Source: Tsinghua Service Economy and Digital Governance Research Institute
On February 22, 2025, the China Digital Economy Development and Governance Academic Annual Conference was held at Nankai University. This annual conference, themed "Artificial Intelligence, Digital Economy and New Productive Forces", actively responded to the strategic call in the report of the 20th National Congress of the CPC to "accelerate the construction of a cyber power and a digital China", and gathered the wisdom of the academic and industrial circles to jointly explore the future development direction of the digital economy. The conference invited more than 40 experts, scholars and institutional representatives to conduct in-depth discussions on core issues such as the digital economy, digital finance, digital trade, data elements, and AI innovation development. Nankai University President Chen Yulu delivered a keynote speech on "The Rise and Challenges of Cryptocurrencies".

Chen Yulu delivers a keynote speech
The theme I want to share today is "The Rise and Challenges of Cryptocurrencies". Cryptocurrencies are a type of digital currency that operates through computer networks, and the ownership of each cryptocurrency unit is recorded and stored in a digital ledger or Blockchain. Blockchain is the underlying technology of cryptocurrencies, with the core being consensus mechanisms such as Proof-of-Work (PoW). Cryptocurrencies can be mainly divided into three categories: payment-type cryptocurrencies such as BTC and ETH; stablecoins, the most famous of which are the US dollar stablecoins USDT and USDC; and central bank digital currencies, also known as sovereign digital currencies, with the largest representative being China's Digital RMB. Cryptocurrencies have seven main characteristics: decentralization, security, scarcity, anonymity, high price volatility, large energy consumption in the mining process, and global instant transactions without considering currency exchange costs and international transfer time costs.
Since Satoshi Nakamoto (the team) mined the first Bitcoin Block (Genesis Block) in January 2009, cryptocurrencies have gradually gained a foothold in the financial ecosystem, from a niche virtual currency experiment. Currently, more than 130 countries and regions have begun to incorporate different forms of cryptocurrencies into the discussion of the mainstream financial system. Against the backdrop of escalating global geopolitical turmoil, persistently high US fiscal deficits, and a sharp rise in US public debt, cryptocurrencies represented by BTC are receiving widespread attention. The latest developments indicate that the US government is accelerating the construction of a "digital US dollar hegemony system" from three aspects: national strategic reserves, cryptocurrency legislation, and cryptocurrency financial infrastructure, and attempting to extend its global hegemony in traditional finance to the digital economy era. Based on the above background, I will focus on elaborating on the global situation and risk challenges of cryptocurrency development.
The Cryptocurrency Market is Experiencing Breakthrough Progress
In January 2024, the BTC spot trading fund ETF was officially launched, becoming a landmark event in the integration of crypto assets and traditional financial assets. In December of the same year, the price of BTC broke through $100,000 per coin, driving the total crypto market capitalization to surge from $800 billion to $3.4 trillion in just 2 years. Meanwhile, the total crypto asset market capitalization has quickly risen from less than 1% of the liquidity of the world's six major central banks (G6) in 2009 to 12% at the end of 2024. In the mainstream market, BTC's investment attributes are shifting from a niche risk asset to a mainstream asset class. The new Trump administration's proposed Strategic BTC Reserve (SBR) program has further stimulated and reinforced this transition process.
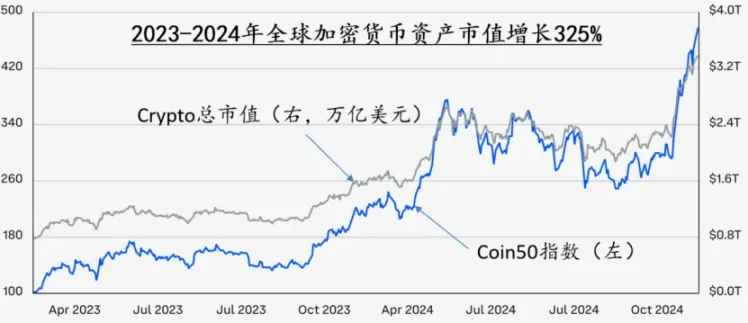
Figure 1 Global capital began to flood into the cryptocurrency market after the second half of 2023, data source: Coinbase: Crypto Market Outlook 2025.
