and innovative ecosystem, it is becoming increasingly difficult for new users to intuitively discover which way is the best option for them to conduct transactions.
The "Intent-Centric" track is designed to solve this problem for new users, thereby achieving Crypto Mass Adoption, allowing a wider user group of Web2 to enjoy a smooth user experience and easily cross over to Web3.
What is intent?
In the Web3 world, "intent" refers to a specific goal that a user wants to achieve in the blockchain ecosystem, and is an expression of the final state of this specific goal. Generally speaking, a transaction explicitly refers to "how" an operation should be performed, while intent refers to what the expected result of the operation should be.
So what do intent protocols bring to the table? In short, let users simply state their goals and leave the “how” to more expert problem solvers.
For example, if you want to get from point A to point E (goal/intention), the current old vision transaction requires you to complete it step by step from A-> B-> C-> D-> E. This is just the tip of the iceberg of the current DeFi world, not to mention that the token needs to be transferred from CEX to the chain. In fact, the complexity of the interaction may be far beyond imagination.
However, in the case of intention protocols, after you put forward the intention of "I want to go from A to E", each step of A-> B-> C-> D-> E is executed by a solver. The solver here can be a person, AI or other protocol.
If a transaction is “go to A first, then go to B, and pay a certain amount of C to get E”, then the intent is “I want X, and I’m willing to pay a certain amount of C”. Users submit their intent to the protocol, and the protocol delegates each step of the task to the solver to execute.
With the intention protocol and solver, in addition to abstracting the cumbersome transaction process for new users, it can also save gas fees to a certain extent, and the solver can execute transactions at the most powerful price to improve efficiency. At a time when blockchain technology is becoming more and more important, such a paradigm will change the landscape, making Web3 interactions more efficient and secure, and easier to attract the experience of billions of Web2 users.
The hot development of the intent track was kicked off by Paradigm's article "Intent Structure and Its Risks" in June 2023. To date, what are the popular projects worth paying attention to?
Overview of recent popular intent networks/protocols
dappOS
The intention execution network dappOS became a trending search on Twitter due to its $300 million Series A financing and the integrated project GMX's large airdrop of 100,000 $ARB to active users.
DappOS recently completed a $15 million Series A round led by Polychain, with a valuation of $300 million, making it one of the new "star projects" in the intent track. Last year, the network also received investments from top VCs such as Binance Labs, Sequoia China, and IDG.

In addition, since GMX V2 integrated dappOS two months ago, 30,596 new users have been added, and 15% of the new TVL in the past 30 days came from dappOS users. In order to motivate active dappOS users, GMX airdropped 100,000 $ARB. As the dappOS network grows further, there will be more and more airdrop opportunities like this, making it a golden shovel tool for Airdrop interaction.
As an intent execution network that solves priceable intent, dappOS is meeting the extremely low threshold for on-chain interaction for users. Users only need to submit their intent, and dappOS and its solver nodes will execute the intent in a decentralized manner. dappOS can execute a variety of intents, including application contract interactions , inscription casting strategies , copy trading , Telegram robot trading , and more.
At the same time, dappOS also provides middleware compatible with the network, so that developers can expand this set of "intention" capabilities to more dApps at a low cost and maintain the decentralized nature. Therefore, dappOS is promoting the transformation of integrated dApps to "decentralized intention applications".
