What is a full-chain game, what are its unique advantages and challenges, and full-chain game cases.
Written by: Chainlink
Blockchain games are an innovative form of gaming that has attracted the attention of gamers from all walks of life. Gaming giants such as Square Enix, Nexon, and Ubisoft are all experimenting with this cutting-edge technology .
However, blockchain is not a panacea for most games. Currently, most first-person shooters cannot run on the blockchain. Blockchains are too slow to support games running smoothly, and sub-second player reaction times using blockchains are simply not realistic. Therefore, most blockchain games actually use blockchain as one of the technology stacks, and the main purpose is to distribute and transfer digital assets and currencies in the game.
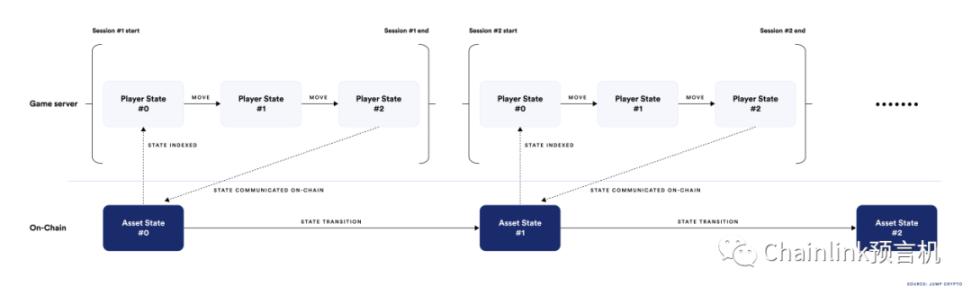
Most blockchain games combine blockchain technology and traditional game servers to protect players' ownership of game items
However, there is now a small group of Web3-native game developers and players trying to create a purely on-chain gaming experience, and this group is growing. We also call this kind of blockchain game "full chain game".
What is a full chain game?
Full-chain games refer to games and NFT ecological collections that run entirely on the blockchain. That is, the game runs on the blockchain except for the front end (i.e. what the gamer sees on the screen).
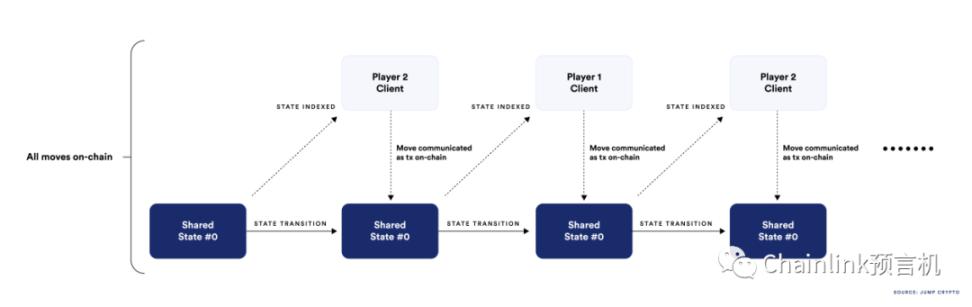
In a full-chain game, all player behavior and data are recorded on the chain, not in the game server
The main difference between full-chain games and traditional blockchain games is that the former implements game logic directly in smart contracts, and uses NFT smart contracts to store game data such as player names and rankings on the blockchain instead of the central in the optimized game server. A game can only be called a "full chain game" when all its game logic and data are stored on the chain.
The operation mechanism of the whole chain game
Full-chain games store game logic and data entirely through smart contracts (note: smart contracts automatically execute lines of code on the blockchain).
In a broad sense, game logic determines the rules of a game, that is: if it is an online card game (TCG), then game logic determines how each game starts, in what order the cards are played, and when the game ends . Rules are the soul of a game. In a full-chain game, these rules will be written into smart contracts, and no one can tamper with them.