Since the second half of 2023, the US government's regulatory stance on the cryptocurrency field has undergone a significant shift, and its strategic intention is likely to be an attempt to extend the US traditional financial hegemony to the digital finance field. Against the backdrop of the US government's high debt and persistent inflation, this strategy can not only ensure the centralized position of the US dollar in the digital finance revolution, but also indirectly support and alleviate its increasingly severe federal debt situation. This strategy may contain short-, medium-, and long-term goals: in the short term, the US government is trying to build the initial framework of global digital currency hegemony through three means: cryptocurrency strategic reserves, encouraging the expansion of US dollar stablecoins, and controlling the core infrastructure of crypto asset transactions; in the medium term, through a relaxed regulatory environment, tax incentives, and long-arm financial sanctions, it will continue to attract (or coerce) the world's top crypto companies to migrate to the US or be incorporated into the US government's regulatory system, promoting industry clustering, employment, and economic growth, and maintaining the US's leading position in blockchain technology R&D; in the long term, the US will ensure that the US dollar maintains a centralized position in global digital economic investment and transactions by dominating the formulation of global digital finance infrastructure and rules, ensuring that the US retains centralized power in the decentralization wave of the digital economy.
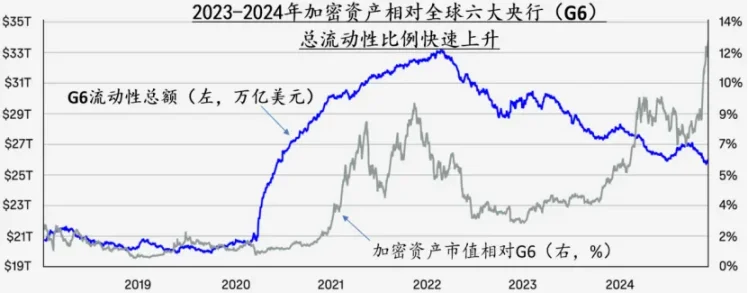
Figure 2 The scale of cryptocurrencies surged and entered the mainstream asset market after the second half of 2023, data source: Coinbase: Crypto Market Outlook 2025.
The Changing Stance of the US Government and Business Circles on Cryptocurrencies and Their Strategic Intentions
1. Since the second half of 2023, there have been five landmark changes in the US government and industry's stance on cryptocurrencies
First, the stance of the US financial regulatory authorities has shifted from "severe crackdown" to "guiding regulation". The new chairman of the Trump administration, Paul Atkins, is a long-term supporter of cryptocurrencies, and after taking office, he actively promoted the compliance path of crypto assets, coupled with his close relationship with the new Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent, reflecting the new US government's positive support for crypto assets and the trend of finding a new balance point between financial innovation and financial investment protection. In December 2024, the SEC approved the listing and trading of Franklin Templeton's crypto index ETF (EZPZ) on the Nasdaq, which is an important milestone in the US financial regulatory stance's comprehensive shift.
Second, from legislative suppression to legislative support. The US Congress is actively promoting the "dual pillar" of crypto regulation legislation - the "21st Century Financial Innovation and Technology Act" (FIT21) and the "Guiding and Establishing the US Stablecoin National Innovation Act" (GENIUS). The FIT21 Act will comprehensively establish the basic framework of crypto regulation, solve many classification and jurisdiction issues, and clarify the regulatory boundaries between the SEC and the CFTC (Commodity Futures Trading Commission), formulate standards for identifying the attributes of digital asset commodities and securities, and establish a legal framework for institutional digital asset custody business. GENIUS aims to establish a comprehensive regulatory framework for stablecoins and bring the two largest stablecoins, USDT and USDC, which account for 90% of the global stablecoin market value, into the regulatory scope. FIT21 was passed in the House of Representatives with bipartisan support in May 2024 and is expected to be passed by the Senate and signed into law by 2025. GENIUS is planned to be voted on in the Senate in March this year. After the passage of these two bills, the US will form the most comprehensive crypto regulatory system in the world, which will significantly influence the direction of crypto industry innovation and market pattern.
Here is the English translation of the text, with the specified terms preserved:Third, the policy has shifted from a stance of severe crackdown to strategic asset-ization. The Trump administration plans to launch a 1 million BTC strategic reserve and include it in the Treasury Department's Exchange Stabilization Fund. In January this year, Trump signed an executive order "Strengthening U.S. Leadership in Digital Assets", the main content of which includes preparing to establish a Bitcoin Strategic Reserve (SBR) and banning the establishment, issuance, and promotion of any form of central bank digital currency within and outside the United States, thereby suppressing any potential competitors to the U.S. dollar stablecoin.
Fourth, the industry has shifted from hesitation and observation to a more proactive response. A large number of star companies such as Apple, Tesla, and MicroStrategy have already or plan to include crypto assets in their corporate asset allocations. Traditional large financial institutions (such as the world's largest asset management financial group BlackRock) are also accelerating their holdings of BTC. The global BTC ETF fund assets have exceeded 1.1 million BTC. Among them, the BlackRock Bitcoin ETF (IBIT) accounts for 45% (market value of about $153 billion as of February 2025). Spot BTC ETFs attracted over $108 billion in 2024, and the crypto market and traditional financial market are accelerating their integration.