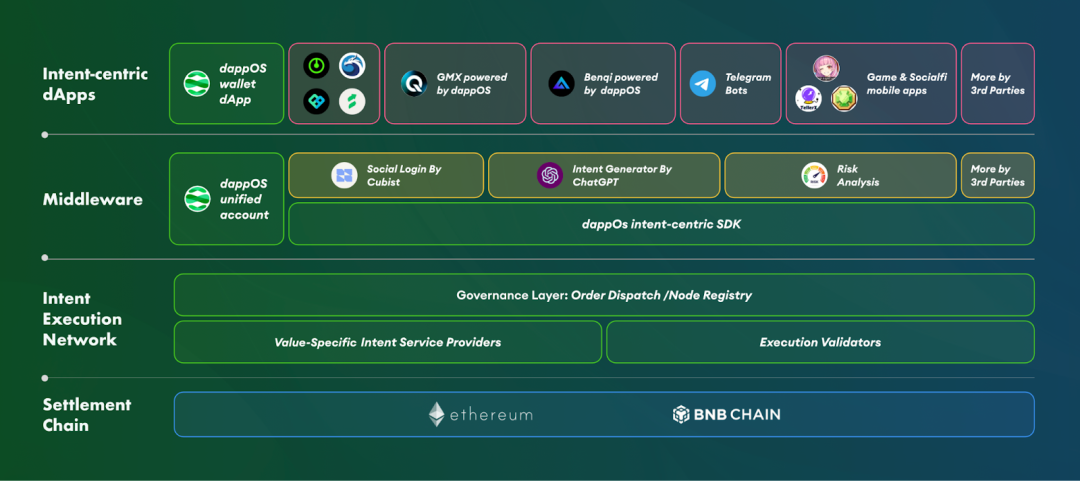
As the dappOS ecosystem grows, it will attract more and more users to participate, especially under the blessing of the "golden shovel" effect, it will accelerate the conversion into sticky users and gradually form a network effect, which will also accelerate the optimization of the dappOS intention network for service nodes. The intention execution network will be lower cost, more efficient, and have a better user experience, which in turn will prompt more dApps to support dappOS. It is also worth mentioning that dappOS is introducing the governance token $DOS, and the growth of network revenue and transactions will further provide benefits for $DOS holders.
Anoma
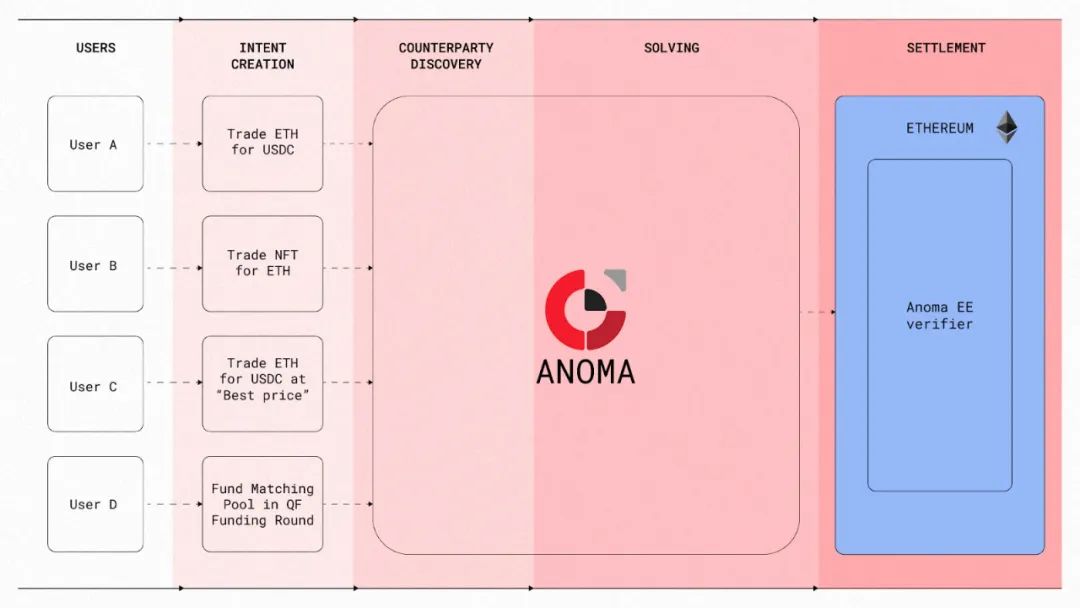
The Anoma protocol is the first protocol to introduce the concept of "intent", providing a general-purpose dApp architecture centered on intent. The architecture is designed to meet a wide range of requests, enabling dApps that provide services to align intent with a network of solvers, facilitating the matching of user intent with solvers across various applications and scenarios. It is worth mentioning that Anoma is actually an "interface", a series of codes that can be freely copied, rather than an intermediary chain, so there will be no Anoma chain. In other words, Anoma can be deployed to any current L1, L1.5, L2 or non-EVM chain, such as the Ethereum mainnet, Arbitrum, Solana, Cosmos, Eigenlayer AVS.
Particle Network
Many friends got to know Particle Network, which provides account abstraction, BTC Connect and other services behind the scenes, through MerlinChain. In fact, in addition to its achievements in the field of chain abstraction, the protocol is also planning to develop the field of intent.