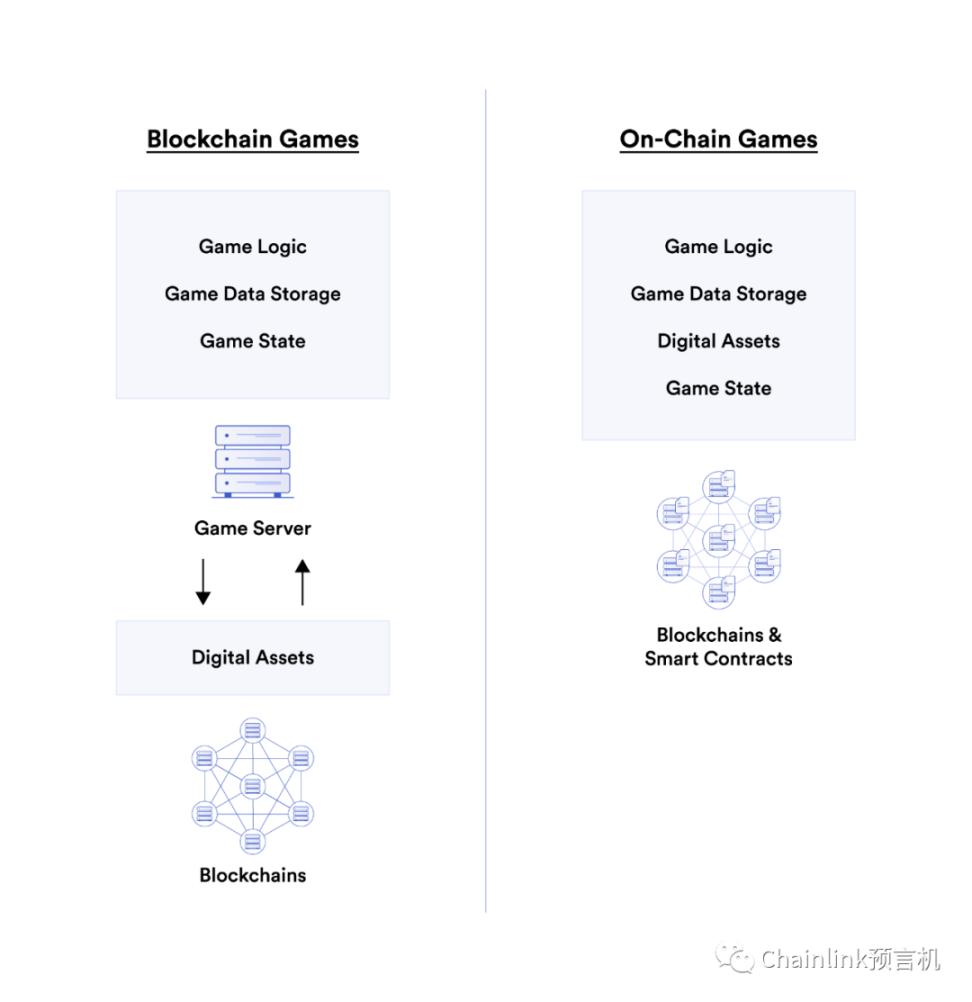
Traditional blockchain games have both smart contracts and game servers, while full-chain games only use blockchain and smart contracts
Smart contracts can also be used to create, distribute and transfer digital assets. In the card game mentioned above, the digital asset is the trading card NFT. Digital assets are the most widely used technology in the field of blockchain games, and various NFT games including Gods Unchained, Axie Infinity, Illuvium, WildCard, and Deadrop have applied such assets.
Challenges faced by full-chain games
Why are most of the games so far not full-chain games? This is because full-chain games are full of challenges, developers must abide by very strict technical specifications, and the user experience of players will be greatly reduced.
Blockchain Speed and Scalability
Blockchain is a shared computer network maintained by thousands of computer nodes around the world. So it has bottlenecks in speed and scalability , two key technical elements for fast-paced games.
These technical bottlenecks have also led to the fact that today's full-chain games are limited to card games or strategy games where players take turns to initiate operations. The speed of smart contracts cannot support fast-paced games such as multiplayer online battle arena games (MOBA), first-person shooters (FPS) or even real-time strategy games (RTS).
Transparent Player Operations
Smart contracts and transactions in contracts are completely transparent and can be viewed by anyone. Transparency is an advantage in financial scenarios, but it becomes a bottleneck in gaming scenarios because privacy cannot be guaranteed.