Fifth, adjustments to tax policies. The U.S. Internal Revenue Service in the 2025 temporary tax relief allowed taxpayers to flexibly choose the accounting method for crypto assets, which temporarily eased the tax burden on CEX users in the short term, but in the long run may drive crypto investments to concentrate on platforms that are controllable by U.S. regulatory authorities.
2. The latest developments in various fields of crypto assets indicate that the strategic orientation behind the change in the stance of the U.S. government and business circles is likely to be the construction of a "trinity" digital-age U.S. dollar hegemony system
The three pillars of this system are the Bitcoin Strategic Reserve (SBR), the U.S. dollar (pegged) stablecoin, and the U.S.-controllable digital financial infrastructure. Within this system, the Bitcoin Strategic Reserve may play the role of the gold reserve in the Bretton Woods system agreement of 1944. BTC, as the "digital gold", occupies the core value anchor position and will bring five potential strategic advantages to the U.S.
One is the first-mover advantage. As the cryptocurrency with the highest global consensus at present, BTC's unique position is conducive to it becoming a safe haven for capital during periods of global geopolitical turmoil and high inflation. The U.S. taking the lead in incorporating BTC, which accounts for more than 60% of the total crypto market capitalization, into the national strategic reserve, this first-mover advantage will help it attract international capital to continue to converge on U.S. dollar-linked on-chain and off-chain assets in the future.
Two is the role as a new tool for financial stability. During financial crises, its low correlation with traditional assets means that the BTC reserve can constitute a second financial stability tool for the U.S. government in addition to traditional U.S. dollar quantitative easing, and can assist in supporting the balance sheets of systemically important U.S. financial institutions and protecting the international status of the U.S. dollar in some emergency situations.
Three is to enhance the competitiveness of the U.S. dollar system in the digital age. Stablecoins pegged to the U.S. dollar currently account for 95% of the global stablecoin market capitalization, and combined with crypto assets that primarily use the U.S. dollar for settlement but are not pegged to the U.S. dollar, this will further consolidate the U.S. dollar's status as the central currency in the digital financial system, helping to extend the U.S. dollar's dominance in the global monetary system from traditional finance to the digital finance domain.
Four is to strengthen the U.S. voice in the formulation of digital finance standards in the digital age. In the future, after occupying a dominant position in the crypto market through the strategic reserve and U.S. dollar stablecoins, the U.S. will lead the formulation of global crypto asset rules and, through platforms such as the G7, IMF, and BIS, export and solidify the U.S. standards based on GENIUS and FIT21, promoting a global crypto asset regulatory framework that serves its own interests, thereby ensuring its top-level discourse power in international digital asset rule-making.
Five is to curb the development of crypto assets by potential competitors. Through financial sanctions and legislative restrictions, the development of digital assets by competing countries will be suppressed, and any institution will be strictly prohibited from establishing, issuing, and promoting CBDC within the United States through executive orders and legislation. Through technical assistance, the U.S. will attract emerging markets to adopt U.S.-led payment systems, squeezing the internationalization space of competing countries' digital currencies.
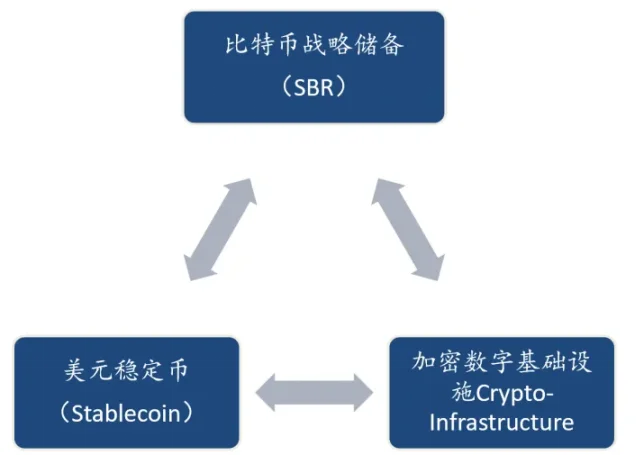
Figure 3 The "Trinity" of the U.S. Digital Currency Hegemony System
3. The policy orientation of the European Union in the field of cryptocurrencies is to unify market regulation and green finance transformation
This is mainly reflected in the following three aspects: First, the EU's "Crypto Asset Markets Regulation" (MiCA) came into full effect on December 31, 2024, aiming to establish a unified and clear crypto asset regulatory framework across the EU. It will classify all crypto assets into three categories and implement differentiated regulation, while strengthening compliance requirements for stablecoin issuance and crypto asset exchange operations. It will promote innovation while managing risks and ensuring consumer rights and financial stability. Second, the unified regulatory framework lays the foundation for the EU to gain the initiative and discourse power in the global crypto currency market competition. Third, it guides the establishment of the green finance development path for cryptocurrencies, with MiCA imposing higher carbon emission taxes on energy-intensive blockchains, driving the crypto industry to shift from PoW to lower-carbon consensus mechanisms like PoS, thereby reshaping the regional landscape of the mining industry.