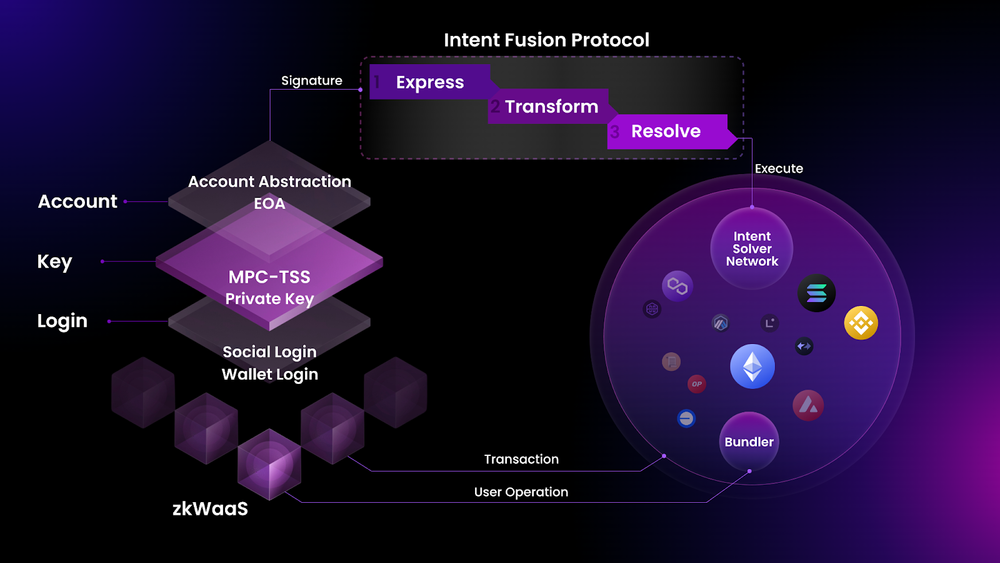
Particle Network is building a universal dApp framework, Intent Fusion Protocol, for expressing, converting, and executing intents. Developers can use it to create intent applications, and the intents expressed by users will be submitted to the solver network for on-chain execution.
In this ecosystem, developers have a direct path to leverage the unique capabilities of Web3 while providing users with the best possible user experience, focusing 100% of their efforts on creating solutions to problems.
By combining the Intent Fusion Protocol with Particle’s mature chain abstraction, modular smart WaaS, and cross-chain atomic swap solutions, developers from Web2 can easily leverage the unique capabilities of Web3 while providing users with the simplest user experience.
Essential
Essential calls itself the first “Declarative Blockchain”, but it still revolves around the concept of “intention”.
Essential believes that since the birth of the first general-purpose blockchain Ethereum, every general-purpose blockchain has used an imperative programming model. Since they rely on the linear execution of code to achieve state updates, the only way for users to interact with these blockchains is through imperative instructions (such as transactions and smart contracts). Indeed, the most common user experience criticisms of blockchains by new Web3 users are uncertain results, failed transactions, MEV, and high slippage - in fact, they are all criticisms of the underlying imperative model.
Next, let’s take a look at how Essential’s “declarative blockchain” works.
According to the official interpretation, a declarative blockchain means a blockchain that uses constraints to implement state updates without execution. Or in other words, Essential allows users to sign their intended transactions with the desired (declarative) results rather than (mandatory) instructions. In fact, it is also within the scope of intent.

Essential has high requirements on solvers. Compared with ordinary solvers of 1+1=2, when the user submits the intent, the solver of the Essential network must do its best to propose the best solution, not only to meet the user's intent, but also to maximize the user's satisfaction. To put it more simply, after the user proposes the intent, each solver will compete to answer the following question: Given the constraints and goals, which new state do I think can maximize the user's satisfaction?
Essential's technology stack has three core pillars:
- Blockchain without execution: Similar to ZK Rollup, the computation of user intent is done off-chain, while the fraud proof verification part is done on-chain, thereby providing greater throughput and lower transaction fees for applications and users.
- Constraint-based Domain Specific Language (DSL): Allows users to express their intentions simply through natural language. Developers can simply describe business logic and outsource transaction or calculation logic to solvers, making it easier for users to get the desired interaction results and for developers to create more complex dApps.
- Solver Network: Provides the best solution for the intent submitted by the user across the entire network.
Self Chain
Self Chain is a new modular, intent-centric blockchain based on the Cosmos SDK. In the incentivized testnet V2 that ended last month, Self Chain achieved a good result of 366 applications and 19,000 users.