For example, the fog of war mechanics in MOBA games or real-time strategy games can hardly be implemented on the chain. Such games need to hide parts of the game from players. Of course, some technical solutions can also be used to solve occasional problems, but this still cannot completely solve the privacy problem in full-chain games.
robot
The design mechanism of full-chain games and smart contracts leads to the coexistence of robots and real game players, because there is no centralized entity to run anti-cheating software. This will lead to a worse experience for gamers in some cases, especially when rare digital assets or NFTs are rewarded in the game, and bots will be more rampant because of generous rewards.
technical bottleneck
Because blockchain and smart contracts are designed with security as the first priority, there are some technical bottlenecks that prevent certain tasks from being performed.
The two biggest bottlenecks of full-chain games are obtaining tamper-proof random numbers and automatically executing game logic.
- Almost all full-chain games must use on-chain random number solutions, and these random numbers are often manipulated by validators (or miners) in the network because they can see the random number before the chain is finalized.
- Some intermediate process operations in the game (such as transmitting a series of game logic based on player operations) need to automatically call smart contract functions to improve the game experience. But smart contracts and the blockchain alone cannot do this. For example, if a player has harvested an asset, the operation of automatically harvesting the asset must be initiated before the asset will appear in the player's inventory.
Advantages of full-chain games
Although many challenges need to be overcome to develop full-chain games, the full-chain game ecosystem can combine the advantages of blockchain and smart contracts to provide a series of values for players and developers.
Composable and open source
Since the full-chain game fully deploys the game on the blockchain, players and developers can reproduce the game logic, create a new game type, develop different interfaces for the game, and develop various applications based on the game to enhance the game experience , enhance the openness and entertainment of the game.
Therefore, the full-chain game can also be regarded as a "game primitive". Like fantasy games such as "Dungeons & Dragons", full-chain games can also provide players with a set of fixed game rules, and players can continue to create subsequent creations based on this set of rules.
Decentralization, digital permanence and immutability
An often overlooked aspect of full-chain games is that they can essentially run automatically once deployed on-chain.
As long as there is a verifier in the blockchain network, it can always be online. This feature provides eternal data protection for the entire chain of games. As long as the blockchain is still running, the game code can run forever. Theoretically, if the blockchain where the game is located can continue to run in the next three hundred years, then the game and game logic will always exist and be stored on the blockchain, and gamers can continue to play.
low-risk technological innovation
Since the blockchain environment is vulnerable to various attacks, and the blockchain guarantees huge assets, it is a very difficult task to implement theoretical research, especially for those who try to apply new technologies in the field of decentralized finance (DeFi) The stakes are extremely high.
Full-chain games provide researchers and developers with a low-risk environment where they can explore cutting-edge technologies such as Zero-knowledge Proof and homomorphic encryption. Full-chain games and higher-risk applications such as DeFi are often in the same infrastructure, but the former is less risky and therefore a better testing ground.
Diversified game front-end interface
Both blockchain and smart contracts are essentially back-end technologies. If players want to play the purest on-chain game, they must use the command line to interact.
Tech-savvy players and developers can develop different front-end interfaces based on the same blockchain game logic and data. They just need to connect the game front-end interface to the back-end smart contract. Therefore, the same game on the chain can have multiple game interfaces. Two players can play the same game, but one is playing a medieval game scene and the other is playing a space game scene.
Full chain game case
The earliest full-chain games appeared in 2013, and since then, the field has continued to move forward.
HunterCoin
Launched in 2013, HunterCoin is widely regarded as the first full-chain game. The game is an experimental attempt to demonstrate the potential of decentralized game development. The game is deployed on its own blockchain, and player operations in the game, such as movement, gathering, and attack, are submitted in the form of transactions.

The Game World of HunterCoin
Dark Forest
Dark Forest is a relatively recent full-chain real-time strategy game set in space. This game is inspired by Liu Cixin's science fiction novel "Three-Body Problem - Dark Forest". Players are placed on an unknown planet in space. The task is to collect resources, expand territory, and occupy new planets.
Dark Forest is the first full-chain game that incorporates the fog of war. The purpose of the team developing this game is to explore Zero-knowledge Proof Zero-knowledge Proof, which they use in the game to hide other players' location information from players.
Dark Forest is an on-chain real-time strategy game where players battle in space
The Development of Web3 Native Games
Full-chain games are relatively niche in the Web3 ecosystem, but there are still some community members, researchers and developers actively exploring the boundaries of full-chain games.