4. Other global economies are facing the competitive game between stablecoins and sovereign digital currencies
This is mainly reflected in three aspects. First, the number of economies exploring and promoting CBDCs is constantly increasing. Currently, about 130 countries and regions around the world are exploring and promoting CBDCs. China's digital renminbi has been continuously expanding its domestic and cross-border pilots in recent years, making it the largest sovereign digital currency in the world. 18 G20 member countries including Japan, South Korea, India, and Russia are also accelerating the deployment of CBDCs or BTC strategic reserves, actively vying for digital finance sovereignty and rule-making discourse. Second, there is a competitive game between sovereign digital currencies and stablecoins. The CBDC model has sovereign advantages, but U.S. dollar stablecoins already have scale advantages. From 2020 to 2024, the market capitalization of USDT increased 5.52 times, while USDC increased 11.35 times, together accounting for 90% of the global stablecoin market. The settlement volume reached $15.6 trillion in 2024. Third, digital currencies may face the risk of regionalization and fragmentation in the future. The U.S. is trying to strengthen its digital finance hegemony through the establishment of the SBR reserve, stablecoin legislation, and restrictions on CBDC issuance and circulation. The EU's MiCA framework will objectively limit the development of non-euro stablecoins. Intensified competition means that the global digital finance payment system may face the risk of market segmentation and fragmentation in the future.
5. Stablecoins are becoming the frontier field for the integration of crypto financial assets and traditional financial assets
This is mainly manifested in two typical facts. On the one hand, stablecoins have enhanced the resilience of off-chain U.S. dollar assets. In 2023-2024, the market capitalization of stablecoins grew rapidly, exceeding the growth rate of U.S. M2, strongly supporting the demand for the U.S. dollar and U.S. Treasuries in the uncertain financial environment of the U.S. continuous fiscal deficit. On the other hand, stablecoins are gradually becoming mainstream payment channels. In the first 11 months of 2024, the stablecoin market completed $27.1 trillion in transactions, including a large amount of P2P and cross-border B2B payments, indicating that enterprises and individuals are increasingly using stablecoins to realize commercial value while meeting regulatory requirements, and are closely integrating with traditional payment platforms such as VISA and Stripe.
Risks and Challenges Posed by the New Trends in Cryptocurrency Development to China
1. Objectively view China's current advantages and disadvantages in the fields of blockchain and cryptocurrencies
Here is the English translation: The main advantages are as follows: First, the layout of the digital RMB and the blockchain industry is leading. In the field of central bank digital currencies (CBDCs), the digital RMB is currently the largest CBDC project globally, and it has received national strategic support. Since its R&D began in 2014, it has steadily progressed, covering retail, wholesale payments, and cross-border settlement. Since 2021, the development and practice of the Cross-Border Digital Currency Bridge (mBridge) project have also been at the forefront globally. These foundations make it possible for the digital RMB to become a financial transaction tool and asset carrier that can compete with the US dollar stablecoin in the future. In the blockchain industry, China has included blockchain technology in the national strategy in the early stages of industry germination and has clearly proposed the direction of integrating blockchain with the real economy. The market size and growth potential are relatively large, and it is estimated that China's blockchain market size will exceed 100 billion RMB by 2025. Blockchain has been widely applied in fields such as finance, supply chain, government affairs, and business services, and the number of registered companies has continued to grow, reaching 63,300 by the end of 2023. Second, the application scenarios are rich. The scenarios of digital currency have expanded from the initial retail, transportation, and government affairs to wholesale, catering, entertainment, education, healthcare, social governance, public services, rural revitalization, and green finance. The blockchain industry has also accumulated many mature cases in areas such as supply chain finance, cross-border trade, and e-government. Third, strict risk prevention and control. China has implemented strict regulations on cryptocurrency trading and initial coin offerings (ICOs), effectively preventing the risks of the virtual economy and providing a more controllable and stable industry environment for the compliant development of digital currencies. The current weaknesses of China mainly lie in the insufficient international competitiveness in some areas. First, the influence of technical standards is relatively lagging. Due to differences in regulations, the US currently dominates in underlying technologies such as ZKP and Layer2 scaling, and the EU has also set technical barriers through the MiCA framework, resulting in China's lack of discourse power in core protocol and global standard setting. Second, the development of public chain ecology is relatively lagging. China's blockchain industry is mainly based on consortium chains and private chains, and the lack of public chains has led to a gap in innovation capabilities with Europe and the US in areas such as decentralized finance (DeFi) and Web3.0.