Actually, I wanted to introduce this project together with Ruby Network, which has already launched its mainnet, because the two are very similar. They both start with the Mass Adoption narrative, from MPC, account abstraction, chain abstraction to intent, and they have taken advantage of all the hot topics. However, compared to the stitched monster Ruby, Self Chain has put much more technical effort in the intent narrative (Ruby seems to just be labeled as "intention").
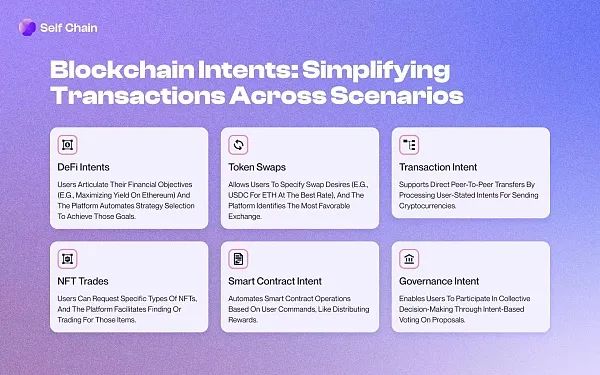
Self Chain integrates the concept of intent into its blockchain architecture through a three-layer structure:
- dApps layer: Users interact with dApps through a simplified interface. This layer collects user intent and translates it into simple, structured intents using a large language model (LLM) similar to GPT-4.
- Intent Access Layer: This layer searches for the various paths required to fulfill the user's intent and finds the best way to satisfy the user's request.
- Intent Solver: The intent solver intervenes to execute transactions efficiently.
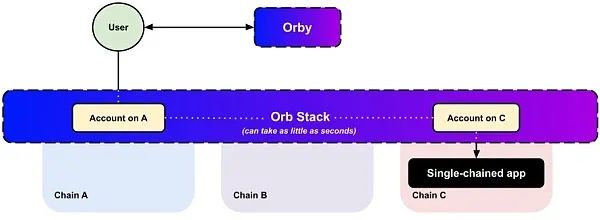
Orb Stack, Orby
Orb Lasb is developing a modular cross-chain intent protocol stack Orb Stack that allows users to issue cross-domain intents. It consists of 5 layers:
- Scalable light client, providing a secure foundation for the system
- Messaging framework, optimized for speed, cost and configurability
- Token packaging protocol, supporting cross-chain assets
- Cross-domain intent protocol
- Unified account system, allowing users to host assets on different chains
In addition, the development team is also developing the intent engine Orby, which can be integrated into any dApp frontend, enabling users from any chain to use it. It can also be integrated into the wallet, allowing users to interact with any dApp on any chain without fragmenting wallet assets to various on-chain addresses. The vision of Orby is to support multi-chain interactions and convert transactions into intents that can be executed on any chain through the Orb Stack.
Orbiter Finance (Orbiter Rollup)
Orbiter Finance is a leading Layer 2 cross-chain protocol, with more than 3 million users using it to cross-chain assets between different L2s. In January, Orbiter Finance announced that it would launch ZK-based Orbiter Rollup in the future, becoming Ethereum's intent layer, mainly used to aggregate Orbiter users' cross-chain intents. With the joint efforts of partners, Orbiter Rollup will solve the execution problem, that is, users can achieve their desired results on the network without having to perform cross-chain operations step by step.
Across v3
Similar to Orbiter is the cross-chain protocol Across. In the recently launched V3 version, Across added a composable intent engine. It consists of the following parts:
- Intent-based RFQ order flow
- A network of third-party solvers with off-chain liquidity
- Settlement system with optimistic verification
Aperture Finance
Aperture Finance is a DeFi platform based on intent architecture that combines AI with intent to build a chatbot where users can express their intent in natural language and leverage a solver network to get results.

This is a typical example of AI + Intent. By directly interacting with AI text and expressing needs, AI automatically extracts, identifies and confirms user intent, submits it to the solver network, and the solver network seeks the best solution. Finally, it is handed over to the best solver for execution through a bidding model.
In addition to trading, another interesting use case is to use Aperture to claim airdrops. We only need to tell the AI, "Help me try to claim the Airdrop, and the system will automatically search for projects with airdrops on various chains based on the user's wallet address and authorization, and automatically complete the claim." This automation can greatly reduce the time for users to directly interact with each project's airdrop claiming website, and eliminate the risk of users being deceived by phishing websites.







